Difference between revisions of "Cytoplasm" - New World Encyclopedia
({{Contracted}}) |
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) (added most recent version from Wikipedia) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Contracted}} | {{Contracted}} | ||
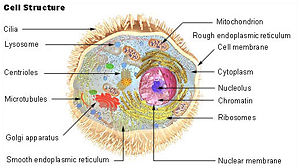
| − | '''Cytoplasm''' is | + | [[Image:Illu cell structure.jpg|thumb|300px|[[Organelles]]. Cytoplasm labeled at center right.]] |
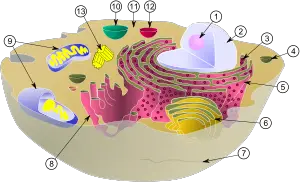
| + | [[Image:Biological cell.svg|thumb|300px|Schematic of typical animal cell, showing subcellular components. [[Organelle]]s: (1) [[nucleolus]] (2) [[cell nucleus|nucleus]] (3) [[ribosome]] (4) [[vesicle (biology)|vesicle]] (5) rough [[endoplasmic reticulum]] (ER) (6) [[Golgi apparatus]] (7) [[Cytoskeleton]] (8) smooth ER (9) [[mitochondrion|mitochondria]] (10) [[vacuole]] (11) [[cytoplasm]] (12) [[lysosome]] (13) [[centriole]]s]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Cytoplasm''' is a water-like substance that fills [[Cell (biology)|cell]]s. The cytoplasm consists of [[cytosol]] and the cellular [[organelles]], except the [[cell nucleus]]. The cytosol is made up of water, salts, organic molecules and many [[enzymes]] that catalyze reactions. The cytoplasm plays an important role in a cell, serving as a "molecular chowder" in which the organelles are suspended and held together by a fatty membrane. It is found within the plasma membrane of a cell and surrounds the nucleus and envelopes the organelles. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Function== | ||
| + | The cytoplasm holds all of the cellular organelles outside of the nucleus and also maintains the shape and consistency of the cell. It is also a storage place for chemical substances indispensable to life, which are involved in vital [[metabolism|metabolic]] reactions, such as [[anaerobic glycolysis]] and [[protein]] [[synthesis]]. It is made up of 80% water. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In bacteria, sequential chemical reactions take place in the cytoplasm and cell. | ||
==Components of the cytoplasm== | ==Components of the cytoplasm== | ||
| − | The | + | The cytoplasm is composed of [[ion]]s and soluble [[macromolecule]]s like [[enzyme]]s, [[carbohydrate]]s, different [[salt]]s and [[protein]]s, as well as a great proportion of [[RNA]]. The cytoplasm's watery component is also known as [[hyaloplasm]]. |
| − | It can be more or less [[ | + | It can be more or less [[water]]-like or liquid depending on the milieu's conditions and the activity phases of the cell. In the first case, it is named [[cytogel]] and is a viscous solid mass. In the second case, called [[cytosol]], it acts like a liquid. In general, margin regions of the cell are water-like, and the cell's interior is RNA. |
| − | The | + | The [[organelle]]s (such as the [[mitochondria]], the [[chloroplast]], [[lysosome]]s, [[peroxysome]]s, [[ribosome]]s, [[vacuole]]s, [[cytoskeleton]]s, and complex [[cell membrane]] structures like the [[endoplasmic reticulum]]s) in the cytoplasm are insoluble. |
| − | ==Differences between animal and plant | + | ==Differences between the animal and plant cytoplasms== |
| − | While all cells possess | + | While all cells possess cytoplasm, cells from different [[Domain (biology)|biological domains]] can differ widely in the characteristics of their cytoplasms. In the animal [[kingdom (biology)|kingdom]], cytoplasm occupies nearly half the cell's volume, while in plant cells, the cytoplasm occupies much less space because of the presence of [[vacuoles]]. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{organelles}} | {{organelles}} | ||
| − | {{credit| | + | {{credit|106244758}} |
[[Category:Life sciences]] | [[Category:Life sciences]] | ||
Revision as of 16:43, 9 February 2007
Cytoplasm is a water-like substance that fills cells. The cytoplasm consists of cytosol and the cellular organelles, except the cell nucleus. The cytosol is made up of water, salts, organic molecules and many enzymes that catalyze reactions. The cytoplasm plays an important role in a cell, serving as a "molecular chowder" in which the organelles are suspended and held together by a fatty membrane. It is found within the plasma membrane of a cell and surrounds the nucleus and envelopes the organelles.
Function
The cytoplasm holds all of the cellular organelles outside of the nucleus and also maintains the shape and consistency of the cell. It is also a storage place for chemical substances indispensable to life, which are involved in vital metabolic reactions, such as anaerobic glycolysis and protein synthesis. It is made up of 80% water.
In bacteria, sequential chemical reactions take place in the cytoplasm and cell.
Components of the cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is composed of ions and soluble macromolecules like enzymes, carbohydrates, different salts and proteins, as well as a great proportion of RNA. The cytoplasm's watery component is also known as hyaloplasm.
It can be more or less water-like or liquid depending on the milieu's conditions and the activity phases of the cell. In the first case, it is named cytogel and is a viscous solid mass. In the second case, called cytosol, it acts like a liquid. In general, margin regions of the cell are water-like, and the cell's interior is RNA.
The organelles (such as the mitochondria, the chloroplast, lysosomes, peroxysomes, ribosomes, vacuoles, cytoskeletons, and complex cell membrane structures like the endoplasmic reticulums) in the cytoplasm are insoluble.
Differences between the animal and plant cytoplasms
While all cells possess cytoplasm, cells from different biological domains can differ widely in the characteristics of their cytoplasms. In the animal kingdom, cytoplasm occupies nearly half the cell's volume, while in plant cells, the cytoplasm occupies much less space because of the presence of vacuoles.
| Organelles of the cell |
|---|
| Acrosome | Chloroplast | Cilium/Flagellum | Centriole | Endoplasmic reticulum | Golgi apparatus | Lysosome | Melanosome | Mitochondrion | Myofibril | Nucleus | Parenthesome | Peroxisome | Plastid | Ribosome | Vacuole | Vesicle |
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.