Difference between revisions of "Bridgetown" - New World Encyclopedia
Mike Butler (talk | contribs) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (42 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Approved}}{{copyedited}} | |
{{Infobox Settlement | {{Infobox Settlement | ||
| − | | | + | | name = Bridgetown |
| − | + | | settlement_type = City | |
| − | + | | image_skyline = Bridgetown barbados chamberlain bridge.jpg | |
| − | + | | imagesize = 250px | |
| − | |settlement_type | + | | image_caption = Chamberlain Bridge spanning the Careenage, Bridgetown |
| − | + | | image_seal = City of Bridgetown, Barbados Armorial bearing.jpg | |
| − | |image_skyline | + | | seal_size = 125px |
| − | |imagesize | + | | image_map = Bridgetown.png |
| − | |image_caption | + | | mapsize = 250px |
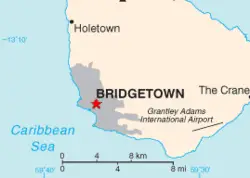
| − | | | + | | map_caption = Location of Bridgetown (red star) |
| − | + | | coordinates_footnotes = | |
| − | + | | coordinates_type = type:city_region:BB | |
| − | |seal_size | + | | coordinates_display = yes |
| − | + | | subdivision_type = Country | |
| − | + | | subdivision_name = [[Barbados]] | |
| − | + | | subdivision_type1 = [[Parishes of Barbados|Parish]] | |
| − | + | | subdivision_name1 = [[Saint Michael, Barbados|Saint Michael]] | |
| − | |image_map | + | | established_title = Established |
| − | |mapsize | + | | established_date = 1628 |
| − | |map_caption | + | | unit_pref = Imperial |
| − | | | + | | area_footnotes = |
| − | + | | area_total_sq_mi = 15 | |
| − | + | | elevation_footnotes =<ref>[http://population.mongabay.com/population/barbados/3374036/bridgetown Population of Bridgetown, Barbados] Mongabay.com. Retrieved March 19, 2012.</ref> | |
| − | + | | elevation_m = 1 | |
| − | + | | population_footnotes = | |
| − | | | + | | population_as_of = 2006 |
| − | + | | population_total = 96578 | |
| − | + | | population_density_sq_mi= auto | |
| − | | | + | | timezone = Eastern Caribbean Time Zone |
| − | | | + | | utc_offset = -4 |
| − | + | | timezone_DST = | |
| − | + | | utc_offset_DST = | |
| − | |subdivision_name | + | | postal_code_type = <!-- ZIP code, Postcode, Post code, Postal code... —> |
| − | |subdivision_type1 | + | | postal_code = |
| − | |subdivision_name1 | + | | area_code = [[Area code 246|246]] |
| − | + | | website = | |
| − | + | | footnotes = | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |established_title | ||
| − | |established_date | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |unit_pref | ||
| − | |area_footnotes | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |population_as_of | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |population_total | ||
| − | |||
| − | |population_density_sq_mi | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |timezone | ||
| − | |utc_offset | ||
| − | |timezone_DST | ||
| − | |utc_offset_DST | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |postal_code_type | ||
| − | |postal_code | ||
| − | |area_code | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |website | ||
| − | |footnotes | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | '''Bridgetown''' is the capital and largest city of [[Barbados]]. Established by the [[Great Britain|British]] in 1628, a major portion of the [[slave trade]] from [[Africa]] to the English [[New World]] passed through Bridgetown by 1712. Today, the culture of Bridgetown is a blend of [[United Kingdom|British]] and [[West Africa]]n influences. [[Religion]] plays an important role, and observances of the various [[faith]]s and [[religious denomination|denomination]]s are commonly shared through [[festival]]s. Bridgetown is a [[Caribbean|West Indies]] [[tourism|tourist]] destination, and acts as an important financial, informatics, and convention center in the [[Caribbean Sea|Caribbean]] region. | |
| + | |||
| + | The [[economics|economy]] of [[Barbados]] is susceptible to various issues, such as fluctuations in tourist seasons. The government has attempted to stabilize the economy by initiatives such as hosting one major sporting event each year and pursuing [[home porting]] agreements with several [[cruise ship|cruise lines]]. The Bridgetown Port or "Deep Water Harbour" is the port of entry for cruise and [[cargo ship]]s docking in Barbados, and is one of the shipping and [[transhipment]] hubs for the entire Eastern Caribbean Sea. | ||
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | Bridgetown benefits from its country's [[standard of living]], which is ranked as one of the highest in the world. The [[literacy]] rate is 98 percent, and [[health care]], [[social services]] and [[family]] programs are well established. | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| − | [[Image:Bridgetown2.jpg|thumb|left|250px|Suburbs of Bridgetown with the | + | [[Image:Bridgetown2.jpg|thumb|left|250px|Suburbs of Bridgetown with the [[harbor]] in the background]] |
| − | Bridgetown is located on a built-up coastal strip that stretches for several miles | + | Bridgetown is located on a built-up southwestern coastal strip of Barbados that stretches for several miles. The city's center was originally a [[swamp]]. |
