Difference between revisions of "Carotene" - New World Encyclopedia
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Claimed}}{{Contracted}} | {{Claimed}}{{Contracted}} | ||
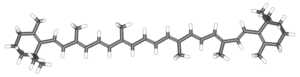
[[Image:BetaCarotene-3d.png|thumb|300px|right|β-Carotene represented by a 3-dimentional stick diagram]] | [[Image:BetaCarotene-3d.png|thumb|300px|right|β-Carotene represented by a 3-dimentional stick diagram]] | ||
| − | [[Image:CarrotDiversityLg.jpg|thumb|right|250px|'''Carotene''' is responsible for the orange color of the [[carrot]]s and many other | + | [[Image:CarrotDiversityLg.jpg|thumb|right|250px|'''Carotene''' is responsible for the orange color of the [[carrot]]s and many other [[fruit]]s and [[vegetable]]s.]] |
| − | The term '''carotene''' is used for several related substances having the formula C<sub>40</sub>H<sub>56</sub> | + | The term '''carotene''' is used for several related substances having the formula C<sub>40</sub>H<sub>56</sub> and that serve as an [[orange (color)|orange]] [[photosynthetic pigment]] important for [[photosynthesis]]. It is responsible for the orange color of the [[carrot]] and many other [[fruit]]s and [[vegetable]]s. It contributes to photosynthesis by transmitting the light energy it absorbs to [[chlorophyll]]. |
| − | It is responsible for the orange color of the [[carrot]] and many other | ||
==Chemical structure and properties== | ==Chemical structure and properties== | ||
| − | Carotenes are [[ | + | Carotenes are [[carotenoid]]s containing no oxygen. Carotenoids containing some oxygen are known as [[xanthophyll]]s. |
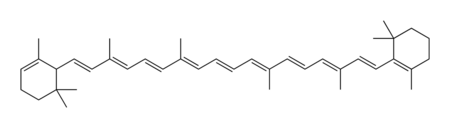
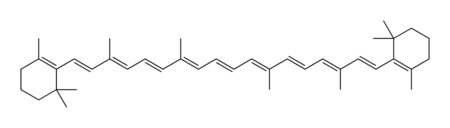
| − | Chemically, carotene is a [[terpene]], synthesized biochemically from eight [[isoprene]] units. It comes in two primary forms designated by characters from the [[Greek alphabet]]: alpha-carotene (α-carotene) and beta-carotene (β-carotene). | + | Chemically, carotene is a [[terpene]], synthesized biochemically from eight [[isoprene]] units. It comes in two primary forms designated by characters from the [[Greek alphabet]]: alpha-carotene (α-carotene) and beta-carotene (β-carotene). Gamma, delta, and epsilon forms (γ, δ, and ε-carotene) also exist. Beta-carotene is composed of two [[retinyl]] groups, and is broken down in the [[mucosa]] of the [[small intestine]] by [[beta-carotene dioxygenase]] to [[retinol]], a form of [[vitamin A]]. |
Carotene can be stored in the [[liver]] and converted to vitamin A as needed, thus making it a [[provitamin]]. | Carotene can be stored in the [[liver]] and converted to vitamin A as needed, thus making it a [[provitamin]]. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 19: | ||
precursor to Vitamin C | precursor to Vitamin C | ||
| − | A wide range of carotenoids and other | + | A wide range of carotenoids and other colorful compounds abound in the plant kingdom, and we can attribute benefits to the plant in expending resources to produce these compounds from their role in attracting insects for pollination, and alluring animals for seed distribution, to protecting vital cell functions against the destructive effects of ultraviolet light; acting as the plants' SPF 30+ [[sunscreen]] . |
β-Carotene is an [[anti-oxidant]] and as such can be useful for curbing the excess of damaging [[free radicals]] in the body. However, the usefulness of β-carotene as a [[dietary supplement]] (i.e. taken as a pill) in cancer prevention is still subject to debate<ref name="fn1" />. β-Carotene is [[fat]]-[[solubility|soluble]]. | β-Carotene is an [[anti-oxidant]] and as such can be useful for curbing the excess of damaging [[free radicals]] in the body. However, the usefulness of β-carotene as a [[dietary supplement]] (i.e. taken as a pill) in cancer prevention is still subject to debate<ref name="fn1" />. β-Carotene is [[fat]]-[[solubility|soluble]]. | ||
