Difference between revisions of "Gas chamber" - New World Encyclopedia
(Submitted) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Gas chambers were used as a method of carrying out [[capital punishment]] for condemned prisoners in the [[United States]], beginning in the 1920s and continuing throughout the twentieth century. | Gas chambers were used as a method of carrying out [[capital punishment]] for condemned prisoners in the [[United States]], beginning in the 1920s and continuing throughout the twentieth century. | ||
| − | During the [[Holocaust]], large-scale gas chambers designed for mass killing were used by [[Nazi]] [[Germany]] in their [[concentration camp]]s as part of their [[genocide]] program.<ref> | + | During the [[Holocaust]], large-scale gas chambers designed for mass killing were used by [[Nazi]] [[Germany]] in their [[concentration camp]]s as part of their [[genocide]] program.<ref>[http://www.yadvashem.org The Holocaust Martyrs' and Heroes' Remembrance Authority] ''yadvashem.org.'' Retrieved August 11, 2007.</ref> This shocking information, coupled with reports of the prolonged [[suffering]] of prisoners executed by this method, led to the gas chamber becoming associated with brutality. Although introduced in an effort to provide a more humane method of killing the condemned criminals than the previously common [[hanging]], the gas chamber itself is now regarded as an inhumane method of execution, generally replaced by [[lethal injection]]. Also, as opposition to the death penalty has increased many [[jurisdiction]]s have abolished this punishment, and thus the age of the gas chamber is coming to a close, marking another significant advance for humankind. |
==History== | ==History== | ||
=== Napoleonic France === | === Napoleonic France === | ||
| − | In his book, ''Le Crime de Napoléon'', [[France|French]] historian [[Claude Ribbe]] claimed that in the early nineteenth century, [[Napoleon]] used poison gas to put down [[slavery|slave]] rebellions in [[Haiti]] and [[Guadeloupe]]. Based on accounts left by French officers, he alleged that enclosed spaces, including the holds of [[ship]]s, were used as makeshift gas chambers where [[sulphur dioxide]] gas (probably generated by burning [[sulphur]]) was used to execute up to 100,000 rebellious slaves. However, these claims are controversial.<ref>Colin Randall, [http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=/news/2005/11/26/wfra26.xml&sSheet=/news/2005/11/26/ixworld.html "Napoleon's genocide 'on a par with Hitler | + | In his book, ''Le Crime de Napoléon'', [[France|French]] historian [[Claude Ribbe]] claimed that in the early nineteenth century, [[Napoleon]] used poison gas to put down [[slavery|slave]] rebellions in [[Haiti]] and [[Guadeloupe]]. Based on accounts left by French officers, he alleged that enclosed spaces, including the holds of [[ship]]s, were used as makeshift gas chambers where [[sulphur dioxide]] gas (probably generated by burning [[sulphur]]) was used to execute up to 100,000 rebellious slaves. However, these claims are controversial.<ref>Colin Randall, [http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=/news/2005/11/26/wfra26.xml&sSheet=/news/2005/11/26/ixworld.html "Napoleon's genocide 'on a par with Hitler'"] ''Daily Telegraph''. Retrieved July 29, 2007.</ref> |
=== United States === | === United States === | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
Generally speaking, in the United States the execution protocol is as follows: First, the execution technician places a quantity of [[potassium cyanide]] (KCN) pellets into a compartment directly below the chair in the chamber. The condemned person is then brought into the chamber and strapped into the chair, and the [[hermetic seal|airtight]] chamber is sealed. At this point the execution technician pours a quantity of concentrated [[sulfuric acid]] (H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub>) down a tube that leads to a small holding tank directly below the compartment containing the cyanide pellets. The