Difference between revisions of "Chemical decomposition" - New World Encyclopedia
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) m |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Images OK}}{{Approved}}{{copyedited}} | ||
[[Image:Chemical decomposition.gif|right|thumb]] | [[Image:Chemical decomposition.gif|right|thumb]] | ||
| − | '''Chemical decomposition''' is the separation (or breakdown) of a [[chemical compound]] into smaller compounds or [[chemical element|elements]]. It is sometimes defined as the opposite of [[chemical synthesis | + | '''Chemical decomposition''' is the separation (or breakdown) of a [[chemical compound]] into smaller compounds or [[chemical element|elements]]. It is sometimes defined as the opposite of [[chemical synthesis]]. The stability that a chemical compound ordinarily has is eventually limited when exposed to extreme environmental conditions like [[heat]], [[radiation]], [[humidity]] or the [[acidity]] of a [[solvent]]. The details of decomposition processes are generally not well defined, as a [[molecule]] may break up into a host of smaller fragments. There are broadly three types of decomposition reactions: Thermal, [[electrolysis|electrolytic]], and [[catalysis|catalytic]]. |
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | Chemical decomposition is often an undesired [[chemical reaction]]. However, chemical decomposition is exploited in several analytical techniques, notably [[mass spectrometry]], traditional [[gravimetric analysis]], and [[thermogravimetric analysis]]. | ||
| − | A broader definition of the term '''decomposition''' also includes the breakdown of one phase into two or more phases.<ref name="Gold"> | + | == Broader definition == |
| − | + | A broader definition of the term '''decomposition''' also includes the breakdown of one phase into two or more phases.<ref name="Gold">Gold Book, [http://goldbook.iupac.org/D01547.html Decomposition.] Retrieved February 25, 2009.</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Reaction formulas== | ==Reaction formulas== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
: 2H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> → 2H<sub>2</sub>O + O<sub>2</sub> | : 2H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> → 2H<sub>2</sub>O + O<sub>2</sub> | ||
| − | [[Carbonate]]s will decompose when heated, a notable exception being that of [[carbonic acid]], H<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub>. | + | [[Carbonate]]s will decompose when heated, a notable exception being that of [[carbonic acid]], H<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub>. Carbonic acid, the "fizz" in sodas, pop cans and other carbonated beverages, will decompose over time (spontaneously) into [[carbon dioxide]] and water |
: H<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub> → H<sub>2</sub>O + CO<sub>2</sub> | : H<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub> → H<sub>2</sub>O + CO<sub>2</sub> | ||
| − | Other carbonates will decompose when heated producing the corresponding [[metal]] [[oxide]] and carbon dioxide. | + | Other carbonates will decompose when heated producing the corresponding [[metal]] [[oxide]] and carbon dioxide. In the following equation ''M'' represents a metal: |
: MCO<sub>3</sub> → MO + CO<sub>2</sub> | : MCO<sub>3</sub> → MO + CO<sub>2</sub> | ||
| Line 34: | Line 35: | ||
: CaCO<sub>3</sub> → CaO + CO<sub>2</sub> | : CaCO<sub>3</sub> → CaO + CO<sub>2</sub> | ||
| − | Metal [[chlorate]]s also decompose when heated. | + | Metal [[chlorate]]s also decompose when heated. A metal [[chloride]] and oxygen gas are the products. |
: MClO<sub>3</sub> → MCl + O<sub>2</sub> | : MClO<sub>3</sub> → MCl + O<sub>2</sub> | ||
| Line 44: | Line 45: | ||
== Thermal decomposition == | == Thermal decomposition == | ||
| − | + | '''Thermal decomposition''', also called '''thermolysis,''' is defined as a [[chemical reaction]] whereby a [[chemical substance]] breaks up into at least two chemical substances when heated. The reaction is usually [[endothermic]] as heat is required to break [[chemical bond]]s in the compound undergoing decomposition. The ''decomposition temperature'' of a substance is the [[temperature]] at which the substance [[Chemical decomposition|decomposes]] into smaller substances or into its constituent [[atoms]]. | |
| − | '''Thermal decomposition''', also called '''thermolysis''' | ||
For example, [[calcium carbonate]] decomposes into [[calcium oxide]] and [[carbon dioxide]]. Some compounds, on the other hand, simply decompose into their constituent elements. [[Water]], when heated to well over 2000 degrees [[Celsius]], breaks up into its components - [[hydrogen]] and [[oxygen]]. | For example, [[calcium carbonate]] decomposes into [[calcium oxide]] and [[carbon dioxide]]. Some compounds, on the other hand, simply decompose into their constituent elements. [[Water]], when heated to well over 2000 degrees [[Celsius]], breaks up into its components - [[hydrogen]] and [[oxygen]]. | ||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
:2H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>(aq) → 2H<sub>2</sub>O(l) + O<sub>2</sub>(g) | :2H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>(aq) → 2H<sub>2</sub>O(l) + O<sub>2</sub>(g) | ||
| − | High temperatures can also induce [[polymerization]], which produces larger molecules, possibly also causing thermal decomposition and evaporation of smaller molecules in the process. Such reactions are called [[pyrolysis]] reactions. | + | High temperatures can also induce [[polymerization]], which produces larger molecules, possibly also causing thermal decomposition and evaporation of smaller molecules in the process. Such reactions are called [[pyrolysis]] reactions. A common example is [[coking]], which is the formation of an amorphous carbon structure along with the evaporation of hydrogen and other pyrolysis gases. |
If thermal decomposition of a substance is significantly exothermic, then the substance is thermodynamically unstable. If initiated, its decomposition forms a positive feedback loop and undergoes [[thermal runaway]] up to the point of causing an explosion. | If thermal decomposition of a substance is significantly exothermic, then the substance is thermodynamically unstable. If initiated, its decomposition forms a positive feedback loop and undergoes [[thermal runaway]] up to the point of causing an explosion. | ||
