Difference between revisions of "Liver" - New World Encyclopedia
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
}} | }} | ||
The '''liver''' is an [[organ (anatomy)|organ]] present in [[vertebrate]]s and some other animals. It plays a major role in [[metabolism]] and has a number of functions in the body, including [[glycogen]] storage, [[plasma protein]] synthesis, and detoxification. This organ also is the largest [[gland]] in the [[human anatomy|human body]]. It lies below the diaphragm in the thoracic region of the abdomen.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.kmle.com/search.php?Search=liver | title = ''KMLE Medical Dictionary Definition of liver'' | author = [http://www.kmle.com KMLE Medical Dictionary]}} Retrieved 2007-02-16</ref> It produces [[bile]], an alkaline compound which aids in [[digestion]], via the emulsification of lipids. It also performs and regulates a wide variety of high-volume biochemical reactions requiring specialized [[biological tissue|tissues]]. | The '''liver''' is an [[organ (anatomy)|organ]] present in [[vertebrate]]s and some other animals. It plays a major role in [[metabolism]] and has a number of functions in the body, including [[glycogen]] storage, [[plasma protein]] synthesis, and detoxification. This organ also is the largest [[gland]] in the [[human anatomy|human body]]. It lies below the diaphragm in the thoracic region of the abdomen.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.kmle.com/search.php?Search=liver | title = ''KMLE Medical Dictionary Definition of liver'' | author = [http://www.kmle.com KMLE Medical Dictionary]}} Retrieved 2007-02-16</ref> It produces [[bile]], an alkaline compound which aids in [[digestion]], via the emulsification of lipids. It also performs and regulates a wide variety of high-volume biochemical reactions requiring specialized [[biological tissue|tissues]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Anatomy== | ==Anatomy== | ||
| − | |||
The adult human liver normally weighs between 1.7 - 3.0 [[kilogram]]s (3.5 - 6.5 pounds), and it is a soft, pinkish-brown "[[boomerang]] shaped" organ. It is the second [[largest body part|largest organ]] (the largest organ being the [[skin]]) and the largest gland within the human body.It is the heaviest organ in the body. | The adult human liver normally weighs between 1.7 - 3.0 [[kilogram]]s (3.5 - 6.5 pounds), and it is a soft, pinkish-brown "[[boomerang]] shaped" organ. It is the second [[largest body part|largest organ]] (the largest organ being the [[skin]]) and the largest gland within the human body.It is the heaviest organ in the body. | ||
It is located on the right side of the upper [[human abdomen|abdomen]] below the [[diaphragm (anatomy)|diaphragm]]. The liver lies on the right of the stomach and makes a kind of bed for the [[gallbladder]] (which stores [[bile]]). | It is located on the right side of the upper [[human abdomen|abdomen]] below the [[diaphragm (anatomy)|diaphragm]]. The liver lies on the right of the stomach and makes a kind of bed for the [[gallbladder]] (which stores [[bile]]). | ||
| Line 82: | Line 78: | ||
==Regeneration== | ==Regeneration== | ||
In [[Greek mythology]], [[Prometheus]] was punished by the gods for revealing fire to humans by being chained to a rock where a [[vulture]] (or an [[eagle]], [[Ethon]]) would peck out his liver, which would regenerate overnight. Curiously, the liver is the only human internal organ that actually can regenerate itself to a significant extent; this characteristic may have already been known to the Greeks due to survived injuries in battle. | In [[Greek mythology]], [[Prometheus]] was punished by the gods for revealing fire to humans by being chained to a rock where a [[vulture]] (or an [[eagle]], [[Ethon]]) would peck out his liver, which would regenerate overnight. Curiously, the liver is the only human internal organ that actually can regenerate itself to a significant extent; this characteristic may have already been known to the Greeks due to