Difference between revisions of "Timbuktu" - New World Encyclopedia
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
[http://www.isesco.org.ma/Capitales2006/Tombouktu/ENG/P1.htm] | [http://www.isesco.org.ma/Capitales2006/Tombouktu/ENG/P1.htm] | ||
| − | Timbuktu is also remembered for its long-lasting contribution to Islamic and world civilization is scholarship.<ref>http://news.yahoo.com/s/nm/20061110/sc_nm/mali_manuscripts_dc_1</ref> By the fourteenth century, important books were written and copied in Timbuktu, establishing the city as the | + | Timbuktu is also remembered for its long-lasting contribution to Islamic and world civilization is scholarship.<ref>http://news.yahoo.com/s/nm/20061110/sc_nm/mali_manuscripts_dc_1</ref> By the fourteenth century, important books were written and copied in Timbuktu, establishing the city as the center of a significant written tradition in Africa.<ref>http://news.yahoo.com/s/nm/20061110/sc_nm/mali_manuscripts_dc_1</ref> |
In contemporary times, Timbuktu is populated by [[Songhay]], [[Tuareg]], [[Fula people|Fulani]], and [[Mandé]] people. and is located about 15 km north of the [[River Niger]]. It is home to the prestigious [[Qur'an]]ic [[Sankore University]] and other [[madrasas]], reminiscent of Timbuktu's heritage as an intellectual and spiritual capital of Islamic West Africa in the 15th and 16th centuries. | In contemporary times, Timbuktu is populated by [[Songhay]], [[Tuareg]], [[Fula people|Fulani]], and [[Mandé]] people. and is located about 15 km north of the [[River Niger]]. It is home to the prestigious [[Qur'an]]ic [[Sankore University]] and other [[madrasas]], reminiscent of Timbuktu's heritage as an intellectual and spiritual capital of Islamic West Africa in the 15th and 16th centuries. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
==Rise of Timbuktu== | ==Rise of Timbuktu== | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Islam}} |
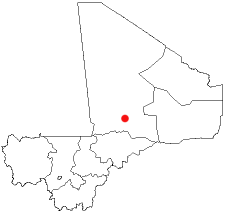
[[Image:ML-Tombouctou.png|right|225px|Location of Timbuktu in Mali]] | [[Image:ML-Tombouctou.png|right|225px|Location of Timbuktu in Mali]] | ||
===Origins=== | ===Origins=== | ||
| − | Timbuktu was founded almost 800 centuries ago along the caravan routes that connected the southern coast of West Africa with the trans-Saharan trade. While conveniently located for trade, the geographic location of | + | Timbuktu was founded almost 800 centuries ago along the caravan routes that connected the southern coast of West Africa with the trans-Saharan trade. While conveniently located for trade, the geographic location of Timbuktu left it vulnerable to attacks from Tuareg raiders from the Sahara. The constant attacks and threats of invasion prevented Timbuktu from growing into a political center,hinderances that were not shared by neighboring [[Gao]]. While Gao grew into a political capital, Timbuktu was never considered safe enough to establish it as stable community. |
Over the long history of Timbuktu the geographical weakness of the city led it to be conquered by the Mali Empire, the Songhay Empire, the Tuareg, and the Fulani before being subdued by French colonial invaders in 1893. | Over the long history of Timbuktu the geographical weakness of the city led it to be conquered by the Mali Empire, the Songhay Empire, the Tuareg, and the Fulani before being subdued by French colonial invaders in 1893. | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
[[Image:Medersa Sankore.jpg|thumb|right|300px|[[Sankore Madrasah]]]] | [[Image:Medersa Sankore.jpg|thumb|right|300px|[[Sankore Madrasah]]]] | ||
