Difference between revisions of "Passamaquoddy" - New World Encyclopedia
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (48 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Approved}}{{Paid}}{{Copyedited}} |
[[Category:Politics and social sciences]] | [[Category:Politics and social sciences]] | ||
[[Category:Anthropology]] | [[Category:Anthropology]] | ||
[[Category:Ethnic group]] | [[Category:Ethnic group]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Bandera Passamakoddy.png|300px|thumb|Passamaquoddy tribal flag]] | ||
| − | + | The '''Passamaquoddy''' ('''Peskotomuhkati''' or '''Pestomuhkati''' in the Passamaquoddy language) are a [[Native Americans in the United States|Native American]]/[[First Nations]] people who live in northeastern [[North America]], primarily in [[Maine]] and [[New Brunswick]]. Although closely related peoples sharing a common language, the [[Maliseet]] kinsfolk and the Passamaquoddy have always considered themselves politically independent. The French referred to both of these tribes as the "Etchmins." [[Passamaquoddy Bay]], which straddles the [[United States-Canada border]] between New Brunswick and Maine, derives its name from the Passamaquoddy people. | |
| − | The '''Passamaquoddy''' ('''Peskotomuhkati''' or '''Pestomuhkati''' in the Passamaquoddy language) are a [[Native Americans in the United States|Native American]]/[[First Nations]] people who live in northeastern [[North America]], primarily in [[Maine]] and [[New Brunswick]]. | + | {{toc}} |
| + | Contemporary Passamaquoddy are known for their arts and crafts, such as [[jewelry]], [[basketry]], wood [[carving]], and building birch bark [[canoe]]s. Efforts are being made to increase the number of children who speak the native language. To modern Western society, the simple Passamaquoddy subsistence lifestyle may appear impoverished, yet, those who grew up in the traditional ways take pride in preserving the beauty and wisdom of such a lifestyle, and making it known to others. In these ways, the Passamoquoddy continue to practice their traditions while finding their place in the contemporary world. | ||
| + | ==History== | ||
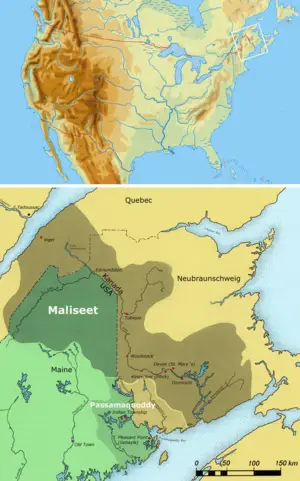
| + | [[Image:Wohngebiet_Maliseet.png|thumb|right|300px|Passamaquoddy Territory]] | ||
| + | The Passamaqoddy lacked a written history before the arrival of Europeans but do have an extensive oral tradition which includes their mythology. | ||
| + | |||
| + | They were a peaceful people, mostly farmers and hunters, maintaining a [[nomad]]ic existence in the well-watered woods and mountains of the coastal regions along the [[Bay of Fundy]] and [[Gulf of Maine]], and also along the [[Saint Croix River]] and its tributaries. They spent most time at the mouths of rivers, where they farmed corn, beans, and squash, and harvested seafood, including [[porpoise]], and traveled inland for game. | ||
| + | |||
| + | European settlers arrived in their lands in the sixteenth century, giving them the name "Passamaquoddy." The word "Passamaquoddy" is an Anglicization of the Passamaquoddy word ''peskotomuhkati,'' the [[prenoun]] form (prenouns being a linguistic feature of Algonquian languages) of ''Peskotomuhkat'' ''(pestəmohkat),'' the name they applied to themselves. Peskotomuhkat literally means "pollock-spearer" or "those of the place where polluck are plentiful,"<ref> [http://www.lib.unb.ca/Texts/Maliseet/dictionary/index.php?command=listAlpha&letter=p Peskotomuhkat] ''Maliseet - Passamaquoddy Dictionary.'' Retrieved November 4, 2007.</ref> reflecting the importance of this fish.<ref>Vincent O. Erickson, "Maliseet-Passamaquoddy." In ''Northeast,'' ed. Bruce G. Trigger. Vol. 15 of ''Handbook of North American Indians,'' ed. William C. Sturtevant. (Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution, 1978), 135. Cited in Lyle Campbell, ''American Indian Languages: The Historical Linguistics of Native America.'' (Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 2000), 401.