survived injuries in battle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Medical terms related to the liver often start in ''hepato-'' or ''hepatic'' from the [[Greek language|Greek]] word for liver, ''hēpar'' (ήπαρ<ref>The Greek word ''"ήπαρ"'' was derived from ''hēpaomai'' (''[http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/cgi-bin/ptext?layout.reflang=greek;layout.refembed=2;layout.refwordcount=1;layout.refdoc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0058;layout.reflookup=h%29ph%2Fsasqai;layout.refcit=entry%3Dh%29pa%2Fomai;doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3D%2347442 ηπάομαι]''): to mend, to repair, hence ''hēpar'' | ||
| + | actually means ''"repairable"'', indicating that this organ can regenerate itself spontaneously in the case of lesion. </ref>). | ||
The liver is among the few internal human organs capable of natural [[regeneration (biology)|regeneration]] of lost [[Biological tissue|tissue]]; as little as 25% of remaining liver can regenerate into a whole liver again. | The liver is among the few internal human organs capable of natural [[regeneration (biology)|regeneration]] of lost [[Biological tissue|tissue]]; as little as 25% of remaining liver can regenerate into a whole liver again. | ||
| Line 111: | Line 110: | ||
For the general reader: | For the general reader: | ||
| − | *Chopra, S. 2002. ''The Liver Book: A Comprehensive Guide to Diagnosis, Treatment, and Recovery''. | + | *Chopra, S. 2002. ''The Liver Book: A Comprehensive Guide to Diagnosis, Treatment, and Recovery''. New York: Atria. ISBN 0-7434-0585-4 |
| − | *Palmer, M. 2004. ''Dr. Melissa Palmer's Guide to Hepatitis and Liver Disease: What You Need to Know'', revised ed. | + | *Palmer, M. 2004. ''Dr. Melissa Palmer's Guide to Hepatitis and Liver Disease: What You Need to Know'', revised ed. New York: Avery Publishing Group; Revised edition ISBN 1-58333-188-3. |
| − | *Worman, H.J. 1999. ''The Liver Disorders Sourcebook''. New York:McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-7373-0090-6. | + | *Worman, H.J. 1999. ''The Liver Disorders Sourcebook''. New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-7373-0090-6. |
==Additional images== | ==Additional images== | ||
Revision as of 18:03, 27 August 2007
| Liver | |
|---|---|
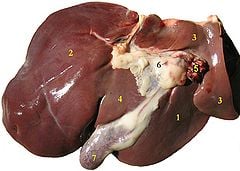
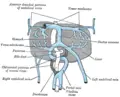
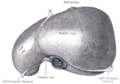
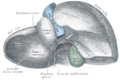
| Liver of a sheep: (1) right lobe, (2) left lobe, (3) caudate lobe, (4) quadrate lobe, (5) hepatic artery and portal vein, (6) hepatic lymph nodes, (7) gall bladder. | |
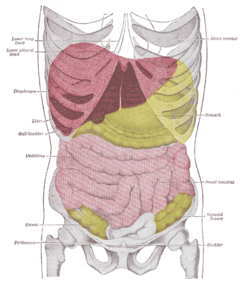
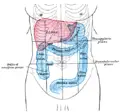
| Position of the liver (red) in the human abdomen. | |
| Gray's | subject #250 1188 |
| Artery | hepatic artery |
| Vein | hepatic vein, portal vein |
| Nerve | celiac ganglia, vagus[1] |
| Precursor | foregut |
| MeSH | Liver |
The liver is an organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It plays a major role in metabolism and has a number of functions in the body, including glycogen storage, plasma protein synthesis, and detoxification. This organ also is the largest gland in the human body. It lies below the diaphragm in the thoracic region of the abdomen.[2] It produces bile, an alkaline compound which aids in digestion, via the emulsification of lipids. It also performs and regulates a wide variety of high-volume biochemical reactions requiring specialized tissues.
Anatomy
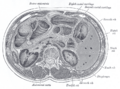
The adult human liver normally weighs between 1.7 - 3.0 kilograms (3.5 - 6.5 pounds), and it is a soft, pinkish-brown "boomerang shaped" organ. It is the second largest organ (the largest organ being the skin) and the largest gland within the human body.It is the heaviest organ in the body. It is located on the right side of the upper abdomen below the diaphragm. The liver lies on the right of the stomach and makes a kind of bed for the gallbladder (which stores bile).
