Difference between revisions of "Oregon Trail" - New World Encyclopedia
(approved) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{approved}}{{Images OK}}{{ | + | {{approved}}{{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Paid}}{{copyedited}} |
{{Infobox_protected_area | name = Oregon National Historic Trail (Oregon Trail) | {{Infobox_protected_area | name = Oregon National Historic Trail (Oregon Trail) | ||
| iucn_category = V | | iucn_category = V | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
| governing_body = [[National Park Service]] | | governing_body = [[National Park Service]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pioneers traveled in wagons across the '''Oregon Trail,''' one of the main overland migration routes on the [[North America]]n [[continent]], in order to settle new parts of the [[United States|United States of America]] during the nineteenth century. The Oregon Trail helped the United States implement its cultural goal of [[Manifest Destiny]], that is, to expand the nation from the [[Atlantic Ocean|Atlantic]] to the [[Pacific Ocean]]. The Oregon Trail spanned over half the continent as the wagon trail proceeded 2,170 miles west through territories and land later to become six [[U.S. state]]s ([[Missouri]], [[Kansas]], [[Nebraska]], [[Wyoming]], [[Idaho]], and [[Oregon]]). Between 1841 and 1869, the Oregon Trail was used by settlers migrating to the [[Pacific Northwest]] of what is now the United States. Once the [[First Transcontinental Railroad|first transcontinental railroad]] was completed in 1869, the use of this trail by long distance travelers diminished. | ||
| + | {{toc}} | ||
[[Image:Oregontrail 1907.jpg|thumb|400px|The Ox Team or the Old Oregon Trail 1852-1906 by Ezra Meeker.]] | [[Image:Oregontrail 1907.jpg|thumb|400px|The Ox Team or the Old Oregon Trail 1852-1906 by Ezra Meeker.]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
===Astorians=== | ===Astorians=== | ||
| − | The first land route across what is now the [[United States]] | + | The first well-mapped land route across what is now the [[United States]] was that taken by [[Lewis and Clark Expedition|Lewis and Clark]], from 1804 to 1805. They, in fact, believed that they had found a practical route to the west coast. However, the pass through the [[Rocky Mountains]] they took, [[Lolo Pass (Idaho-Montana)|Lolo Pass]], turned out to be too difficult for wagon travel. In 1810, [[John Jacob Astor]] outfitted an expedition (known popularly as the [[Astor Expedition]] or ''Astorians'') to find an overland supply route for establishing a [[fur trading]] post at the mouth of the [[Columbia River]] at [[Fort Astoria]]. Most of Astor's partners and all of his staff were former employees of the [[Northwest Company]], known as Nor'Westers. |
| − | Fearing attack by [[Blackfeet]], the expedition veered south of the Lewis and Clark route in what is now South Dakota and in the process passed through what is now Wyoming and then down the [[Snake River]] to the [[Columbia River]]. | + | Fearing attack by [[Blackfeet]], the expedition veered south of the Lewis and Clark route in what is now South Dakota and in the process passed through what is now Wyoming, and then down the [[Snake River]] to the [[Columbia River]]. |
| − | Members of the party, including [[Robert Stuart]], one of the Nor'wester partners, returned back east after the [[American Fur Company]] staff there sold the fort to [[British]] [[Northwest Company]] staff, who took over the outpost in the [[War of 1812]] via the Snake River. The party stumbled upon [[South Pass]]: | + | Members of the party, including [[Robert Stuart]], one of the Nor'wester partners, returned back east after the [[American Fur Company]] staff there sold the fort to [[British]] [[Northwest Company]] staff, who took over the outpost in the [[War of 1812]] via the Snake River. The party stumbled upon [[South Pass]]: A wide, low pass through the Rockies in Wyoming. The party continued via the [[Platte River]]. This turned out to be a practical wagon route, and Stuart's journals offered a meticulous account of it.<ref>Robert Stuart and Philip Ashton Rollins. ''The Discovery of the Oregon Trail Robert Stuart's Narratives of his Overland Trip Eastward From Astoria in 1812-13'' (Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press 1995). ISBN 9780803292345</ref> |
