Difference between revisions of "Pilgrim Fathers" - New World Encyclopedia
Eric Olsen (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
==Separatists in Southwark and Scrooby== | ==Separatists in Southwark and Scrooby== | ||
| − | In 1586 a group of people were sent to The Clink, the prison in [[Southwark]] near London, for refusing to obey the religious laws of Elizabeth I. The dissenters founded a church in the prison under the guidance of [[John Greenwood]], a clergyman, and [[Henry Barrowe]], a lawyer. They called themselves 'Independents' but were also known as 'Brownists' because of the free thinking of [[Browne, Robert|Robert Browne]]. Browne was from a prominent Northamptonshire family and kinsman of [[William Cecil]], the Lord Treasurer, who had Puritan sympathies. At Cambridge he came under the influence of Puritan theologians. He burned with criticism of the established church and soon found himself imprisoned. He came to reject the Church of England as unscriptural and under the influence of Anabaptists | + | In 1586 a group of people were sent to The Clink, the prison in [[Southwark]] near London, for refusing to obey the religious laws of Elizabeth I. The dissenters founded a church in the prison under the guidance of [[John Greenwood]], a clergyman, and [[Henry Barrowe]], a lawyer. They called themselves 'Independents' but were also known as 'Brownists' because of the free thinking of [[Browne, Robert|Robert Browne]]. Browne was from a prominent Northamptonshire family and kinsman of [[William Cecil]], the Lord Treasurer, who had Puritan sympathies. At Cambridge he came under the influence of Puritan theologians. He burned with criticism of the established church and soon found himself imprisoned. He came to reject the Church of England as unscriptural and under the influence of Anabaptists he rejected the Puritan view that the Church could be reformed from within and became a Separatist advocating what came to be known as [[Congregationalism]]. Browne spent the years 1575-78 teaching and preaching in Southwark. After this he travelled around England and Scotland preaching his dissident views for which he was imprisoned many times. In 1586 later returned to Southwark as Headteacher of St. Olaves School. Around this time the clergyman, [[Francis Johnson]], joined the Brownists. He had been ordered by the English Ambassador to Holland to buy and burn the books by Greenwood and Barrowe. Inspired by them he came to visit the authors and found himself being jailed with them. |
In 1592 Greenwood, Barrowe and John Penry were released and began meeting at a house in the Borough and formally constituted the Southwark Independent Church. However the reprieve was short-lived and Greenwood, Barrowe and Penry were executed the following year. Roger Rippon, whose house was used for worship, was arrested and died of disease in prison. Many of the Southwark dissenters, including Francis Johnson, fled to Holland and later joined the Mayflower. | In 1592 Greenwood, Barrowe and John Penry were released and began meeting at a house in the Borough and formally constituted the Southwark Independent Church. However the reprieve was short-lived and Greenwood, Barrowe and Penry were executed the following year. Roger Rippon, whose house was used for worship, was arrested and died of disease in prison. Many of the Southwark dissenters, including Francis Johnson, fled to Holland and later joined the Mayflower. | ||
Revision as of 19:09, 26 February 2008

The Pilgrims is the common name for a group of English separatists who fled an environment of religious intolerance in Protestant England during the reign of James I to establish the second English colony in the New World. Unlike the colonists who settled Jamestown as a commercial venture of the joint-stock Virginia Company in 1607, the Pilgrims migrated primarily in search of religious freedom.
Worshiping in various separatist churches in the East Midlands of England, the Pilgrims escaped to religiously liberal Holland in 1608. Concerned with losing their cultural identity, the group arranged with English investors to establish a new colony in North America and made the dangerous trans-Atlantic crossing on the Mayflower in 1620.
The founding of the Plymouth Colony in Massachusetts and its historic charter, the Mayflower Compact, established early precedents for autonomous self rule and the recognition that political and civil rights were God-given. The Compact promised "all due submission and obedience [to such] just and equal laws" that the fledgling community might pass and, according to Samuel Eliot Morrison, was "a startling revelation of the capacity of Englishmen in that era for self-government."[1]
The Plymouth colony's relations with Native Americans were largely peaceful, despite profound cultural misunderstandings. The devout Christian settlers not only won the sincere friendship of Indian leaders, they "set a model for interracial diplomacy that was followed, with varying success, by later Puritan colonies," according to New England colonial historian Alden Vaughn. "Justice, tolerance, decisiveness, and amity became the keystones of Plymouth's Indian policy." [2] Relations deteriorated with the passing of the first generation and the expansion of English settlement in New England, culminating in the regional King Phillip's War (1675), a watershed event that permanently altered the balance of power in favor of the numerically and technologically superior English colonists.