curtain is then opened, allowing the witnesses to observe the inside of the chamber. The prison warden then asks the condemned individual if he or she wishes to make a final statement. Following this, the executioner throws a switch to cause the cyanide pellets to drop into the sulfuric acid, initiating a [[chemical reaction]] that generates [[hydrogen cyanide]] (HCN) gas. | Generally speaking, in the United States the execution protocol is as follows: First, the execution technician places a quantity of [[potassium cyanide]] (KCN) pellets into a compartment directly below the chair in the chamber. The condemned person is then brought into the chamber and strapped into the chair, and the [[hermetic seal|airtight]] chamber is sealed. At this point the execution technician pours a quantity of concentrated [[sulfuric acid]] (H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub>) down a tube that leads to a small holding tank directly below the compartment containing the cyanide pellets. The curtain is then opened, allowing the witnesses to observe the inside of the chamber. The prison warden then asks the condemned individual if he or she wishes to make a final statement. Following this, the executioner throws a switch to cause the cyanide pellets to drop into the sulfuric acid, initiating a [[chemical reaction]] that generates [[hydrogen cyanide]] (HCN) gas. | ||
| − | The condemned individual can see the visible [[gas]], and is advised to take several deep breaths to speed [[unconsciousness]] in order to prevent unnecessary [[suffering]]. Prisoners have, however, been reported to try to hold their breath.<ref>[http://deathpenaltyinfo.msu.edu/c/about/methods/gaschamber.htm "Methods of Execution - Gas Chamber"] Retrieved July 29, 2007</ref> Death from hydrogen cyanide is usually painful and unpleasant, although theoretically the condemned individual should lose consciousness before dying. | + | The condemned individual can see the visible [[gas]], and is advised to take several deep breaths to speed [[unconsciousness]] in order to prevent unnecessary [[suffering]]. Prisoners have, however, been reported to try to hold their breath.<ref>[http://deathpenaltyinfo.msu.edu/c/about/methods/gaschamber.htm "Methods of Execution - Gas Chamber"] Retrieved July 29, 2007. </ref> Death from hydrogen cyanide is usually painful and unpleasant, although theoretically the condemned individual should lose consciousness before dying. |
The chamber is then purged of the gas through special scrubbers, and must be neutralized with [[ammonia|anhydrous ammonia]] (NH<sub>3</sub>) before it can be opened. Guards wearing [[oxygen mask]]s remove the body from the chamber. Finally, the prison doctor examines the individual in order to officially declare that he or she is dead and release the body to the next of kin. | The chamber is then purged of the gas through special scrubbers, and must be neutralized with [[ammonia|anhydrous ammonia]] (NH<sub>3</sub>) before it can be opened. Guards wearing [[oxygen mask]]s remove the body from the chamber. Finally, the prison doctor examines the individual in order to officially declare that he or she is dead and release the body to the next of kin. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
Gas chambers were used in the [[Nazism|German]] [[Third Reich]] during the 1930s and 1940s as part of the so-called "public [[Action T4|euthanasia program]]" aimed at eliminating [[physical disability|physically]] and [[intellectually disabled]] people, and later the [[mentally ill]]. At that time, the preferred gas was [[carbon monoxide]], often provided by the [[exhaust gas]] of cars or trucks or army [[tank]]s. | Gas chambers were used in the [[Nazism|German]] [[Third Reich]] during the 1930s and 1940s as part of the so-called "public [[Action T4|euthanasia program]]" aimed at eliminating [[physical disability|physically]] and [[intellectually disabled]] people, and later the [[mentally ill]]. At that time, the preferred gas was [[carbon monoxide]], often provided by the [[exhaust gas]] of cars or trucks or army [[tank]]s. | ||