| − | The most prominent of the Islamic institutions of Timbuktu, the University of Sankore, was established in 1581 C.E. Considered the center of Islamic study in Timbuktu, it was built on the remains of an older site, which archaeologists date to the 13th or 14th century. It exhibited a dramatically different structure than contemporary European universities and consisted of multiple, entirely independent colleges , as opposed to the European idea of a single college at a university. Students at Sankore dedicated themselves to individualized study under one single teacher, and often attended courses in the open courtyards of mosque complexes or private residences. Due to the religious affiliation of the university, most | + | The most prominent of the Islamic institutions of Timbuktu, the University of Sankore, was established in 1581 C.E. Considered the center of Islamic study in Timbuktu, it was built on the remains of an older site, which archaeologists date to the 13th or 14th century. It exhibited a dramatically different structure than contemporary European universities and consisted of multiple, entirely independent colleges , as opposed to the European idea of a single college at a university. Students at Sankore dedicated themselves to individualized study under one single teacher, and often attended courses in the open courtyards of mosque complexes or private residences. Due to the religious affiliation of the university, most instruction focused on teaching the [[Qur'an]], although broader instruction in fields such as logic, astronomy, and history also took place. As part of their education, students were expected to write books based on their research, the profits of which were second only to the gold-salt trade. The most famous scholar of Sanhore was [[Ahmed Baba]] &ndash, a highly distinguished historian frequently quoted in the [[Tarikh-es-Sudan]] and other works. |
=====The Libraries of Timbuktu===== | =====The Libraries of Timbuktu===== | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
[[Image:Timbuktu map 1855.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Map from 1855]] | [[Image:Timbuktu map 1855.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Map from 1855]] | ||
| − | The historical importance of Timbuktu has preserved for posterity through a system of libraries that cross the city and West Africa in general. Among the libraries that play a vital role in preserving the history of Timbuktu are: | + | The historical importance of Timbuktu has preserved for posterity through a system of libraries that cross the city and West Africa in general. Among the libraries that play a vital role in preserving the history of Timbuktu are: Institute des Hautes Etudes et de Recherche Islamique — Ahmed Baba, Timbuktu, Mamma Haidara Library, Fondo Kati Library, Al-Wangari Library, and Mohamed Tahar Library. Considered part of the [[African Ink Road]] that connects West Africa to North Africa and East Africa, these libraries are just a few of the 120 libraries that previously existed in Timbuktu and the surrounding areas. |
| − | The manuscripts housed in Timbuktu libraries document all aspects of daily life and cover all aspects of human endeavor. As a historical source, the Timbuktu manuscripts have proven | + | The manuscripts housed in Timbuktu libraries document all aspects of daily life and cover all aspects of human endeavor. As a historical source, the Timbuktu manuscripts have proven particularly valuable due to their detailed historical documents. Over one million objects have been preserved through the library system, most of which are found in [[Sokoto]], [[Nigeria]]. The complete extent of the collections is not known, however, as many documents and artifacts were hidden after colonialists removed complete libraries to [[Paris]], [[London]] and other parts of Europe. Many of the hidden libraries have not been discovered to this day. |
===Timbuktu as a Mythical City=== | ===Timbuktu as a Mythical City=== | ||
| − | [[Image:Tombouctou sign.jpg|thumb|200px|left|A sign in the [[Sahara]] about the distance to Timbuktu in [[Caravan ( | + | [[Image:Tombouctou sign.jpg|thumb|200px|left|A sign in the [[Sahara]] about the distance to Timbuktu in [[Caravan (travelers)|caravan]]]] |