| − | Barbados has a tropical climate, with mostly sunny and fair weather. | + | [[Barbados]] has a tropical [[climate]], with mostly sunny and fair weather. [[Temperature]]s in January range from 69.8°F (21°C) to 82.4°F (28°C), and in July from 73.4°F (23°C) to 86°F (30°C). Prevailing cool northeast [[trade wind]]s moderate the heat. The dry season occurs from January to June, and the [[hurricane]] season extends from June to October, although hurricanes usually miss Barbados. Instead, there are spectacular tropical [[rain]]storms, which are short and heavy. Total mean annual rainfall is 32.6 inches (829.8mm). |
| − | The Constitution River | + | The [[Constitution River]] empties on the west coast a half kilometer south of Bridgetown port. The Careenage, which has an obsolete dry dock and wharves, provides anchorage for [[pleasure craft]] or [[fishing boat]]s, and has two main bridges near the city center. |
The city of Bridgetown, and the wider Greater Bridgetown area, cover around 15 square miles (39 square kilometers). The Central Bank, Treasury Building, and National Insurance Building dominate the skyline. | The city of Bridgetown, and the wider Greater Bridgetown area, cover around 15 square miles (39 square kilometers). The Central Bank, Treasury Building, and National Insurance Building dominate the skyline. | ||
| − | The main street is Broad | + | The main street is Broad Street, which runs parallel to the Careenage, directly through the center of the city, past the Parliament Buildings, and is clustered with stores, restaurants, banks, and other services. Bay Street is another traffic artery into the city. The Spring Garden Highway, which lies to the west of the city, plays host to over 85,000 bystanders and participants in the annual Grand Kadooment Carnival Parade. Ribbon development stretches inland and along the coasts. Numerous [[business]]es have relocated to suburban malls. |
==History== | ==History== | ||
| − | [[Image:The Barbadoes Mulatto Girl.jpg|thumb|right|250px|'' | + | [[Image:The Barbadoes Mulatto Girl.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The ''Barbadoes Mulatto Girl,'' an engraving published at London in 1779, after a c. 1764 painting by [[Agostino Brunias]]. From the Barbados Museum & Historical Society, Bridgetown, [[Barbados]].]] |
| − | [[Image:Bridgetown barbados nelson statue.jpg|thumb|right|250px| | + | [[Image:Bridgetown barbados nelson statue.jpg|thumb|right|250px|British Admiral [[Horatio Nelson]] statue on Trafalgar Square in Bridgetown, Barbados.]] |
| − | [[ | + | The earliest inhabitants of Barbados were [[Indigenous peoples of the Americas|indigenous]] nomads migrating toward [[North America]]. The first group, the Salodoid-Barrancoids, arrived by canoe from [[Venezuela]]'s [[Orinoco River|Orinoco Valley]] around 350 C.E., the second group, the [[Arawak]] people, arrived around 800 C.E., and the third wave, the [[Carib]]s, arrived in the 13th century, displacing both the Arawak and the Salodoid-Barrancoids. |
| − | |||
| − | The earliest inhabitants of Barbados were [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Portugal|Portuguese]] [[Conquistadors]] seized many Caribs on Barbados and used them as [[Slavery|slave labor]] on [[plantation]]s, while other Caribs fled. | |
| − | + | British sailors who landed on Barbados, at first to collect water in 1620, then permanently in 1625, at the site of present-day Holetown on the Caribbean coast, found the island uninhabited. On July 25, 1628, settlers financed by the Earl of Carlisle established a settlement at the mouth of the Constitution River, to stake a rival claim to that established at Jamestown (Holetown) by colonists representing the Earl of Pembroke. | |
| − | + | Although the island was uninhabited when the British landed, one of the few traces of indigenous preexistence was a primitive, possibly [[Arawak]], bridge constructed over the Careenage area's swamp. British settlers began to call what is now the Bridgetown area, “the Indian Bridge” or “the Indian Bridgetown.” It was also called St. Michael’s town after the parish in which it was situated. Many of the streets of the city date to their seventeenth century origins. | |
| − | + | Beginning in the 1620s, an increasing number of [[Africa]]n slaves were brought to the island. Five thousand locals died of fever in 1647, and hundreds of slaves were executed by [[Cavalier|Royalist]] planters during the [[English Civil War]] (1642-1651) because they feared that the ideas of the [[Levellers]] might spread to the slave population if Parliament took control of Barbados. | |
| − | + | As the [[sugar]] industry developed, Barbados was divided into large plantation estates that replaced the smallholdings of the early British settlers. The Bridgetown port in 1697 exported goods to [[England]] valued at some £196,532. [[Virginia]] and [[Maryland]] were the only colonies to exceed Barbados' trade with an export trade valued at £227,759. | |
| − | + | Large numbers of Irishmen and Scots were shipped to Barbados as [[indentured servant]]s and slaves. But increased emigration of Celtic servants and slaves, and increased importation of African slaves, meant Barbados turned from mainly Celtic in the seventeenth century to overwhelmingly black by the nineteenth century. | |
| − | By 1712, Bridgetown’s population was 10, 641, while Boston had | + | By 1712, Bridgetown’s population was 10,641, while in comparison [[Boston]] had 9,500, [[Philadelphia]] 6,500, and [[New York City]] 5,700. Bridgetown’s population included African slaves. A major portion of the slave trade from Africa to the English New World passed through Bridgetown at that time. |
