Carson, Kit
Laura Brooks (talk | contribs) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (30 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{approved}}{{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Paid}}{{Copyedited}} | ||
{{epname|Carson, Kit}} | {{epname|Carson, Kit}} | ||
| − | [[Image:Kit-carson-photograph-loc.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:Kit-carson-photograph-loc.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Christopher 'Kit' Carson (1809-1868), American explorer]] |
| − | '''Christopher Houston "Kit" Carson''' (December 24, 1809 – May 23, 1868) was an [[United States|American]] [[frontier]]sman. | + | '''Christopher Houston "Kit" Carson''' (December 24, 1809 – May 23, 1868) was an [[United States|American]] [[frontier]]sman. He pioneered much of the American west and rode as a scout for the Untied States Cavalry. Trusted by white settlers and [[Native Americans]] alike, Carson's legacy is that of someone who saw, the frontier, went to it and became absorbed by it. His two consecutive trans-continental [[courier]] missions stand as an unrepeated testament to both ability and endurance. |
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | When resources such as [[beaver]] became depleted, Carson learned the need for [[wildlife conservation]]. In 1845, he teamed with [[John C. Fremont]] and headed west exploring passage to the [[Pacific Ocean]]. Together with Fremont, Carson enabled the westward expansion across the North American continent and helped foster the ideals of [[Manifest Destiny]]. | ||
==Early life== | ==Early life== | ||
| − | + | Carson was born in [[Madison County]], [[Kentucky]] and raised in [[Franklin, Missouri]] Carson's father, Lindsey Carson, was a farmer of [[Scots-Irish]] descent, who had fought in the [[American Revolution|Revolutionary War]] under [[Wade Hampton I|General Wade Hampton]]. There were a total of 15 Carson children. The Carson family settled on a tract of land owned by the sons of [[Daniel Boone]], who had purchased the land from the [[Spain|Spanish]], prior to the [[Louisiana Purchase]]. The Boone and Carson families became good friends, working, socializing, and intermarrying. | |
| − | Kit | + | Kit Carson was seven when his father was killed by a falling tree while clearing land. Lindsey Carson's death reduced the Carson family to a desperate poverty, forcing young Kit to drop out of school to work on the family farm, as well as engage in hunting. At age 14, Kit was apprenticed to a [[saddle maker]] in the settlement of Franklin, Missouri. Franklin was situated at the eastern end of the [[Santa Fe Trail]], which had opened two years earlier. Many of the clientèle at the [[saddle shop]] were trappers and traders themselves. Carson was so fascinated hearing their stirring tales of the Far West that he ran away. |
| − | At | + | At age 16, without telling his family, Carson secretly signed on with a large merchant caravan heading to [[Santa Fe]], which at that time, of course, belonged to Mexico. His job was tending the [[horse]]s, [[mule]]s, and [[oxen]]. The saddler posted notice of Carson absconding in the local paper offering a reward of one cent for his return. Nobody ever collected one cent or any sort of reward for the capture of Kit Carson because he had luck and a publicist as well as courage and skillful ability.<ref>Evan Jones. ''Trappers and Mountain Men.'' (New York, American Heritage Pub. Co; 1961), 124 </ref> During the winter of 1826-1827 he stayed with [[Matthew Kinkead]], a trapper and explorer, in [[Taos, New Mexico]], which was known as the capital of the fur trade in the Southwest. Kinkead had been a friend of Carson's father in Missouri, and Kit began learning animal trapping skills from him. At the same time Carson learned languages and became fluent in Spanish, [[Navajo]], [[Apache]], [[Cheyenne]], [[Arapaho]], [[Paiute]], [[Shoshone]], and [[Ute]]. |
| − | == The trapper years (1829- | + | == The trapper years (1829-1840) == |
| − | After gaining experience along the [[Santa Fe Trail]] and in [[Mexico]] on various expeditions, Carson signed on with Ewing Young and | + | After gaining experience along the [[Santa Fe Trail]] and in [[Mexico]] on various expeditions, Carson signed on with [[Ewing Young]] and 40 other fur men in the Spring of 1829. The journey took the band into unexplored [[Apache]] country along the [[Gila River]]. Ewing's group was approached and attacked by a band of Apache Indians. It was during this encounter that Carson shot and killed one of the attacking Indians, the first time circumstances required him to act in a way that resulted in another's death. Carson was profoundly shaken by this experience. |
| − | Carson | + | Carson considered his years as a trapper to be "the happiest days of my life." Accompanied by Singing Grass, he worked with the British firm based in Canada, the [[Hudson's Bay Company]], as well as the renowned frontiersman [[Jim Bridger]], trapping beaver along the [[Yellowstone River|Yellowstone]], [[Powder River|Powder]], and [[Big Horn River|Big Horn]] Rivers, and was found throughout what is now [[Colorado]], [[Utah]], [[Wyoming]], [[Idaho]], and [[Montana]]. Like many other white trappers, Carson traveled and lived extensively among [[Native American]]s. His first wife was an [[Arapaho]] named Singing Grass; their first child, a daughter, was born in 1837, named Adeline. Carson's wife developed a fever after the child's birth, and died soon after. By 1842 he met and became engaged to the daughter of a prominent [[Taos, New Mexico|Taos]] family, Josefa Jaramillo. He was 34 years old, when he married 14-year-old Josefa on February 6, 1843. Together they raised 15 children, the descendants of whom remain in the Arkansas Valley of Colorado. |
| − | + | At this time, the nation was undergoing its first severe depression. The economy was in part dependent upon the fur industry which was undermined by changing fashion styles. A new demand for silk hats replaced the demand for beaver fur. Also, the trapping industry had devastated the [[beaver]] population. This combination of facts ended the need for trappers. Carson stated, "Beaver was getting scarce, it became necessary to try our hand at something else".<ref>Hampton Sides. ''Blood and thunder an epic of the American West.'' (New York: Doubleday 2006. ISBN 9780385507776), 33</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | At this time, the nation was undergoing | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Guide with Frémont == | == Guide with Frémont == | ||
| − | Carson decided early in 1842 to return east to bring his daughter Adeline to live with relatives near Carson's former home of Franklin, for the purpose of providing her with an education. That summer | + | Carson decided early in 1842 to return east to bring his daughter Adeline alternately to live with relatives near Carson's former home of Franklin, and for the purpose of providing her with an [[education]] some reports have it that Adeline was placed in a boarding school. That summer Carson met U.S. Army Captain [[John C. Fremont]] on a [[Missouri River]] [[steamboat]] in [[Saint Louis, Missouri]]. Frémont was preparing to lead his first expedition and was looking for a guide to take him to South Pass. The two men made acquaintance, and Carson offered his services, as he had spent much time in the area. The five month journey, made with 25 men, was a success, and Fremont's report was published by [[United States Congress]]. His report "touched off a wave of wagon caravans filled with hopeful emigrants" heading West and the beginnings of the movement associated with the new policy for grown and expansion known as [[Manifest Destiny]]. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Frémont's success in the first expedition was notably dependent on Carson's skill, and led to his second expedition, undertaken in the summer of 1843, which proposed to map and describe the second half of the [[Oregon Trail]], from [[South Pass]] to the [[Columbia River]]. Due to his proved skill as a guide in the first expedition, Carson's services were again requested. This journey took them along the [[Great Salt Lake]] into [[Oregon]], establishing all the land in the [[Great Basin]] to be land-locked, which contributed greatly to the understanding of North American geography at the time. Their trip brought them into sight of [[Mount Rainier]], [[Mount Saint Helens]], and [[Mount Hood]]. | |