The Pilgrims' epic voyage, perseverance amid crushing hardships, and settlement in the New England wilderness have come to be regarded as a birth narrative of the United States. The Pilgrims' motivation to risk everything for the freedom to worship according to conscience set a precedent that would come to be enshrined in the First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution guaranteeing the free exercise of religion.
Separatists in Southwark and Scrooby
In 1586 a group of people were sent to The Clink, the prison in Southwark near London, for refusing to obey the religious laws of Elizabeth I. The dissenters founded a church in the prison under the guidance of John Greenwood, a clergyman, and Henry Barrowe, a lawyer. They called themselves 'Independents' but were also known as 'Brownists' because of the free thinking of Robert Browne. Browne was from a prominent Northamptonshire family and kinsman of William Cecil, the Lord Treasurer, who had Puritan sympathies. At Cambridge he came under the influence of Puritan theologians. He burned with criticism of the established church and soon found himself imprisoned. He came to reject the Church of England as unscriptural and under the influence of Anabaptists he rejected the Puritan view that the Church could be reformed from within and became a Separatist advocating what came to be known as Congregationalism. Browne spent the years 1575-78 teaching and preaching in Southwark. After this he travelled around England and Scotland preaching his dissident views for which he was imprisoned many times. In 1586 later returned to Southwark as Headteacher of St. Olaves School. Around this time the clergyman, Francis Johnson, joined the Brownists. He had been ordered by the English Ambassador to Holland to buy and burn the books by Greenwood and Barrowe. Inspired by them he came to visit the authors and found himself being jailed with them.
In 1592 Greenwood, Barrowe and John Penry were released and began meeting at a house in the Borough and formally constituted the Southwark Independent Church. However the reprieve was short-lived and Greenwood, Barrowe and Penry were executed the following year. Roger Rippon, whose house was used for worship, was arrested and died of disease in prison. Many of the Southwark dissenters, including Francis Johnson, fled to Holland and later joined the Mayflower.
Another significant group of people who would formed the nucleus of the future Pilgrims were brought together through the teachings of Richard Clyfton, parson at All Saints' Parish Church in Babworth, Nottinghamshire, between 1586 and 1605. This congregation held Separatist beliefs similar to the nonconforming movements led by Barrowe and Browne. Unlike conforming Puritan groups, Separatists held that their differences with the Church of England were irreconcilable and that their worship should be organized independently of the trappings and organization of a central church.[3] William Brewster, another Cambridge graduate and a former diplomatic assistant to the Netherlands, was living in the Scrooby manor house, serving as postmaster for the village and bailiff to the Archbishop of York. Having been favorably impressed by Clyfton's services, he had begun participating in Separatist services led by John Smyth in Gainsborough, Lincolnshire.[4] The Separatists had long been controversial. Under the 1559 Act of Uniformity, it was illegal not to attend official Church of England services, with a fine of twelve pence (Pound sterling £.05; 2005 equivalent: about £5)[5] for each missed Sunday and holy day. The penalties for conducting unofficial services included imprisonment and larger fines. Under the policy of this time Barrowe and Greenwood, who had organized the Southwark Independent Church in 1592, were executed for sedition in 1593. Many of the Southwark dissenters, including Francis Johnson, fled to Holland and later joined the Mayflower.
During much of Brewster's tenure (1595-1606), the Archbishop of Canterbury was Matthew Hutton. He displayed some sympathy for the Puritan cause, writing in 1604 to Robert Cecil, a relative of Robert Browne and secretary of state to James I:
The Puritans (whose phantasticall zeale I mislike) though they differ in Ceremonies & accidentes, yet they agree wth us in substance of religion, & I thinke all or the moste p[ar]te of them love his Ma[jes]tie, & the p[re]sente state, & I hope will yield to conformitie. But the Papistes are opposite & contrarie in very many substantiall pointes of religion, & cannot but wishe the Popes authoritie & popish religion to be established.[6]
It had been hoped that when James came to power, a reconciliation allowing independence would be possible, but the Hampton Court Conference of 1604 denied substantially all the concessions requested by Puritans, save for an English translation of the Bible. Following the Conference, in 1605 Clyfton was declared a nonconformist and stripped of his position at Babworth. Brewster invited Clyfton to live at his home.