Bridgetown is the only city outside continental North America that [[George Washington]] (1732-1799), the first President of the [[United States]], visited. George Washington House, the actual house where he stayed, is now part of the [[Garrison Historic Area]]. | Bridgetown is the only city outside continental North America that [[George Washington]] (1732-1799), the first President of the [[United States]], visited. George Washington House, the actual house where he stayed, is now part of the [[Garrison Historic Area]]. | ||
| − | The [[slave trade]] ceased in 1804. In 1816, the continuation of slavery caused the largest major slave rebellion in the island's history. One thousand people died in the revolt, with 144 slaves executed and 123 deported. Slavery was abolished in the British Empire 18 years later in 1834. | + | The [[slave trade]] ceased in 1804. In 1816, the continuation of slavery caused the largest major slave rebellion in the island's history. One thousand people died in the revolt, with 144 slaves executed and 123 deported. Slavery was abolished in the [[British Empire]] 18 years later, in 1834. A [[cholera]] epidemic killed about 20,000 people in 1854. |
| − | |||
| − | A cholera epidemic killed about 20,000 people in 1854. | ||
| − | From 1800 until 1885, Bridgetown served as the main seat of Government for the former [[United Kingdom|British]] colonies of the [[Windward Islands]]. During this period, the resident [[Governor of Barbados]] also served as the | + | From 1800 until 1885, Bridgetown served as the main seat of Government for the former [[United Kingdom|British]] colonies of the [[Windward Islands]]. During this period, the resident [[Governor of Barbados]] also served as the Colonial head of the Windward Islands. |
| − | After the Government of Barbados | + | After the Government of Barbados left the Windward Island Union in 1885, the seat was moved from Bridgetown to [[St. George's, Grenada|St. George's]] on the neighboring island of [[Grenada]]. |
| − | + | According to a law requiring high income qualification, more than 70 percent of the population was excluded from voting. It was not until the 1930s that the descendants of emancipated slaves began a movement for political rights. [[Grantley Adams|Sir Grantley Adams]] (1898-1971), founded the [[Barbados Progressive League]] in 1938, which became the [[Barbados Labour Party]]. In 1942, the exclusive income qualification was lowered and women were given the right to vote. By 1949, governmental control was wrested from the planters and, in 1958, Adams became premier. | |
| − | From 1958 to 1962, Barbados was one of the 10 members of the [[West Indies Federation]]. By 1961, [[Errol Walton Barrow]] (1920-1987) had replaced Adams as | + | From 1958 to 1962, Barbados was one of the 10 members of the [[West Indies Federation]]. By 1961, [[Errol Walton Barrow]] (1920-1987) had replaced Adams as premier, and his Democratic Labour Party controlled the government. Barrow served as premier from 1961 until 1966, when Barbados achieved independence from [[Great Britain]]. Beginning in 1966, he served continuously as prime minister, as well as serving as Minister of Finance, and Minister of Foreign Affairs for the next 10 years. |
| − | In 2004, Bridgetown celebrated its 375th anniversary with a year of events and twinning agreements with [[ | + | In 2004, Bridgetown celebrated its 375th anniversary with a year of events and twinning agreements with Bridgetown, [[Nova Scotia]] ([[Canada]]), and with Wilmington, [[Delaware]] ([[United States]]). |
==Government== | ==Government== | ||
[[Image:Bridgetown barbados parliament building.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Parliament Building.]] | [[Image:Bridgetown barbados parliament building.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Parliament Building.]] | ||
| − | Barbados is a parliamentary democracy within the British Commonwealth. The chief of state Queen Elizabeth II represented by a | + | Barbados is a parliamentary democracy within the British Commonwealth. The chief of state is Queen Elizabeth II of the [[United Kingdom]], represented by a governor general. The head of government is the prime minister. The bicameral parliament consists of the Senate, of 21 appointed members, and the House of Assembly, of 30 directly elected members. |
| − | Formerly | + | Formerly the Town of Saint Michael, the city of Bridgetown, and the Greater Bridgetown area, occupied most of the parish of Saint Michael. Parts of the Greater Bridgetown area lie along the borders of the neighboring parishes [[Christ Church, Barbados|Christ Church]] and [[Saint James, Barbados|St. James]]. |
| − | Barbados has been governed by the Barbados Labour Party, commonly called the "Owen Arthur Administration" | + | Barbados has been governed by the Barbados Labour Party, commonly called the "Owen Arthur Administration," for 13 years to 2008. Prime Minister Owen S. Arthur was chosen from among leaders around the globe to deliver the William Wilberforce lecture on the 200th Anniversary of the Abolition of the Atlantic Slave Trade, in 2004. |
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