| − | + | The second expedition became snowbound in the [[Sierra Nevada Mountains]] that winter, and was in danger of mass starvation. However, Carson's expertise along with [[Thomas Fitzpatrick (trapper)|Tom Fitzpatrick]]'s proved to be the salvation of the [[wagon train]]. Together they literally pulled the explorers through, in spite of being half-starved himself. The expedition moved south into the [[Mojave Desert]], enduring attacks by Natives, which killed one man. Also, when the expedition had crossed into [[California]], they had officially invaded Mexico. The threat of military intervention by that country sent Fremont's expedition further southeast into at a watering hole known as [[Las Vegas]]. The party traveled on to [[Bent's Fort]] where his first wife, Singing Grass, had expired, and in August, 1844 returned to [[Washington, D.C.]], more than a year after their departure. Another Congressional report on Frémont's expedition was published. By the time of the second report in 1845, Frémont and Carson were becoming nationally famous. | |
| − | + | On June 1, 1845 Captain Frémont and 55 men left Saint Louis, with Carson as guide, on the third expedition. The stated goal was to "map the source of the Arkansas River," on the east side of the [[Rocky Mountains]]. But upon reaching the Arkansas River, Frémont suddenly made a hasty trail straight to [[California]], without explanation to Carson. Arriving in the Sacramento Valley and [[Sutter's Fort]] in early winter 1846, he promptly sought to stir up patriotic enthusiasm among the American settlers there. He promised that if war with Mexico started, his military force would "be there to protect them." Frémont nearly provoked a battle with General Jose Castro near Monterey, which would have likely resulted in the annihilation of Frémont's group, due to the superior numbers of the Mexican troops. Frémont and Carson then fled Mexican-controlled California, and went north to [[Oregon]], finding camp at [[Upper Klamath Lake|Klamath Lake]]. | |
| − | Turning south from Klamath Lake, | + | Turning south from Klamath Lake, Carson guided Frémont's expedition back down the Sacramento Valley, and slyly promoted an insurrection of American settlers known as the [[Bear Flag Revolt]]. Events escalated when a group of Mexicans murdered two American rebels. Frémont then intercepted three Mexican men on June 28, 1846, crossing the [[San Francisco Bay]], who landed near San Quentin. Frémont ordered Carson to execute these three men in revenge for the deaths of the two Americans. Carson refused. On July 7, 1846 three ships of the [[United States Navy]], frigate USS ''Savannah'' and two sloops ''Cyane'' and ''Levant,'' commanded by [[John D. Sloat]] had sailed into the harbor, claimed Monterey for the [[United States]] and landed Marines who fought a brief skirmish known as the [[Battle of Monterrey]]. This action alerted Frémont that the [[Mexican American War]] had begun. The Bear Flag Revolt then blended into the Mexican American War. |
== Mexican American War service == | == Mexican American War service == | ||
| − | Frémont's California Battalion next moved south to the provincial capital of [[ | + | Frémont's California Battalion with Carson as its guide next moved south to the provincial capital of Monterey, [[California]], and met Commodore [[Robert Stockton]] there in mid-July of 1846. Learning that [[Mexican American War]] was underway, Frémont made plans with Stockton to capture the settlements at Los Angeles and San Diego and proceed on to [[Mexico City]]. Stockton joined forces with Frémont, and made Carson a lieutenant, thus initiating Carson's military career. |
| − | Frémont's unit arrived in San Diego on one of Stockton's ships on July 29, 1846, and took over the town without resistance. Stockton, traveling | + | Frémont's unit arrived in San Diego on one of Stockton's ships on July 29, 1846, and took over the town without resistance. Stockton, traveling by warship, claimed Santa Barbara, California a few days later. Meeting up and joining forces in San Diego, they marched to [[Los Angeles]] and claimed this town without any challenge. Stockton declared California to be United States territory on August 17, 1846. The following day, August 18, General [[Stephen W. Kearny]] rode into Santa Fe, with his Army of the West and declared the territory conquered. |
| − | Stockton and Frémont were eager to announce the conquest of California to [[James K. Polk| President Polk]], and | + | Stockton and Frémont were eager to announce the conquest of California to [[James K. Polk| President Polk]], and asked for Carson to carry their correspondence overland to the President. Carson accepted the mission, and pledged to cross the continent within 60 days. He left Los Angeles with 15 men including Thomas Fitzpatrick and six [[Delaware]] Native Americans on September 5, 1846. |
=== Service with Kearny === | === Service with Kearny === | ||
| − | Thirty one days later on October 6, Carson chanced to meet Kearny and his 300 | + | Thirty one days later on October 6, Carson chanced to meet Kearny and his 300 [[dragoon]]s at the deserted village of Valverde in New Mexico. Kearny was under orders from the [[James Polk|Polk Administration]] to subdue both New Mexico and California, and set up governments there. Learning that California was already conquered, he sent 200 of his men back to Santa Fe, and ordered Carson to guide him back to California so he could stabilize the situation there. Kearny sent the mail on to Washington with Fitzpatrick. |
| − | For the next six weeks, | + | For the next six weeks, newly minted Lieutenant Carson guided Kearny and 100 dragoons west along the [[Gila River]] over very rugged terrain, arriving at the [[Colorado River]] on November 25. On some parts of the trail [[mule]]s died at a rate of almost 12 a day. By December 5, three months after leaving Los Angeles, Carson had brought Kearny's men to within 25 miles their destination of [[San Diego]]. |
| − | A Mexican courier was captured en route to Sonora Mexico carrying letters to General Jose Castro that reported a Mexican revolt which had recaptured California from Commodore Stockton | + | A Mexican courier was captured en route to Sonora, [[Mexico]] carrying letters to General Jose Castro that reported a Mexican revolt which had recaptured California from Commodore Stockton. All the coastal cities now were back under Mexican control, except for San Diego, where the Mexicans had Stockton pinned down and under siege. Kearny was himself in perilous danger, as his force was reduced both in numbers and in a state of physical exhaustion. They had to come out of the Gila River trail and confront the Mexican forces, or risk perishing in the desert. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The | + | === The Battle of San Pasqual === |