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Europeans brought with them [[smallpox]] and other [[disease]]s, which ultimately took a very heavy toll on the natives, reducing their numbers from over 20,000 to around 4,000 practically overnight. In 1586, an epidemic of [[typhus]] broke out, also devastating the population. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This caused the Passamaquoddy to band together with their neighboring [[Abenaki]]s, [[Penobscot]]s, [[Micmac]]s (95 percent of who were wiped out by typhoid fever), and [[Maliseet]] tribes, forming the short-lived [[Wabanaki Confederacy]]. ''Wabanaki'' means "people of the dawn" or "dawnland people," referring to these peoples as the easterners. The name "Wabanaki" itself, however, may be a corruption of the Passamquoddy term ''Wub-bub-nee-hig,'' from ''Wub-bub-phun'' meaning the "first light of dawn before the early sunrise."<ref> Allen J. Sockabasin, ''An Upriver Passamaquoddy'' (Tilbury House Publishers, 2007)</ref> The confederacy was a semi-loose alliance formed to help keep the European aggressors and [[Iroquois]] at bay. It was officially disbanded in 1862, although five Wabanaki nations still exist and remain friends and allies to this day. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Passamaquoddy Indians were restrained and limited in the United States to the current [[Passamaquoddy Pleasant Point Reservation]] and [[Passamaquoddy Indian Township Reservation]], both in Washington County, [[Maine]]. There are also Passamaquoddy off-reservation trust lands in five Maine counties; these lands total almost four times the size of the reservation proper. They are located in northern and western [[Somerset County, Maine|Somerset County]], northern [[Franklin County, Maine|Franklin County]], northeastern [[Hancock County, Maine|Hancock County]], western Washington County, and several locations in eastern and western [[Penobscot County, Maine|Penobscot County]]. Their total land area is 373.888 km² (144.359 sq mi). There was no resident population on these trust lands as of the 2000 census. The Passamaquoddy also live in [[Charlotte County, New Brunswick]], and maintain active land claims but have no legal status in Canada as a [[First Nation]]. Some Passamaquoddy continue to seek the return of territory now comprised in [[Saint Andrews, New Brunswick]] which they claim as [[Qonasqamkuk]], a Passamaquoddy ancestral capital and burial ground. | ||
==Culture== | ==Culture== | ||
| − | + | {{readout||left|250px|Passamaquoddy are known for their arts and crafts, such as [[jewelry]], [[basketry]], wood [[carving]], and building birch bark [[canoe]]s}} | |
| + | [[Image:PaulKane-Sketch-Canoe-ROM.jpg|thumb|right|250 px|Sketch of birchbark canoe]] | ||
| + | The Passamaquoddy traditionally were [[nomad]]ic farmers and hunters. Their method of [[fishing]] was spear-fishing rather than angling. | ||
| − | + | They were world-class craftsmen when it came to birch-bark [[canoe]]s, which provided a lucrative trade industry with other [[Algonquin]] tribes. They also practiced highly decorative forms of [[basket]]-weaving, and carpentry, as well as enjoying many colorful forms of [[jewelry]]. Their crafts can be found on the Pleasant Point Reservation and in surrounding areas today. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ===Mythology=== | |
| + | In Passamaquoddy [[mythology]], the main spirit is known as ''Kci Niwesq'' (also spelled Kihci Niweskw, Kichi Niwaskw, and several other ways.) This means "Great Spirit" in the Passamaquoddy language, and is the Passamaquoddy name for the Creator ([[God]]) who is sometimes also referred to as ''Keluwosit.'' ''Kci Niwesq'' is a divine spirit with no human form or attributes (including [[gender]]) and is never personified in Passamaquoddy folklore. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The "Little People" of the [[Maliseet]] and Passamaquoddy tribes were considered to be dangerous if disrespected, but are generally benevolent nature spirits. They are known by a variety of names such as the Mikumwesuk, Wunagmeswook, and Geow-lud-mo-sis-eg. | ||