| − | + | Since independence, the island nation of [[Barbados]] has transformed itself from a low-income economy dependent upon [[sugar]] production, into an upper-middle-income economy based on [[tourism]] and the offshore sector. Barbados went into a deep [[recession]] in the 1990s, after three years of steady decline brought on by fundamental macroeconomic imbalances. After a painful readjustment process, the economy began to grow again in 1993. Growth rates have averaged between three and five percent since that time. | |
| − | Since independence, the island nation of [[Barbados]] has transformed itself from a low-income economy dependent upon [[sugar]] production, into an upper-middle-income economy based on [[tourism]] and the offshore sector. Barbados went into a deep [[recession]] in the 1990s after three years of steady decline brought on by fundamental macroeconomic imbalances. After a painful readjustment process, the economy began to grow again in 1993. Growth rates have averaged between three and five percent since | + | [[Image:Bridgetown1.jpg|thumb|left|250px|Bridgetown, Barbados harbor and downtown area.]] |
| − | + | Bridgetown serves as the administrative center of Barbados, houses most government ministries and departments, is a principal center for wholesale and retail commerce and trade, as well as a central hub for the island's public transport system. Bridgetown has branches of some of the largest [[Banking|banks]] in the world, and is internationally recognized as an emerging financial domicile. The City of Bridgetown also has a well regulated [[stock exchange]] with securities of Barbadian and regional Caribbean companies. Per capita GDP of Barbados was estimated at US$19,300 in 2007. | |
| − | Bridgetown serves as the administrative | ||
| − | + | All seven of Barbados's primary highways begin close to the City of Bridgetown. Public transport services in Barbados are operated by buses, mini-buses and by "route-taxis," or "ZRs," which are privately owned mini vans. | |
| − | + | The Grantley Adams International Airport is located in Seawell, Christ Church. The city of Bridgetown and New York City in the United States, were the only cities in the [[western hemisphere]] to be served by the now retired British Airways [[Concorde]] flights, and the Grantley Adams airport is one of four global display sites for the retired [[supersonic aircraft]]. | |
| − | + | The Bridgetown Port (or "Deep Water Harbour," as it is also known) is the port of entry for cruise and cargo ships docking in Barbados, and is one of the shipping and [[transhipment]] hubs for the entire Eastern [[Caribbean]]. The Deep Water Harbour lies a short distance across Carlisle Bay northwest of the Careenage Canal. | |
| − | |||
| − | The Bridgetown Port (or "Deep Water Harbour" as | ||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
[[Image:Bridgetown, Barbados, April 2007.jpg|thumb|right|250px|View from National Heroes Square.]] | [[Image:Bridgetown, Barbados, April 2007.jpg|thumb|right|250px|View from National Heroes Square.]] | ||
| − | Bridgetown's metropolitan population was 96,578 in 2006. Close to 90 percent of all Barbadians (also known colloquially as Bajan) are | + | Bridgetown's metropolitan population was 96,578 in 2006. Close to 90 percent of all Barbadians (also known colloquially as Bajan) are mostly descendants of the African slave laborers on the sugar plantations. The remainder of the population includes groups of [[Europe]]ans (mainly from [[United Kingdom|Britain]] and [[Ireland]]), Chinese, Bajan Hindus from [[India]], and [[Muslim]]s from [[Bangladesh]] and [[Pakistan]], and an influential "Arab-Bajans" group mainly of [[Syria]]n and [[Lebanon|Lebanese]] descent. There are numerous Creoles, a mixture of Afro-Caribbean and European. Many Afro-Bajans do have some British or Scottish antecedents. |
The country's official language is [[English language|British English]], the local dialect of which is referred to as [[Bajan]], spoken by most. | The country's official language is [[English language|British English]], the local dialect of which is referred to as [[Bajan]], spoken by most. | ||
| − | + | [[Protestant]]s make up 67 percent of the population ([[Anglican]] 40 percent, [[Pentecostal]] eight percent, [[Methodist]] seven percent, other 12 percent), [[Roman Catholic]] four percent, none 17 percent, other 12 percent. | |
| − | The city serves as the seat of one of the three campuses of the [[University of the West Indies | + | The city serves as the seat of one of the three campuses of the [[University of the West Indies]]. The campus sits on a bluff offering a spectacular view of Bridgetown and its port. The [[Barbados Community College]] is located in a suburb known as "The Ivy," while the sprawling campus of the [[Samuel Jackman Prescod Polytechnic]] is located just beyond the eastern limits of the city at "The Pine." The city has three distinguished secondary schools—[[Harrison College]], [[Combermere]], and The St. Michael School. |
| − | == | + | ==Society and culture== |
| − | [[Image:High street Barbados.jpg|thumb|right|250px| | + | [[Image:High street Barbados.jpg|thumb|right|250px|A colorful Bridgetown street.]] |