Upon Hutton's 1606 death, Tobias Matthew was elected as his replacement. Matthew, one of James' chief supporters at the 1604 conference, promptly began a campaign to purge the archdiocese of nonconforming influences, both separatists and papists. Disobedient clergy were replaced, and prominent Separatists were confronted, fined, imprisoned, or driven out of the country.[7]
At about the same time, Brewster arranged for a congregation to meet privately at the Scrooby manor house. Beginning in 1606, services were held with Clyfton as pastor, John Robinson as teacher, and Brewster as the presiding elder. Shortly thereafter, Smyth and members of the Gainsborough group moved on to Amsterdam. In September 1607 Brewster resigned from his postmaster position and according to records was fined £20 (2005 equivalent: about £2000) in absentia for his noncompliance with the church.[8] Facing increasing harrassment, the Scrooby congregation decided shortly after to follow the Smyth party to Amsterdam. Scrooby member William Bradford of Austerfield kept a journal of the congregation's events that would later be published as Of Plymouth Plantation. Of this time, he wrote:
But after these things they could not long continue in any peaceable condition, but were hunted & persecuted on every side, so as their former afflictions were but as flea-bitings in comparison of these which now came upon them. For some were taken & clapt up in prison, others had their houses besett & watcht night and day, & hardly escaped their hands; and ye most were faine to flie & leave their howses & habitations, and the means of their livelehood.[9]
Migration to Holland
Unable to obtain the papers necessary to leave England, members of the congregation agreed to leave surreptitiously, resorting to bribery to obtain passage. One documented attempt was in 1607, following Brewster's resignation, when members of the congregation chartered a boat in Boston, Lincolnshire. This turned out to be a sting operation, with all arrested upon boarding. The entire party was jailed for one month awaiting arraignment, at which time all but seven were released. Missing from the record is for how long the remainder was held, but it is known that the leaders made it to Amsterdam about a year later.
In a second departure attempt in the spring of 1608, arrangements were made with a Dutch merchant to pick up church members along the Humber estuary at Immingham near Grimsby, Lincolnshire. The men had boarded the ship, at which time the sailors spotted an armed contingent approaching. The ship quickly departed before the women and children could board; the stranded members were rounded up but then released without charges.
Ultimately, at least 150 of the congregation did make their way to Amsterdam, meeting up with the Smyth party, who had joined with the Exiled English Church led by Francis Johnson (1562-1617), Barrowe's successor. The Scrooby party remained there for about one year, citing growing tensions between Smyth and Johnson. Smyth had embraced the idea of believer's baptism, which Clyfton and Johnson opposed. [10]
Robinson decided that it would be best to remove his congregation from the fray, and permission to settle in Leiden was secured in 1609. With the congregation reconstituted as the English Exiled Church in Leyden, Robinson now became pastor; Clyfton, advanced in age, chose to stay behind in Amsterdam.
Leiden
The success of the congregation in Leiden was mixed. Leiden was a thriving industrial center, and many members were well able to support themselves working at Leiden University or in the textile, printing and brewing trades. Others were less able to bring in sufficient income, hampered by their rural backgrounds and the language barrier; for those, accommodations were made on an estate bought by Robinson and three partners.[11]
Of their years in Leiden, Bradford wrote:
For these & some other reasons they removed to Leyden, a fair & bewtifull citie, and of a sweete situation, but made more famous by ye universitie wherwith it is adorned, in which of late had been so many learned man. But wanting that traffike by sea which Amerstdam injoyes, it was not so beneficiall for their outward means of living & estats. But being now hear pitchet they fell to such trads & imployments as they best could; valewing peace & their spirituall comforte above any other riches whatsoever. And at length they came to raise a competente & comforteable living, but with hard and continuall labor.
Brewster had been teaching English at the university, and in 1615, Robinson enrolled to pursue his doctorate. There, he participated in a series of debates, particularly regarding the contentious issue of Calvinism versus Arminianism (siding with the Calvinists against the Remonstrants). Brewster, in a venture financed by Thomas Brewer, acquired typesetting equipment about 1616 and began publishing the debates through a local press.[12]
Holland was, however, a land whose culture and language were strange and difficult for the English congregation to understand or learn. Their children were becoming more and more Dutch as the years passed by. The congregation came to believe that they faced eventual extinction if they remained in Holland.
Decision to leave
By 1617, although the congregation was stable and relatively secure, there were ongoing issues that needed to be resolved. Bradford noted that the congregation was aging, compounding the difficulties some had in supporting themselves. Some, having spent their savings, gave up and returned to England. It was feared that more would follow and that the congregation would become unsustainable. The employment issues made it unattractive for others to come to Leiden, and younger members had begun leaving to find employment and adventure elsewhere. Also compelling was the possibility of missionary work, an opportunity that rarely arose in a Protestant stronghold.[13]
Reasons for departure are suggested by Bradford, when he notes the "discouragements" of the hard life they had in Holland, and the hope of attracting others by finding "a better, and easier place of living"; the "children" of the group being "drawn away by evil examples into extravagance and dangerous courses"; the "great hope, for the propagating and advancing the gospel of the kingdom of Christ in those remote parts of the world."