| − | + | One of the infamous animal spirits of the Passamaquoddy was called [[Loks]] (also spelled Luks or Lox), also known as Wolverine, a malevolent Passamaquoddy deity. He usually demonstrates inappropriate behavior like [[gluttony]], rudeness, and [[bullying]], but in some stories he also plays the role of a dangerous monster. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Glooskap]] (also spelled Glooscap, Koluskap, Gluskabe, Gluskabi, and several other ways) is the benevolent culture hero of the [[Wabanaki]] tribes (sometimes referred to as a "transformer" by folklorists.) His name is spelled so many different ways because the Passamaquoddy and the other Wabanaki languages were originally unwritten, so English speakers just spelled it however it sounded to them at the time. The correct Passamaquoddy pronounciation is similar to klue-skopp, but with very soft k and p sounds. Glooskap shares some similarities with other Algonquian heroes such as the [[Anishinabe]] [[Manabozho]], [[Blackfoot]] [[Napi]], and [[Cree]] [[Wesakechak]], and many of the same stories are told in different Algonquian tribes with only the identity of the protagonist differing. | |
| − | + | Grandmother Woodchuck (Nuhkomoss Munimqehs) was Glooskap's wise old grandmother, who raised him. | |
| − | + | Chenoo and Kewahqu were giant [[cannibal]] monsters, similar to the [[Wendigo]] of the Cree and other northern tribes. The name "Chenoo" comes from the neighboring [[Micmac]] tribe and is pronounced cheh-noo. | |
| − | The | + | ==Contemporary Passamaquoddy== |
| + | Contemporary Passamaquoddy reside in two reservations in [[Maine]]: The Indian Township Reservation and Pleasant Point (also known as Sipayik). The population of Indian Township Reservation was 676 at the 2000 census, and the Pleasant Point population was 640 at the 2000 census. | ||
| − | + | The Indian Township and Pleasant Point Passamaquoddy tribal councils form the Passamaquoddy Joint Tribal Council which is responsible for issues that affect both groups, such as jointly owned businesses, tribal land issues, and trust responsibility concerns. | |
| − | The Passamaquoddy | ||
| − | + | The Passamaquoddy, along with the neighboring [[Penobscot]] Nation, are given special political status in the U.S. state of Maine. Both groups are allowed to send a non-voting representative to the [[Maine House of Representatives]]. Although these representatives cannot vote, they may sponsor any legislation regarding Native American affairs, and may co-sponsor any other legislation. They are also entitled to serve on House committees. | |
| − | + | The total Passamaquoddy population in Maine is about 2,500 people, with more than half of adults still speaking the [[Maliseet-Passamaquoddy]] language, shared (other than minor differences in [[dialect]]) with the neighboring and related [[Maliseet]] people, and which belongs to the [[Algonquian]] branch of the [[Algic languages|Algic]] language family. | |
| − | [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | There is also a small Passamaquoddy population in [[New Brunswick]], [[Canada]]. They are not, however, recognized by the Canadian government as constituting a [[First Nations|First Nation]]. | |
| − | + | To modern Western society, the simple Passamaquoddy subsistence lifestyle of [[hunting]], [[fishing]], [[basketweaving]] and other crafts, storytelling and music may appear impoverished. Yet, to those who grew up in the traditional ways like Allen Sockabasin, preserving the beauty and wisdom of such a lifestyle has become their life's work.<ref> Sockabasin (2007)</ref> | |