| − | The Public Buildings or [[Parliament of Barbados|parliament]], which stand at the heart of the city directly north of Heroes Square, house the third oldest continuous parliament in the [[British Empire|British Commonwealth]]. Bridgetown was the most important | + | The Public Buildings or [[Parliament of Barbados|parliament]], which stand at the heart of the city directly north of Heroes Square, house the third oldest continuous parliament in the [[British Empire|British Commonwealth]]. Bridgetown was the most important British New World possession due to its easterly location in the Caribbean region. |
The City of Bridgetown played host to the 1994 United Nations Global Conference on Sustainable Development of Small Islands States. The 2007 ICC Cricket World Cup tournament attracted thousands of visitors to the island and to the Kensington Oval. | The City of Bridgetown played host to the 1994 United Nations Global Conference on Sustainable Development of Small Islands States. The 2007 ICC Cricket World Cup tournament attracted thousands of visitors to the island and to the Kensington Oval. | ||
Places of interest include: | Places of interest include: | ||
| − | * National Heroes Square (formerly [[Trafalgar Square, Barbados|Trafalgar Square]]) and Fountain Garden | + | * National Heroes Square (formerly [[Trafalgar Square, Barbados|Trafalgar Square]]) and Fountain Garden |
| − | * The Cathedral Church of Saint Michaels and All Angels, the St Mary's Anglican Church, the St Patrick's Roman Catholic Cathedral, and the Bridgetown Synagogue | + | * The Cathedral Church of Saint Michaels and All Angels, the St Mary's Anglican Church, the St. Patrick's Roman Catholic Cathedral, and the Bridgetown Synagogue |
| − | * The Garrison Savannah and National Historic Area, and the Barbados Museum | + | * The Garrison Savannah and National Historic Area, and the Barbados Museum |
| − | * The Pelican Village and Craft Centre | + | * The Pelican Village and Craft Centre |
| − | * The Tom Adams Financial Complex, and the Pierhead Development Complex | + | * The Tom Adams Financial Complex, and the Pierhead Development Complex |
| − | * The Frank Collymore Hall of the Performing Arts | + | * The Frank Collymore Hall of the Performing Arts |
* The Cathedral Plaza, Sagicor Plaza | * The Cathedral Plaza, Sagicor Plaza | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Looking to the future== | ||
| + | [[Image:Barbadoscoast.jpg|thumb|250px|Beach near Bridgetown, Barbados.]] | ||
| + | Bridgetown is the capital and largest [[city]] of an island nation which has one of the highest standards of living and literacy rates in the world. Despite its small size, [[Barbados]] constantly ranks in the top 35 countries in the Human Development Index (HDI) rankings, and in 2008 is ranked third in [[the Americas]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The island is a major tourist destination, with offshore finance and information services important economic earners, along with a healthy light-manufacturing sector. Bridgetown serves as the administrative center of Barbados, houses most government ministries and departments, is a principal center for wholesale and retail commerce and trade, as well as a central hub for the island's public transport system. Bridgetown has branches of some of the largest [[Banking|banks]] in the world, and is internationally recognized as an emerging financial domicile. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The economy of Barbados is susceptible to various issues, such as fluctuations in tourist arrivals. The government has attempted to stabilize the economy by such things as hosting one major sporting event each year and pursuing "home porting" agreements with several cruise-lines. The Bridgetown Port is the port of entry for cruise and cargo ships docking in Barbados, and is one of the shipping and [[transhipment]] hubs for the entire Eastern [[Caribbean]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The culture of Bridgetown is a blend of [[Great Britain|British]] and [[West Africa]]n influences. [[Religion]] plays an important role, and observances of the various faiths and denominations are commonly shared through festivals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The city's economic, political, and cultural importance to the island is unquestioned. Its location in the Caribbean and its relaxed and leisurely pace makes it an attractive place to live or visit. The country's political stability helps to ensure a lifestyle of stability and growth for its people. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Notes== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | * Alleyne, Warren | + | * Alleyne, Warren. ''Historic Bridgetown''. Bridgetown: Barbados National Trust, 1978. {{OCLC|4468683}} |
| − | * | + | * ''Encyclopaedia Britannica''. [http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/79373/Bridgetown#tab=active~checked%2Citems~checked&title=Bridgetown%20—%20Britannica%20Online%20Encyclopedia.htm Bridgetown.] Retrieved April 28, 2020. |
| − | + | * Welch, Pedro L.V. ''Slave Society in the City: Bridgetown, Barbados, 1680-1834''. Kingston: I. Randle, 2003. ISBN 978-0974215556 | |
| − | * | + | * ''World Fact Book''. Barbados. |
| − | * World | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | + | All links retrieved November 20, 2023. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | * [http://www.barbadosport.com/ Barbados Port] | + | * [http://www.barbadosport.com/ Barbados Port] |
