Difference between revisions of "Natural satellite" - New World Encyclopedia
(imported latest version of article from Wikipedia) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | A '''natural satellite''' is an object that orbits a [[planet]] or other body larger than itself and which is not man-made. Such objects are often called '''moons'''. Technically, the term could also refer to a | + | {{Claimed}} |
| + | A '''natural satellite''' is an object that orbits a [[planet]] or other body larger than itself and which is not man-made. Such objects are often called '''moons'''. Technically, the term could also refer to a planet orbiting a [[star]], or even to a star orbiting a [[galactic center]], but these uses are rare. Instead, the term is normally used to identify non-artificial [[satellite]]s of planets, [[dwarf planet]]s, or [[minor planet]]s. | ||
There are 240 known moons within the [[Solar System]], including 163 orbiting the planets,<ref>[http://www.ifa.hawaii.edu/~sheppard/satellites/ List of natural satellites orbiting the planets.]</ref> 4 orbiting [[dwarf planet]]s, and dozens more orbiting [[small solar system bodies]]. Other stars and their planets also have natural satellites. | There are 240 known moons within the [[Solar System]], including 163 orbiting the planets,<ref>[http://www.ifa.hawaii.edu/~sheppard/satellites/ List of natural satellites orbiting the planets.]</ref> 4 orbiting [[dwarf planet]]s, and dozens more orbiting [[small solar system bodies]]. Other stars and their planets also have natural satellites. | ||
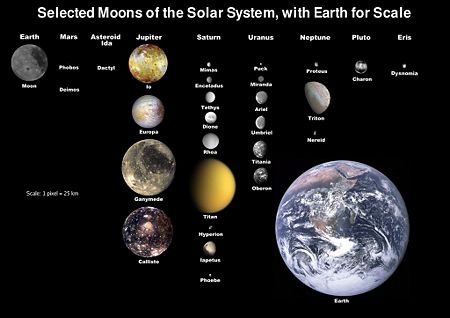
The large [[gas giant]]s have extensive systems of natural satellites, including half a dozen comparable in size to [[Earth]]'s moon. Of the inner planets, [[Mercury (planet)|Mercury]] and [[Venus]] have no moons at all; Earth has one large moon (the [[Moon]]); and [[Mars]] has two tiny moons, [[Phobos (moon)|Phobos]] and [[Deimos (moon)|Deimos]]. Among the [[dwarf planet]]s, [[Ceres (dwarf planet)|Ceres]] has no moons (though many objects in the asteroid belt do), [[Eris (dwarf planet)|Eris]] has one, [[Dysnomia (moon)|Dysnomia]], and [[Pluto]] has three known satellites, [[Nix (moon)|Nix]], [[Hydra (moon)|Hydra]], and a large companion called [[Charon (moon)|Charon]]. The Pluto-Charon system is unusual in that the [[barycenter|center of mass]] lies in open space between the two, a characteristic of a [[double planet]] system. | The large [[gas giant]]s have extensive systems of natural satellites, including half a dozen comparable in size to [[Earth]]'s moon. Of the inner planets, [[Mercury (planet)|Mercury]] and [[Venus]] have no moons at all; Earth has one large moon (the [[Moon]]); and [[Mars]] has two tiny moons, [[Phobos (moon)|Phobos]] and [[Deimos (moon)|Deimos]]. Among the [[dwarf planet]]s, [[Ceres (dwarf planet)|Ceres]] has no moons (though many objects in the asteroid belt do), [[Eris (dwarf planet)|Eris]] has one, [[Dysnomia (moon)|Dysnomia]], and [[Pluto]] has three known satellites, [[Nix (moon)|Nix]], [[Hydra (moon)|Hydra]], and a large companion called [[Charon (moon)|Charon]]. The Pluto-Charon system is unusual in that the [[barycenter|center of mass]] lies in open space between the two, a characteristic of a [[double planet]] system. | ||
| − | [[Image:Moons of solar system v7.jpg|thumb| | + | |
| + | [[Image:Moons of solar system v7.jpg|thumb|450px]] | ||
| + | |||
==Origin== | ==Origin== | ||
| Line 12: | Line 15: | ||
==Orbital characteristics== | ==Orbital characteristics== | ||
===Tidal locking=== | ===Tidal locking=== | ||
| + | |||
Most regular natural satellites in the solar system are [[tidal locking|tidally locked]] to their primaries, meaning that one side of the moon is always turned toward the planet. Exceptions include [[Saturn]]'s moon [[Hyperion (moon)|Hyperion]], which rotates chaotically because of a variety of external influences. | Most regular natural satellites in the solar system are [[tidal locking|tidally locked]] to their primaries, meaning that one side of the moon is always turned toward the planet. Exceptions include [[Saturn]]'s moon [[Hyperion (moon)|Hyperion]], which rotates chaotically because of a variety of external influences. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 21: | ||
===Satellites of satellites=== | ===Satellites of satellites=== | ||
| + | |||