| − | + | ===Land claims lawsuit === | |
| + | The Passamaquoddy may be best known outside the region for ''[[Passamaquoddy v. Morton]],'' a 1975 land claims lawsuit in the United States which opened the door to successful land claims negotiations for many eastern tribes, giving federal recognition and millions of dollars to purchase trust lands. The Passamaquoddy tribe was awarded $40 million at the resolution of this case by the [[Maine Land Claims Act]] of 1980, signed on March 15, 1980, with a similar sum paid to the Penobscot tribe, in return for relinquishing their rights to 19,500 square miles, for roughly 60 percent of the State of Maine. | ||
| − | + | They invested the money well enough that they quickly increased it to $100 million. Their investing strategy was written up as a case study by [[Harvard Business School]]. <ref>Ian Frazier, ''On the Rez'' (Picador, 2001, ISBN 978-0312278595), 78-79</ref> | |
| − | The Chief Melvin Francis Memorial Fund was set up in his remembrance to improve the education, health, welfare, safety and lives of tribal members.<ref> | + | ===Notable Passamaquoddy=== |
| + | ;Melvin Joseph Francis | ||
| + | [[Melvin Joseph Francis]] (August 6, 1945–January 12, 2006) was the governor of the [[Passamaquoddy Pleasant Point Reservation]], one of two reservations in [[Maine]] of the Passamaquoddy Indian tribe, from 1980 until 1990 and again since 2002.<ref name=Carrier>Paul Carrier [http://mytwobeadsworth.com/GovFrancis11406.html Tribal governor dies in crash] Retrieved May 30, 2007.</ref> Born and raised in Pleasant Point, he attend local schools. After graduating from Shead High School he earned a [[journeyman]]'s certificate and specialized in carpentry.<ref> Melvin Joseph Francis "Passamaquoddy Tribe at Pleasant Point."</ref> He spoke the Passamaquoddy language and was engaged in the preservation of his communities traditions. But alike in the betterment of living conditions for his people as a devoted advocate, peacemaker and lending his professional skills were needed. As governor he strongly supported a proposed [[Liquefied natural gas|LNG]] terminal on tribal land and legislation allowing an [[Native American gambling enterprises|Indian-run racetrack casino]] in [[Washington County, Maine|Washington County]]. Both proposals were not without controversy.<ref name=Carrier/> Francis died when his car crashed head first into a tanker truck. He had been on his way home from the signing of an agreement with the Venezuelan-owned [[Citgo|Citgo Petroleum Corporation]] at [[Penobscot Indian Island Reservation|Indian Island]] providing affordable oil to the Passamaquoddy, [[Penobscot]], [[Mi'kmaq]] and [[Maliseet]] tribes in Maine.<ref> Leader dies after signing CITGO agreement AP (January 24, 2006) ''Indian Country Today.''</ref> The Chief Melvin Francis Memorial Fund was set up in his remembrance to improve the education, health, welfare, safety and lives of tribal members.<ref> Chief Melvin Francis Memorial Foundation Passamaquoddy Tribe at Pleasant Point.</ref> | ||
| − | + | ;David Francis | |
| − | + | Passamaquoddy Tribe elder David Francis of Pleasant Point was awarded an honorary doctorate by the [[University of Maine]] at its graduation service in May 2009. Francis worked for decades to develop a written form of the Passamaquoddy language, and was a lead collaborator in the creation of a Passamaquoddy-Maliseet [[dictionary]].<ref>David A. Francis and Robert M. Leavitt, ''A Passamaquoddy - Maliseet Dictionary Peskotomuhkati Wolastoqewi Latuwewakon'' (Orono, ME: University of Maine Press, 2008, ISBN 978-0891011170).</ref> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Other notable Passamaquoddy people include: | |
| − | + | *Maggie Paul, singer<ref> Maggie Paul, Passamaquoddy Oyate Online.</ref> | |