| − | + | * [http://www.barbados.org/maps/printsize/map_bridgetown.jpg Bridgetown picture map] | |
| − | * [http://www.barbados.org/maps/printsize/map_bridgetown.jpg Bridgetown picture map] | + | * [http://barbadosphotogallery.com/jpgees/070318/Dsc_0255.jpg Bridgetown centre aerial view] |
| − | * [http://barbadosphotogallery.com/jpgees/070318/Dsc_0255.jpg Bridgetown centre aerial view] | + | * [http://www.caribbean-on-line.com/br/btmap.shtml Bridgetown map] |
| − | * [http://www.caribbean-on-line.com/br/btmap.shtml Bridgetown map] | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Geography]] | [[Category:Geography]] | ||
[[Category:Cities]] | [[Category:Cities]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Central America]] | ||
| + | [[Category:The Americas]] | ||
{{credit|Bridgetown|227434621|Holetown|220914498|Economy_of_Barbados|225998681|}} | {{credit|Bridgetown|227434621|Holetown|220914498|Economy_of_Barbados|225998681|}} | ||
Latest revision as of 23:06, 20 November 2023
| Bridgetown | |||
| — City — | |||
| Chamberlain Bridge spanning the Careenage, Bridgetown | |||
|
|||
| Location of Bridgetown (red star) | |||
| Country | Barbados | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parish | Saint Michael | ||
| Established | 1628 | ||
| Area | |||
| - Total | 15 sq mi (38.8 km²) | ||
| Elevation [1] | 3 ft (1 m) | ||
| Population (2006) | |||
| - Total | 96,578 | ||
| - Density | 6,438.5/sq mi (2,485.9/km²) | ||
| Time zone | Eastern Caribbean Time Zone (UTC-4) | ||
| Area code(s) | 246 | ||
Bridgetown is the capital and largest city of Barbados. Established by the British in 1628, a major portion of the slave trade from Africa to the English New World passed through Bridgetown by 1712. Today, the culture of Bridgetown is a blend of British and West African influences. Religion plays an important role, and observances of the various faiths and denominations are commonly shared through festivals. Bridgetown is a West Indies tourist destination, and acts as an important financial, informatics, and convention center in the Caribbean region.
The economy of Barbados is susceptible to various issues, such as fluctuations in tourist seasons. The government has attempted to stabilize the economy by initiatives such as hosting one major sporting event each year and pursuing home porting agreements with several cruise lines. The Bridgetown Port or "Deep Water Harbour" is the port of entry for cruise and cargo ships docking in Barbados, and is one of the shipping and transhipment hubs for the entire Eastern Caribbean Sea.
Bridgetown benefits from its country's standard of living, which is ranked as one of the highest in the world. The literacy rate is 98 percent, and health care, social services and family programs are well established.
Geography

Bridgetown is located on a built-up southwestern coastal strip of Barbados that stretches for several miles. The city's center was originally a swamp.
Barbados has a tropical climate, with mostly sunny and fair weather. Temperatures in January range from 69.8°F (21°C) to 82.4°F (28°C), and in July from 73.4°F (23°C) to 86°F (30°C). Prevailing cool northeast trade winds moderate the heat. The dry season occurs from January to June, and the hurricane season extends from June to October, although hurricanes usually miss Barbados. Instead, there are spectacular tropical rainstorms, which are short and heavy. Total mean annual rainfall is 32.6 inches (829.8mm).
The Constitution River empties on the west coast a half kilometer south of Bridgetown port. The Careenage, which has an obsolete dry dock and wharves, provides anchorage for pleasure craft or fishing boats, and has two main bridges near the city center.
The city of Bridgetown, and the wider Greater Bridgetown area, cover around 15 square miles (39 square kilometers). The Central Bank, Treasury Building, and National Insurance Building dominate the skyline.
The main street is Broad Street, which runs parallel to the Careenage, directly through the center of the city, past the Parliament Buildings, and is clustered with stores, restaurants, banks, and other services. Bay Street is another traffic artery into the city. The Spring Garden Highway, which lies to the west of the city, plays host to over 85,000 bystanders and participants in the annual Grand Kadooment Carnival Parade. Ribbon development stretches inland and along the coasts. Numerous businesses have relocated to suburban malls.
History


The earliest inhabitants of Barbados were indigenous nomads migrating toward North America. The first group, the Salodoid-Barrancoids, arrived by canoe from Venezuela's Orinoco Valley around 350 C.E., the second group, the Arawak people, arrived around 800 C.E., and the third wave, the Caribs, arrived in the 13th century, displacing both the Arawak and the Salodoid-Barrancoids.
Portuguese Conquistadors seized many Caribs on Barbados and used them as slave labor on plantations, while other Caribs fled.
British sailors who landed on Barbados, at first to collect water in 1620, then permanently in 1625, at the site of present-day Holetown on the Caribbean coast, found the island uninhabited. On July 25, 1628, settlers financed by the Earl of Carlisle established a settlement at the mouth of the Constitution River, to stake a rival claim to that established at Jamestown (Holetown) by colonists representing the Earl of Pembroke.