| − | Later, during the [[Holocaust]], gas chambers were modified and enhanced to accept even larger groups as part of the German policy of [[genocide]] against [[Jews]], and others. In January or February, 1940, 250 [[Roma]] children from [[Brno]] in the [[Buchenwald]] [[concentration camp]] were used for testing the [[Zyklon B]] ([[hydrogen cyanide]] absorbed into various solid substrates).<ref>Emil Proester, ''Vraždeni čs. cikanu v Buchenwaldu | + | Later, during the [[Holocaust]], gas chambers were modified and enhanced to accept even larger groups as part of the German policy of [[genocide]] against [[Jews]], and others. In January or February, 1940, 250 [[Roma]] children from [[Brno]] in the [[Buchenwald]] [[concentration camp]] were used for testing the [[Zyklon B]] ([[hydrogen cyanide]] absorbed into various solid substrates).<ref>Emil Proester, ''Vraždeni čs. cikanu v Buchenwaldu (The murder of Czech Gypsies in Buchenwald)'' (1940).</ref> On September 3, 1941, 600 [[Soviet Union|Soviet]] [[prisoner of war|POW]]s were gassed with Zyklon B at [[Auschwitz|Auschwitz camp I]]. |
[[Image:Komora gazowa.jpg|thumb|250 px|Gas chamber at Stutthof concentration camp]] | [[Image:Komora gazowa.jpg|thumb|250 px|Gas chamber at Stutthof concentration camp]] | ||
| − | Carbon monoxide was also used in large purpose-built gas chambers. They were generally disguised as bathhouses and inmates were herded naked into the building, having been told they were to take showers. The doors were then closed and the poisonous gas introduced, killing all those inside. The gas was provided by petrol engines (detailed in the [[Gerstein Report]]).<ref>Kurt Gerstein, [http://www.ns-archiv.de/verfolgung/gerstein/gerstein-bericht.php ''Der Gerstein-Bericht'' | + | Carbon monoxide was also used in large purpose-built gas chambers. They were generally disguised as bathhouses and inmates were herded naked into the building, having been told they were to take showers. The doors were then closed and the poisonous gas introduced, killing all those inside. The gas was provided by petrol engines (detailed in the [[Gerstein Report]]).<ref>Kurt Gerstein, [http://www.ns-archiv.de/verfolgung/gerstein/gerstein-bericht.php ''Der Gerstein-Bericht'' (''The Gerstein Report'')] Retrieved July 29, 2007. </ref> |
| − | Nazi gas chambers in mobile vans and at least eight concentration camps were used to kill several million people between 1941 and 1945. Some stationary gas chambers could kill 2,500 people at once. Numerous sources record the use of gas chambers in the Holocaust, including the direct testimony of [[Rudolf Höß]], Commandant of the Auschwitz concentration camp.<ref>[http://www.fordham.edu/halsall/mod/1946hoess.html ''Modern History Sourcebook: Rudolf Hess, Commandant of Auschwitz: Testimony at Nuremburg, 1946''] Fordham University. Retrieved July 29, 2007. </ref> | + | Nazi gas chambers in mobile vans and at least eight concentration camps were used to kill several million people between 1941 and 1945. Some stationary gas chambers could kill 2,500 people at once. Numerous sources record the use of gas chambers in the Holocaust, including the direct testimony of [[Rudolf Höß]], Commandant of the Auschwitz concentration camp.<ref>[http://www.fordham.edu/halsall/mod/1946hoess.html ''Modern History Sourcebook: Rudolf Hess, Commandant of Auschwitz: Testimony at Nuremburg, 1946''] (Fordham University). Retrieved July 29, 2007. </ref> |
The gas chambers were dismantled when Soviet troops got close, except at [[Dachau]], [[Sachsenhausen]], and [[Majdanek]]. The gas chamber at Auschwitz I was reconstructed after the war as a memorial, but without a door in its doorway and without the wall that originally separated the gas chamber from a washroom. | The gas chambers were dismantled when Soviet troops got close, except at [[Dachau]], [[Sachsenhausen]], and [[Majdanek]]. The gas chamber at Auschwitz I was reconstructed after the war as a memorial, but without a door in its doorway and without the wall that originally separated the gas chamber from a washroom. | ||