Fort Astoria was returned to United States control at the end of the war. However, the British [[Hudson's Bay Company]] came to control the [[fur trade]] in the region, especially after its merger with the [[North West Company]] in 1821. | Fort Astoria was returned to United States control at the end of the war. However, the British [[Hudson's Bay Company]] came to control the [[fur trade]] in the region, especially after its merger with the [[North West Company]] in 1821. | ||
===Great American Desert=== | ===Great American Desert=== | ||
| − | Westward expansion did not begin immediately. Reports from expeditions in 1806 by Lieutenant [[Zebulon Pike]] and in 1819 by Major [[Stephen Long]] described the [[Great Plains]] as "unfit for human habitation" and "The [[Great American Desert]]" | + | Westward expansion did not begin immediately. Reports from expeditions in 1806, by Lieutenant [[Zebulon Pike]] and in 1819, by Major [[Stephen Long]] described the [[Great Plains]] as "unfit for human habitation" and "The [[Great American Desert]]." These descriptions were mainly based on the relative lack of timber and surface water. The images of sandy wastelands conjured up by terms like "desert" were tempered by the many reports of vast herds of bison. It was not until later that the [[Ogallala Aquifer]] would be discovered and used for irrigation, and railroads would allow lumber and farm products to be transported to distant markets. In the meantime, the Great Plains remained unattractive for general settlement, especially when compared to the fertile lands, big rivers, and seaports of Oregon. |
| − | The route of the Oregon Trail began to be scouted out as early as 1823 by [[fur traders]] and explorers. The trail began to be regularly used by fur traders, missionaries, and military expeditions during the 1830s. At the same time, small groups of individuals and the occasional family attempted to follow the trail | + | The route of the Oregon Trail began to be scouted out as early as 1823, by [[fur traders]] and explorers. The trail began to be regularly used by fur traders, missionaries, and military expeditions during the 1830s. At the same time, small groups of individuals and the occasional family attempted to follow the trail. Not all succeeded in arriving at [[Vancouver, Washington|Fort Vancouver]] in [[Washington]]. |
===Elm Grove Expedition=== | ===Elm Grove Expedition=== | ||
| − | On | + | On May 16, 1842, the first organized [[wagon train]] on the Oregon Trail set out from [[Elm Grove, Missouri]], with more than 100 pioneers (members of the party later disagreed over the size of the party, one stating 160 adults and children were in the party, while another counted only 105). The party was led by [[Elijah White]], appointed Indian Sub-Agent to Oregon, the first U.S. official in the region (never confirmed by Congress). Despite company policy to discourage U.S. emigration, [[John McLoughlin]], Factor of the [[Hudson's Bay Company]] at [[Vancouver, Washington|Fort Vancouver]], offered the American settlers food and farming equipment on credit, unwilling to watch able-bodied people starve. |
===Free land=== | ===Free land=== | ||
The biggest driving force for settlement was the offer of free land. | The biggest driving force for settlement was the offer of free land. | ||
| − | In 1843 the settlers of the [[Willamette Valley]] by a vote of 52 to 50 drafted a constitution that organized the land claim process in the state. Married couples were allowed to claim up to 640 acres (a "section" which is a square mile) at no cost and singles could claim 320 acres. <ref>[http://www.endoftheoregontrail.org/road2oregon/sa28claims.html Claiming the Farm] Retrieved October 18, 2007.</ref> | + | In 1843, the settlers of the [[Willamette Valley]], by a vote of 52 to 50, drafted a constitution that organized the land claim process in the state. Married couples were allowed to claim up to 640 acres (a "section" which is a square mile) at no cost and singles could claim 320 acres.<ref>End of the Oregon Trail, [http://www.endoftheoregontrail.org/road2oregon/sa28claims.html Claiming the Farm.] Retrieved October 18, 2007.</ref> |