Pilgrim Edward Winslow's recollections support Bradford's account: In addition to the economic worries and missionary possibilities, Winslow stressed that it was important for the people to retain their English identity, culture and language. They also believed that the English Church in Leiden could do little to benefit the larger community there.[14]
At the same time, there were many uncertainties about moving to such a place as America. Stories had come back about the failed Sagadahoc colony in today's Maine and of the hardships faced by the Jamestown settlement in Virginia. There were fears that the native people would be violent, that there would be no source of food or water, that exposure to unknown diseases was possible, and that travel by sea was always hazardous. Balancing all this was a local political situation that was in danger of becoming unstable: the truce in what would be known as the Eighty Years' War was faltering, and there was fear over what the attitudes of Spain toward them might be.
Possible destinations included Guiana, where the Dutch had already established Essequibo; or somewhere near the existing Virginia settlement. Virginia was an attractive destination because the presence of the older colony might offer better security. It was thought, however, that they should not settle too near and thus fall into the same restrictive political environment as in England.
Negotiations
Robert Cushman and John Carver were sent to England to solicit a land patent. Their negotiations were delayed because of conflicts internal to the London Company, but ultimately a patent was secured in the name of John Wincob on June 9, 1619.[15] The charter was granted with the king's condition that the Leiden group's religion would not receive official recognition.[16]
Because of the continued problems within the London Company, preparations stalled. The congregation was approached by competing Dutch companies, and the possibility of settling in the Hudson River area was discussed with them. These negotiations were broken off at the encouragement of another English merchant, Thomas Weston, who assured the anxious group that he could resolve the London Company delays.[17]
Weston did come back with a substantial change, telling the Leiden group that parties in England had obtained a land grant north of the existing Virginia territory, to be called New England. This was only partially true; the new grant would come to pass, but not until late in 1620 when the Plymouth Council for New England received its charter. It was expected that this area could be fished profitably, and it was not under the control of the existing Virginia government.[18]
A second change was known only to parties in England who chose not to inform the larger group. New investors who had been brought into the venture wanted the terms altered so that at the end of the seven-year contract, half of the settled land and property would revert to them; and that the provision for each settler to have two days per week to work on personal business was dropped.
Brewster's diversion
Amid these negotiations, William Brewster found himself involved with religious unrest emerging in Scotland. In 1618, James had promulgated the Five Articles of Perth, which were seen in Scotland as an attempt to encroach on their Presbyterian tradition. Pamphlets critical of this law were published by Brewster and smuggled into Scotland by April 1619. These pamphlets were traced back to Leiden, and a failed attempt to apprehend Brewster was made in July when his presence in England became known.
Also in July in Leiden, English ambassador Dudley Carleton became aware of the situation and began leaning on the Dutch government to extradite Brewster. Brewster's type was seized, but only the financier Thomas Brewer was in custody. Brewster's whereabouts between then and the colonists' departure remain unknown. After several months of delay, Brewer was sent to England for questioning, where he stonewalled government officials until well into 1620. One resulting concession that England did obtain from the Netherlands was a restriction on the press that would make such publications illegal to produce. Brewster was ultimately convicted in England in absentia for his continued religious publication activities and sentenced in 1626 to a 14-year prison term.[19]
Preparations
As many members were not be able to settle their affairs within the time constraints and the budget for travel and supplies was limited, it was decided that the initial settlement should be undertaken primarily by younger and stronger members. Accordingly, the decision was made for Robinson to remain in Leiden with the larger portion of the congregation, and Brewster to lead the American congregation. While the church in America would be run independently, it was agreed that membership would automatically be granted in either congregation to members who moved between the continents.
With personal and business matters agreed upon, supplies and a small ship were procured. The Speedwell was to bring some passengers from the Netherlands to England, then on to America where the ship would be kept for the fishing business, with a crew hired for support services during the first year. A second, larger ship, the Mayflower, was leased for transport and exploration services.[20]
Voyage on the Mayflower
In July 1620, the Speedwell departed Delfshaven with the Leiden colonists. Reaching Southampton, Hampshire, they met with the Mayflower and the additional colonists hired by the investors. With final arrangements made, the two vessels set out on August 15.