==Modern Usage== | ==Modern Usage== | ||
| − | The gas chamber has fallen out of favor in most of the modern world. There were several reports of terribly painful deaths during state mandated [[execution]]s in which the prisoners violently gasped for air, convulsed, and suffered spasms throughout the proceedings. One witness to such an execution said, "Jimmy Lee Gray died banging his head against a steel pole in the gas chamber while reporters counted his moans."<ref>[http://www.ccadp.org/botchedx.htm Botched Executions] Canadian Coalition Against the Death Penalty. Retrieved August 10, 2007.</ref> A witness of another gas chamber execution said, | + | The gas chamber has fallen out of favor in most of the modern world. There were several reports of terribly painful deaths during state mandated [[execution]]s in which the prisoners violently gasped for air, convulsed, and suffered spasms throughout the proceedings. One witness to such an execution said, "Jimmy Lee Gray died banging his head against a steel pole in the gas chamber while reporters counted his moans."<ref>[http://www.ccadp.org/botchedx.htm Botched Executions] ''Canadian Coalition Against the Death Penalty.'' Retrieved August 10, 2007.</ref> A witness of another gas chamber execution said, |
| − | <blockquote>I watched Harding go into violent spasms for 57 seconds. ... Then he began to convulse less frequently. His back muscles rippled. The spasms grew less violent. I timed them as ending 6 minutes and 37 seconds after they began. His head went down in little jerking motions. Obviously the gentleman was suffering. This was a violent death, make no mistake about it. [...] It was an ugly event. We put animals to death more humanely. This was not a clean and simple death.<ref>[http://www.phadp.org/botched.html Botched Executions] Project Hope. Retrieved August 10, 2007.</ref></blockquote> | + | <blockquote>I watched Harding go into violent spasms for 57 seconds. ... Then he began to convulse less frequently. His back muscles rippled. The spasms grew less violent. I timed them as ending 6 minutes and 37 seconds after they began. His head went down in little jerking motions. Obviously the gentleman was suffering. This was a violent death, make no mistake about it. [...] It was an ugly event. We put animals to death more humanely. This was not a clean and simple death.<ref>[http://www.phadp.org/botched.html Botched Executions] ''Project Hope.'' Retrieved August 10, 2007.</ref></blockquote> |
| − | Reports in the early twenty-first century indicated that gas chambers were used by [[North Korea]] both as [[punishment]] and for testing of lethal agents on humans: <ref>[http://www.guardian.co.uk/korea/article/0,2763,1136483,00.html | + | Reports in the early twenty-first century indicated that gas chambers were used by [[North Korea]] both as [[punishment]] and for testing of lethal agents on humans: <ref>[http://www.guardian.co.uk/korea/article/0,2763,1136483,00.html Revealed: the gas chamber horror of North Korea's gulag] ''The Guardian''. (Feb. 1, 2004). Retrieved August 16, 2007. </ref> They claimed that North Korea has used gas chambers to execute political prisoners at a [[concentration camp]] known as Camp 22 near the [[China|Chinese]] and [[Russia]]n borders.<ref>[http://observer.guardian.co.uk/international/story/0,6903,1136440,00.html Revealed: the gas chamber horror of North Korea's gulag] ''The Guardian''. Retrieved August 8, 2007. </ref><ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/programmes/this_world/3440771.stm Within Prison Walls] ''BBC.'' Retrieved August 8, 2007.</ref> However, questions have been raised about the truthfulness of these reports, since the witnesses were North Korean refugees, telling their stories to the [[Japan]]ese and [[South Korea]]n press. Some have dismissed these reports as mere [[propaganda]], with the [[refugee]]s being paid money for telling horrific stories that seem to equate the North Korean regime with the Nazi regime of Germany. |