No "moons of moons" (natural satellites that orbit the natural satellite of another body) are known. It is uncertain whether such objects can be stable in the long term. In most cases, the tidal effects of their primaries make such a system unstable; the gravity from other nearby objects (most notably the primary) would perturb the orbit of the moon's moon until it broke away or impacted its primary. In theory, a secondary satellite could exist in a primary satellite's [[Hill sphere]], outside of which it would be lost because of the greater gravitational pull of the planet (or other object) that the primary satellite orbits. For example, the Moon orbits the Earth because the Moon is 370,000 km from Earth, well within Earth's Hill sphere, which has a radius of 1.5 million km (0.01 AU or 235 Earth radii). If a Moon-sized object were to orbit the Earth outside its Hill sphere, it would soon be captured by the Sun and become a [[dwarf planet]] in a near-Earth orbit. | No "moons of moons" (natural satellites that orbit the natural satellite of another body) are known. It is uncertain whether such objects can be stable in the long term. In most cases, the tidal effects of their primaries make such a system unstable; the gravity from other nearby objects (most notably the primary) would perturb the orbit of the moon's moon until it broke away or impacted its primary. In theory, a secondary satellite could exist in a primary satellite's [[Hill sphere]], outside of which it would be lost because of the greater gravitational pull of the planet (or other object) that the primary satellite orbits. For example, the Moon orbits the Earth because the Moon is 370,000 km from Earth, well within Earth's Hill sphere, which has a radius of 1.5 million km (0.01 AU or 235 Earth radii). If a Moon-sized object were to orbit the Earth outside its Hill sphere, it would soon be captured by the Sun and become a [[dwarf planet]] in a near-Earth orbit. | ||
===Trojan satellites=== | ===Trojan satellites=== | ||
| + | |||
Two moons are known have small companions at their L<sub>4</sub> and L<sub>5</sub> [[Lagrangian point]]s, which are about sixty degrees ahead of and behind the body in its orbit. These companions are called [[Trojan moon]]s, because their positions are comparable to the positions of the [[Trojan asteroid]]s relative to [[Jupiter]]. Such objects are [[Telesto (moon)|Telesto]] and [[Calypso (moon)|Calypso]], which are the leading and following companions respectively of [[Tethys (moon)|Tethys]]; and [[Helene (moon)|Helene]] and [[Polydeuces (moon)|Polydeuces]], which are the leading and following companions of [[Dione (moon)|Dione]]. | Two moons are known have small companions at their L<sub>4</sub> and L<sub>5</sub> [[Lagrangian point]]s, which are about sixty degrees ahead of and behind the body in its orbit. These companions are called [[Trojan moon]]s, because their positions are comparable to the positions of the [[Trojan asteroid]]s relative to [[Jupiter]]. Such objects are [[Telesto (moon)|Telesto]] and [[Calypso (moon)|Calypso]], which are the leading and following companions respectively of [[Tethys (moon)|Tethys]]; and [[Helene (moon)|Helene]] and [[Polydeuces (moon)|Polydeuces]], which are the leading and following companions of [[Dione (moon)|Dione]]. | ||
===Asteroid satellites=== | ===Asteroid satellites=== | ||
| − | The discovery of [[243 Ida]]'s moon [[Dactyl (asteroid)|Dactyl]] in the early | + | |
| + | The discovery of [[243 Ida]]'s moon [[Dactyl (asteroid)|Dactyl]] in the early 1990s confirms that some [[asteroid]]s also have [[Asteroid moon|moon]]s. Some, like [[90 Antiope]], are double asteroids with two equal-sized components. The asteroid [[87 Sylvia]] has two moons. See asteroid moon for further information. | ||
==Natural satellites of the Solar System== | ==Natural satellites of the Solar System== | ||
| Line 33: | Line 40: | ||
<div style="font-size:90%;"> | <div style="font-size:90%;"> | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="white-space:nowrap;" | {| class="wikitable" style="white-space:nowrap;" | ||
| − | !rowspan="2" valign="bottom" style="font-size:90%;"| Mean diameter<br>(km) | + | !rowspan="2" valign="bottom" style="font-size:90%;"| Mean diameter<br/>(km) |
!colspan="6" style="background:#cae1ff; text-align:center;"| Satellites of planets | !colspan="6" style="background:#cae1ff; text-align:center;"| Satellites of planets | ||
!colspan="2" style="background:#ffdead; text-align:center;"| Dwarf planet satellites | !colspan="2" style="background:#ffdead; text-align:center;"| Dwarf planet satellites | ||
| − | !rowspan="2" width="10%" style="background:#b2e5cd;"| Satellites of<br>[[Small solar system body|SSSB]]s<ref>This column lists objects that are moons of [[small solar system bodies]], not small solar system bodies themselves.</ref> | + | !rowspan="2" width="10%" style="background:#b2e5cd;"| Satellites of<br/>[[Small solar system body|SSSB]]s<ref>This column lists objects that are moons of [[small solar system bodies]], not small solar system bodies themselves.</ref> |