| − | * | + | *Allen Sockabasin, singer, writer, and translator<ref>[http://www.tilburyhouse.com/Children's%20Frames/child_thanking.html Thanks to the Animals] By Allen Sockabasin, Passamaquoddy Storyteller. Retrieved November 4, 2007.</ref> |
| − | * | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| Line 59: | Line 78: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | * | + | |
| + | *Campbell, Lyle. ''American Indian Languages: The Historical Linguistics of Native America''. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 2000. ISBN 0195140508 | ||
| + | *Fewkes, J. Walter. ''Contribution to Passamaquoddy Folk-Lore''. Dodo Press, 2007. ISBN 9781406523843 | ||
| + | *Francis, David A., and Robert M. Leavitt. ''A Passamaquoddy - Maliseet Dictionary Peskotomuhkati Wolastoqewi Latuwewakon''. Orono, ME: University of Maine Press, 2008. ISBN 978-0891011170 | ||
| + | *Sockabasin, Allen J. ''An Upriver Passamaquoddy''. Tilbury House Publishers, 2007. ISBN 9780884482932 | ||
| + | *Waldman, Carl. ''Encyclopedia of Native American Tribes''. New York, NY: Checkmark Books, 2006. ISBN 9780816062744 | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| + | All links retrieved November 18, 2022. | ||
| + | |||
*[http://www.wabanaki.com Passamaquoddy Tribal Government Web Site (Pleasant Point)] | *[http://www.wabanaki.com Passamaquoddy Tribal Government Web Site (Pleasant Point)] | ||
| − | *[http://www.passamaquoddy.com Passamaquoddy | + | *[http://www.passamaquoddy.com/ Passamaquoddy Tribe (Indian Township)] |
| − | *[ | + | *[https://pmportal.org/ Passamaquoddy-Maliseet Language Portal] |
| − | *[http://www.gutenberg.org/etext/17997 Contribution to Passamaquoddy Folk-Lore], by J. Walter Fewkes, reprinted from the Journal of American Folk-Lore, October-December, 1890, from | + | *[http://www.gutenberg.org/etext/17997 Contribution to Passamaquoddy Folk-Lore], by J. Walter Fewkes, reprinted from the Journal of American Folk-Lore, October-December, 1890, from Project Gutenberg |
| − | *[http://www. | + | *[http://www.quoddyloop.com/pssmqddy.htm The Passamaquoddy Tribe] Quoddy Loop Tour Guide |
| − | + | *[http://www.wabanaki.com/wabanaki_new/Arts_&_Crafts.html Passamaquoddy Artists and Crafts People] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {{Wabanaki Confederacy}} | ||
{{Credits|Passamaquoddy|160941574|Passamaquoddy_Pleasant_Point_Reservation|128868160|}} | {{Credits|Passamaquoddy|160941574|Passamaquoddy_Pleasant_Point_Reservation|128868160|}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:56, 23 March 2023
The Passamaquoddy (Peskotomuhkati or Pestomuhkati in the Passamaquoddy language) are a Native American/First Nations people who live in northeastern North America, primarily in Maine and New Brunswick. Although closely related peoples sharing a common language, the Maliseet kinsfolk and the Passamaquoddy have always considered themselves politically independent. The French referred to both of these tribes as the "Etchmins." Passamaquoddy Bay, which straddles the United States-Canada border between New Brunswick and Maine, derives its name from the Passamaquoddy people.
Contemporary Passamaquoddy are known for their arts and crafts, such as jewelry, basketry, wood carving, and building birch bark canoes. Efforts are being made to increase the number of children who speak the native language. To modern Western society, the simple Passamaquoddy subsistence lifestyle may appear impoverished, yet, those who grew up in the traditional ways take pride in preserving the beauty and wisdom of such a lifestyle, and making it known to others. In these ways, the Passamoquoddy continue to practice their traditions while finding their place in the contemporary world.
History
The Passamaqoddy lacked a written history before the arrival of Europeans but do have an extensive oral tradition which includes their mythology.