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | * Fost, Dan. "Death watch: should TV cover the gas chamber?" ''Columbia Journalism Review'' | + | * Fost, Dan. 1991. "Death watch: should TV cover the gas chamber?" ''Columbia Journalism Review,'' Vol. 29, No. 6, 15. |
| − | * McMurry, Kelly. 1996. "Ninth Circuit shuts down California's gas chamber" ''Trial'' | + | * McMurry, Kelly. 1996. "Ninth Circuit shuts down California's gas chamber." ''Trial,'' Vol. 32, No. 5, 17. |
* Muller, Filip. 1999. ''Eyewitness Auschwitz: Three Years in the Gas Chambers''. Ivan R. Dee. ISBN 1566632714 | * Muller, Filip. 1999. ''Eyewitness Auschwitz: Three Years in the Gas Chambers''. Ivan R. Dee. ISBN 1566632714 | ||
| − | * Neumann, A. Lin. "Death watch: a night at the gas chamber. | + | * Neumann, A. Lin. 1992. "Death watch: a night at the gas chamber." ''Columbia Journalism Review,'' Vol. 31, No. 2, 17 |
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| − | *[http://www.rotten.com/library/death/execution/gas-chamber/ Gas chamber] Rotten Library Retrieved August 11, 2007. | + | *[http://www.angelfire.com/fl3/starke/gaschamber.html Execution by Gas Chamber: Mississippi] by Fred Leuchter. Retrieved August 11, 2007. |
| + | *[http://www.rotten.com/library/death/execution/gas-chamber/ Gas chamber] Rotten Library. Retrieved August 11, 2007. | ||
*[http://www.richard.clark32.btinternet.co.uk/gascham.html The Gas chamber] Retrieved August 11, 2007. | *[http://www.richard.clark32.btinternet.co.uk/gascham.html The Gas chamber] Retrieved August 11, 2007. | ||
| − | + | ||
{{Credits|Gas_chamber|125529834|}} | {{Credits|Gas_chamber|125529834|}} | ||
Revision as of 14:34, 16 August 2007
A gas chamber is an apparatus consisting of a sealed chamber into which a poisonous or asphyxiant gas is introduced in order to kill the occupant(s). The most commonly used poisonous agent is hydrogen cyanide; carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide have also been used.
Gas chambers were used as a method of carrying out capital punishment for condemned prisoners in the United States, beginning in the 1920s and continuing throughout the twentieth century.
During the Holocaust, large-scale gas chambers designed for mass killing were used by Nazi Germany in their concentration camps as part of their genocide program.[1] This shocking information, coupled with reports of the prolonged suffering of prisoners executed by this method, led to the gas chamber becoming associated with brutality. Although introduced in an effort to provide a more humane method of killing the condemned criminals than the previously common hanging, the gas chamber itself is now regarded as an inhumane method of execution, generally replaced by lethal injection. Also, as opposition to the death penalty has increased many jurisdictions have abolished this punishment, and thus the age of the gas chamber is coming to a close, marking another significant advance for humankind.
History
Napoleonic France
In his book, Le Crime de Napoléon, French historian Claude Ribbe claimed that in the early nineteenth century, Napoleon used poison gas to put down slave rebellions in Haiti and Guadeloupe. Based on accounts left by French officers, he alleged that enclosed spaces, including the holds of ships, were used as makeshift gas chambers where sulphur dioxide gas (probably generated by burning sulphur) was used to execute up to 100,000 rebellious slaves. However, these claims are controversial.[2]
United States
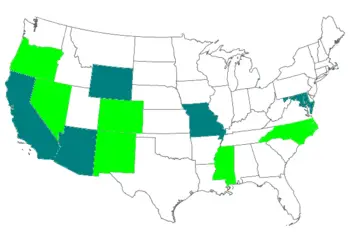
Gas chambers have been used for capital punishment in the United States to execute criminals, especially convicted murderers. Five states (Wyoming, California, Maryland, Missouri, and Arizona) technically retain this method, but all allow lethal injection as an alternative. In fact, it is highly unlikely that any of the states technically retaining the method will ever again utilize the gas chamber, unless an inmate specifically requests to die by this method.