| − | !rowspan="2" width="10%" style="background:#7ec0ee;"| Non-satellites<br>for comparison | + | !rowspan="2" width="10%" style="background:#7ec0ee;"| Non-satellites<br/>for comparison |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 217: | Line 224: | ||
| <!--Minor planets—> many | | <!--Minor planets—> many | ||
| <!--Other objects—> many | | <!--Other objects—> many | ||
| − | |} | + | |}</div> |
| − | </div> | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
==Terminology== | ==Terminology== | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | The first known natural satellite was the [[Moon]] (''luna'' in [[Latin]]). Until the discovery of the [[Galilean moons|Galilean satellites]] in 1610, however, there was no opportunity for referring to such objects as a class. [[Galileo]] chose to refer to his discoveries as ''Planetæ'' ("[[planet]]s"), but later discoverers chose other terms to distinguish them from the objects they orbited. |
| − | + | [[Christiaan Huygens]], the discoverer of [[Titan (moon)|Titan]], was the first to use the term ''moon'' for such objects, calling Titan ''Luna Saturni'' or ''Luna Saturnia'' – "[[Saturn]]'s moon" or "The Saturnian moon," because it stood in the same relation to Saturn as the Moon did to the [[Earth]]. | |
| − | The term ''satellite'' thus became the normal one for referring to an object orbiting a planet, as it avoided the ambiguity of "moon" | + | As additional moons of Saturn were discovered, however, this term was abandoned. [[Giovanni Domenico Cassini]] sometimes referred to his discoveries as ''planètes'' in French, but more often as ''satellites'', using a term derived from the Latin ''satelles'', meaning "guard," "attendant," or "companion," because the ''satellites'' accompanied their primary planet in their journey through the heavens. |
| + | |||
| + | The term ''satellite'' thus became the normal one for referring to an object orbiting a planet, as it avoided the ambiguity of "moon." In 1957, however, the launching of the artificial object [[Sputnik]] created a need for new terminology. The terms ''man-made satellite'' or ''artificial moon'' were very quickly abandoned in favor of the simpler ''satellite'', and as a consequence, the term has come to be linked primarily with artificial objects flown in space – including, sometimes, even those which are not in orbit around a planet. | ||
As a consequence of this shift in meaning, the term ''moon'', which had continued to be used in a generic sense in works of popular science and in fiction, has regained respectability and is now used interchangeably with ''satellite'', even in scientific articles. When it is necessary to avoid both the ambiguity of confusion with the Earth's moon on the one hand, and artificial satellites on the other, the term ''natural satellite'' (using "natural" in a sense opposed to "artificial") is used. | As a consequence of this shift in meaning, the term ''moon'', which had continued to be used in a generic sense in works of popular science and in fiction, has regained respectability and is now used interchangeably with ''satellite'', even in scientific articles. When it is necessary to avoid both the ambiguity of confusion with the Earth's moon on the one hand, and artificial satellites on the other, the term ''natural satellite'' (using "natural" in a sense opposed to "artificial") is used. | ||
| Line 242: | Line 249: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| + | |||
* [[Asteroid moon]] | * [[Asteroid moon]] | ||
* [[Co-orbital moon]] | * [[Co-orbital moon]] | ||
* [[Extrasolar moon]] | * [[Extrasolar moon]] | ||
* [[Inner satellite]] | * [[Inner satellite]] | ||
| − | |||
* [[List of natural satellites]] | * [[List of natural satellites]] | ||
* [[List of natural satellites by diameter]] | * [[List of natural satellites by diameter]] | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=====Natural satellites of planets and dwarf planets===== | =====Natural satellites of planets and dwarf planets===== | ||
* Earth's natural satellite, see [[Moon]] | * Earth's natural satellite, see [[Moon]] | ||
| Line 262: | Line 266: | ||
* [[Pluto's natural satellites]] | * [[Pluto's natural satellites]] | ||
* Eris' natural satellite, see [[Dysnomia (moon)|Dysnomia]] | * Eris' natural satellite, see [[Dysnomia (moon)|Dysnomia]] | ||
| + | |||
=====Natural satellites of small Solar System bodies===== | =====Natural satellites of small Solar System bodies===== | ||