Soon thereafter, the Speedwell crew reported that their ship was taking in water, so both were diverted to Dartmouth, Devon. There it was inspected for leaks and sealed, but a second attempt to depart also failed, bringing them only so far as Plymouth, Devon. An inspection of the Speedwell determined that the ship was not seaworthy, and it was sold. It would later be learned that crew members had deliberately caused the ship to leak, allowing them to abandon their year-long commitments. The ship's master and some of the crew did transfer to Mayflower for the trip.
Of the 120 combined passengers, 102 were chosen to travel on Mayflower with the supplies consolidated. Of these, about half had come by way of Leiden, and about 28 of the adults were members of the congregation.[21] The reduced party finally sailed successfully on September 16, 1620.
Initially the trip went smoothly, but under way they were met with strong winds and storms. One of these caused a main beam to crack, and although they were more than half the way to their destination, the possibility of turning back was considered. Using a "great iron screw" (probably a piece of house construction equipment) brought along by the colonists,[22] they repaired the ship sufficiently to continue. One passenger, John Howland, was washed overboard in the storm but caught a rope and was rescued. One crew member and one passenger died before they reached land, and one child was born at sea, and named "Oceanus."[23]
Arrival in America
Land was sighted on November 20, 1620. It was confirmed that the area was Cape Cod, within the New England territory recommended by Weston. An attempt was made to sail the ship around the cape towards the Hudson River, also within the New England grant area, but they encountered shoals and difficult currents around Malabar (a land mass that formerly existed in the vicinity of present-day Monomoy). It was decided to turn around, and by November 21 the ship was anchored in what is today known as Provincetown Harbor.
Mayflower Compact

With the charter for the Plymouth Council for New England incomplete by the time the colonists departed England (it would be granted while they were in transit, on November 13), the Pilgrims arrived without a patent. Some of the passengers, aware of the situation, suggested that without a patent in place, they were free to do as they chose upon landing and ignore the contract with the investors.[24]
To address this issue and in response to certain "mutinous speeches", a brief contract, signed on 11 November 1620 on board the Mayflower, later to be known as the Mayflower Compact, was drafted promising cooperation among the settlers "for the general good of the Colony unto which we promise all due submission and obedience." The document was ratified by majority rule, with 41 adult male passengers signing.[25]
The original document has been lost, but Bradford's transcription is as follows:
In the name of God, Amen. We whose names are underwritten, the loyal subjects of our dread Sovereign Lord King James, by the Grace of God of Great Britain, France and Ireland, King, Defender of the Faith, etc. Having undertaken, for the Glory of God and advancement of the Christian Faith and Honour of our King and Country, a Voyage to plant the First Colony in the Northern Parts of Virginia, do by these presents solemnly and mutually in the presence of God and one of another, Covenant and Combine ourselves together into a Civil Body Politic, for our better ordering and preservation and furtherance of the ends aforesaid; and by virtue hereof to enact, constitute and frame such just and equal Laws, Ordinances, Acts, Constitutions and Offices, from time to time, as shall be thought most meet and convenient for the general good of the Colony, unto which we promise all due submission and obedience. In witness whereof we have hereunder subscribed our names at Cape Cod, the 11th of November, in the year of the reign of our Sovereign Lord King James, of England, France and Ireland the eighteenth, and of Scotland the fifty-fourth. Anno Domini 1620.
At this time, John Carver was chosen as the colony's first governor.
Exploration and settlement
Thorough exploration of the area were delayed for over two weeks because the shallop or pinnace (a smaller sailing vessel) they brought had been partially dismantled to fit aboard Mayflower and was further damaged in transit. Small parties did wade to the beach to fetch firewood and attend to long-deferred personal hygiene.
While awaiting the shallop, exploratory parties led by Myles Standish—an English soldier the colonists had met while in Leiden—and Christopher Jones were undertaken. They encountered several old buildings, both European- and Native-built, and a few recently cultivated fields.
An artificial mound was found near the dunes, which they partially uncovered and found to be a Native grave. Further along, a similar mound, more recently made, was found, and as the colonists feared they might otherwise starve, they ventured to remove some of the provisions which had been placed in the grave. Baskets of maize were found inside, some of which the colonists took and placed into an iron kettle they also found nearby, while they reburied the rest, intending to use the borrowed corn as seed for planting.
Bradford later recorded that after the shallop had been repaired,
They also found two of the Indian's houses covered with mats, and some of their implements in them; but the people had run away and could not be seen. They also found more corn, and beans of various colours. These they brought away, intending to give them full satisfaction (repayment) when they should meet with any of them, – as about six months afterwards they did.
And it is to be noted as a special providence of God, and a great mercy to this poor people, that they thus got seed to plant corn the next year, or they might have starved; for they had none, nor any likelihood of getting any, till too late for the planting season.