They were a peaceful people, mostly farmers and hunters, maintaining a nomadic existence in the well-watered woods and mountains of the coastal regions along the Bay of Fundy and Gulf of Maine, and also along the Saint Croix River and its tributaries. They spent most time at the mouths of rivers, where they farmed corn, beans, and squash, and harvested seafood, including porpoise, and traveled inland for game.
European settlers arrived in their lands in the sixteenth century, giving them the name "Passamaquoddy." The word "Passamaquoddy" is an Anglicization of the Passamaquoddy word peskotomuhkati, the prenoun form (prenouns being a linguistic feature of Algonquian languages) of Peskotomuhkat (pestəmohkat), the name they applied to themselves. Peskotomuhkat literally means "pollock-spearer" or "those of the place where polluck are plentiful,"[1] reflecting the importance of this fish.[2]
The Europeans brought with them smallpox and other diseases, which ultimately took a very heavy toll on the natives, reducing their numbers from over 20,000 to around 4,000 practically overnight. In 1586, an epidemic of typhus broke out, also devastating the population.
This caused the Passamaquoddy to band together with their neighboring Abenakis, Penobscots, Micmacs (95 percent of who were wiped out by typhoid fever), and Maliseet tribes, forming the short-lived Wabanaki Confederacy. Wabanaki means "people of the dawn" or "dawnland people," referring to these peoples as the easterners. The name "Wabanaki" itself, however, may be a corruption of the Passamquoddy term Wub-bub-nee-hig, from Wub-bub-phun meaning the "first light of dawn before the early sunrise."[3] The confederacy was a semi-loose alliance formed to help keep the European aggressors and Iroquois at bay. It was officially disbanded in 1862, although five Wabanaki nations still exist and remain friends and allies to this day.
The Passamaquoddy Indians were restrained and limited in the United States to the current Passamaquoddy Pleasant Point Reservation and Passamaquoddy Indian Township Reservation, both in Washington County, Maine. There are also Passamaquoddy off-reservation trust lands in five Maine counties; these lands total almost four times the size of the reservation proper. They are located in northern and western Somerset County, northern Franklin County, northeastern Hancock County, western Washington County, and several locations in eastern and western Penobscot County. Their total land area is 373.888 km² (144.359 sq mi). There was no resident population on these trust lands as of the 2000 census. The Passamaquoddy also live in Charlotte County, New Brunswick, and maintain active land claims but have no legal status in Canada as a First Nation. Some Passamaquoddy continue to seek the return of territory now comprised in Saint Andrews, New Brunswick which they claim as Qonasqamkuk, a Passamaquoddy ancestral capital and burial ground.
Culture
The Passamaquoddy traditionally were nomadic farmers and hunters. Their method of fishing was spear-fishing rather than angling.
They were world-class craftsmen when it came to birch-bark canoes, which provided a lucrative trade industry with other Algonquin tribes. They also practiced highly decorative forms of basket-weaving, and carpentry, as well as enjoying many colorful forms of jewelry. Their crafts can be found on the Pleasant Point Reservation and in surrounding areas today.
Mythology
In Passamaquoddy mythology, the main spirit is known as Kci Niwesq (also spelled Kihci Niweskw, Kichi Niwaskw, and several other ways.) This means "Great Spirit" in the Passamaquoddy language, and is the Passamaquoddy name for the Creator (God) who is sometimes also referred to as Keluwosit. Kci Niwesq is a divine spirit with no human form or attributes (including gender) and is never personified in Passamaquoddy folklore.
The "Little People" of the Maliseet and Passamaquoddy tribes were considered to be dangerous if disrespected, but are generally benevolent nature spirits. They are known by a variety of names such as the Mikumwesuk, Wunagmeswook, and Geow-lud-mo-sis-eg.
One of the infamous animal spirits of the Passamaquoddy was called Loks (also spelled Luks or Lox), also known as Wolverine, a malevolent Passamaquoddy deity. He usually demonstrates inappropriate behavior like gluttony, rudeness, and bullying, but in some stories he also plays the role of a dangerous monster.