| − | Tales of Timbuktu's fabulous wealth helped prompt European [[exploration]] of the west coast of Africa. Exploration of Timbuktu was often motivated by | + | Tales of Timbuktu's fabulous wealth helped prompt European [[exploration]] of the west coast of Africa. Exploration of Timbuktu was often motivated by outrageous tales of wealth that glossed over the reality of the city and cemented its reputation as a mythical land of wealth. Among the earliest descriptions of Timbuktu are those of [[Leo Africanus]] and [[Shabeni]]. |
=====Leo Africanus ===== | =====Leo Africanus ===== | ||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
==Decline of Timbuktu== | ==Decline of Timbuktu== | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | The decline of Timbuktu began began with the influx of Portuguese traders, who undercut the importance of Timbuktu on the Niger River by using the mouth of the river as a trading location. The destruction of Timbuktu was cemented with the invasion of [[Morisco]] mercenaries armed with European-style guns in the service of the [[Morocco|Moroccan]] sultan in 1591. The military invasion was the final blow to an already deteriorated nation. | |
| − | [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Timbuktu today== | |
| − | |||
[[Image:Timbuktu Caille House Street Scene.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Street Scene - Caille House]] | [[Image:Timbuktu Caille House Street Scene.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Street Scene - Caille House]] | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:Timbuktu Street Scene 1.jpg|thumb|right|240px|Street Scene - Children]] | [[Image:Timbuktu Street Scene 1.jpg|thumb|right|240px|Street Scene - Children]] | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:Street Timbuktu Mali Africa 2000.jpg|thumb|right|240px|A typical street scene at Timbuktu, Mali, with omnipresent bread-baking ovens]] | [[Image:Street Timbuktu Mali Africa 2000.jpg|thumb|right|240px|A typical street scene at Timbuktu, Mali, with omnipresent bread-baking ovens]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | Timbuktu is a | + | Despite its history of auspicious wealth, modern day Timbuktu is a deeply impoverished city. While the city offers few economic attractions it still attracts visitors based on its mythical status and the fabled existence. Tourists to Timbuktu wishing to explore the truth behind the myth can reach the city through its international airport. However, he image of the city as mysterious or mythical has survived to the present day in other countries: a poll among young [[Great Britain|Briton]]s in 2006 found 34% did not believe the town existed, while the other 66% considered it "a mythical place".<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/6062360.stm "Search on for Timbuktu's twin"] BBC News, 18 October 2006. Retrieved 28 March 2007</ref> |
| − | Timbuktu | + | Timbuktu is a [[UNESCO]] [[World Heritage Site]], listed since 1988. In 1990, it was added to the list of [[List of World Heritage Sites in danger|world heritage sites in danger]] due to the threat of [[desert]] sands and desertification. A program was set up to preserve the historical sites of Timbuktu. In 2005, it was taken off the list of endangered sites. |
| − | + | Timbuktu is currently (beginning 2007) a candidate in a competition to choose the [[New Seven Wonders of the World]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.spiegel.de/international/0,1518,452293,00.html |title=From Machu Picchu to Timbuktu — The Search for the World's Seven New Wonders |accessdate=2006-12-29 |format= |work=[[Der Spiegel]] }}</ref> | |
| + | |||