By December, most of the passengers and crew had become ill, coughing violently. Many were also suffering from the effects of scurvy. There had already been ice and snowfall, hampering exploration efforts.
Contact
Explorations resumed on December 16. The shallop party—seven colonists from Leiden, three from London, and seven crew—headed down the cape and chose to land at the area inhabited by the Nauset people (roughly, present-day Brewster, Chatham, Eastham, Harwich, and Orleans, Massachusetts) where they saw some native people on the shore, who ran when the colonists approached. Inland they found more mounds, one containing acorns, which they exhumed and left, and more graves, which they decided not to dig.
Remaining ashore overnight, they heard cries near the encampment. The following morning, they were met by native people who proceeded to shoot at them with arrows. The colonists retrieved their firearms and shot back, then chased the native people into the woods but did not find them. There was no more contact with native people for several months.
The local people were already familiar with the English, who had intermittently visited the area for fishing and trade before Mayflower arrived. In the Cape Cod area, relations were poor following a visit several years earlier by Thomas Hunt. Hunt kidnapped 20 people from Patuxet (the place that would become New Plymouth) and another seven from Nausett, and he attempted to sell them as slaves in Europe. One of the Patuxet abductees was Squanto, who would become an ally of the Plymouth colony. The Pokanoket, who also lived nearby, had developed a particular dislike for the English after one group came in, captured numerous people, and shot them aboard their ship. There had by this time already been reciprocal killings at Martha's Vineyard and Cape Cod.
Founding of Plymouth
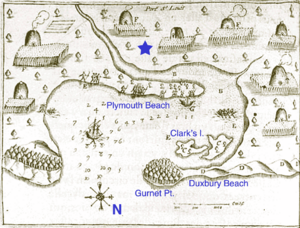
Continuing westward, the shallop's mast and rudder were broken by storms, and their sail was lost. Rowing for safety, they encountered the harbor formed by the current Duxbury and Plymouth barrier beaches and stumbled on land in the darkness. They remained at this spot—Clark's Island—for two days to recuperate and repair equipment.
Resuming exploration on December 21, the party crossed over to the mainland and surveyed the area that ultimately became the settlement. The anniversary of this survey is observed in Massachusetts as Forefathers' Day and is traditionally associated with the Plymouth Rock landing legend. This land was especially suited to winter building because the land had already been cleared, and the tall hills provided a good defensive position.
The cleared village, known as Patuxet to the Wampanoag people, was abandoned about three years earlier following a plague that killed all of its residents. Because the disease involved hemorrhaging, the "Indian fever" is assumed to have been fulminating smallpox introduced by European traders. The outbreak had been severe enough that the colonists discovered unburied skeletons in abandoned dwellings.[26] With the local population in such a weakened state, the colonists faced no resistance to settling there.
The exploratory party returned to the Mayflower, which was then brought to the harbor on December 26. Only nearby sites were evaluated, with a hill in Plymouth (so named on earlier charts) chosen on December 29.[27]
Construction commenced immediately, with the first common house nearly completed by January 19. At this point, single men were ordered to join with families. Each extended family was assigned a plot and built its own dwelling. Supplies were brought ashore, and the settlement was mostly complete by early February.
Between the landing and March, only 47 colonists had survived the diseases they contracted on the ship. During the worst of the sickness, only six or seven of the group were able and willing to feed and care for the rest. In this time, half the Mayflower crew also died.
On March 16, 1621, the colonists were surprised when an Indian boldly entered the Plymouth settlement and greeted them in English. Samoset was a sagamore (subordinate chief) of an Abenaki tribe from Pemaquid, Maine, and had learned some English from the English fishermen that frequented Maine's coastal waters. After spending the night with the Pilgrims, he returned two days later with Squanto, who spoke English much better than Samoset and arranged for the Pilgrims to meet with the chief sachem of the Wampanoag, Massasoit.
On March 22, 1621, the Pilgrims signed a peace treaty with Massasoit guaranteeing the English their security in exchange for their alliance against the Narragansett. Massasoit held the allegiance of seven lesser Wampanoag sachems and actively sought the alliance since two significant outbreaks of smallpox brought by the English had devastated the Wampanoag during the previous six years.