| Line 69: | Line 68: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| − | *Lodish | + | * Lodish, Harvey; Berk, Arnold; Zipursky, S. Lawrence; Matsudaira, Paul; Baltimore, David; Darnell, James E. (1999). [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?call=bv.View..ShowTOC&rid=mcb.TOC ''Molecular Cell Biology'' (4th ed.)]. New York: W. H. Freeman & Co. ISBN 0-7167-3706-X |
| − | *Stryer | + | |
| + | * Stryer, L. 1995. ''Biochemistry'', 4th edition. New York: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 0716720094. | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
[[Category:Vitamins]] | [[Category:Vitamins]] | ||
| − | {{credit|Carotene|130817648}} | + | {{credit|Carotene|130817648|Carotenoid|137925956|Carotenodermia|141742075}} |
[[Category:Life sciences]] | [[Category:Life sciences]] | ||
Revision as of 14:51, 14 July 2007
The term carotene is used for several related substances having the formula C40H56 and that serve as an orange photosynthetic pigment important for photosynthesis. It is responsible for the orange color of the carrot and many other fruits and vegetables. It contributes to photosynthesis by transmitting the light energy it absorbs to chlorophyll.
Chemical structure and properties
Carotenes are carotenoids containing no oxygen. Carotenoids containing some oxygen are known as xanthophylls.
Chemically, carotene is a terpene, synthesized biochemically from eight isoprene units. It comes in two primary forms designated by characters from the Greek alphabet: alpha-carotene (α-carotene) and beta-carotene (β-carotene). Gamma, delta, and epsilon forms (γ, δ, and ε-carotene) also exist. Beta-carotene is composed of two retinyl groups, and is broken down in the mucosa of the small intestine by beta-carotene dioxygenase to retinol, a form of vitamin A. Carotene can be stored in the liver and converted to vitamin A as needed, thus making it a provitamin.
The two primary isomers of carotene, α-carotene and β-carotene, differ in the position of double bonds in the cyclic group at the end.
Function
role in photosynthesis antioxidant precursor to Vitamin C
A wide range of carotenoids and other colorful compounds abound in the plant kingdom, and we can attribute benefits to the plant in expending resources to produce these compounds from their role in attracting insects for pollination, and alluring animals for seed distribution, to protecting vital cell functions against the destructive effects of ultraviolet light; acting as the plants' SPF 30+ sunscreen .
β-Carotene is an anti-oxidant and as such can be useful for curbing the excess of damaging free radicals in the body. However, the usefulness of β-carotene as a dietary supplement (i.e. taken as a pill) in cancer prevention is still subject to debate[1]. β-Carotene is fat-soluble.
Sources
Dietary sources
β-Carotene is the more common form and can be found in yellow, orange, and green leafy fruits and vegetables. These can be carrots, spinach, lettuce, tomatoes, sweet potatoes, broccoli, cantaloupe, oranges, and winter squash. As a rule of thumb, the greater the intensity of the colour of the fruit or vegetable, the more β-carotene it contains.
β-carotene is present in yellow orange bell peppers (called yellow capsicum in Australia) but is not the principal colour in red bell peppers, chillis and other varieties and species in the genus Capsicum. Carotene is also found in corn, and in the milk of Guernsey dairy cows. Carotene causes the milk of the Guernsey cow to turn yellow.
Carotene supplements
Most of the world's synthetic supply of carotene comes from a manufacturing complex located in Freeport, Texas and owned by DSM. In Spain Vitatene produces natural beta carotene form Blakeslea trispora. In Australia, organic beta-carotene is produced by Aquacarotene Limited from dried marine algae Dunaliella salina grown in harvesting ponds situated in Karratha, Western Australia.