* [[2003 EL61's natural satellites]] | * [[2003 EL61's natural satellites]] | ||
| − | ==Notes | + | == Notes == |
<!-- ---------------------------------------------------------- | <!-- ---------------------------------------------------------- | ||
See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Footnotes for a | See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Footnotes for a | ||
| Line 274: | Line 279: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <<This article needs at least 3 reliable references here, properly formatted.>> | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| Line 306: | Line 314: | ||
{{Footer_SolarSystem}} | {{Footer_SolarSystem}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Physical sciences]] |
| + | [[Category:Astronomy]] | ||
| − | + | {{credit|125853429}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 03:58, 27 April 2007
A natural satellite is an object that orbits a planet or other body larger than itself and which is not man-made. Such objects are often called moons. Technically, the term could also refer to a planet orbiting a star, or even to a star orbiting a galactic center, but these uses are rare. Instead, the term is normally used to identify non-artificial satellites of planets, dwarf planets, or minor planets.
There are 240 known moons within the Solar System, including 163 orbiting the planets,[1] 4 orbiting dwarf planets, and dozens more orbiting small solar system bodies. Other stars and their planets also have natural satellites.
The large gas giants have extensive systems of natural satellites, including half a dozen comparable in size to Earth's moon. Of the inner planets, Mercury and Venus have no moons at all; Earth has one large moon (the Moon); and Mars has two tiny moons, Phobos and Deimos. Among the dwarf planets, Ceres has no moons (though many objects in the asteroid belt do), Eris has one, Dysnomia, and Pluto has three known satellites, Nix, Hydra, and a large companion called Charon. The Pluto-Charon system is unusual in that the center of mass lies in open space between the two, a characteristic of a double planet system.
Origin
Natural satellites orbiting relatively close to the planet on prograde orbits (regular satellites) are generally believed to have been formed out of the same collapsing region of the protoplanetary disk that gave rise to its primary. In contrast, irregular satellites (generally orbiting on distant, inclined, eccentric and/or retrograde orbits) are thought to be captured asteroids possibly further fragmented by collisions. The Earth-Moon[2] and possibly Pluto-Charon systems[3] are exceptions among large bodies in that they are believed to have originated by the collision of two large proto-planetary objects (see the giant impact hypothesis). The material that would have been placed in orbit around the central body is predicted to have reaccreted to form one or more orbiting moons. As opposed to planetary-sized bodies, asteroid moons are thought to commonly form by this process.
Orbital characteristics
Tidal locking
Most regular natural satellites in the solar system are tidally locked to their primaries, meaning that one side of the moon is always turned toward the planet. Exceptions include Saturn's moon Hyperion, which rotates chaotically because of a variety of external influences.
In contrast, the outer moons of the gas giants (irregular satellites) are too far away to become 'locked'. For example, Jupiter's moon Himalia, Saturn's moon Phoebe and Neptune's Nereid have rotation period in the range of 10 hours compared with their orbital periods of hundreds of days.
Satellites of satellites
No "moons of moons" (natural satellites that orbit the natural satellite of another body) are known. It is uncertain whether such objects can be stable in the long term. In most cases, the tidal effects of their primaries make such a system unstable; the gravity from other nearby objects (most notably the primary) would perturb the orbit of the moon's moon until it broke away or impacted its primary. In theory, a secondary satellite could exist in a primary satellite's Hill sphere, outside of which it would be lost because of the greater gravitational pull of the planet (or other object) that the primary satellite orbits. For example, the Moon orbits the Earth because the Moon is 370,000 km from Earth, well within Earth's Hill sphere, which has a radius of 1.5 million km (0.01 AU or 235 Earth radii). If a Moon-sized object were to orbit the Earth outside its Hill sphere, it would soon be captured by the Sun and become a dwarf planet in a near-Earth orbit.