William Bradford became governor in 1621 upon the death of Carver and served for 11 consecutive years. (He was elected to various other terms until his death in 1657.) After their first harvest in 1621, Bradford invited Massasoit and the Wampanoag people to join in a feast of thanksgiving. Edward Winslow provided an account of this near-mythical first Thanksgiving in his diary:
Our harvest being gotten in, our governor sent four men on fowling, that so we might after a special manner rejoice together after we had gathered the fruits of our labor. They four in one day killed as much fowl as, with a little help beside, served the company almost a week. At which time, amongst other recreations, we exercised our arms, many of the Indians coming amongst us, and among the rest their greatest king Massasoit, with some ninety men, whom for three days we entertained and feasted, and they went out and killed five deer, which we brought to the plantation and bestowed on our governor, and upon the captain and others. And although it be not always so plentiful as it was at this time with us, yet by the goodness of God, we are so far from want that we often wish you partakers of our plenty.
An annual Thanksgiving after harvest became traditional in the seventeenth century. George Washington created the first Thanksgiving Day designated by the national government of the United States on October 3, 1789. The modern Thanksgiving holiday is often credited to Sarah Josepha Hale, editor of Boston's Ladies' Magazine. Beginning in 1827, she wrote editorials calling for a national, annual day of thanksgiving to commemorate the Pilgrim's first harvest feast. After nearly 40 years, in 1863, Abraham Lincoln declared the first modern Thanksgiving to fall on the last Thursday in November. President Franklin Roosevelt and Congress ultimately moved it to the fourth Thursday in November, and in 1941, the holiday was recognized by Congress as an official federal holiday.[28]
Growth and prosperity

According to Bradford and other sources, Massasoit prevented the failure of Plymouth Colony and the almost certain starvation that the Pilgrims faced during the earliest years of the colony's establishment. Moreover, Massasoit forged critical political and personal ties with the colonial leaders John Carver, Stephen Hopkins , Edward Winslow, William Bradford, and Myles Standish. Massasoit's alliance ensured that the Wampanoag remained neutral during the Pequot War in 1636. Winslow maintained that Massasoit held a deep friendship and trust with the English and felt duty-bound to observe that "whilst I live I will never forget this kindness they have showed me." [29] Unfortunately, the peaceful relationship that Massasoit had worked so diligently to create and protect had unforeseen dire consequences for the Wampanoag.
In November 1621, one year after the Pilgrims first set foot in New England, a second ship sent by the Merchant Adventurers arrived. Named the Fortune, it arrived with 37 new settlers for Plymouth. However, as the ship had arrived unexpectedly, and also without many supplies, the additional settlers put a strain on the resources of the colony. Among the passengers of the Fortune were several additional members of the original Leiden congregation, including William Brewster's son Jonathan, Edward Winslow's brother John, and Philip de la Noye (the family name was later changed to "Delano") whose descendants include President Franklin Delano Roosevelt. The Fortune also carried a letter from the Merchant Adventurers chastising the colony for failure to return goods with the Mayflower that had been promised in return for their support. The Fortune began its return to England laden with ₤500 worth of goods, more than enough to keep the colonists on schedule for repayment of their debt, however the Fortune was captured by the French before she could deliver her cargo to England, creating an even larger deficit for the colony.[30]
In July 1623, two more ships arrived, carrying 90 new settlers, among them Leideners, including William Bradford's future wife, Alice. Some of the settlers were unprepared for frontier life and returned to England the next year. In September 1623, another ship carrying settlers destined to refound the failed colony at Weymouth arrived and temporarily stayed at Plymouth. In March 1624, a ship bearing a few additional settlers and the first cattle arrived. A 1627 division of cattle lists 156 colonists divided into twelve lots of thirteen colonists each.[31] Another ship also named the Mayflower arrived in August 1629 with 35 additional members of the Leiden congregation. Ships arrived throughout the period between 1629 and 1630 carrying new settlers; though the exact number is unknown, contemporary documents claimed that by January 1630 the colony had almost 300 people. In 1643 the colony had an estimated 600 males fit for military service, implying a total population of about 2,000. By 1690, on the eve of the dissolution of the colony, the estimated total population of Plymouth County, the most populous, was 3,055 people. It is estimated that the entire population of the colony at the point of its dissolution was around 7,000.[32] For comparison it is estimated that between 1630 and 1640, a period known as the Great Migration, over 20,000 settlers had arrived in Massachusetts Bay Colony alone, and by 1678 the English population of all of New England was estimated to be in the range of 60,000. Despite the fact that Plymouth was the first colony in the region, by the time of its absorption it was much smaller than Massachusetts Bay Colony.[33]
Based on the early friendship with the Plymouth colonists, for nearly forty years the Wampanoag and the English Puritans of Massachusetts Bay Colony maintained an increasingly uneasy peace until Massasoit's death. Growing tensions between English colonists and Native Americans, who found their lands being lost and traditions being eroded, led to the decisive event of seventeenth-century English colonial history, the region-wide King Phillips War. The war pitted English colonists and their numerous Indian allies against militant Indian tribes led by Massasoit's son, Metacomet, known to the English as "King Philip." The war killed nearly 7 of every 8 Indians and was proportionately one of the bloodiest and costliest in the history of America.[34]
The Plymouth colony contained roughly what now comprises Bristol, Plymouth, and Barnstable counties in Massachusetts. When the Massachusetts Bay Colony was reorganized and issued a new charter as the Province of Massachusetts Bay in 1691, Plymouth ended its history as a separate colony.