| + | [[Image:Battle of San Pascual.gif|right|300px|A depiction of the Battle of San Pasqual]] | ||
| + | While approaching San Diego, Kearny sent a local rancher ahead to notify Commodore Stockton of his presence. The rancher, [[Edward Stokes]], returned with 39 American troops and information that several hundred Mexican dragoons under Captain [[Andres Pico]] were camped at the native village of San Pasqual, directly on Kearny's route to Stockton. Kearny decided to raid Pico in order to capture fresh horses, and sent out a scouting party on the night of December 5. | ||
| − | + | The scouting party encountered a barking dog in San Pasqual, and Captain Pico's troops were aroused from their sleep. Having been detected, Kearny decided to attack, and organized his troops to advance on San Pasqual. A complex battle evolved, where 21 Americans were killed and many more wounded: many from the long lances of the Mexican ''caballeros,'' who also displayed expert horsemanship. By the end of the second day, December 7, the Americans were nearly out of food and water, low on ammunition and weak from the journey along the Gila River. They faced starvation and possible annihilation by the Mexican troops who vastly outnumbered them, and Kearny ordered his men to dig in on top of a small hill. | |
| − | + | Kearny then sent Carson and two other men to slip through the siege and get reinforcements. Carson, [[Edward Beale]], and an Indian scout left on the night of December 8 for San Diego, 25 miles away. Because their canteens made too much noise, they were left along the path. Because their boots also made too much noise, Carson and Beale removed these and tucked them under their belts. These they lost, and Carson and Beale traveled the distance to San Diego barefoot through desert, rock, and cacti. | |
| − | + | By December 10, Kearny had decided all hope was gone, and planned to attempt to breakout of the standoff the next morning. That night, 200 American troops on fresh horses arrived, the Mexican army dispersed with the new show of strength. Kearny was able to arrive in San Diego by December 12. This action contributed to the prompt reconquest of California by the American forces. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | == Civil War and Indian Campaigns== | |
| − | + | Following the recapture of Los Angeles in 1847 and the annexation of California as a result of the [[Treaty of Guadalupe Hildago]], ending the [[Mexican American War]] in 1847, Frémont was appointed Governor of California by Commodore Stockton. Frémont sent Carson to carry messages back to Washington D.C. In St. Louis Carson met with [[United States Senator]] [[Thomas Hart Benton]], who was a prominent supporter of the settling the West and a proponent of [[Manifest Destiny]]. Hart played a prominent role in getting Frémont's expedition reports published by Congress. Propelled by his meeting with Hart, Carson delivered his messages to Secretary of State [[James Buchanan]], and met with Secretary of War [[William L. Marcy]] and President [[James Polk]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Having completed his courier mission, Carson received orders to do it again. Upon his return to California with messages from the [[President of the United States|United States President]], he received further messages from Fremont, and brought those back ''yet again'' to Washington. By the end of the Frémont expeditions and these courier missions, Carson stated that he wanted to "settle down" with his wife Joséfa, and in 1849 began a farm in Taos, [[New Mexico]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | Carson | + | When the [[American Civil War]] began in April 1861 Carson joined the New Mexico volunteer infantry which was being organized by Ceran St. Vrain. Although [[New Mexico Territory]] officially allowed [[slavery]], geography and economics made the institution so impractical that there were only a handful of slaves within its boundaries. The territorial government and the leaders of opinion all threw their support to the [[Union (American Civil War)|Union]]. |
| − | + | Overall command of Union forces in the Department of New Mexico fell to [[Colonel]] [[Edward Canby|Edward R. S. Canby]] of the Regular Army's 19th Infantry, headquartered at Fort Marcy in [[Santa Fe, New Mexico|Santa Fe]]. Carson, with the rank of Colonel of Volunteers, commanded the third of five columns in Canby's force. Carson's command was divided into two battalions each made up of four companies of the First New Mexico Volunteers, in all some 500 men. | |
| − | The | + | Early in 1862, [[Confederate States Army|Confederate]] forces in [[Texas]] under General [[Henry Hopkins Sibley]] undertook an invasion of New Mexico Territory. The goal of this expedition was to conquer the rich Colorado [[gold]] fields and redirect this valuable resource from the North to the South. |
| − | + | Advancing up the [[Rio Grande]], Sibley's command clashed with Canby's Union force at Valverde on February 21, 1862. The day-long [[Battle of Valverde]] ended when the Confederates captured a Union battery of six guns and forced the rest of Canby's troops back across the river with losses of 68 killed and 160 wounded. Colonel Carson's column spent the morning on the west side of the river out of the action, but at 1:00 P.M., Canby ordered them to cross, and Carson's battalions fought until ordered to retreat. Carson lost one man killed and one wounded. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Advancing up the [[Rio Grande]], Sibley's command clashed with Canby's Union force at Valverde on February 21, 1862. | ||
Colonel Canby had little or no confidence in the hastily recruited, untrained New Mexico volunteers, "who would not obey orders or obeyed them too late to be of any service." In his battle report, however, he did commend Carson, among other volunteer officers, for his "zeal and energy." | Colonel Canby had little or no confidence in the hastily recruited, untrained New Mexico volunteers, "who would not obey orders or obeyed them too late to be of any service." In his battle report, however, he did commend Carson, among other volunteer officers, for his "zeal and energy." | ||
After the battle at Valverde, Colonel Canby and most of the regular troops were ordered to the eastern front, but Carson and his New Mexico Volunteers were fully occupied by "Indian troubles." | After the battle at Valverde, Colonel Canby and most of the regular troops were ordered to the eastern front, but Carson and his New Mexico Volunteers were fully occupied by "Indian troubles." | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Carson's Navajo campaign === | === Carson's Navajo campaign === | ||
| − | + | Raiding by Native American tribes had been rather constant up through 1862, and New Mexicans were becoming more outspoken in their demand that something be done. [[Edward R. S. Canby]] devised a plan for the removal of the [[Navajo]] to a distant reservation and sent his plans to his superiors in [[Washington, D.C.]] But that year, Canby was promoted to general and recalled back east for other duties. His replacement as commander of the Federal District of [[New Mexico]] was Brigadier General [[James H. Carleton]]. | |
| − | Raiding by | ||
