Difference between revisions of "Roman Gaul" - New World Encyclopedia
(New page: {{History_of_France}} :''For Gaul before the Roman conquest, see Gaul.'' '''Roman Gaul''' consisted of an area of provincial rule in the Roman Empire, in modern day France, [[B...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ||
:''For Gaul before the Roman conquest, see [[Gaul]].'' | :''For Gaul before the Roman conquest, see [[Gaul]].'' | ||
| − | '''Roman Gaul''' consisted of an area of provincial rule in the [[Roman Empire]], in modern day [[France]], [[Belgium]], [[Luxembourg]], and western [[Germany]]. Roman control of the area lasted for 600 years. | + | '''Roman Gaul''' consisted of an area of provincial rule in the [[Roman Empire]], in modern day [[France]], [[Belgium]], [[Luxembourg]], and western [[Germany]]. Roman control of the area lasted for 600 years. The Roman Empire began its takeover of what was Celtic Gaul in 121 B.C.E., when it conquered and annexed the southern reaches of the area. [[Julius Caesar]] completed the task by defeating the Celtic tribes in the Gallic Wars of 58-51 B.C.E. and the romanization was quick and large; [[Latin]] was spoken by a majority of Gauls in the first century AD but with some remains of the [[Gaulish language|Gallic language]]. Following the Romans defeat by the [[Franks|Frankish]] at the Battle of Soissons in 486 CE, Gaul came under the rule of the [[Merovingian]]s, the first kings of France. The only attempt at a rebellion against Rome was an unsuccessful uprising in 257 C.E. under Postumus. |
| + | |||
| + | Gaul was not only closer to the imperial center than [[Roman Britain]] but served as an important buffer between Rome and the area then known as Germania, where fighting was constant on the borders of the Roman province. Culturally, France absorbed Roman [[civilization]] to a greater degree than either Britain or Germany. | ||
| + | |||
==Geographical divisions== | ==Geographical divisions== | ||
| − | * | + | * Gallia Cisalpina or "Gaul this side of the [[Alps]]," covered most of present-day northern [[Italy]]. |
| − | * | + | * Gallia Narbonensis, formerly Gallia Transalpina or "Gaul across the [[Alps]]" was originally conquered and annexed in 121 B.C.E. in an attempt to solidify communications between Rome and the Iberian peninsula. It comprised the present-day region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, most of Languedoc-Roussillon, and roughly the southeastern half of Rhône-Alpes. |
| − | * | + | *Gallia Comata or "long haired Gaul." Comata encompassed the remainder of present-day France, Belgium, and westernmost Germany, which the Romans gained through the victory over the Celts in the Gallic Wars. The Romans divided Gallia Comata into three provinces: |
| − | ** | + | ** Gallia Aquitania |
| − | ** | + | ** Gallia Belgica |
| − | ** | + | ** Gallia Lugdunensis |
| − | The Romans gave these divisions the term ''pagi'' (from which comes the French word ''pays'', "region"); these ''pagi'' were organized into '' | + | The Romans gave these divisions the term ''pagi'' (from which comes the French word ''pays'', "region"); these ''pagi'' were organized into ''civitates'' (provinces). These administrative groupings would be taken over by the Romans in their system of local control, and these ''civitates'' would also be the basis of France's eventual division into 7464075 |
| + | [[bishop|bishoprics]] and dioceses]], which would remain in place—with slight changes—until the [[French Revolution]]. Roman Gaul was adminsitered from Lyon. | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
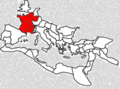
Image:REmpire-Gallia.png|Gaul in the Roman Empire | Image:REmpire-Gallia.png|Gaul in the Roman Empire | ||
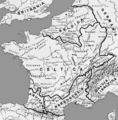
| − | Image:Map Gallia Tribes Towns.png|Map of Gaul circa 58 | + | Image:Map Gallia Tribes Towns.png|Map of Gaul circa 58 B.C.E. |
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Language and culture== | ==Language and culture== | ||
| − | [[Image:Gaul warrior Vacheres 2.jpg|thumb|220px|The Vachères warrior, a statue of a Gaulish warrior wearing roman clothing(ca. 1st century | + | [[Image:Gaul warrior Vacheres 2.jpg|thumb|220px|The Vachères warrior, a statue of a Gaulish warrior wearing roman clothing(ca. 1st century B.C.E.).]] |