| − | In 1848, the United States formally declared what was left of the [[Oregon Country]] a U.S. territory, after it effectively partitioned | + | In 1848, the United States formally declared what was left of the [[Oregon Country]] a U.S. territory, after it effectively partitioned in 1846. The [[Donation Land Act]] of 1850 superseded the earlier laws, but it did recognize the earlier claims. Settlers after 1850 could be granted half a section (320 acres) if married and a quarter section if single. A four-year residence and cultivation was required. In 1854, the land was no longer free. |
===Opening of the trail=== | ===Opening of the trail=== | ||
| − | In what was dubbed "The Great Migration of 1843" or the "Wagon Train of 1843" | + | In what was dubbed "The Great Migration of 1843," or the "Wagon Train of 1843,"<ref>Oregon Pioneers, [http://www.peak.org/~mransom/pioneers.html The Wagon Train of 1843.] Retrieved October 18, 2007. </ref> an estimated 800 immigrants, led by [[Marcus Whitman]], arrived in the Willamette Valley. Hundreds of thousands more followed, especially after [[California Gold Rush|gold was discovered]] in [[California]] in 1848. The trail was still in use during the [[American Civil War|Civil War]], but traffic declined after 1869, when the [[transcontinental railroad]] was completed. The trail continued to be used into the 1890s, and modern highways eventually paralleled large portions of it. |
| − | Other migration paths for early settlers prior to the establishment of the transcontinental railroads involved taking passage on a ship rounding | + | Other migration paths for early settlers prior to the establishment of the transcontinental railroads involved taking passage on a ship rounding [[Cape Horn]] of [[South America]], or to the [[Isthmus]] (now [[Panama]]) between North and South America. There, an arduous mule trek through hazardous swamps and rain forests awaited the traveler. A ship was typically then taken to [[San Francisco, California]]. |
==Routes== | ==Routes== | ||
| − | The trail is marked by numerous cutoffs and shortcuts from [[Missouri]] to [[Oregon]]. The basic route follows river valleys. | + | The trail is marked by numerous cutoffs and shortcuts from [[Missouri]] to [[Oregon]]. The basic route follows river valleys. Beginning initially in [[Independence, Missouri|Independence]]/[[Kansas City, Missouri|Kansas City]], the trail followed the [[Santa Fe Trail]] south of the [[Wakarusa River]]. After crossing [[Mount Oread|The Hill]] at [[Lawrence, Kansas]], it crossed the [[Kansas River]] near [[Topeka, Kansas]], and angled to [[Nebraska]], paralleling the [[Little Blue River]] until reaching the south side of the [[Platte River]]. It followed the Platte, North Platte, and Sweetwater Rivers to [[South Pass]] in the Rocky Mountains in Wyoming. From South Pass, the trail parallels the [[Snake River]] to the [[Columbia River]] before arriving at [[Oregon City, Oregon|Oregon City]], or taking the [[Barlow Road]] to the Willamette Valley and other destinations in what are now the states of Washington and Oregon. |
[[U.S. Highway 26]] follows the Oregon Trail for much of its length. | [[U.S. Highway 26]] follows the Oregon Trail for much of its length. | ||
| − | While the first few parties organized and departed from Elm Grove, the Oregon Trail's generally designated starting point was Independence or [[Westport, Kansas City|Westport]] on the [[Missouri River]]. Several towns along the Missouri River had feeder trails and make claims to being the starting point including [[Weston, Missouri]], [[Fort Leavenworth, Kansas]], [[Atchison, Kansas]], and [[St. Joseph, Missouri]]. | + | While the first few parties organized and departed from Elm Grove, the Oregon Trail's generally designated starting point was Independence or [[Westport, Kansas City|Westport]], on the [[Missouri River]]. Several towns along the Missouri River had feeder trails, and make claims to being the starting point, including [[Weston, Missouri]], [[Fort Leavenworth, Kansas]], [[Atchison, Kansas]], and [[St. Joseph, Missouri]]. |