The first person to be executed in the United States via gas chamber was Gee Jon, on February 8, 1924 in Nevada. German national Walter LaGrand, who was executed in Arizona on March 4, 1999, may be the last.
Initially introduced in an effort to provide a more humane method of execution (compared to hanging), the use of the gas chamber became controversial because of the use of large chambers to kill millions in Nazi concentration camps. Additionally, despite claims that death is quick and painless if the prisoner takes deep breaths of the poisonous gas, there were reports of prolonged suffering during executions. Following the videotaped execution of Robert Alton Harris in 1992, a federal court in California declared this method of execution as "cruel and unusual punishment." Most states have now switched to methods considered less inhumane by officials, such as lethal injection.
The gas chamber that San Quentin State Prison in California used for capital punishment, has since been converted to an execution chamber for execution by lethal injection. The restraining table was placed where there used to be two chairs used.
Method
Generally speaking, in the United States the execution protocol is as follows: First, the execution technician places a quantity of potassium cyanide (KCN) pellets into a compartment directly below the chair in the chamber. The condemned person is then brought into the chamber and strapped into the chair, and the airtight chamber is sealed. At this point the execution technician pours a quantity of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) down a tube that leads to a small holding tank directly below the compartment containing the cyanide pellets. The curtain is then opened, allowing the witnesses to observe the inside of the chamber. The prison warden then asks the condemned individual if he or she wishes to make a final statement. Following this, the executioner throws a switch to cause the cyanide pellets to drop into the sulfuric acid, initiating a chemical reaction that generates hydrogen cyanide (HCN) gas.
The condemned individual can see the visible gas, and is advised to take several deep breaths to speed unconsciousness in order to prevent unnecessary suffering. Prisoners have, however, been reported to try to hold their breath.[3] Death from hydrogen cyanide is usually painful and unpleasant, although theoretically the condemned individual should lose consciousness before dying.
The chamber is then purged of the gas through special scrubbers, and must be neutralized with anhydrous ammonia (NH3) before it can be opened. Guards wearing oxygen masks remove the body from the chamber. Finally, the prison doctor examines the individual in order to officially declare that he or she is dead and release the body to the next of kin.
As with all judicially mandated executions in the United States, witnesses are present during the procedure. These include members of the media, citizen witnesses, prison legal and spiritual staff, and certain family members. One of the problems with the gas chamber is the inherent danger to all involved in dealing with such a toxic gas. Additionally, both the ammonia and the contaminated acid that must be drained and disposed of are very poisonous.
Nazi Germany
Gas chambers were used in the German Third Reich during the 1930s and 1940s as part of the so-called "public euthanasia program" aimed at eliminating physically and intellectually disabled people, and later the mentally ill. At that time, the preferred gas was carbon monoxide, often provided by the exhaust gas of cars or trucks or army tanks.
Later, during the Holocaust, gas chambers were modified and enhanced to accept even larger groups as part of the German policy of genocide against Jews, and others. In January or February, 1940, 250 Roma children from Brno in the Buchenwald concentration camp were used for testing the Zyklon B (hydrogen cyanide absorbed into various solid substrates).[4] On September 3, 1941, 600 Soviet POWs were gassed with Zyklon B at Auschwitz camp I.
Carbon monoxide was also used in large purpose-built gas chambers. They were generally disguised as bathhouses and inmates were herded naked into the building, having been told they were to take showers. The doors were then closed and the poisonous gas introduced, killing all those inside. The gas was provided by petrol engines (detailed in the Gerstein Report).[5]
Nazi gas chambers in mobile vans and at least eight concentration camps were used to kill several million people between 1941 and 1945. Some stationary gas chambers could kill 2,500 people at once. Numerous sources record the use of gas chambers in the Holocaust, including the direct testimony of Rudolf Höß, Commandant of the Auschwitz concentration camp.[6]
The gas chambers were dismantled when Soviet troops got close, except at Dachau, Sachsenhausen, and Majdanek. The gas chamber at Auschwitz I was reconstructed after the war as a memorial, but without a door in its doorway and without the wall that originally separated the gas chamber from a washroom.