| − | This process can be seen in almost every office as a coffee pot is left on the hot plate. | + | This process can be seen in almost every office as a coffee pot is left on the hot plate. When examined, one can see an oily substance on the top that is the organic components of the coffee coming out of solution due to over or re-heating. |
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| − | |||
* [[Analytical chemistry]] | * [[Analytical chemistry]] | ||
* [[Carbonate]] | * [[Carbonate]] | ||
| + | * [[Catalysis]] | ||
* [[Chemical reaction]] | * [[Chemical reaction]] | ||
* [[Combustion]] | * [[Combustion]] | ||
| + | * [[Electrolysis]] | ||
| + | * [[Heat]] | ||
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
| Line 76: | Line 78: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | + | * McMurry, John. 2004. ''Organic Chemistry,'' 6th ed. Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole. ISBN 0534420052. | |
| − | * McMurry, John. 2004. ''Organic Chemistry'' | + | * Solomons, T.W. Graham, and Craig B. Fryhle. 2004. ''Organic Chemistry,'' 8th ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley. ISBN 0471417998. |
| − | * Solomons, T.W. Graham, and Craig B. Fryhle. 2004. ''Organic Chemistry'' | + | * Zumdahl, Steven S. 2005. ''Chemical Principles''. New York, NY: Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 0618372067. |
| − | * Zumdahl, Steven S. 2005. ''Chemical Principles''. New York, NY: Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 0618372067 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Physical sciences]] | [[Category:Physical sciences]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:17, 8 February 2017
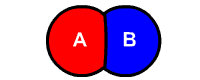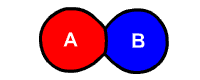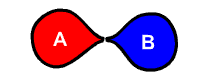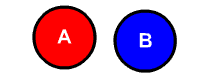
Chemical decomposition is the separation (or breakdown) of a chemical compound into smaller compounds or elements. It is sometimes defined as the opposite of chemical synthesis. The stability that a chemical compound ordinarily has is eventually limited when exposed to extreme environmental conditions like heat, radiation, humidity or the acidity of a solvent. The details of decomposition processes are generally not well defined, as a molecule may break up into a host of smaller fragments. There are broadly three types of decomposition reactions: Thermal, electrolytic, and catalytic.
Chemical decomposition is often an undesired chemical reaction. However, chemical decomposition is exploited in several analytical techniques, notably mass spectrometry, traditional gravimetric analysis, and thermogravimetric analysis.
Broader definition
A broader definition of the term decomposition also includes the breakdown of one phase into two or more phases.[1]
Reaction formulas
The generalized reaction formula for chemical decomposition is:
- AB → A + B
with a specific example being the electrolysis of water to gaseous hydrogen and oxygen:
- 2H2O → 2H2 + O2
Additional examples
An example of spontaneous decomposition is that of hydrogen peroxide, which will slowly decompose into water and oxygen:
- 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2
Carbonates will decompose when heated, a notable exception being that of carbonic acid, H2CO3. Carbonic acid, the "fizz" in sodas, pop cans and other carbonated beverages, will decompose over time (spontaneously) into carbon dioxide and water
- H2CO3 → H2O + CO2
Other carbonates will decompose when heated producing the corresponding metal oxide and carbon dioxide. In the following equation M represents a metal:
- MCO3 → MO + CO2
A specific example of this involving calcium carbonate:
- CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Metal chlorates also decompose when heated. A metal chloride and oxygen gas are the products.
- MClO3 → MCl + O2
A common decomposition of a chlorate to evolve oxygen utilizes potassium chlorate as follows:
- 2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2
Thermal decomposition
Thermal decomposition, also called thermolysis, is defined as a chemical reaction whereby a chemical substance breaks up into at least two chemical substances when heated. The reaction is usually endothermic as heat is required to break chemical bonds in the compound undergoing decomposition. The decomposition temperature of a substance is the temperature at which the substance decomposes into smaller substances or into its constituent atoms.
For example, calcium carbonate decomposes into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. Some compounds, on the other hand, simply decompose into their constituent elements. Water, when heated to well over 2000 degrees Celsius, breaks up into its components - hydrogen and oxygen.
A common example is the decomposition of copper carbonate into copper oxide and carbon dioxide, seen here:
The copper carbonate turns from a green powder into a black copper oxide, and carbon dioxide is released in a gaseous state.
Decomposition may be aided by the presence of a catalyst. For example, hydrogen peroxide decomposes more quickly with the use of manganese(IV) oxide:
- 2H2O2(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
High temperatures can also induce polymerization, which produces larger molecules, possibly also causing thermal decomposition and evaporation of smaller molecules in the process. Such reactions are called pyrolysis reactions. A common example is coking, which is the formation of an amorphous carbon structure along with the evaporation of hydrogen and other pyrolysis gases.
If thermal decomposition of a substance is significantly exothermic, then the substance is thermodynamically unstable. If initiated, its decomposition forms a positive feedback loop and undergoes thermal runaway up to the point of causing an explosion.
This process can be seen in almost every office as a coffee pot is left on the hot plate. When examined, one can see an oily substance on the top that is the organic components of the coffee coming out of solution due to over or re-heating.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Gold Book, Decomposition. Retrieved February 25, 2009.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- McMurry, John. 2004. Organic Chemistry, 6th ed. Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole. ISBN 0534420052.
- Solomons, T.W. Graham, and Craig B. Fryhle. 2004. Organic Chemistry, 8th ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley. ISBN 0471417998.
- Zumdahl, Steven S. 2005. Chemical Principles. New York, NY: Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 0618372067.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.