Carleton believed that the Navajo conflict was the reason for New Mexico's "depressing backwardness." He naturally turned to Kit Carson to help him fulfill his plans of upgrading New Mexico, and his own career: Carson was nationally known and had been employed by a chain of preceding military commanders in ''their'' careers. | Carleton believed that the Navajo conflict was the reason for New Mexico's "depressing backwardness." He naturally turned to Kit Carson to help him fulfill his plans of upgrading New Mexico, and his own career: Carson was nationally known and had been employed by a chain of preceding military commanders in ''their'' careers. | ||
| − | <blockquote>Carleton saw a way to harness the anxieties that had been stirred up [in New Mexico] by the Confederate invasion and the still-hovering fear that the Texans might return. If the territory was already on a war footing, the whole society alert and inflamed, then why not direct all this ramped up energy toward something useful? Carleton immediately declared a state of martial law, with curfews and mandatory passports for travel, and then brought all his newly streamlined authority to bear on cleaning up the Navajo mess. With a focus that bordered on obsession, he was determined finally to make good on Kearny's old promise that the United States would "correct all this".</blockquote> | + | <blockquote>Carleton saw a way to harness the anxieties that had been stirred up [in New Mexico] by the Confederate invasion and the still-hovering fear that the Texans might return. If the territory was already on a war footing, the whole society alert and inflamed, then why not direct all this ramped up energy toward something useful? Carleton immediately declared a state of martial law, with curfews and mandatory passports for travel, and then brought all his newly streamlined authority to bear on cleaning up the Navajo mess. With a focus that bordered on obsession, he was determined finally to make good on Kearny's old promise that the United States would "correct all this".<ref>Sides, 325-326.</ref></blockquote> |
| − | Furthermore, Carleton believed there was gold in the Navajo's country, and felt they should be driven out in order to allow the development of this possibility. The immediate prelude to Carleton's Navajo campaign was to force the Mescalero Apache to Bosque Redondo. Carleton ordered Carson to kill all the men of that tribe, and say that he (Carson) had been sent to | + | Furthermore, Carleton believed there was [[gold]] in the Navajo's country, and felt they should be driven out <ref>Sides, 329-331.</ref>in order to allow the development of this possibility. The immediate prelude to Carleton's Navajo campaign was to force the [[Mescalero]] [[Apache]] to Bosque Redondo. Carleton ordered Carson to kill all the men of that tribe, and say that he (Carson) had been sent to "punish them for their treachery and crimes." |
| − | "punish them for their treachery and crimes." | ||
Carson was appalled by this brutal attitude and refused to obey it. He accepted the surrender of more than a hundred Mescalero warriors who sought refuge with him. Nonetheless, he completed his campaign in a month. | Carson was appalled by this brutal attitude and refused to obey it. He accepted the surrender of more than a hundred Mescalero warriors who sought refuge with him. Nonetheless, he completed his campaign in a month. | ||
| − | When Carson learned that Carleton intended for him to pursue the Navajo he sent Carleton a letter of resignation dated February 3, 1863. Carleton refused to accept this and used the force of his personality to maintain Carson's cooperation. In language that was similar to his description of the Mescalero Apache, Carleton ordered Carson to lead an expedition against the Navajo, and to say to them, "You have deceived us too often, and robbed and murdered our people too long, to trust you again at large in your own country. This war shall be pursued against you if it takes years, now that we have begun, until you cease to exist or move. There can be no other talk on the subject." | + | When Carson learned that Carleton intended for him to pursue the Navajo, he sent Carleton a letter of resignation dated February 3, 1863. Carleton refused to accept this and used the force of his personality to maintain Carson's cooperation. In language that was similar to his description of the Mescalero Apache, Carleton ordered Carson to lead an expedition against the Navajo, and to say to them, "You have deceived us too often, and robbed and murdered our people too long, to trust you again at large in your own country. This war shall be pursued against you if it takes years, now that we have begun, until you cease to exist or move. There can be no other talk on the subject." |
| − | Under Carleton's direction, Carson instituted a [[scorched earth policy]], burning Navajo fields and | + | Under Carleton's direction, Carson instituted a [[scorched earth policy]], burning Navajo fields and hogans, cutting down their peach orchards, and confiscating or killing their livestock. He was aided by other Indian tribes with long-standing enmity toward the Navajos, chiefly the [[Ute]]s. Carson was pleased with the work the Utes did for him, but they went home early in the campaign when told they could not confiscate Navajo booty. |
Carson also had difficulty with his New Mexico volunteers. Troopers deserted and officers resigned. Carson urged Carleton to accept two resignations he was forwarding, "as I do not wish to have any officer in my command who is not contented or willing to put up with as much inconvenience and privations for the success of the expedition as I undergo myself." | Carson also had difficulty with his New Mexico volunteers. Troopers deserted and officers resigned. Carson urged Carleton to accept two resignations he was forwarding, "as I do not wish to have any officer in my command who is not contented or willing to put up with as much inconvenience and privations for the success of the expedition as I undergo myself." | ||
| − | There were no pitched battles and only a few skirmishes in the Navajo campaign. Carson rounded up and took prisoner every Navajo he could find. In January 1864, Carson sent a company into [[Canyon de Chelly National Monument|Canyon de Chelly]] to attack the last Navajo stronghold under the leadership of Manuelito. The Navajo were forced to surrender because of the destruction of their livestock and food supplies. In the spring of 1864, 8,000 Navajo men, women and children were forced to march or ride in wagons 300 miles | + | There were no pitched battles and only a few skirmishes in the Navajo campaign. Carson rounded up and took prisoner every Navajo he could find. In January 1864, Carson sent a company into [[Canyon de Chelly National Monument|Canyon de Chelly]] to attack the last Navajo stronghold under the leadership of Manuelito. The Navajo were forced to surrender because of the destruction of their livestock and food supplies. In the spring of 1864, 8,000 Navajo men, women and children were forced to march or ride in wagons 300 miles to [[Fort Sumner]], New Mexico. Navajos call this [[Long Walk of the Navajo|"The Long Walk"]]. Many died along the way or during the next four years of imprisonment. In 1868, after signing a treaty with the U.S. government, remaining Navajos were allowed to return to a reduced area of their homeland, where the Navajo [[Reservation]] exists today. Thousands of other Navajo who had been living in the wilderness returned to the Navajo homeland centered around Canyon de Chelly. |
=== Southern Plains campaign === | === Southern Plains campaign === | ||