| − | The Oregon Trail's designated termination point was Oregon City, at | + | The Oregon Trail's designated termination point was Oregon City, which at that time was the proposed capital of [[Oregon Territory]]. However, many settlers branched off or stopped short of this goal and settled at convenient or promising locations along the trail. Commerce with pioneers going further west greatly assisted these early settlements in getting established and launched local micro-economies critical to these settlements' prosperity. |
At many places along the trail, alternate routes called "cutoffs" were established either to shorten the trail or to get around difficult terrain. The Lander and Sublette cutoffs provided shorter routes through the mountains than the main route, bypassing [[Fort Bridger]]. In later years, the Salt Lake cutoff provided a route to [[Salt Lake City]]. | At many places along the trail, alternate routes called "cutoffs" were established either to shorten the trail or to get around difficult terrain. The Lander and Sublette cutoffs provided shorter routes through the mountains than the main route, bypassing [[Fort Bridger]]. In later years, the Salt Lake cutoff provided a route to [[Salt Lake City]]. | ||
| Line 60: | Line 61: | ||
===Landmarks=== | ===Landmarks=== | ||
| − | Many rock formations became famous landmarks that the Oregon Trail pioneers used to navigate | + | Many rock formations became famous landmarks that the Oregon Trail pioneers used to navigate and leave messages for pioneers following behind them. The first landmarks that the pioneers encountered were in western Nebraska, such as [[Courthouse and Jail Rocks]], [[Chimney Rock National Historic Site|Chimney Rock]], and [[Scotts Bluff National Monument|Scotts Bluff]]. In Wyoming, names of pioneers can be seen carved into a landmark bluff called Register Cliff. One Wyoming landmark along the trail, [[Ayres Natural Bridge]], is now a state park of the same name. |
==Travel equipment== | ==Travel equipment== | ||
| − | The Oregon Trail was too long and arduous for the standard [[Conestoga wagon]]s used in the [[Eastern United States]] | + | The Oregon Trail was too long and arduous for the standard [[Conestoga wagon]]s used in the [[Eastern United States]] for freight transport. These big wagons had a reputation for killing their oxen teams approximately two thirds along the trail and leaving their unfortunate owners stranded in desolate, isolated territory. The only solution was to abandon all belongings and traipse onward with the supplies and tools that could be carried or dragged. In one case in 1846, on the [[California Trail]], the [[Donner Party]], en route to California, was stranded in the [[Sierra Nevada (U.S.)|Sierra Nevada]] in November and three members are reported to have resorted to [[cannibalism]] to survive. |
| − | This led to the rapid development of the [[Conestoga Wagon#Prairie schooners|prairie schooners]]. The wagon was approximately half the size of the big Conestogas | + | This led to the rapid development of the [[Conestoga Wagon#Prairie schooners|prairie schooners]]. The wagon was approximately half the size of the big Conestogas and was manufactured in quantity. It was designed for the Oregon Trail's conditions and was a marvel of engineering for its time. The covers of the wagons were treated with linseed oil to keep out the rain. However, the covers eventually leaked anyway. |
The recommended amount of food to take for an adult was: | The recommended amount of food to take for an adult was: | ||
| Line 75: | Line 76: | ||
*15 pounds of [[dried fruit]] | *15 pounds of [[dried fruit]] | ||
*5 pounds of [[salt]] | *5 pounds of [[salt]] | ||
| − | *1/2 | + | *1/2 pound [[baking soda]] |
*2 pounds of [[tea]] | *2 pounds of [[tea]] | ||
*5 pounds of [[rice]] | *5 pounds of [[rice]] | ||
| Line 81: | Line 82: | ||
==Statistics== | ==Statistics== | ||
| − | Immigration to Oregon Territory increased vastly between 1840 and 1852 | + | Immigration to Oregon Territory increased vastly between 1840 and its peak in 1852. According to ''Oregon Trail Statistics,'' by William E. Hill, the figures rocketed from 13 in 1840, to 1,475 four years later, nearly doubled the following year, and hit 4,000 in 1847. Emigration declined considerably prior to 1850, when 6,000 people made the trek to Oregon. In 1851, the number dropped again (3,600) but sustained a huge comeback with 10,000 in 1852. (That same year some 60,000 people emigrated to Utah and California, a stand-alone record.) |