Modern Usage
The gas chamber has fallen out of favor in most of the modern world. There were several reports of terribly painful deaths during state mandated executions in which the prisoners violently gasped for air, convulsed, and suffered spasms throughout the proceedings. One witness to such an execution said, "Jimmy Lee Gray died banging his head against a steel pole in the gas chamber while reporters counted his moans."[7] A witness of another gas chamber execution said,
I watched Harding go into violent spasms for 57 seconds. ... Then he began to convulse less frequently. His back muscles rippled. The spasms grew less violent. I timed them as ending 6 minutes and 37 seconds after they began. His head went down in little jerking motions. Obviously the gentleman was suffering. This was a violent death, make no mistake about it. [...] It was an ugly event. We put animals to death more humanely. This was not a clean and simple death.[8]
Reports in the early twenty-first century indicated that gas chambers were used by North Korea both as punishment and for testing of lethal agents on humans: [9] They claimed that North Korea has used gas chambers to execute political prisoners at a concentration camp known as Camp 22 near the Chinese and Russian borders.[10][11] However, questions have been raised about the truthfulness of these reports, since the witnesses were North Korean refugees, telling their stories to the Japanese and South Korean press. Some have dismissed these reports as mere propaganda, with the refugees being paid money for telling horrific stories that seem to equate the North Korean regime with the Nazi regime of Germany.
Notes
- ↑ The Holocaust Martyrs' and Heroes' Remembrance Authority yadvashem.org. Retrieved August 11, 2007.
- ↑ Colin Randall, "Napoleon's genocide 'on a par with Hitler'" Daily Telegraph. Retrieved July 29, 2007.
- ↑ "Methods of Execution - Gas Chamber" Retrieved July 29, 2007.
- ↑ Emil Proester, Vraždeni čs. cikanu v Buchenwaldu (The murder of Czech Gypsies in Buchenwald) (1940).
- ↑ Kurt Gerstein, Der Gerstein-Bericht (The Gerstein Report) Retrieved July 29, 2007.
- ↑ Modern History Sourcebook: Rudolf Hess, Commandant of Auschwitz: Testimony at Nuremburg, 1946 (Fordham University). Retrieved July 29, 2007.
- ↑ Botched Executions Canadian Coalition Against the Death Penalty. Retrieved August 10, 2007.
- ↑ Botched Executions Project Hope. Retrieved August 10, 2007.
- ↑ Revealed: the gas chamber horror of North Korea's gulag The Guardian. (Feb. 1, 2004). Retrieved August 16, 2007.
- ↑ Revealed: the gas chamber horror of North Korea's gulag The Guardian. Retrieved August 8, 2007.
- ↑ Within Prison Walls BBC. Retrieved August 8, 2007.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Fost, Dan. 1991. "Death watch: should TV cover the gas chamber?" Columbia Journalism Review, Vol. 29, No. 6, 15.
- McMurry, Kelly. 1996. "Ninth Circuit shuts down California's gas chamber." Trial, Vol. 32, No. 5, 17.
- Muller, Filip. 1999. Eyewitness Auschwitz: Three Years in the Gas Chambers. Ivan R. Dee. ISBN 1566632714
- Neumann, A. Lin. 1992. "Death watch: a night at the gas chamber." Columbia Journalism Review, Vol. 31, No. 2, 17
External links
- Execution by Gas Chamber: Mississippi by Fred Leuchter. Retrieved August 11, 2007.
- Gas chamber Rotten Library. Retrieved August 11, 2007.
- The Gas chamber Retrieved August 11, 2007.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.