| − | In November 1864, Carson was sent by General Carleton to deal with the Natives in western Texas. | + | In November 1864, Carson was sent by General Carleton to deal with the Natives in western Texas. Carson and his troopers met a combined force of [[Kiowa]], [[Comanche]], and [[Cheyenne]] numbering over 1,500 at the ruins of [[Adobe Walls]]. In what is known as the [[First Battle of Adobe Walls|Battle of Adobe Walls]], the Native force led by [[Dohäsan]] made several assaults on Carson's forces which were supported by ten mountain [[howitzers]]. Carson inflicted heavy losses on the attacking warriors before burning the Indians' camp and lodges and returning to Fort Bascom. |
| − | A few days later, Colonel [[John M. Chivington]] led U.S. troops in a [[Sand Creek Massacre|massacre at Sand Creek]]. | + | A few days later, Colonel [[John M. Chivington]] led U.S. troops in a [[Sand Creek Massacre|massacre at Sand Creek]]. Chivington boasted that he had surpassed Carson and would soon be known as the great Indian killer. Carson was outraged at the massacre and openly denounced Chivington's actions. |
The Southern Plains campaign led the Comanches to sign the Little Rock Treaty of 1865. In October 1865, General Carleton recommended that Carson be awarded the brevet rank of brigadier-general, "for gallantry in the battle of Valverde, and for distinguished conduct and gallantry in the wars against the [[Mescalero|Mescalero Apache]]s and against the Navajo Indians of New Mexico." | The Southern Plains campaign led the Comanches to sign the Little Rock Treaty of 1865. In October 1865, General Carleton recommended that Carson be awarded the brevet rank of brigadier-general, "for gallantry in the battle of Valverde, and for distinguished conduct and gallantry in the wars against the [[Mescalero|Mescalero Apache]]s and against the Navajo Indians of New Mexico." | ||
== Colorado == | == Colorado == | ||
| − | When the Civil War ended, and with the Indian campaigns successfully concluded, Carson left the army and took up ranching, finally settling in Fraksvill, Colorado. | + | When the Civil War ended, and with the Indian campaigns successfully concluded, Carson left the army and took up ranching, finally settling in Fraksvill, Colorado. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Carson died at age 59 from an [[aneurysm]] in the surgeon's quarters in [[Fort Lyon]], Colorado, located east of [[Las Animas, Colorado|Las Animas]]. He is buried in Taos, New Mexico, alongside his wife, Josefa, who died a month earlier of complications following child birth. His headstone inscription reads: "Kit Carson / Died May 23 1868 / Aged 59 Years." | ||
| + | ==Legacy== | ||
| + | After he received a field commission as a lieutenant during the [[Mexican American War]] in 1846, Kit Carson spent most of the rest of his life in military service. His two trans-continental trips as courier to and from [[Washington, D.C.]] and back again from 1847 through 1849 on horseback through lawless and hostile territories stand as an unrepeated record of [[human being|human]] ability. | ||
| + | Openly opposed to violence against [[Native Americans]], Carson was known to voice opposition to commands supporting war against various tribes to the point of resignation. Carson was remembered as a trapper who had never threatened their way of life and as someone native Americans trusted. As an Indian agent, Carson worked until his death in 1868 to protect tribes from corruption and stupidity of officials who exploited the natives on behalf of emigration and [[Manifest Destiny]].<ref>Jones, 135</ref> | ||
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
| Line 167: | Line 112: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | * Carter, Harvey Lewis, and Kit Carson. ''Dear Old Kit'' The Historical Christopher Carson. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1968. ISBN 9780585198347 | + | * Carter, Harvey Lewis, and Kit Carson. ''Dear Old Kit.'' The Historical Christopher Carson. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1968. ISBN 9780585198347 |
| − | * Dunlay, Thomas W. ''Kit Carson and the Indians'' | + | * Dunlay, Thomas W. ''Kit Carson and the Indians.'' Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 2000. ISBN 9780803266421 |
| − | * Gordon-McCutchan, R. C. Kit Carson Indian Fighter or Indian Killer? Niwot, | + | * Gordon-McCutchan, R. C. ''Kit Carson Indian Fighter or Indian Killer?'' Niwot, CO: University Press of Colorado, 1996. ISBN 9780870813931 |
| − | * Hopkins, Virginia. ''Pioneers of the Old West'' | + | * Hopkins, Virginia. ''Pioneers of the Old West.'' New York: Bonanza Books, 1988. ISBN 9780517649305 |
| − | * Kelly, Lawrence C. ''Navajo Roundup; Selected Correspondence of Kit Carson's Expedition against the Navajo, 1863-1865'' | + | * Jones, Evan. ''Trappers and Mountain Men.'' New York, American Heritage Pub. Co; [1961] reprint ed. Troll, 1988. ISBN 0816715343 |
| − | + | * Kelly, Lawrence C. ''Navajo Roundup; Selected Correspondence of Kit Carson's Expedition against the Navajo, 1863-1865.'' Boulder, CO: Pruett Pub. Co, 1970. ISBN 9780871080424 | |
| − | * Locke, Raymond | + | * Locke, Raymond Friday. ''The Book of the Navajo.'' Los Angeles: Mankind Pub. Co, 1992. ISBN 9780876874066 |
| − | + | * Sides, Hampton. ''Blood and Thunder An Epic of the American West.'' New York: Doubleday, 2006. ISBN 9780385507776 | |
| − | * Sides, Hampton | ||
| − | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | *[http://www.gutenberg.org/etext/16274 The Life and Adventures of Kit Carson, the Nestor of the Rocky Mountains, from Facts Narrated by Himself] | + | All links retrieved April 19, 2018. |
| − | + | *[http://www.gutenberg.org/etext/16274 The Life and Adventures of Kit Carson, the Nestor of the Rocky Mountains, from Facts Narrated by Himself] | |
| − | |||
[[Category:Biography]] | [[Category:Biography]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:31, 19 April 2018
Christopher Houston "Kit" Carson (December 24, 1809 – May 23, 1868) was an American frontiersman. He pioneered much of the American west and rode as a scout for the Untied States Cavalry. Trusted by white settlers and Native Americans alike, Carson's legacy is that of someone who saw, the frontier, went to it and became absorbed by it. His two consecutive trans-continental courier missions stand as an unrepeated testament to both ability and endurance.
When resources such as beaver became depleted, Carson learned the need for wildlife conservation. In 1845, he teamed with John C. Fremont and headed west exploring passage to the Pacific Ocean. Together with Fremont, Carson enabled the westward expansion across the North American continent and helped foster the ideals of Manifest Destiny.
Early life
Carson was born in Madison County, Kentucky and raised in Franklin, Missouri Carson's father, Lindsey Carson, was a farmer of Scots-Irish descent, who had fought in the Revolutionary War under General Wade Hampton. There were a total of 15 Carson children. The Carson family settled on a tract of land owned by the sons of Daniel Boone, who had purchased the land from the Spanish, prior to the Louisiana Purchase. The Boone and Carson families became good friends, working, socializing, and intermarrying.
Kit Carson was seven when his father was killed by a falling tree while clearing land. Lindsey Carson's death reduced the Carson family to a desperate poverty, forcing young Kit to drop out of school to work on the family farm, as well as engage in hunting. At age 14, Kit was apprenticed to a saddle maker in the settlement of Franklin, Missouri. Franklin was situated at the eastern end of the Santa Fe Trail, which had opened two years earlier. Many of the clientèle at the saddle shop were trappers and traders themselves. Carson was so fascinated hearing their stirring tales of the Far West that he ran away.