Another 13,500 people moved to Oregon in 1853-54, with 5,000 more making the trip as of 1859, the year of statehood. | Another 13,500 people moved to Oregon in 1853-54, with 5,000 more making the trip as of 1859, the year of statehood. | ||
In the 20 years from 1840-1859 some 52,000 emigrants moved to Oregon, but nearly five times that number opted for California or Utah. | In the 20 years from 1840-1859 some 52,000 emigrants moved to Oregon, but nearly five times that number opted for California or Utah. | ||
| − | Though the numbers appear | + | Though the numbers appear significant—and they were, especially in context of the times—considerably more people chose to remain at home in the 31 states. Part of the explanation is attributed to scout [[Kit Carson]], who reputedly said, "The cowards never started and the weak died on the way." According to some sources, one tenth of the emigrants perished on the way west. <ref>Lloyd W. Coffman, ''Blazing a Wagon Trail to Oregon: A Weekly Chronicle of the Great Migration of 1843'' (Enterprise, Or: Echo Books 1993). ISBN 9780963598400</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| Line 94: | Line 93: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | *Crawford, Medorum. ''Journal of Medorem Crawford | + | *Crawford, Medorum. ''Journal of Medorem Crawford: An Account of His Trip Across the Plains with the Oregon Pioneers of 1842.'' Fairfield, Washington: Ye Galleon Press, 1967. |
| − | *Hewitt, Randall H. ''Notes by the | + | *Hewitt, Randall H. ''Notes by the Way: Memoranda of a Journey Across the Plains, from Dundee, Ill., to Olympia, W.T. May 7, to November 3, 1862.'' Seattle: Frank McCaffrey Publishers, 1955. |
| − | *Smedley, William. ''Across the | + | *Smedley, William. ''Across the Plains: An 1862 Journey from Omaha to Oregon.'' Boulder: Johnson Books, 1994. ISBN 9780585020785 |
| − | *Ward, D. B. ''Across the | + | *Ward, D. B. ''Across the Plains in 1853''. Seattle: Shorey Bookstore, 1965. ISBN 9780846600619 |
| − | *Williams, Joseph. ''Narrative of a | + | *Williams, Joseph. ''Narrative of a Tour From the State of Indiana to the Oregon Territory in the Years 1841-2.'' Fairfield, Washington: Ye Galleon Press, 1977. ISBN 9780877701729 |
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | + | All links retrieved November 17, 2022. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | *[ | + | *[https://www.nps.gov/oreg/learn/historyculture/index.htm Oregon National Historic Trail] |
| − | + | *[http://www.IndependenceRock.org Photos and History of the Oregon Trail in Central Wyoming] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | *[http://www.IndependenceRock.org Photos and History of the Oregon Trail in Central Wyoming] | ||
| − | |||
{{TrailSystem}} | {{TrailSystem}} | ||
Latest revision as of 01:12, 18 November 2022
| Oregon National Historic Trail (Oregon Trail) | |
|---|---|
| IUCN Category V (Protected Landscape/Seascape) | |
| | |
| Location: | Missouri, Kansas, Nebraska, Wyoming, Idaho, Oregon |
| Established: | 1978 |
| Governing body: | National Park Service |
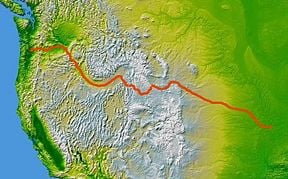
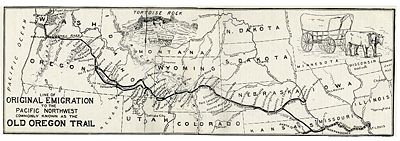
Pioneers traveled in wagons across the Oregon Trail, one of the main overland migration routes on the North American continent, in order to settle new parts of the United States of America during the nineteenth century. The Oregon Trail helped the United States implement its cultural goal of Manifest Destiny, that is, to expand the nation from the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean. The Oregon Trail spanned over half the continent as the wagon trail proceeded 2,170 miles west through territories and land later to become six U.S. states (Missouri, Kansas, Nebraska, Wyoming, Idaho, and Oregon). Between 1841 and 1869, the Oregon Trail was used by settlers migrating to the Pacific Northwest of what is now the United States. Once the first transcontinental railroad was completed in 1869, the use of this trail by long distance travelers diminished.