Beta-carotene and human health
Carotenemia
Carotene is often labeled as good for you. However, your body converts this yellow pigment to Vitamin A, and too much Vitamin A can be harmful to your body. Carotenemia or hypercarotenemia is excess carotene, but unlike excess vitamin A, carotene is non-toxic. Although hypercarotenemia is not particularly dangerous, it can lead to a yellowing of the skin (carotenodermia). It is most commonly associated with consumption of an abundance of carrots, but it also can be a medical sign of more dangerous conditions. A randomised trial into the use of β-carotene and vitamin A for prevention of lung cancer had to be stopped early due to the apparent increase in the incidence of lung cancer in those with lung irritation from smoking or asbestos exposure.[1]
Possible health risk for those suffering from lung cancer?
condense this section
It has been shown in trials that the use of synthetically-produced beta carotene (that is, beta carotene in supplement form such as the pills typically sold in stores) increases the rate of lung cancer and prostate cancer, and increases mortality in smokers. These results have been observed in beta carotene supplements and not in foods with naturally occurring beta carotene.[2]
An article on the American Cancer Society says that The Cancer Research Campaign has called for warning labels on beta carotene supplements to caution smokers that such supplements may increase the risk of lung cancer.[3]
The New England Journal of Medicine published an article (Vol. 330, No. 15) in 1994 about a trial which examined the relationship between daily supplementation of beta carotene and vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) and the incidence of lung cancer. The study was done using supplements and researchers were aware of the relationship between carotenoid-rich fruits and vegetables and lower lung cancer rates. The research concluded that no reduction in lung cancer was found in the participants using these supplements (beta-carotene), and furthermore, these supplements may, in fact, have harmful effects.
The Journal of the National Cancer Institute published an article (Vol. 88, No. 21) in 1996 about a trial that was conducted to determine if vitamin A (in the form of retinyl palmitate) and beta carotene had any beneficial effects to prevent cancer. The results indicate an increased risk of lung cancer for the participants who consumed the beta-carotene supplement.[4]
A review of all randomized controlled trials in the scientific literature by the Cochrane Collaboration published in JAMA in 2007 found that beta carotine increased mortality by 5% (Relative Risk 1.05, 95% confidence interval 1.01-1.08).[5]
Nomenclature
The two ends of the β-carotene molecule are structurally identical, and are called β-rings. Specifically, the group of nine carbon atoms at each end form a β-ring.
The α-carotene molecule has a β-ring at one end; the other end is called an ε-ring. There is no such thing as an "α-ring".
These and similar names for the ends of the carotenoid molecules form the basis of a systematic naming scheme, according to which:
- α-carotene is β,ε-carotene;
- β-carotene is β,β-carotene;
- γ-carotene (with one β ring and one uncyclized end that is labelled psi) is β,ψ-carotene;
- δ-carotene (with one ε ring and one uncyclized end) is ε,ψ-carotene;
- ε-carotene is ε,ε-carotene,
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Effects of a Combination of Beta Carotene and Vitamin A on Lung Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease
- ↑ Mayo Clinic
- ↑ British Cancer Organization Calls for Warning Labels on Beta-Carotene (2000-07-31). Retrieved 2007-03-15.
- ↑ Abstract
- ↑ Bjelakovic et al., Mortality in randomized trials of antioxidant supplements for primary and secondary prevention: Systematic review and meta-analysis, JAMA, 297:842; Feb. 28, 2007 [1]
- Lodish, Harvey; Berk, Arnold; Zipursky, S. Lawrence; Matsudaira, Paul; Baltimore, David; Darnell, James E. (1999). Molecular Cell Biology (4th ed.). New York: W. H. Freeman & Co. ISBN 0-7167-3706-X
- Stryer, L. 1995. Biochemistry, 4th edition. New York: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 0716720094.
External links
- Beta-carotene website by Martha Evens, School of Chemistry, University of Bristol
- Berkeley Wellness Guide to Dietary Supplements
- Beta-carotene on University of Maryland
Template:ChemicalSources
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.