| − | The [[Gaulish language]] and cultural identity would, in the five centuries between Caesar's conquest and the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, undergo a [[syncretism]], and evolve into a hybrid | + | The [[Gaulish language]] and cultural identity would, in the five centuries between Caesar's conquest and the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, undergo a [[syncretism]], and evolve into a hybrid Gallo-Roman culture. Current historical research believes that Roman Gaul was "Roman" only in certain (albeit major) social contexts (the importance of which hindered a better historical understanding of the permanence of many Celtic elements). The Roman influence was most apparent in the following areas: |
| − | *The [[ | + | *The [[Druids|Druidic]] religion which existed in the area was ordered suppressed by Emperor Claudius I, and in later centuries [[Christianity]] was introduced. The prohibition of Druids and the syncretic nature of the Roman religion led to disappearance of the Celtic religion (which remains to this day poorly understood: current knowledge of the Celtic religion is based on archeology and via literary sources from several isolated areas such as [[Ireland]] and [[Wales]]). |
| − | |||
| − | + | *The Romans easily imposed their administrative, [[economics|economic]], artistic (especially in terms of monumental [[art]] and [[architecture]]) and [[literature|literary]] [[culture]], all the more so given that there was little in the pre-existing Celtic culture to compete with these areas. | |
| − | + | After the Roman conquest of Gaul (finished in 51 B.C.E.), "romanisation" of the Celtic upper classes proceeded more rapidly than the "romanisation" of the lower classes. These classes may have spoken a Latin language mixed with Gallic. The Gauls wore the roman tunic instead of local vestimentary inhabits. The roman-gauls generally lived in the vici, small villages built like in Italy or in villae, for the richest. | |
| − | + | Surviving Celtic influences also infiltrated back into the Roman Imperial culture in the 3rd century. For example, the Gaulish tunic—which gave Emperor Caracalla his surname—had not been replaced by Roman vestimentary fashion. Similarly, certain Gaulish artisan techniques, such as the barrel (more durable than the Roman amphora) and chain mail were adopted by the Romans. | |
| − | Germanic placenames were first attested in limitrophe areas settled by Germanic | + | The Celtic heritage also continued in the spoken language. In the 5th century, a Gaulish spelling and pronunciation of Latin are apparent in several poets and transcribers of popular farces. The last pockets of Gaulish speakers appear to have lingered until the [[6th century]]. |
| + | |||
| + | Germanic placenames were first attested in limitrophe areas settled by Germanic colonizers (with Roman approval) from the 4th to 5th centuries as the Franks settled northern France and [[Belgium]], the Alemanni in [[Alsace]] and [[Switzerland]] and the [[Burgundians]] in Savoie. | ||
==After the fall of Rome== | ==After the fall of Rome== | ||
| − | The Roman administration finally collapsed as remaining troops were withdrawn southeast to protect Italy. Between [[5th century|455 and 475]], the [[Visigoths]], the Burgundians, and the [[Franks]] assumed power in Gaul. | + | The Roman administration finally collapsed as remaining troops were withdrawn southeast to protect Italy. Between [[5th century|455 and 475]], the [[Visigoths]], the Burgundians, and the [[Franks]] assumed power in Gaul. Certain aspects of the ancient Celtic culture continued however after the fall of Roman administration. |
| − | Certain Gallo-Roman aristocratic families continued to exert power in episcopal cities (as the Mauronitus family in | + | Certain Gallo-Roman aristocratic families continued to exert power in episcopal cities (as the Mauronitus family in Marseille, or the Bishop Gregory of Tours). The appearance of Germanic given and family names becomes noticeable in France from the middle of the 7th century on, most notably in powerful families, indicating thus that the center of gravity had definitely shifted. |
The Gallo-Roman, or [[Vulgar Latin]], dialect of the late Roman period evolved into the dialects of the [[Oïl languages]] and [[Old French]] in the north, and [[Occitan]] in the south. | The Gallo-Roman, or [[Vulgar Latin]], dialect of the late Roman period evolved into the dialects of the [[Oïl languages]] and [[Old French]] in the north, and [[Occitan]] in the south. | ||
| − | The words "gaul" and "gaulois" continued to be used, at least in writing, until the end of the [[Merovingian]] period. | + | The words "gaul" and "gaulois" continued to be used, at least in writing, until the end of the [[Merovingian]] period. Slowly, during the [[Carolingian Dynasty|Carolingian]] period, the expression "Francie"' (first ''Francia'', then ''Francia occidentalis'') spread to describe the [[politics|political]] reality of the Frankish kingdom ''(regnum francorum)''. |