History
Astorians
The first well-mapped land route across what is now the United States was that taken by Lewis and Clark, from 1804 to 1805. They, in fact, believed that they had found a practical route to the west coast. However, the pass through the Rocky Mountains they took, Lolo Pass, turned out to be too difficult for wagon travel. In 1810, John Jacob Astor outfitted an expedition (known popularly as the Astor Expedition or Astorians) to find an overland supply route for establishing a fur trading post at the mouth of the Columbia River at Fort Astoria. Most of Astor's partners and all of his staff were former employees of the Northwest Company, known as Nor'Westers.
Fearing attack by Blackfeet, the expedition veered south of the Lewis and Clark route in what is now South Dakota and in the process passed through what is now Wyoming, and then down the Snake River to the Columbia River.
Members of the party, including Robert Stuart, one of the Nor'wester partners, returned back east after the American Fur Company staff there sold the fort to British Northwest Company staff, who took over the outpost in the War of 1812 via the Snake River. The party stumbled upon South Pass: A wide, low pass through the Rockies in Wyoming. The party continued via the Platte River. This turned out to be a practical wagon route, and Stuart's journals offered a meticulous account of it.[1]
Fort Astoria was returned to United States control at the end of the war. However, the British Hudson's Bay Company came to control the fur trade in the region, especially after its merger with the North West Company in 1821.
Great American Desert
Westward expansion did not begin immediately. Reports from expeditions in 1806, by Lieutenant Zebulon Pike and in 1819, by Major Stephen Long described the Great Plains as "unfit for human habitation" and "The Great American Desert." These descriptions were mainly based on the relative lack of timber and surface water. The images of sandy wastelands conjured up by terms like "desert" were tempered by the many reports of vast herds of bison. It was not until later that the Ogallala Aquifer would be discovered and used for irrigation, and railroads would allow lumber and farm products to be transported to distant markets. In the meantime, the Great Plains remained unattractive for general settlement, especially when compared to the fertile lands, big rivers, and seaports of Oregon.
The route of the Oregon Trail began to be scouted out as early as 1823, by fur traders and explorers. The trail began to be regularly used by fur traders, missionaries, and military expeditions during the 1830s. At the same time, small groups of individuals and the occasional family attempted to follow the trail. Not all succeeded in arriving at Fort Vancouver in Washington.
Elm Grove Expedition
On May 16, 1842, the first organized wagon train on the Oregon Trail set out from Elm Grove, Missouri, with more than 100 pioneers (members of the party later disagreed over the size of the party, one stating 160 adults and children were in the party, while another counted only 105). The party was led by Elijah White, appointed Indian Sub-Agent to Oregon, the first U.S. official in the region (never confirmed by Congress). Despite company policy to discourage U.S. emigration, John McLoughlin, Factor of the Hudson's Bay Company at Fort Vancouver, offered the American settlers food and farming equipment on credit, unwilling to watch able-bodied people starve.
Free land
The biggest driving force for settlement was the offer of free land.
In 1843, the settlers of the Willamette Valley, by a vote of 52 to 50, drafted a constitution that organized the land claim process in the state. Married couples were allowed to claim up to 640 acres (a "section" which is a square mile) at no cost and singles could claim 320 acres.[2]
In 1848, the United States formally declared what was left of the Oregon Country a U.S. territory, after it effectively partitioned in 1846. The Donation Land Act of 1850 superseded the earlier laws, but it did recognize the earlier claims. Settlers after 1850 could be granted half a section (320 acres) if married and a quarter section if single. A four-year residence and cultivation was required. In 1854, the land was no longer free.
Opening of the trail
In what was dubbed "The Great Migration of 1843," or the "Wagon Train of 1843,"[3] an estimated 800 immigrants, led by Marcus Whitman, arrived in the Willamette Valley. Hundreds of thousands more followed, especially after gold was discovered in California in 1848. The trail was still in use during the Civil War, but traffic declined after 1869, when the transcontinental railroad was completed. The trail continued to be used into the 1890s, and modern highways eventually paralleled large portions of it.