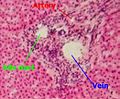
Approximately 60% to 80% of the blood flow to the liver is from the portal venous system, and 1/4 is from the hepatic artery.
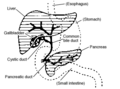
The bile produced in the liver is collected in bile canaliculi, which merge to form bile ducts. These eventually drain into the right and left hepatic ducts, which in turn merge to form the common hepatic duct. The cystic duct (from the gallbladder) joins with the common hepatic duct to form the common bile duct. Bile can either drain directly into the duodenum via the common bile duct or be temporarily stored in the gallbladder via the cystic duct.
The central area where the common bile duct, portal vein, and hepatic artery enter the liver is the hilum or "porta hepatis". The duct, vein, and artery divide into left and right branches, and the portions of the liver supplied by these branches constitute the functional left and right lobes.
The functional lobes are separated by a plane joining the gallbladder fossa to the inferior vena cava. This separates the liver into the true right and left lobes. The middle hepatic vein also demarcates the true right and left lobes. The right lobe is further divided into an anterior and posterior segment by the right hepatic vein. The left lobe is divided into the medial and lateral segments by the left hepatic vein. The fissure for the ligamentum teres (the ligamentum teres becomes the falciform ligament) also separates the medial and lateral segmants. The medial segment is what used to be called the quadrate lobe. In the widely used Couinaud or "French" system, the functional lobes are further divided into a total of eight subsegments based on a transverse plane through the bifurcation of the main portal vein. The caudate lobe is a separate structure which receives blood flow from both the right- and left-sided vascular branches.[3][4]
Functions
The various functions of the liver are carried out by the liver cells or hepatocytes.
- The liver produces and excretes bile (a greenish liquid) required for emulsifying fats. Some of the bile drains directly into the duodenum, and some is stored in the gallbladder.
- The liver performs several roles in carbohydrate metabolism:
- Gluconeogenesis (the synthesis of glucose from certain amino acids, lactate or glycerol)
- Glycogenolysis (the breakdown of glycogen into glucose) (muscle tissues can also do this)
- Glycogenesis (the formation of glycogen from glucose)
- The breakdown of insulin and other hormones
- The liver is responsible for the mainstay of protein metabolism.
- The liver also performs several roles in lipid metabolism:
- Cholesterol synthesis
- The production of triglycerides (fats).
- The liver produces coagulation factors I (fibrinogen), II (prothrombin), V, VII, IX, X and XI, as well as protein C, protein S and antithrombin.
- The liver breaks down hemoglobin, creating metabolites that are added to bile as pigment (bilirubin and biliverdin).
- The liver breaks down toxic substances and most medicinal products in a process called drug metabolism. This sometimes results in toxication, when the metabolite is more toxic than its precursor.
- The liver converts ammonia to urea.
- The liver stores a multitude of substances, including glucose in the form of glycogen, vitamin B12, iron, and copper.
- In the first trimester fetus, the liver is the main site of red blood cell production. By the 32nd week of gestation, the bone marrow has almost completely taken over that task.
- The liver is responsible for immunological effects- the reticuloendothelial system of the liver contains many immunologically active cells, acting as a 'sieve' for antigens carried to it via the portal system.
Currently, there is no artificial organ or device capable of emulating all the functions of the liver. Some functions can be emulated by liver dialysis, an experimental treatment for liver failure.
Fetal blood supply
In the growing fetus, a major source of blood to the liver is the umbilical vein which supplies nutrients to the growing fetus. The umbilical vein enters the abdomen at the umbilicus, and passes upward along the free margin of the falciform ligament of the liver to the inferior surface of the liver. There it joins with the left branch of the portal vein. The ductus venosus carries blood from the left portal vein to the left hepatic vein and then to the inferior vena cava, allowing placental blood to bypass the liver.