| + | |||
| + | ==Legacy== | ||
| + | The Roman Gaul was one of the most important and stable provinces of the empire. It was through Gaul that other significant Roman provinces, such as Britain and Germania ([[Germany]] were accessed. On occasions when rebel armies controlled Gaul, Britain was cut off from the imperial center. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
'''Notes''' | '''Notes''' | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| − | == | + | ==References== |
| − | + | * Caesar, Julius, and S. A. Handford. 1951. ''The conquest of Gaul.'' Harmondsworth, Eng: Penguin Books. ISBN 9780140440218 | |
| − | *[ | + | * King, Anthony. 1990. ''Roman Gaul and Germany.'' Exploring the Roman world. [Berkeley]: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520069893 |
| − | * | + | * Latouche, Robert. 1968. ''Caesar to Charlemagne: the beginning of France.'' London: Phoenix House. ISBN 9780460077286 |
| + | * Drinkwater, J. F. 1984. ''Roman Gaul: the three provinces, 58 BC-AD 260.'' London: Croom Helm. ISBN 9780709903512 | ||
| + | * Woolf, Greg. 1998. ''Becoming Roman: the origins of provincial civilization in Gaul.'' Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521414456 | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
*[http://people.hsc.edu/drjclassics/romansin/gallia/webliography.shtm Romans in Gaul : A Webliography] - A Teacher Workshop held at Temple University, November 3, 2001. Dr. Janice Siegel, Department of Classics, [[Hampden-Sydney College]], Virginia | *[http://people.hsc.edu/drjclassics/romansin/gallia/webliography.shtm Romans in Gaul : A Webliography] - A Teacher Workshop held at Temple University, November 3, 2001. Dr. Janice Siegel, Department of Classics, [[Hampden-Sydney College]], Virginia | ||
| − | + | [[Category:History]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [[Category: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Credit|246185612}} | {{Credit|246185612}} | ||
Revision as of 16:00, 22 October 2008
- For Gaul before the Roman conquest, see Gaul.
Roman Gaul consisted of an area of provincial rule in the Roman Empire, in modern day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and western Germany. Roman control of the area lasted for 600 years. The Roman Empire began its takeover of what was Celtic Gaul in 121 B.C.E., when it conquered and annexed the southern reaches of the area. Julius Caesar completed the task by defeating the Celtic tribes in the Gallic Wars of 58-51 B.C.E. and the romanization was quick and large; Latin was spoken by a majority of Gauls in the first century AD but with some remains of the Gallic language. Following the Romans defeat by the Frankish at the Battle of Soissons in 486 C.E., Gaul came under the rule of the Merovingians, the first kings of France. The only attempt at a rebellion against Rome was an unsuccessful uprising in 257 C.E. under Postumus.
Gaul was not only closer to the imperial center than Roman Britain but served as an important buffer between Rome and the area then known as Germania, where fighting was constant on the borders of the Roman province. Culturally, France absorbed Roman civilization to a greater degree than either Britain or Germany.
Geographical divisions
- Gallia Narbonensis, formerly Gallia Transalpina or "Gaul across the Alps" was originally conquered and annexed in 121 B.C.E. in an attempt to solidify communications between Rome and the Iberian peninsula. It comprised the present-day region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, most of Languedoc-Roussillon, and roughly the southeastern half of Rhône-Alpes.
- Gallia Comata or "long haired Gaul." Comata encompassed the remainder of present-day France, Belgium, and westernmost Germany, which the Romans gained through the victory over the Celts in the Gallic Wars. The Romans divided Gallia Comata into three provinces:
- Gallia Aquitania
- Gallia Belgica
- Gallia Lugdunensis
The Romans gave these divisions the term pagi (from which comes the French word pays, "region"); these pagi were organized into civitates (provinces). These administrative groupings would be taken over by the Romans in their system of local control, and these civitates would also be the basis of France's eventual division into 7464075 bishoprics and dioceses]], which would remain in place—with slight changes—until the French Revolution. Roman Gaul was adminsitered from Lyon.