| + | Timbuktu was one of the major stops during [[Henry Louis Gates]]' [[Public Broadcasting Service|PBS]] special "Wonders of the African World". Gates visited with Abdel Kadir Haidara, curator of the [[Mamma Haidara Library]] together with [[Ali Ould Sidi]] from the [[Cultural Mission of Mali]]. It is thanks to Gates that an [[Andrew W. Mellon Foundation|Andrew Mellon Foundation grant]] was obtained to finance the construction of the library's facilities, later inspiring the work of the [[Timbuktu Manuscripts Project]]. The town is home to an institute dedicated to preserving historic documents from the region, in addition to two small museums (one of them the house in which the great German explorer Heinrich Barth spent six months in 1853-54), and the symbolic ''Flame of Peace'' monument commemorating the reconciliation between the Tuareg and the government of Mali. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The city continues to face political threats, however, and in the 1990s Timbuktu came under attack from Tuareg people hoping to build their own state. The [[Tuareg Rebellion]] was symbolically ended with a burning of [[weapon]]s in the town in [[1996]]. | ||
===Attractions=== | ===Attractions=== | ||
| − | Timbuktu's | + | |
| + | Timbuktu's main attractions are the intellectual and religious centers that have existed in the cities for centuries. The most prominent of the Islamic sites are the proliferate mud [[mosque]]s, which are said to have inspired [[Antoni Gaudí]]. These include: | ||
| + | |||
* [[Djinguereber Mosque]], built in 1327 by [[El Saheli]] | * [[Djinguereber Mosque]], built in 1327 by [[El Saheli]] | ||
* ''Sankore Mosque'', also known as [[Sankore University]], built in the early [[fifteenth century]] | * ''Sankore Mosque'', also known as [[Sankore University]], built in the early [[fifteenth century]] | ||
| Line 120: | Line 123: | ||
===Language=== | ===Language=== | ||
| − | The main language of Timbuktu is | + | |
| + | The main language of Timbuktu is [[Koyra Chiini language|Koyra Chiini]], a variety of [[Songhay languages|Songhay]] spoken by over 80% of residents. Some smaller population groups speak [[Hassaniya]] Arabic and [[Tuareg languages|Tamashek]]. | ||
===Famous people connected with Timbuktu=== | ===Famous people connected with Timbuktu=== | ||
| + | |||
* [[Ali Farka Toure]] (1939–2006) Born in Timbuktu.<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/africa/4782176.stm "African star Ali Farka Toure dies"] BBC News, 7 March 2006. Retrieved 7 March 2006</ref> | * [[Ali Farka Toure]] (1939–2006) Born in Timbuktu.<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/africa/4782176.stm "African star Ali Farka Toure dies"] BBC News, 7 March 2006. Retrieved 7 March 2006</ref> | ||
| − | * [[Heinrich Barth]] (1821-1865) German | + | * [[Heinrich Barth]] (1821-1865) German traveler and scholar and the first European to investigate into African history |
* [[Peter de Neumann|Bernard Peter de Neumann, GM]] (1917–1972) "The Man From Timbuctoo".<ref>The Daily Express, 10 February 1943. Front Page: ''The Man From Timbuctoo''</ref> Held prisoner of war there along with other members of the crew of the ''Criton'' during 1941-1942. | * [[Peter de Neumann|Bernard Peter de Neumann, GM]] (1917–1972) "The Man From Timbuctoo".<ref>The Daily Express, 10 February 1943. Front Page: ''The Man From Timbuctoo''</ref> Held prisoner of war there along with other members of the crew of the ''Criton'' during 1941-1942. | ||
===Sister cities=== | ===Sister cities=== | ||
| + | |||
* {{flagicon|Germany}} - [[Chemnitz]], [[Germany]] | * {{flagicon|Germany}} - [[Chemnitz]], [[Germany]] | ||
* {{flagicon|Wales}} - Y Gelli Gandryll ([[Hay-on-Wye]]), [[Wales]] | * {{flagicon|Wales}} - Y Gelli Gandryll ([[Hay-on-Wye]]), [[Wales]] | ||
| Line 143: | Line 149: | ||
* Auster, Paul. 1999. ''Timbuktu: a novel''. New York: Henry Holt. ISBN 0805054073 and ISBN 9780805054071 | * Auster, Paul. 1999. ''Timbuktu: a novel''. New York: Henry Holt. ISBN 0805054073 and ISBN 9780805054071 | ||
* Smith, David N. 1983. ''Timbuktu''. New York: Dodd, Mead. ISBN 0396082327 and ISBN 9780396082323 | * Smith, David N. 1983. ''Timbuktu''. New York: Dodd, Mead. ISBN 0396082327 and ISBN 9780396082323 | ||
| − | * Jenkins, Mark. 1997. To Timbuktu. New York: W. Morrow. ISBN 0688115853 and ISBN 9780688115852 | + | * Jenkins, Mark. 1997. ''To Timbuktu''. New York: W. Morrow. ISBN 0688115853 and ISBN 9780688115852 |