Trojan satellites
Two moons are known have small companions at their L4 and L5 Lagrangian points, which are about sixty degrees ahead of and behind the body in its orbit. These companions are called Trojan moons, because their positions are comparable to the positions of the Trojan asteroids relative to Jupiter. Such objects are Telesto and Calypso, which are the leading and following companions respectively of Tethys; and Helene and Polydeuces, which are the leading and following companions of Dione.
Asteroid satellites
The discovery of 243 Ida's moon Dactyl in the early 1990s confirms that some asteroids also have moons. Some, like 90 Antiope, are double asteroids with two equal-sized components. The asteroid 87 Sylvia has two moons. See asteroid moon for further information.
Natural satellites of the Solar System
The largest natural satellites in the Solar System (those bigger than about 3000 km across) are Earth's moon, Jupiter's Galilean moons (Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto), Saturn's moon Titan, and Neptune's captured moon Triton. For smaller moons see the articles on the appropriate planet. In addition to the moons of the various planets there are also over 80 known moons of the dwarf planets, asteroids and other small solar system bodies. Some studies estimate that up to 15% of all trans-Neptunian objects could have satellites.
The following is a comparative table classifying the moons of the solar system by diameter. The column on the right includes some notable planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, and Trans-Neptunian Objects for comparison.
| Mean diameter (km) |
Satellites of planets | Dwarf planet satellites | Satellites of SSSBs[4] |
Non-satellites for comparison | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Earth | Mars | Jupiter | Saturn | Uranus | Neptune | Pluto | Eris | |||
| 6000-7000 | Mars | |||||||||
| 5000-6000 | Ganymede | Titan | ||||||||
| 4000-5000 | Callisto | Mercury | ||||||||
| 3000-4000 | The Moon[5] | Io Europa |
||||||||
| 2000-3000 | Triton | Eris Pluto | ||||||||
| 1500-2000 | Rhea | Titania Oberon |
(136472) 2005 FY9 90377 Sedna | |||||||
| 1000-1500 | Iapetus Dione Tethys |
Umbriel Ariel |
Charon | (136108) 2003 EL61 90482 Orcus 50000 Quaoar | ||||||
| 500-1000 | Enceladus | Ceres 20000 Varuna 28978 Ixion 2 Pallas, 4 Vesta many more TNOs | ||||||||
| 250-500 | Mimas Hyperion |
Miranda | Proteus Nereid |
Dysnomia | S/2005 (2003 EL61) 1 S/2005 (79360) 1 |
10 Hygiea 511 Davida 704 Interamnia and many others | ||||
| 100-250 | Amalthea Himalia Thebe |
Phoebe Janus Epimetheus |
Sycorax Puck Portia |
Larissa Galatea Despina |
S/2005 (2003 EL61) 2 many more TNOs |
many | ||||
| 50-100 | Elara Pasiphaë |
Prometheus Pandora |
Caliban Juliet Belinda Cressida Rosalind Desdemona Bianca |
Thalassa Halimede Neso Naiad |
Nix[6] Hydra[6] |
Menoetius[7] S/2000 (90) 1 many more TNOs |
many | |||
| 10-50 | Phobos Deimos |
Carme Metis Sinope Lysithea Ananke Leda Adrastea |
Siarnaq Helene Albiorix Atlas Pan Telesto Paaliaq Calypso Ymir Kiviuq Tarvos Ijiraq Erriapo |
Ophelia Cordelia Setebos Prospero Perdita Mab Stephano Cupid Francisco Ferdinand Margaret Trinculo |
Sao Laomedeia Psamathe |
Linus[8] S/2000 (762) 1 S/2002 (121) 1 Romulus[9] Petit-Prince[10] S/2003 (283) 1 S/2004 (1313) 1 and many TNOs |
many | |||
| less than 10 | at least 47 | at least 21 | many | many | ||||||
Terminology
The first known natural satellite was the Moon (luna in Latin). Until the discovery of the Galilean satellites in 1610, however, there was no opportunity for referring to such objects as a class. Galileo chose to refer to his discoveries as Planetæ ("planets"), but later discoverers chose other terms to distinguish them from the objects they orbited.
Christiaan Huygens, the discoverer of Titan, was the first to use the term moon for such objects, calling Titan Luna Saturni or Luna Saturnia – "Saturn's moon" or "The Saturnian moon," because it stood in the same relation to Saturn as the Moon did to the Earth.
As additional moons of Saturn were discovered, however, this term was abandoned. Giovanni Domenico Cassini sometimes referred to his discoveries as planètes in French, but more often as satellites, using a term derived from the Latin satelles, meaning "guard," "attendant," or "companion," because the satellites accompanied their primary planet in their journey through the heavens.