Although the island was uninhabited when the British landed, one of the few traces of indigenous preexistence was a primitive, possibly Arawak, bridge constructed over the Careenage area's swamp. British settlers began to call what is now the Bridgetown area, “the Indian Bridge” or “the Indian Bridgetown.” It was also called St. Michael’s town after the parish in which it was situated. Many of the streets of the city date to their seventeenth century origins.
Beginning in the 1620s, an increasing number of African slaves were brought to the island. Five thousand locals died of fever in 1647, and hundreds of slaves were executed by Royalist planters during the English Civil War (1642-1651) because they feared that the ideas of the Levellers might spread to the slave population if Parliament took control of Barbados.
As the sugar industry developed, Barbados was divided into large plantation estates that replaced the smallholdings of the early British settlers. The Bridgetown port in 1697 exported goods to England valued at some £196,532. Virginia and Maryland were the only colonies to exceed Barbados' trade with an export trade valued at £227,759.
Large numbers of Irishmen and Scots were shipped to Barbados as indentured servants and slaves. But increased emigration of Celtic servants and slaves, and increased importation of African slaves, meant Barbados turned from mainly Celtic in the seventeenth century to overwhelmingly black by the nineteenth century.
By 1712, Bridgetown’s population was 10,641, while in comparison Boston had 9,500, Philadelphia 6,500, and New York City 5,700. Bridgetown’s population included African slaves. A major portion of the slave trade from Africa to the English New World passed through Bridgetown at that time.
Bridgetown is the only city outside continental North America that George Washington (1732-1799), the first President of the United States, visited. George Washington House, the actual house where he stayed, is now part of the Garrison Historic Area.
The slave trade ceased in 1804. In 1816, the continuation of slavery caused the largest major slave rebellion in the island's history. One thousand people died in the revolt, with 144 slaves executed and 123 deported. Slavery was abolished in the British Empire 18 years later, in 1834. A cholera epidemic killed about 20,000 people in 1854.
From 1800 until 1885, Bridgetown served as the main seat of Government for the former British colonies of the Windward Islands. During this period, the resident Governor of Barbados also served as the Colonial head of the Windward Islands.
After the Government of Barbados left the Windward Island Union in 1885, the seat was moved from Bridgetown to St. George's on the neighboring island of Grenada.
According to a law requiring high income qualification, more than 70 percent of the population was excluded from voting. It was not until the 1930s that the descendants of emancipated slaves began a movement for political rights. Sir Grantley Adams (1898-1971), founded the Barbados Progressive League in 1938, which became the Barbados Labour Party. In 1942, the exclusive income qualification was lowered and women were given the right to vote. By 1949, governmental control was wrested from the planters and, in 1958, Adams became premier.
From 1958 to 1962, Barbados was one of the 10 members of the West Indies Federation. By 1961, Errol Walton Barrow (1920-1987) had replaced Adams as premier, and his Democratic Labour Party controlled the government. Barrow served as premier from 1961 until 1966, when Barbados achieved independence from Great Britain. Beginning in 1966, he served continuously as prime minister, as well as serving as Minister of Finance, and Minister of Foreign Affairs for the next 10 years.
In 2004, Bridgetown celebrated its 375th anniversary with a year of events and twinning agreements with Bridgetown, Nova Scotia (Canada), and with Wilmington, Delaware (United States).
Government
Barbados is a parliamentary democracy within the British Commonwealth. The chief of state is Queen Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom, represented by a governor general. The head of government is the prime minister. The bicameral parliament consists of the Senate, of 21 appointed members, and the House of Assembly, of 30 directly elected members.
Formerly the Town of Saint Michael, the city of Bridgetown, and the Greater Bridgetown area, occupied most of the parish of Saint Michael. Parts of the Greater Bridgetown area lie along the borders of the neighboring parishes Christ Church and St. James.
Barbados has been governed by the Barbados Labour Party, commonly called the "Owen Arthur Administration," for 13 years to 2008. Prime Minister Owen S. Arthur was chosen from among leaders around the globe to deliver the William Wilberforce lecture on the 200th Anniversary of the Abolition of the Atlantic Slave Trade, in 2004.
Economy
Since independence, the island nation of Barbados has transformed itself from a low-income economy dependent upon sugar production, into an upper-middle-income economy based on tourism and the offshore sector. Barbados went into a deep recession in the 1990s, after three years of steady decline brought on by fundamental macroeconomic imbalances. After a painful readjustment process, the economy began to grow again in 1993. Growth rates have averaged between three and five percent since that time.
Bridgetown serves as the administrative center of Barbados, houses most government ministries and departments, is a principal center for wholesale and retail commerce and trade, as well as a central hub for the island's public transport system. Bridgetown has branches of some of the largest banks in the world, and is internationally recognized as an emerging financial domicile. The City of Bridgetown also has a well regulated stock exchange with securities of Barbadian and regional Caribbean companies. Per capita GDP of Barbados was estimated at US$19,300 in 2007.