| + | * Davidson, Basil. 1998. ''West Africa Before the Colonial Era: A History to 1850''. Essex: Pearson Education Limited. ISBN 0582318521 and ISBN 9780582318526 | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| Line 152: | Line 159: | ||
* Rashidi, Runoko. [http://www.cwo.com/~lucumi/timbuktu.html The Great University of Sankore at Timbuktu a Brief Note]. ''The Global African Presence''. Retrieved June 21, 2007. | * Rashidi, Runoko. [http://www.cwo.com/~lucumi/timbuktu.html The Great University of Sankore at Timbuktu a Brief Note]. ''The Global African Presence''. Retrieved June 21, 2007. | ||
* [http://www.sum.uio.no/research/mali/timbuktu/libraries.html The Timbuktu Libraries]. ''Libraries of Timbuktu''. Retrieved June 21, 2007. | * [http://www.sum.uio.no/research/mali/timbuktu/libraries.html The Timbuktu Libraries]. ''Libraries of Timbuktu''. Retrieved June 21, 2007. | ||
| − | * Pearce, Justin. October 3, 2005. [http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/4304922.stm Saving Mali's written treasures]. ''British Broadcasting | + | * Pearce, Justin. October 3, 2005. [http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/4304922.stm Saving Mali's written treasures]. ''British Broadcasting Corporation''. Retrieved June 21, 2007. |
* [http://www.loc.gov/exhibits/mali/ Ancient Manuscripts from the Desert Libraries of Timbuktu]. ''Library of Congress''. Retrieved June 21, 2007. | * [http://www.loc.gov/exhibits/mali/ Ancient Manuscripts from the Desert Libraries of Timbuktu]. ''Library of Congress''. Retrieved June 21, 2007. | ||
* Hammer, Joshua. [http://www.smithsonianmagazine.org/issues/2006/december/timbuktu.php The Treasures of Timbuktu]. ''Smithsonian''. Retrieved June 21, 2007. | * Hammer, Joshua. [http://www.smithsonianmagazine.org/issues/2006/december/timbuktu.php The Treasures of Timbuktu]. ''Smithsonian''. Retrieved June 21, 2007. | ||
Revision as of 21:36, 2 July 2007
| Timbuktu* | |
|---|---|
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |

| |
| State Party | |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | ii, iv, v |
| Reference | 119 |
| Region** | Africa |
| Inscription history | |
| Inscription | 1988 (12th Session) |
| Endangered | 1990-2005 |
| * Name as inscribed on World Heritage List. ** Region as classified by UNESCO. | |
Timbuktu (Archaic English: Timbuctoo; Koyra Chiini: Tumbutu; French: Tombouctou) is a city in Tombouctou Region of modern day Mali that was founded over 800 years ago. Geographically, the location of Timbuktu served as a convenient meeting place for neighboring African civilizations, nomadic Berber and Arab peoples from the north. This led to the establishment of Timbuktu as a premier trading center for West Africa that often attracted European traders. It was important historically (and still is today) as an entrepot for rock-salt from Taoudenni. Due to the extensive trade through Timbuktu the city acquired a mythical status, especially in Europe. In the West it was for long a metaphor for exotic, distant lands, e.g. "from here to Timbuktu." The French orientalist René Basset propagated the idea that the mythical status of Timbuktu garnered the name for the city , as in the Berber languages "buqt" means ""far away", so "Tin-Buqt(u)" means a place almost at the other end of the world ( in this case the Sahara). [1]
Timbuktu is also remembered for its long-lasting contribution to Islamic and world civilization is scholarship.[1] By the fourteenth century, important books were written and copied in Timbuktu, establishing the city as the center of a significant written tradition in Africa.[2]
In contemporary times, Timbuktu is populated by Songhay, Tuareg, Fulani, and Mandé people. and is located about 15 km north of the River Niger. It is home to the prestigious Qur'anic Sankore University and other madrasas, reminiscent of Timbuktu's heritage as an intellectual and spiritual capital of Islamic West Africa in the 15th and 16th centuries.