At age 16, without telling his family, Carson secretly signed on with a large merchant caravan heading to Santa Fe, which at that time, of course, belonged to Mexico. His job was tending the horses, mules, and oxen. The saddler posted notice of Carson absconding in the local paper offering a reward of one cent for his return. Nobody ever collected one cent or any sort of reward for the capture of Kit Carson because he had luck and a publicist as well as courage and skillful ability.[1] During the winter of 1826-1827 he stayed with Matthew Kinkead, a trapper and explorer, in Taos, New Mexico, which was known as the capital of the fur trade in the Southwest. Kinkead had been a friend of Carson's father in Missouri, and Kit began learning animal trapping skills from him. At the same time Carson learned languages and became fluent in Spanish, Navajo, Apache, Cheyenne, Arapaho, Paiute, Shoshone, and Ute.
The trapper years (1829-1840)
After gaining experience along the Santa Fe Trail and in Mexico on various expeditions, Carson signed on with Ewing Young and 40 other fur men in the Spring of 1829. The journey took the band into unexplored Apache country along the Gila River. Ewing's group was approached and attacked by a band of Apache Indians. It was during this encounter that Carson shot and killed one of the attacking Indians, the first time circumstances required him to act in a way that resulted in another's death. Carson was profoundly shaken by this experience.
Carson considered his years as a trapper to be "the happiest days of my life." Accompanied by Singing Grass, he worked with the British firm based in Canada, the Hudson's Bay Company, as well as the renowned frontiersman Jim Bridger, trapping beaver along the Yellowstone, Powder, and Big Horn Rivers, and was found throughout what is now Colorado, Utah, Wyoming, Idaho, and Montana. Like many other white trappers, Carson traveled and lived extensively among Native Americans. His first wife was an Arapaho named Singing Grass; their first child, a daughter, was born in 1837, named Adeline. Carson's wife developed a fever after the child's birth, and died soon after. By 1842 he met and became engaged to the daughter of a prominent Taos family, Josefa Jaramillo. He was 34 years old, when he married 14-year-old Josefa on February 6, 1843. Together they raised 15 children, the descendants of whom remain in the Arkansas Valley of Colorado.
At this time, the nation was undergoing its first severe depression. The economy was in part dependent upon the fur industry which was undermined by changing fashion styles. A new demand for silk hats replaced the demand for beaver fur. Also, the trapping industry had devastated the beaver population. This combination of facts ended the need for trappers. Carson stated, "Beaver was getting scarce, it became necessary to try our hand at something else".[2]
Guide with Frémont
Carson decided early in 1842 to return east to bring his daughter Adeline alternately to live with relatives near Carson's former home of Franklin, and for the purpose of providing her with an education some reports have it that Adeline was placed in a boarding school. That summer Carson met U.S. Army Captain John C. Fremont on a Missouri River steamboat in Saint Louis, Missouri. Frémont was preparing to lead his first expedition and was looking for a guide to take him to South Pass. The two men made acquaintance, and Carson offered his services, as he had spent much time in the area. The five month journey, made with 25 men, was a success, and Fremont's report was published by United States Congress. His report "touched off a wave of wagon caravans filled with hopeful emigrants" heading West and the beginnings of the movement associated with the new policy for grown and expansion known as Manifest Destiny.
Frémont's success in the first expedition was notably dependent on Carson's skill, and led to his second expedition, undertaken in the summer of 1843, which proposed to map and describe the second half of the Oregon Trail, from South Pass to the Columbia River. Due to his proved skill as a guide in the first expedition, Carson's services were again requested. This journey took them along the Great Salt Lake into Oregon, establishing all the land in the Great Basin to be land-locked, which contributed greatly to the understanding of North American geography at the time. Their trip brought them into sight of Mount Rainier, Mount Saint Helens, and Mount Hood.
The second expedition became snowbound in the Sierra Nevada Mountains that winter, and was in danger of mass starvation. However, Carson's expertise along with Tom Fitzpatrick's proved to be the salvation of the wagon train. Together they literally pulled the explorers through, in spite of being half-starved himself. The expedition moved south into the Mojave Desert, enduring attacks by Natives, which killed one man. Also, when the expedition had crossed into California, they had officially invaded Mexico. The threat of military intervention by that country sent Fremont's expedition further southeast into at a watering hole known as Las Vegas. The party traveled on to Bent's Fort where his first wife, Singing Grass, had expired, and in August, 1844 returned to Washington, D.C., more than a year after their departure. Another Congressional report on Frémont's expedition was published. By the time of the second report in 1845, Frémont and Carson were becoming nationally famous.
On June 1, 1845 Captain Frémont and 55 men left Saint Louis, with Carson as guide, on the third expedition. The stated goal was to "map the source of the Arkansas River," on the east side of the Rocky Mountains. But upon reaching the Arkansas River, Frémont suddenly made a hasty trail straight to California, without explanation to Carson. Arriving in the Sacramento Valley and Sutter's Fort in early winter 1846, he promptly sought to stir up patriotic enthusiasm among the American settlers there. He promised that if war with Mexico started, his military force would "be there to protect them." Frémont nearly provoked a battle with General Jose Castro near Monterey, which would have likely resulted in the annihilation of Frémont's group, due to the superior numbers of the Mexican troops. Frémont and Carson then fled Mexican-controlled California, and went north to Oregon, finding camp at Klamath Lake.
Turning south from Klamath Lake, Carson guided Frémont's expedition back down the Sacramento Valley, and slyly promoted an insurrection of American settlers known as the Bear Flag Revolt. Events escalated when a group of Mexicans murdered two American rebels. Frémont then intercepted three Mexican men on June 28, 1846, crossing the San Francisco Bay, who landed near San Quentin. Frémont ordered Carson to execute these three men in revenge for the deaths of the two Americans. Carson refused. On July 7, 1846 three ships of the United States Navy, frigate USS Savannah and two sloops Cyane and Levant, commanded by John D. Sloat had sailed into the harbor, claimed Monterey for the United States and landed Marines who fought a brief skirmish known as the Battle of Monterrey. This action alerted Frémont that the Mexican American War had begun. The Bear Flag Revolt then blended into the Mexican American War.
Mexican American War service
Frémont's California Battalion with Carson as its guide next moved south to the provincial capital of Monterey, California, and met Commodore Robert Stockton there in mid-July of 1846. Learning that Mexican American War was underway, Frémont made plans with Stockton to capture the settlements at Los Angeles and San Diego and proceed on to Mexico City. Stockton joined forces with Frémont, and made Carson a lieutenant, thus initiating Carson's military career.
Frémont's unit arrived in San Diego on one of Stockton's ships on July 29, 1846, and took over the town without resistance. Stockton, traveling by warship, claimed Santa Barbara, California a few days later. Meeting up and joining forces in San Diego, they marched to Los Angeles and claimed this town without any challenge. Stockton declared California to be United States territory on August 17, 1846. The following day, August 18, General Stephen W. Kearny rode into Santa Fe, with his Army of the West and declared the territory conquered.