All seven of Barbados's primary highways begin close to the City of Bridgetown. Public transport services in Barbados are operated by buses, mini-buses and by "route-taxis," or "ZRs," which are privately owned mini vans.
The Grantley Adams International Airport is located in Seawell, Christ Church. The city of Bridgetown and New York City in the United States, were the only cities in the western hemisphere to be served by the now retired British Airways Concorde flights, and the Grantley Adams airport is one of four global display sites for the retired supersonic aircraft.
The Bridgetown Port (or "Deep Water Harbour," as it is also known) is the port of entry for cruise and cargo ships docking in Barbados, and is one of the shipping and transhipment hubs for the entire Eastern Caribbean. The Deep Water Harbour lies a short distance across Carlisle Bay northwest of the Careenage Canal.
Demographics
Bridgetown's metropolitan population was 96,578 in 2006. Close to 90 percent of all Barbadians (also known colloquially as Bajan) are mostly descendants of the African slave laborers on the sugar plantations. The remainder of the population includes groups of Europeans (mainly from Britain and Ireland), Chinese, Bajan Hindus from India, and Muslims from Bangladesh and Pakistan, and an influential "Arab-Bajans" group mainly of Syrian and Lebanese descent. There are numerous Creoles, a mixture of Afro-Caribbean and European. Many Afro-Bajans do have some British or Scottish antecedents.
The country's official language is British English, the local dialect of which is referred to as Bajan, spoken by most.
Protestants make up 67 percent of the population (Anglican 40 percent, Pentecostal eight percent, Methodist seven percent, other 12 percent), Roman Catholic four percent, none 17 percent, other 12 percent.
The city serves as the seat of one of the three campuses of the University of the West Indies. The campus sits on a bluff offering a spectacular view of Bridgetown and its port. The Barbados Community College is located in a suburb known as "The Ivy," while the sprawling campus of the Samuel Jackman Prescod Polytechnic is located just beyond the eastern limits of the city at "The Pine." The city has three distinguished secondary schools—Harrison College, Combermere, and The St. Michael School.
Society and culture
The Public Buildings or parliament, which stand at the heart of the city directly north of Heroes Square, house the third oldest continuous parliament in the British Commonwealth. Bridgetown was the most important British New World possession due to its easterly location in the Caribbean region.
The City of Bridgetown played host to the 1994 United Nations Global Conference on Sustainable Development of Small Islands States. The 2007 ICC Cricket World Cup tournament attracted thousands of visitors to the island and to the Kensington Oval.
Places of interest include:
- National Heroes Square (formerly Trafalgar Square) and Fountain Garden
- The Cathedral Church of Saint Michaels and All Angels, the St Mary's Anglican Church, the St. Patrick's Roman Catholic Cathedral, and the Bridgetown Synagogue
- The Garrison Savannah and National Historic Area, and the Barbados Museum
- The Pelican Village and Craft Centre
- The Tom Adams Financial Complex, and the Pierhead Development Complex
- The Frank Collymore Hall of the Performing Arts
- The Cathedral Plaza, Sagicor Plaza
Looking to the future
Bridgetown is the capital and largest city of an island nation which has one of the highest standards of living and literacy rates in the world. Despite its small size, Barbados constantly ranks in the top 35 countries in the Human Development Index (HDI) rankings, and in 2008 is ranked third in the Americas.
The island is a major tourist destination, with offshore finance and information services important economic earners, along with a healthy light-manufacturing sector. Bridgetown serves as the administrative center of Barbados, houses most government ministries and departments, is a principal center for wholesale and retail commerce and trade, as well as a central hub for the island's public transport system. Bridgetown has branches of some of the largest banks in the world, and is internationally recognized as an emerging financial domicile.
The economy of Barbados is susceptible to various issues, such as fluctuations in tourist arrivals. The government has attempted to stabilize the economy by such things as hosting one major sporting event each year and pursuing "home porting" agreements with several cruise-lines. The Bridgetown Port is the port of entry for cruise and cargo ships docking in Barbados, and is one of the shipping and transhipment hubs for the entire Eastern Caribbean.
The culture of Bridgetown is a blend of British and West African influences. Religion plays an important role, and observances of the various faiths and denominations are commonly shared through festivals.
The city's economic, political, and cultural importance to the island is unquestioned. Its location in the Caribbean and its relaxed and leisurely pace makes it an attractive place to live or visit. The country's political stability helps to ensure a lifestyle of stability and growth for its people.
Notes
- ↑ Population of Bridgetown, Barbados Mongabay.com. Retrieved March 19, 2012.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Alleyne, Warren. Historic Bridgetown. Bridgetown: Barbados National Trust, 1978. OCLC 4468683
- Encyclopaedia Britannica. Bridgetown. Retrieved April 28, 2020.
- Welch, Pedro L.V. Slave Society in the City: Bridgetown, Barbados, 1680-1834. Kingston: I. Randle, 2003. ISBN 978-0974215556
- World Fact Book. Barbados.
External links
All links retrieved November 20, 2023.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.