Glooskap (also spelled Glooscap, Koluskap, Gluskabe, Gluskabi, and several other ways) is the benevolent culture hero of the Wabanaki tribes (sometimes referred to as a "transformer" by folklorists.) His name is spelled so many different ways because the Passamaquoddy and the other Wabanaki languages were originally unwritten, so English speakers just spelled it however it sounded to them at the time. The correct Passamaquoddy pronounciation is similar to klue-skopp, but with very soft k and p sounds. Glooskap shares some similarities with other Algonquian heroes such as the Anishinabe Manabozho, Blackfoot Napi, and Cree Wesakechak, and many of the same stories are told in different Algonquian tribes with only the identity of the protagonist differing.
Grandmother Woodchuck (Nuhkomoss Munimqehs) was Glooskap's wise old grandmother, who raised him.
Chenoo and Kewahqu were giant cannibal monsters, similar to the Wendigo of the Cree and other northern tribes. The name "Chenoo" comes from the neighboring Micmac tribe and is pronounced cheh-noo.
Contemporary Passamaquoddy
Contemporary Passamaquoddy reside in two reservations in Maine: The Indian Township Reservation and Pleasant Point (also known as Sipayik). The population of Indian Township Reservation was 676 at the 2000 census, and the Pleasant Point population was 640 at the 2000 census.
The Indian Township and Pleasant Point Passamaquoddy tribal councils form the Passamaquoddy Joint Tribal Council which is responsible for issues that affect both groups, such as jointly owned businesses, tribal land issues, and trust responsibility concerns.
The Passamaquoddy, along with the neighboring Penobscot Nation, are given special political status in the U.S. state of Maine. Both groups are allowed to send a non-voting representative to the Maine House of Representatives. Although these representatives cannot vote, they may sponsor any legislation regarding Native American affairs, and may co-sponsor any other legislation. They are also entitled to serve on House committees.
The total Passamaquoddy population in Maine is about 2,500 people, with more than half of adults still speaking the Maliseet-Passamaquoddy language, shared (other than minor differences in dialect) with the neighboring and related Maliseet people, and which belongs to the Algonquian branch of the Algic language family.
There is also a small Passamaquoddy population in New Brunswick, Canada. They are not, however, recognized by the Canadian government as constituting a First Nation.
To modern Western society, the simple Passamaquoddy subsistence lifestyle of hunting, fishing, basketweaving and other crafts, storytelling and music may appear impoverished. Yet, to those who grew up in the traditional ways like Allen Sockabasin, preserving the beauty and wisdom of such a lifestyle has become their life's work.[4]
Land claims lawsuit
The Passamaquoddy may be best known outside the region for Passamaquoddy v. Morton, a 1975 land claims lawsuit in the United States which opened the door to successful land claims negotiations for many eastern tribes, giving federal recognition and millions of dollars to purchase trust lands. The Passamaquoddy tribe was awarded $40 million at the resolution of this case by the Maine Land Claims Act of 1980, signed on March 15, 1980, with a similar sum paid to the Penobscot tribe, in return for relinquishing their rights to 19,500 square miles, for roughly 60 percent of the State of Maine.