Other migration paths for early settlers prior to the establishment of the transcontinental railroads involved taking passage on a ship rounding Cape Horn of South America, or to the Isthmus (now Panama) between North and South America. There, an arduous mule trek through hazardous swamps and rain forests awaited the traveler. A ship was typically then taken to San Francisco, California.
Routes
The trail is marked by numerous cutoffs and shortcuts from Missouri to Oregon. The basic route follows river valleys. Beginning initially in Independence/Kansas City, the trail followed the Santa Fe Trail south of the Wakarusa River. After crossing The Hill at Lawrence, Kansas, it crossed the Kansas River near Topeka, Kansas, and angled to Nebraska, paralleling the Little Blue River until reaching the south side of the Platte River. It followed the Platte, North Platte, and Sweetwater Rivers to South Pass in the Rocky Mountains in Wyoming. From South Pass, the trail parallels the Snake River to the Columbia River before arriving at Oregon City, or taking the Barlow Road to the Willamette Valley and other destinations in what are now the states of Washington and Oregon.
U.S. Highway 26 follows the Oregon Trail for much of its length.
While the first few parties organized and departed from Elm Grove, the Oregon Trail's generally designated starting point was Independence or Westport, on the Missouri River. Several towns along the Missouri River had feeder trails, and make claims to being the starting point, including Weston, Missouri, Fort Leavenworth, Kansas, Atchison, Kansas, and St. Joseph, Missouri.
The Oregon Trail's designated termination point was Oregon City, which at that time was the proposed capital of Oregon Territory. However, many settlers branched off or stopped short of this goal and settled at convenient or promising locations along the trail. Commerce with pioneers going further west greatly assisted these early settlements in getting established and launched local micro-economies critical to these settlements' prosperity.
At many places along the trail, alternate routes called "cutoffs" were established either to shorten the trail or to get around difficult terrain. The Lander and Sublette cutoffs provided shorter routes through the mountains than the main route, bypassing Fort Bridger. In later years, the Salt Lake cutoff provided a route to Salt Lake City.
Numerous other trails followed the Oregon Trail for part of its length. These include the Mormon Trail from Illinois to Utah, and the California Trail to the gold fields of California.
Remnants of the trail in Idaho, Kansas, Oregon, and Wyoming, have been listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Landmarks
Many rock formations became famous landmarks that the Oregon Trail pioneers used to navigate and leave messages for pioneers following behind them. The first landmarks that the pioneers encountered were in western Nebraska, such as Courthouse and Jail Rocks, Chimney Rock, and Scotts Bluff. In Wyoming, names of pioneers can be seen carved into a landmark bluff called Register Cliff. One Wyoming landmark along the trail, Ayres Natural Bridge, is now a state park of the same name.
Travel equipment
The Oregon Trail was too long and arduous for the standard Conestoga wagons used in the Eastern United States for freight transport. These big wagons had a reputation for killing their oxen teams approximately two thirds along the trail and leaving their unfortunate owners stranded in desolate, isolated territory. The only solution was to abandon all belongings and traipse onward with the supplies and tools that could be carried or dragged. In one case in 1846, on the California Trail, the Donner Party, en route to California, was stranded in the Sierra Nevada in November and three members are reported to have resorted to cannibalism to survive.
This led to the rapid development of the prairie schooners. The wagon was approximately half the size of the big Conestogas and was manufactured in quantity. It was designed for the Oregon Trail's conditions and was a marvel of engineering for its time. The covers of the wagons were treated with linseed oil to keep out the rain. However, the covers eventually leaked anyway.