In the fetus, the liver develops throughout normal gestation, and does not perform the normal filtration of the infant liver. The liver does not perform digestive processes because the fetus does not consume meals directly, but receives nourishment from the mother via the placenta. The fetal liver releases some blood stem cells that migrate to the fetal thymus, so initially the lymphocytes, called T-cells, are created from fetal liver stem cells. Once the fetus is delivered, the formation of blood stem cells in infants shifts to the red bone marrow.
After birth, the umbilical vein and ductus venosus are completely obliterated two to five days postpartum; the former becomes the ligamentum teres and the latter becomes the ligamentum venosum. In the disease state of cirrhosis and portal hypertension, the umbilical vein can open up again.
Diseases of the liver
Many diseases of the liver are accompanied by jaundice caused by increased levels of bilirubin in the system. The bilirubin results from the breakup of the hemoglobin of dead red blood cells; normally, the liver removes bilirubin from the blood and excretes it through bile.
- Hepatitis, inflammation of the liver, caused mainly by various viruses but also by some poisons, autoimmunity or hereditary conditions.
- Cirrhosis is the formation of fibrous tissue in the liver, replacing dead liver cells. The death of the liver cells can for example be caused by viral hepatitis, alcoholism or contact with other liver-toxic chemicals.
- Haemochromatosis, a hereditary disease causing the accumulation of iron in the body, eventually leading to liver damage.
- Cancer of the liver (primary hepatocellular carcinoma or cholangiocarcinoma and metastatic cancers, usually from other parts of the gastrointestinal tract).
- Wilson's disease, a hereditary disease which causes the body to retain copper.
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis, an inflammatory disease of the bile duct, autoimmune in nature.
- Primary biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune disease of small bile ducts.
- Budd-Chiari syndrome, obstruction of the hepatic vein.
- Gilbert's syndrome, a genetic disorder of bilirubin metabolism, found in about 5% of the population.
- Glycogen storage disease type II,The build-up of glycogen causes progressive muscle weakness (myopathy) throughout the body and affects various body tissues, particularly in the heart, skeletal muscles, liver and nervous system.
Regeneration
In Greek mythology, Prometheus was punished by the gods for revealing fire to humans by being chained to a rock where a vulture (or an eagle, Ethon) would peck out his liver, which would regenerate overnight. Curiously, the liver is the only human internal organ that actually can regenerate itself to a significant extent; this characteristic may have already been known to the Greeks due to survived injuries in battle.
Medical terms related to the liver often start in hepato- or hepatic from the Greek word for liver, hēpar (ήπαρ[5]).
The liver is among the few internal human organs capable of natural regeneration of lost tissue; as little as 25% of remaining liver can regenerate into a whole liver again.
This is predominantly due to the hepatocytes acting as unipotential stem cells (i.e. a single hepatocyte can divide into two hepatocyte daughter cells). There is also some evidence of bipotential stem cells, called oval cells, which can differentiate into either hepatocytes or cholangiocytes (cells that line the bile ducts).
Human liver transplant was first performed by Thomas Starzl in USA and Roy Calne in England in 1963 and 1965 respectively.
Liver transplantation is the only option for those with irreversible liver failure. Most transplants are done for chronic liver diseases leading to cirrhosis, such as chronic hepatitis C, alcoholism, autoimmune hepatitis, and many others. Less commonly, liver transplantation is done for fulminant hepatic failure, in which liver failure occurs over days to weeks.
Liver allografts for transplant usually come from non-living donors who have died from fatal brain injury. Living donor liver transplantation is a technique in which a portion of a living person's liver is removed and used to replace the entire liver of the recipient. This was first performed in 1989 for pediatric liver transplantation. Only 20% of an adult's liver (Couinaud segments 2 and 3) is needed to serve as a liver allograft for an infant or small child.
More recently, adult-to-adult liver transplantation has been done using the donor's right hepatic lobe which amounts to 60% of the liver. Due to the ability of the liver to regenerate, both the donor and recipient end up with normal liver function if all goes well. This procedure is more controversial as it entails performing a much larger operation on the donor, and indeed there have been at least 2 donor deaths out of the first several hundred cases. A recent publication has addressed the problem of donor mortality, and at least 14 cases have been found.[6] The risk of postoperative complications (and death) is far greater in right sided hepatectomy than left sided operations.