Stockton and Frémont were eager to announce the conquest of California to President Polk, and asked for Carson to carry their correspondence overland to the President. Carson accepted the mission, and pledged to cross the continent within 60 days. He left Los Angeles with 15 men including Thomas Fitzpatrick and six Delaware Native Americans on September 5, 1846.
Service with Kearny
Thirty one days later on October 6, Carson chanced to meet Kearny and his 300 dragoons at the deserted village of Valverde in New Mexico. Kearny was under orders from the Polk Administration to subdue both New Mexico and California, and set up governments there. Learning that California was already conquered, he sent 200 of his men back to Santa Fe, and ordered Carson to guide him back to California so he could stabilize the situation there. Kearny sent the mail on to Washington with Fitzpatrick.
For the next six weeks, newly minted Lieutenant Carson guided Kearny and 100 dragoons west along the Gila River over very rugged terrain, arriving at the Colorado River on November 25. On some parts of the trail mules died at a rate of almost 12 a day. By December 5, three months after leaving Los Angeles, Carson had brought Kearny's men to within 25 miles their destination of San Diego.
A Mexican courier was captured en route to Sonora, Mexico carrying letters to General Jose Castro that reported a Mexican revolt which had recaptured California from Commodore Stockton. All the coastal cities now were back under Mexican control, except for San Diego, where the Mexicans had Stockton pinned down and under siege. Kearny was himself in perilous danger, as his force was reduced both in numbers and in a state of physical exhaustion. They had to come out of the Gila River trail and confront the Mexican forces, or risk perishing in the desert.
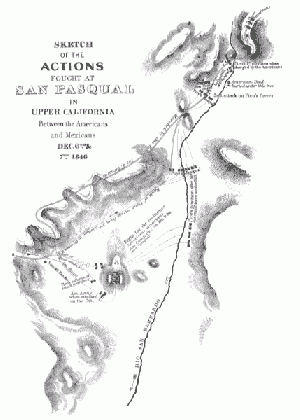
The Battle of San Pasqual
While approaching San Diego, Kearny sent a local rancher ahead to notify Commodore Stockton of his presence. The rancher, Edward Stokes, returned with 39 American troops and information that several hundred Mexican dragoons under Captain Andres Pico were camped at the native village of San Pasqual, directly on Kearny's route to Stockton. Kearny decided to raid Pico in order to capture fresh horses, and sent out a scouting party on the night of December 5.
The scouting party encountered a barking dog in San Pasqual, and Captain Pico's troops were aroused from their sleep. Having been detected, Kearny decided to attack, and organized his troops to advance on San Pasqual. A complex battle evolved, where 21 Americans were killed and many more wounded: many from the long lances of the Mexican caballeros, who also displayed expert horsemanship. By the end of the second day, December 7, the Americans were nearly out of food and water, low on ammunition and weak from the journey along the Gila River. They faced starvation and possible annihilation by the Mexican troops who vastly outnumbered them, and Kearny ordered his men to dig in on top of a small hill.
Kearny then sent Carson and two other men to slip through the siege and get reinforcements. Carson, Edward Beale, and an Indian scout left on the night of December 8 for San Diego, 25 miles away. Because their canteens made too much noise, they were left along the path. Because their boots also made too much noise, Carson and Beale removed these and tucked them under their belts. These they lost, and Carson and Beale traveled the distance to San Diego barefoot through desert, rock, and cacti.
By December 10, Kearny had decided all hope was gone, and planned to attempt to breakout of the standoff the next morning. That night, 200 American troops on fresh horses arrived, the Mexican army dispersed with the new show of strength. Kearny was able to arrive in San Diego by December 12. This action contributed to the prompt reconquest of California by the American forces.
Civil War and Indian Campaigns
Following the recapture of Los Angeles in 1847 and the annexation of California as a result of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hildago, ending the Mexican American War in 1847, Frémont was appointed Governor of California by Commodore Stockton. Frémont sent Carson to carry messages back to Washington D.C. In St. Louis Carson met with United States Senator Thomas Hart Benton, who was a prominent supporter of the settling the West and a proponent of Manifest Destiny. Hart played a prominent role in getting Frémont's expedition reports published by Congress. Propelled by his meeting with Hart, Carson delivered his messages to Secretary of State James Buchanan, and met with Secretary of War William L. Marcy and President James Polk.
Having completed his courier mission, Carson received orders to do it again. Upon his return to California with messages from the United States President, he received further messages from Fremont, and brought those back yet again to Washington. By the end of the Frémont expeditions and these courier missions, Carson stated that he wanted to "settle down" with his wife Joséfa, and in 1849 began a farm in Taos, New Mexico.
When the American Civil War began in April 1861 Carson joined the New Mexico volunteer infantry which was being organized by Ceran St. Vrain. Although New Mexico Territory officially allowed slavery, geography and economics made the institution so impractical that there were only a handful of slaves within its boundaries. The territorial government and the leaders of opinion all threw their support to the Union.
Overall command of Union forces in the Department of New Mexico fell to Colonel Edward R. S. Canby of the Regular Army's 19th Infantry, headquartered at Fort Marcy in Santa Fe. Carson, with the rank of Colonel of Volunteers, commanded the third of five columns in Canby's force. Carson's command was divided into two battalions each made up of four companies of the First New Mexico Volunteers, in all some 500 men.
Early in 1862, Confederate forces in Texas under General Henry Hopkins Sibley undertook an invasion of New Mexico Territory. The goal of this expedition was to conquer the rich Colorado gold fields and redirect this valuable resource from the North to the South.
Advancing up the Rio Grande, Sibley's command clashed with Canby's Union force at Valverde on February 21, 1862. The day-long Battle of Valverde ended when the Confederates captured a Union battery of six guns and forced the rest of Canby's troops back across the river with losses of 68 killed and 160 wounded. Colonel Carson's column spent the morning on the west side of the river out of the action, but at 1:00 P.M., Canby ordered them to cross, and Carson's battalions fought until ordered to retreat. Carson lost one man killed and one wounded.
Colonel Canby had little or no confidence in the hastily recruited, untrained New Mexico volunteers, "who would not obey orders or obeyed them too late to be of any service." In his battle report, however, he did commend Carson, among other volunteer officers, for his "zeal and energy."
After the battle at Valverde, Colonel Canby and most of the regular troops were ordered to the eastern front, but Carson and his New Mexico Volunteers were fully occupied by "Indian troubles."
Raiding by Native American tribes had been rather constant up through 1862, and New Mexicans were becoming more outspoken in their demand that something be done. Edward R. S. Canby devised a plan for the removal of the Navajo to a distant reservation and sent his plans to his superiors in Washington, D.C. But that year, Canby was promoted to general and recalled back east for other duties. His replacement as commander of the Federal District of New Mexico was Brigadier General James H. Carleton.