The recommended amount of food to take for an adult was:
- 150 pounds of flour
- 20 pounds of corn meal
- 50 pounds of bacon
- 40 pounds of sugar
- 10 pounds of coffee
- 15 pounds of dried fruit
- 5 pounds of salt
- 1/2 pound baking soda
- 2 pounds of tea
- 5 pounds of rice
- 15 pounds of beans
Statistics
Immigration to Oregon Territory increased vastly between 1840 and its peak in 1852. According to Oregon Trail Statistics, by William E. Hill, the figures rocketed from 13 in 1840, to 1,475 four years later, nearly doubled the following year, and hit 4,000 in 1847. Emigration declined considerably prior to 1850, when 6,000 people made the trek to Oregon. In 1851, the number dropped again (3,600) but sustained a huge comeback with 10,000 in 1852. (That same year some 60,000 people emigrated to Utah and California, a stand-alone record.) Another 13,500 people moved to Oregon in 1853-54, with 5,000 more making the trip as of 1859, the year of statehood.
In the 20 years from 1840-1859 some 52,000 emigrants moved to Oregon, but nearly five times that number opted for California or Utah.
Though the numbers appear significant—and they were, especially in context of the times—considerably more people chose to remain at home in the 31 states. Part of the explanation is attributed to scout Kit Carson, who reputedly said, "The cowards never started and the weak died on the way." According to some sources, one tenth of the emigrants perished on the way west. [4]
Notes
- ↑ Robert Stuart and Philip Ashton Rollins. The Discovery of the Oregon Trail Robert Stuart's Narratives of his Overland Trip Eastward From Astoria in 1812-13 (Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press 1995). ISBN 9780803292345
- ↑ End of the Oregon Trail, Claiming the Farm. Retrieved October 18, 2007.
- ↑ Oregon Pioneers, The Wagon Train of 1843. Retrieved October 18, 2007.
- ↑ Lloyd W. Coffman, Blazing a Wagon Trail to Oregon: A Weekly Chronicle of the Great Migration of 1843 (Enterprise, Or: Echo Books 1993). ISBN 9780963598400
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Crawford, Medorum. Journal of Medorem Crawford: An Account of His Trip Across the Plains with the Oregon Pioneers of 1842. Fairfield, Washington: Ye Galleon Press, 1967.
- Hewitt, Randall H. Notes by the Way: Memoranda of a Journey Across the Plains, from Dundee, Ill., to Olympia, W.T. May 7, to November 3, 1862. Seattle: Frank McCaffrey Publishers, 1955.
- Smedley, William. Across the Plains: An 1862 Journey from Omaha to Oregon. Boulder: Johnson Books, 1994. ISBN 9780585020785
- Ward, D. B. Across the Plains in 1853. Seattle: Shorey Bookstore, 1965. ISBN 9780846600619
- Williams, Joseph. Narrative of a Tour From the State of Indiana to the Oregon Territory in the Years 1841-2. Fairfield, Washington: Ye Galleon Press, 1977. ISBN 9780877701729
External links
All links retrieved November 17, 2022.
| |||||||||||

|
Pioneer History of Oregon (1806–1890) |
|---|---|
| Topics |
American Fur Company · Executive Committee · Ferries · Hudson's Bay Company · Oregon boundary dispute · Oregon Country · Oregon Lyceum · Oregon missionaries · Oregon Spectator · Oregon Territory · Oregon Trail · Oregon Treaty · Pacific Fur Company · Provisional Government |
| Events |
Treaty of 1818 · Russo-American Treaty · Willamette Cattle Company · Champoeg Meetings · Whitman massacre · Cayuse War · Donation Land Claim Act · Rogue River Wars · Oregon Constitutional Convention |
| Places |
Barlow Road · Champoeg · Fort Astoria · Fort Dalles · Fort Vancouver · Fort William · French Prairie · Methodist Mission · Oregon City · Oregon Institute · Whitman Mission |
| People |
George Abernethy · Ira L. Babcock · Sam Barlow · François Norbert Blanchet · Tabitha Brown · Abigail Scott Duniway · Philip Foster · Peter French · Joseph Gale · William Gilpin · David Hill · Jason Lee · Asa Lovejoy · John McLoughlin · Joseph Meek · Ezra Meeker · John Minto · Robert Newell · Joel Palmer · Sager orphans · Henry H. Spalding · Marcus Whitman · Narcissa Whitman · Ewing Young |
| Oregon History |
Native Peoples History · History to 1806 · Pioneer History · Modern History |
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.