Liver in the diet
Mammal and bird livers are commonly eaten as food: products include liver pâté, Leberwurst, Braunschweiger, foie gras, chopped liver, liver and onions, leverpostej and liver sashimi.
Both animal and fish livers are rich in iron and Vitamin A and cod liver oil is commonly used as a supplement. Very high doses of Vitamin A can be toxic; Antarctic explorers Douglas Mawson and Xavier Mertz were both poisoned, the latter fatally, from eating husky liver. In the US, the USDA specifies 3000 μg per day as a tolerable upper limit, which amounts to about 50 g of raw pork liver or, as reported in a non scientific source, 3 g of polar-bear liver.[7] However, acute vitamin A poisoning is not likely to result from liver consumption, since it is present in a less toxic form than in many dietary supplements.[8]
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Purves
- Stryer
Further reading
Standard medical textbooks:
- Schiff, E.R., Sorrell, M.F., and W.C. Maddrey, eds. 2003. Schiff's diseases of the liver, 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-3007-4
- Sherlock, S. and J. Dooley. 2002. Diseases of the liver and biliary system, 11th ed. Oxford, UK; Malden, MA: Blackwell Science. ISBN 0-632-05582-0
- Zakim, D. and T.D. Boyer. eds. 2003. Hepatology: a textbook of liver disease, 4th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-9051-3
For the general reader:
- Chopra, S. 2002. The Liver Book: A Comprehensive Guide to Diagnosis, Treatment, and Recovery. New York: Atria. ISBN 0-7434-0585-4
- Palmer, M. 2004. Dr. Melissa Palmer's Guide to Hepatitis and Liver Disease: What You Need to Know, revised ed. New York: Avery Publishing Group; Revised edition ISBN 1-58333-188-3.
- Worman, H.J. 1999. The Liver Disorders Sourcebook. New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-7373-0090-6.
Additional images
External links
- Children's Liver Association for Support Services, C.L.A.S.S. A large non-profit organization. An online Support Group full of resources, materials and stories; includes a Community Discussion Forum and Chat Room
- The American Liver Foundation
- Liver disorders - Read patient Queries
- American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD)
- American Liver Society (ALS)
- WikiLiver — a wiki dedicated to the liver
- "It's Dangerous to Ignore Your Liver" — information provided by the American Liver Foundation
- "The Liver and its Diseases" — information at h2g2
- Liver Families — an online support group for families whose lives have been affected by pediatric liver disease and transplant issues
- Children's Liver Disease Foundation — an organisation dedicated to fighting childhood liver disease and supporting affected families
- Liver Specialists of Texas: a site designed for patients with liver disease, located in Houston, Texas USA
- Autoimmune immune liver disease
- British Liver Trust - includes patient info oriented to British situations.
| ||||||||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
- ↑ Physiology at MCG 6/6ch2/s6ch2_30
- ↑ KMLE Medical Dictionary. KMLE Medical Dictionary Definition of liver. Retrieved 2007-02-16
- ↑ http://dpi.radiology.uiowa.edu/nlm/app/livertoc/liver/liver.html
- ↑ http://www.uni-bonn.de/~umm705/quiz0403.htm
- ↑ The Greek word "ήπαρ" was derived from hēpaomai (ηπάομαι): to mend, to repair, hence hēpar actually means "repairable", indicating that this organ can regenerate itself spontaneously in the case of lesion.
- ↑ Bramstedt K (2006). Living liver donor mortality: where do we stand?. Am J Gastroenterol 101 (4): 755-9. PMID 16494593.
- ↑ A. Aggrawal, Death by Vitamin A
- ↑ Myhre et al., "Water-miscible, emulsified, and solid forms of retinol supplements are more toxic than oil-based preparations", Am. J. Clinical Nutrition, 78, 1152 (2003)