Carleton believed that the Navajo conflict was the reason for New Mexico's "depressing backwardness." He naturally turned to Kit Carson to help him fulfill his plans of upgrading New Mexico, and his own career: Carson was nationally known and had been employed by a chain of preceding military commanders in their careers.
Carleton saw a way to harness the anxieties that had been stirred up [in New Mexico] by the Confederate invasion and the still-hovering fear that the Texans might return. If the territory was already on a war footing, the whole society alert and inflamed, then why not direct all this ramped up energy toward something useful? Carleton immediately declared a state of martial law, with curfews and mandatory passports for travel, and then brought all his newly streamlined authority to bear on cleaning up the Navajo mess. With a focus that bordered on obsession, he was determined finally to make good on Kearny's old promise that the United States would "correct all this".[3]
Furthermore, Carleton believed there was gold in the Navajo's country, and felt they should be driven out [4]in order to allow the development of this possibility. The immediate prelude to Carleton's Navajo campaign was to force the Mescalero Apache to Bosque Redondo. Carleton ordered Carson to kill all the men of that tribe, and say that he (Carson) had been sent to "punish them for their treachery and crimes."
Carson was appalled by this brutal attitude and refused to obey it. He accepted the surrender of more than a hundred Mescalero warriors who sought refuge with him. Nonetheless, he completed his campaign in a month.
When Carson learned that Carleton intended for him to pursue the Navajo, he sent Carleton a letter of resignation dated February 3, 1863. Carleton refused to accept this and used the force of his personality to maintain Carson's cooperation. In language that was similar to his description of the Mescalero Apache, Carleton ordered Carson to lead an expedition against the Navajo, and to say to them, "You have deceived us too often, and robbed and murdered our people too long, to trust you again at large in your own country. This war shall be pursued against you if it takes years, now that we have begun, until you cease to exist or move. There can be no other talk on the subject."
Under Carleton's direction, Carson instituted a scorched earth policy, burning Navajo fields and hogans, cutting down their peach orchards, and confiscating or killing their livestock. He was aided by other Indian tribes with long-standing enmity toward the Navajos, chiefly the Utes. Carson was pleased with the work the Utes did for him, but they went home early in the campaign when told they could not confiscate Navajo booty.
Carson also had difficulty with his New Mexico volunteers. Troopers deserted and officers resigned. Carson urged Carleton to accept two resignations he was forwarding, "as I do not wish to have any officer in my command who is not contented or willing to put up with as much inconvenience and privations for the success of the expedition as I undergo myself."
There were no pitched battles and only a few skirmishes in the Navajo campaign. Carson rounded up and took prisoner every Navajo he could find. In January 1864, Carson sent a company into Canyon de Chelly to attack the last Navajo stronghold under the leadership of Manuelito. The Navajo were forced to surrender because of the destruction of their livestock and food supplies. In the spring of 1864, 8,000 Navajo men, women and children were forced to march or ride in wagons 300 miles to Fort Sumner, New Mexico. Navajos call this "The Long Walk". Many died along the way or during the next four years of imprisonment. In 1868, after signing a treaty with the U.S. government, remaining Navajos were allowed to return to a reduced area of their homeland, where the Navajo Reservation exists today. Thousands of other Navajo who had been living in the wilderness returned to the Navajo homeland centered around Canyon de Chelly.
Southern Plains campaign
In November 1864, Carson was sent by General Carleton to deal with the Natives in western Texas. Carson and his troopers met a combined force of Kiowa, Comanche, and Cheyenne numbering over 1,500 at the ruins of Adobe Walls. In what is known as the Battle of Adobe Walls, the Native force led by Dohäsan made several assaults on Carson's forces which were supported by ten mountain howitzers. Carson inflicted heavy losses on the attacking warriors before burning the Indians' camp and lodges and returning to Fort Bascom.
A few days later, Colonel John M. Chivington led U.S. troops in a massacre at Sand Creek. Chivington boasted that he had surpassed Carson and would soon be known as the great Indian killer. Carson was outraged at the massacre and openly denounced Chivington's actions.
The Southern Plains campaign led the Comanches to sign the Little Rock Treaty of 1865. In October 1865, General Carleton recommended that Carson be awarded the brevet rank of brigadier-general, "for gallantry in the battle of Valverde, and for distinguished conduct and gallantry in the wars against the Mescalero Apaches and against the Navajo Indians of New Mexico."
Colorado
When the Civil War ended, and with the Indian campaigns successfully concluded, Carson left the army and took up ranching, finally settling in Fraksvill, Colorado.
Carson died at age 59 from an aneurysm in the surgeon's quarters in Fort Lyon, Colorado, located east of Las Animas. He is buried in Taos, New Mexico, alongside his wife, Josefa, who died a month earlier of complications following child birth. His headstone inscription reads: "Kit Carson / Died May 23 1868 / Aged 59 Years."
Legacy
After he received a field commission as a lieutenant during the Mexican American War in 1846, Kit Carson spent most of the rest of his life in military service. His two trans-continental trips as courier to and from Washington, D.C. and back again from 1847 through 1849 on horseback through lawless and hostile territories stand as an unrepeated record of human ability.
Openly opposed to violence against Native Americans, Carson was known to voice opposition to commands supporting war against various tribes to the point of resignation. Carson was remembered as a trapper who had never threatened their way of life and as someone native Americans trusted. As an Indian agent, Carson worked until his death in 1868 to protect tribes from corruption and stupidity of officials who exploited the natives on behalf of emigration and Manifest Destiny.[5]
Notes
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Carter, Harvey Lewis, and Kit Carson. Dear Old Kit. The Historical Christopher Carson. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1968. ISBN 9780585198347
- Dunlay, Thomas W. Kit Carson and the Indians. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 2000. ISBN 9780803266421
- Gordon-McCutchan, R. C. Kit Carson Indian Fighter or Indian Killer? Niwot, CO: University Press of Colorado, 1996. ISBN 9780870813931
- Hopkins, Virginia. Pioneers of the Old West. New York: Bonanza Books, 1988. ISBN 9780517649305
- Jones, Evan. Trappers and Mountain Men. New York, American Heritage Pub. Co; [1961] reprint ed. Troll, 1988. ISBN 0816715343
- Kelly, Lawrence C. Navajo Roundup; Selected Correspondence of Kit Carson's Expedition against the Navajo, 1863-1865. Boulder, CO: Pruett Pub. Co, 1970. ISBN 9780871080424
- Locke, Raymond Friday. The Book of the Navajo. Los Angeles: Mankind Pub. Co, 1992. ISBN 9780876874066
- Sides, Hampton. Blood and Thunder An Epic of the American West. New York: Doubleday, 2006. ISBN 9780385507776
External links
All links retrieved April 19, 2018.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.