They invested the money well enough that they quickly increased it to $100 million. Their investing strategy was written up as a case study by Harvard Business School. [5]
Notable Passamaquoddy
- Melvin Joseph Francis
Melvin Joseph Francis (August 6, 1945–January 12, 2006) was the governor of the Passamaquoddy Pleasant Point Reservation, one of two reservations in Maine of the Passamaquoddy Indian tribe, from 1980 until 1990 and again since 2002.[6] Born and raised in Pleasant Point, he attend local schools. After graduating from Shead High School he earned a journeyman's certificate and specialized in carpentry.[7] He spoke the Passamaquoddy language and was engaged in the preservation of his communities traditions. But alike in the betterment of living conditions for his people as a devoted advocate, peacemaker and lending his professional skills were needed. As governor he strongly supported a proposed LNG terminal on tribal land and legislation allowing an Indian-run racetrack casino in Washington County. Both proposals were not without controversy.[6] Francis died when his car crashed head first into a tanker truck. He had been on his way home from the signing of an agreement with the Venezuelan-owned Citgo Petroleum Corporation at Indian Island providing affordable oil to the Passamaquoddy, Penobscot, Mi'kmaq and Maliseet tribes in Maine.[8] The Chief Melvin Francis Memorial Fund was set up in his remembrance to improve the education, health, welfare, safety and lives of tribal members.[9]
- David Francis
Passamaquoddy Tribe elder David Francis of Pleasant Point was awarded an honorary doctorate by the University of Maine at its graduation service in May 2009. Francis worked for decades to develop a written form of the Passamaquoddy language, and was a lead collaborator in the creation of a Passamaquoddy-Maliseet dictionary.[10]
Other notable Passamaquoddy people include:
Notes
- ↑ Peskotomuhkat Maliseet - Passamaquoddy Dictionary. Retrieved November 4, 2007.
- ↑ Vincent O. Erickson, "Maliseet-Passamaquoddy." In Northeast, ed. Bruce G. Trigger. Vol. 15 of Handbook of North American Indians, ed. William C. Sturtevant. (Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution, 1978), 135. Cited in Lyle Campbell, American Indian Languages: The Historical Linguistics of Native America. (Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 2000), 401.
- ↑ Allen J. Sockabasin, An Upriver Passamaquoddy (Tilbury House Publishers, 2007)
- ↑ Sockabasin (2007)
- ↑ Ian Frazier, On the Rez (Picador, 2001, ISBN 978-0312278595), 78-79
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Paul Carrier Tribal governor dies in crash Retrieved May 30, 2007.
- ↑ Melvin Joseph Francis "Passamaquoddy Tribe at Pleasant Point."
- ↑ Leader dies after signing CITGO agreement AP (January 24, 2006) Indian Country Today.
- ↑ Chief Melvin Francis Memorial Foundation Passamaquoddy Tribe at Pleasant Point.
- ↑ David A. Francis and Robert M. Leavitt, A Passamaquoddy - Maliseet Dictionary Peskotomuhkati Wolastoqewi Latuwewakon (Orono, ME: University of Maine Press, 2008, ISBN 978-0891011170).
- ↑ Maggie Paul, Passamaquoddy Oyate Online.
- ↑ Thanks to the Animals By Allen Sockabasin, Passamaquoddy Storyteller. Retrieved November 4, 2007.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Campbell, Lyle. American Indian Languages: The Historical Linguistics of Native America. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 2000. ISBN 0195140508
- Fewkes, J. Walter. Contribution to Passamaquoddy Folk-Lore. Dodo Press, 2007. ISBN 9781406523843
- Francis, David A., and Robert M. Leavitt. A Passamaquoddy - Maliseet Dictionary Peskotomuhkati Wolastoqewi Latuwewakon. Orono, ME: University of Maine Press, 2008. ISBN 978-0891011170
- Sockabasin, Allen J. An Upriver Passamaquoddy. Tilbury House Publishers, 2007. ISBN 9780884482932
- Waldman, Carl. Encyclopedia of Native American Tribes. New York, NY: Checkmark Books, 2006. ISBN 9780816062744
External links
All links retrieved November 18, 2022.
- Passamaquoddy Tribal Government Web Site (Pleasant Point)
- Passamaquoddy Tribe (Indian Township)
- Passamaquoddy-Maliseet Language Portal
- Contribution to Passamaquoddy Folk-Lore, by J. Walter Fewkes, reprinted from the Journal of American Folk-Lore, October-December, 1890, from Project Gutenberg
- The Passamaquoddy Tribe Quoddy Loop Tour Guide
- Passamaquoddy Artists and Crafts People
| |||||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.