The term satellite thus became the normal one for referring to an object orbiting a planet, as it avoided the ambiguity of "moon." In 1957, however, the launching of the artificial object Sputnik created a need for new terminology. The terms man-made satellite or artificial moon were very quickly abandoned in favor of the simpler satellite, and as a consequence, the term has come to be linked primarily with artificial objects flown in space – including, sometimes, even those which are not in orbit around a planet.
As a consequence of this shift in meaning, the term moon, which had continued to be used in a generic sense in works of popular science and in fiction, has regained respectability and is now used interchangeably with satellite, even in scientific articles. When it is necessary to avoid both the ambiguity of confusion with the Earth's moon on the one hand, and artificial satellites on the other, the term natural satellite (using "natural" in a sense opposed to "artificial") is used.
The definition of a moon

There has been some debate about the precise definition of a moon. This debate has been caused by the presence of orbital systems where the difference in mass between the larger body and its satellite are not as pronounced as in more typical systems. Two examples are the Pluto-Charon system and the Earth-Moon System. The presence of these systems has caused a debate about where to precisely draw the line between a double body system, and a main body-satellite system. The most common definition rests upon whether the barycentre is below the surface of the larger body, though this is unofficial and somewhat arbitrary. At the other end of the spectrum there are many ice/rock clumps that form ring systems around the Solar System's gas giants, and there is no set point to define when one of these clumps is large enough to be classified as a moon. The term "moonlet" is sometimes used to refer to extremely small objects in orbit around a larger body, but again there is no official definition.
See also
- Asteroid moon
- Co-orbital moon
- Extrasolar moon
- Inner satellite
- List of natural satellites
- List of natural satellites by diameter
Natural satellites of planets and dwarf planets
- Earth's natural satellite, see Moon
- Mars' natural satellites
- Jupiter's natural satellites
- Saturn's natural satellites
- Uranus' natural satellites
- Neptune's natural satellites
- Pluto's natural satellites
- Eris' natural satellite, see Dysnomia
Natural satellites of small Solar System bodies
- 2003 EL61's natural satellites
Notes
- ↑ List of natural satellites orbiting the planets.
- ↑ R. Canup and E. Asphaug (2001). Origin of the Moon in a giant impact near the end of the Earth's formation. Nature 412: 708-712.
- ↑ S. Stern, H. Weaver, A. Steffl, M. Mutchler, W. Merline, M. Buie, E. Young, L. Young, and J. Spencer (2006). A giant impact origin for Pluto’s small moons and satellite multiplicity in the Kuiper belt. Nature 439: 946-949.
- ↑ This column lists objects that are moons of small solar system bodies, not small solar system bodies themselves.
- ↑ Sometimes referred to as "Luna".
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Diameters of the new Plutonian satellites are still very poorly known, but they are estimated to lie between 44 and 130 km.
- ↑ (617) Patroclus I Menoetius
- ↑ (22) Kalliope I Linus
- ↑ (87) Sylvia I Romulus
- ↑ (45) Eugenia I Petit-Prince
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
<<This article needs at least 3 reliable references here, properly formatted.>>
External links
Jupiter's moons
- Data on Jupiter's satellites
- Jupiter's new moons (discovered in 2000)
- Jupiter's new moons (discovered in 2002)
- Jupiter's new moons (discovered in 2003)
Saturn's moons
Neptune's moons
All moons
- Natural Satellite Physical Parameters (JPL-NASA, with refs)
- Moons of the Solar System (The Planetary Society)
- Scott Sheppard's page
- Major moons in order from the Sun
- JPL's Solar System Dynamics page
- Moon of an Object? First Photo of Satellite Beyond the Solar System
- USGS list of named moons
- Upper size limit for moons explained
- Asteroids with Satellites
| Natural satellites of the Solar System | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| The Sun · Mercury · Venus · Earth · Mars · Ceres · Jupiter · Saturn · Uranus · Neptune · Pluto · Eris | |||
| Planets · Dwarf planets · Moons: Terran · Martian · Asteroidal · Jovian · Saturnian · Uranian · Neptunian · Plutonian · Eridian | |||
| SSSBs: Meteoroids · Asteroids (Asteroid belt) · Centaurs · TNOs (Kuiper belt/Scattered disc) · Comets (Oort cloud) | |||
| See also astronomical objects and the solar system's list of objects, sorted by radius or mass. |
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.