Language and culture
The Gaulish language and cultural identity would, in the five centuries between Caesar's conquest and the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, undergo a syncretism, and evolve into a hybrid Gallo-Roman culture. Current historical research believes that Roman Gaul was "Roman" only in certain (albeit major) social contexts (the importance of which hindered a better historical understanding of the permanence of many Celtic elements). The Roman influence was most apparent in the following areas:
- The Druidic religion which existed in the area was ordered suppressed by Emperor Claudius I, and in later centuries Christianity was introduced. The prohibition of Druids and the syncretic nature of the Roman religion led to disappearance of the Celtic religion (which remains to this day poorly understood: current knowledge of the Celtic religion is based on archeology and via literary sources from several isolated areas such as Ireland and Wales).
- The Romans easily imposed their administrative, economic, artistic (especially in terms of monumental art and architecture) and literary culture, all the more so given that there was little in the pre-existing Celtic culture to compete with these areas.
After the Roman conquest of Gaul (finished in 51 B.C.E.), "romanisation" of the Celtic upper classes proceeded more rapidly than the "romanisation" of the lower classes. These classes may have spoken a Latin language mixed with Gallic. The Gauls wore the roman tunic instead of local vestimentary inhabits. The roman-gauls generally lived in the vici, small villages built like in Italy or in villae, for the richest.
Surviving Celtic influences also infiltrated back into the Roman Imperial culture in the 3rd century. For example, the Gaulish tunic—which gave Emperor Caracalla his surname—had not been replaced by Roman vestimentary fashion. Similarly, certain Gaulish artisan techniques, such as the barrel (more durable than the Roman amphora) and chain mail were adopted by the Romans.
The Celtic heritage also continued in the spoken language. In the 5th century, a Gaulish spelling and pronunciation of Latin are apparent in several poets and transcribers of popular farces. The last pockets of Gaulish speakers appear to have lingered until the 6th century.
Germanic placenames were first attested in limitrophe areas settled by Germanic colonizers (with Roman approval) from the 4th to 5th centuries as the Franks settled northern France and Belgium, the Alemanni in Alsace and Switzerland and the Burgundians in Savoie.
After the fall of Rome
The Roman administration finally collapsed as remaining troops were withdrawn southeast to protect Italy. Between 455 and 475, the Visigoths, the Burgundians, and the Franks assumed power in Gaul. Certain aspects of the ancient Celtic culture continued however after the fall of Roman administration.
Certain Gallo-Roman aristocratic families continued to exert power in episcopal cities (as the Mauronitus family in Marseille, or the Bishop Gregory of Tours). The appearance of Germanic given and family names becomes noticeable in France from the middle of the 7th century on, most notably in powerful families, indicating thus that the center of gravity had definitely shifted.
The Gallo-Roman, or Vulgar Latin, dialect of the late Roman period evolved into the dialects of the Oïl languages and Old French in the north, and Occitan in the south.
The words "gaul" and "gaulois" continued to be used, at least in writing, until the end of the Merovingian period. Slowly, during the Carolingian period, the expression "Francie"' (first Francia, then Francia occidentalis) spread to describe the political reality of the Frankish kingdom (regnum francorum).
Legacy
The Roman Gaul was one of the most important and stable provinces of the empire. It was through Gaul that other significant Roman provinces, such as Britain and Germania (Germany were accessed. On occasions when rebel armies controlled Gaul, Britain was cut off from the imperial center.
Notes
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Caesar, Julius, and S. A. Handford. 1951. The conquest of Gaul. Harmondsworth, Eng: Penguin Books. ISBN 9780140440218
- King, Anthony. 1990. Roman Gaul and Germany. Exploring the Roman world. [Berkeley]: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520069893
- Latouche, Robert. 1968. Caesar to Charlemagne: the beginning of France. London: Phoenix House. ISBN 9780460077286
- Drinkwater, J. F. 1984. Roman Gaul: the three provinces, 58 B.C.E.-AD 260. London: Croom Helm. ISBN 9780709903512
- Woolf, Greg. 1998. Becoming Roman: the origins of provincial civilization in Gaul. Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521414456
External links
- Romans in Gaul : A Webliography - A Teacher Workshop held at Temple University, November 3, 2001. Dr. Janice Siegel, Department of Classics, Hampden-Sydney College, Virginia
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.