Notes
- ↑ Samuel Eliot Morrison, The Oxford History of the American People (New York: Oxford University Press, 1965) 55
- ↑ Alden T. Vaughn, New England Frontier: Puritans and Indians 1620-1675 (New York: W.W. Norton, 1979 ISBN 0-393-00950-5) 65
- ↑ William Bradford, Bradford's History "Of Plimoth Plantation" (PDF), chap. 1. Edited by Ted Hildebrandt. Boston: Wright & Potter, 1898. Retrieved June 18, 2007.
- ↑ Brown, Cornelius. A History of Nottinghamshire. London: Elliot Stock, 1896. Retrieved June 18, 2007.
- ↑ Lawrence H. Officer (2005). What Were the UK Earnings and Prices Then?. Economic History Services. Retrieved June 18, 2007.
- ↑ The Bawdy Court: Exhibits - Belief and Persecution. University of Nottingham. Retrieved June 18, 2007.
- ↑ William Joseph Sheils. (2004). "Matthew, Tobie (1544?–1628)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford University Press.
- ↑ Cornelius Brown (1896). A History of Nottinghamshire. London: Elliot Stock. Retrieved June 18, 2007.
- ↑ Bradford, History
- ↑ Bradford, History
- ↑ Contract of Sale, De Groene Poort. Leiden Pilgrim Archives. Retrieved June 18, 2007.
- ↑ Griffis, William. The Pilgrim Press in Leyden. New England Magazine 19/25 (January 1899): 559-575.
- ↑ Bradford, History, chapter 4
- ↑ Edward Winslow. Hypocricie Unmasked, second section. Caleb Johnson. Retrieved June 18, 2007.
- ↑ (1908) in Susan Myra Kingsbury: The records of the Virginia Company of London: The Court Book, vol. I. United States Government Printing Office, 228.
- ↑ Bradford,History, chapter 5
- ↑ Bradford, History, chapter 6.
- ↑ The Charter of New England: 1620. The Avalon Project at Yale Law School. Retrieved June 18, 2007.
- ↑ Griffis, 559-575
- ↑ Bradford, History, chapter 7
- ↑ Patricia Scott Deetz; James F. Deetz. Passengers on the Mayflower: Ages & Occupations, Origins & Connections. The Plymouth Colony Archive Project. Retrieved June 18, 2007.
- ↑ Bangs, Jeremy. Pilgrim Life: Two Myths — Ancient and Modern. Retrieved June 18, 2007.
- ↑ Bradford, History, chapter 8-9
- ↑ Winslow, Edward; Bradford, William. Mourt's Relation. Johnson, Caleb. Retrieved June 18, 2007.
- ↑ Patricia Scott Deetz; Christopher Fennell. Mayflower Compact, 1620.
- ↑ Bradford, History, Book 2
- ↑ Smith's Map of New England, 1614. The Plymouth Colony Archive Project. Retrieved 2006-06-02.
- ↑ Wilson, Jerry (2001). The Thanksgiving Story. Holiday Page. Wilstar.com. Retrieved 2007-04-05.
- ↑ Winslow
- ↑ Philbrick (2006) pp 123–126, 134
- ↑ Residents of Plymouth according to the 1627 Division of Cattle. Plimoth Plantation: Living, Breathing History. Plimoth Plantation. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ↑ Leach, Douglas Edward (Sep., 1951). The Military System of Plymouth Colony. The New England Quarterly 24 (3): pp. 342–364. note: login required for access
- ↑ Taylor, Norris (1998). The Massachusetts Bay Colony. Retrieved 2007-03-30.
- ↑ Schultz, Eric B. and Michael J. Touglas (2000). "King Philip's War: The History and Legacy of America's Forgotten Conflict. W.W. Norton and Co., 5. ISBN 0-88150-483-1.
External links
All links retrieved June 18, 2007.
- The Pilgrims' History in a Nutshell – Pilgrim Archives in Nederlands
- First Parish Church in Plymouth, Massachusetts
- Church of the Pilgrimage, Plymouth, Massachusetts
- America's Museum of Pilgrim Possessions – Pilgrim Hall Museum
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.