Timbuktu's physical history is being threatened by a process called desertification, where the harsh winds off the Sahara drive sand against historical monuments. [3] Its three great mosques, Djingareyber, Sankore and Sidi Yahya, recall Timbuktu's golden age and are most threatened by the process. Although continuously restored, the sands continue to wreck a devastating effect and effects to maintain the monuments have proven ineffectual.
Rise of Timbuktu
| Part of the series on History of Islam |
| Beliefs and practices |
|
Oneness of God |
| Major figures |
|
Muhammad |
| Texts & law |
|
Qur'an · Hadith · Sharia |
| Branches of Islam |
| Sociopolitical aspects |
|
Art · Architecture |
| See also |
|
Vocabulary of Islam |
Origins
Timbuktu was founded almost 800 centuries ago along the caravan routes that connected the southern coast of West Africa with the trans-Saharan trade. While conveniently located for trade, the geographic location of Timbuktu left it vulnerable to attacks from Tuareg raiders from the Sahara. The constant attacks and threats of invasion prevented Timbuktu from growing into a political center,hinderances that were not shared by neighboring Gao. While Gao grew into a political capital, Timbuktu was never considered safe enough to establish it as stable community.
Over the long history of Timbuktu the geographical weakness of the city led it to be conquered by the Mali Empire, the Songhay Empire, the Tuareg, and the Fulani before being subdued by French colonial invaders in 1893.
Timbuktu as a Trading Center
Like its predecessor, Tiraqqa (a neighboring trading city of the Wangara) , Timbuktu became immensely wealthy due to its role in the traffic in gold, ivory, slaves, salt trans-Saharan trade. These goods originated mainly from the Tuareg, Mandé and Fulani merchants in the north who used Timbuktu as a stepping stone to connect to the southern coast of West Africa. After stopping in Timbuktu and trading with other merchants, traders would bring transfer their Saharan goods to boats on the Niger River. Eventually these boats were destined for larger ports, including major coastal trading ports where European traders purchased goods to take back to their home countries.
Timbuktu's prime trade position made it a obvious target for West African empires looking to expand their wealth or control over the trade routes. While Timbuktu's history is punctuated by repeated attacks, and it often fell victim to conquering armies, it maintained its position as a trading center despite the political entity that held it in thrall. For example, it retained its status as a key city in the Ghana Empire, the Mali Empire from 1324, and the Songhai Empire from 1468. Under Songhai rule Timbuktu dramatically increased its wealth, and set itself on the road towards reaching its height in the 16th century. The eventual decline of the city, while due in some part to its military losses at the hands of a Moroccan adventurers in 1591, can be primarily traced to the influx of Portuguese goods into the West African trading system. By choosing to send goods to the Niger River's mouth instead of up the river, Portuguese traders bypassed Timbuktu and caused the economic authority of the city to deteriorate.
Timbuktu as an Intellectual Center
Timbuktu, while a prominent trading center, also gained recognition in the early 15th century as a center for intellectual and religious study. The physical history of the intellectual past of Timbuktu is found in the many mosques and other Islamic institutions that can be found throughout the city. The most famous of these is the Sankore mosque, also known as the University of Sankore. While Islam was the prominent religion in the city, the majority of the rural population were non-Muslim traditionalists .
University of Sankore
The most prominent of the Islamic institutions of Timbuktu, the University of Sankore, was established in 1581 C.E. Considered the center of Islamic study in Timbuktu, it was built on the remains of an older site, which archaeologists date to the 13th or 14th century. It exhibited a dramatically different structure than contemporary European universities and consisted of multiple, entirely independent colleges , as opposed to the European idea of a single college at a university. Students at Sankore dedicated themselves to individualized study under one single teacher, and often attended courses in the open courtyards of mosque complexes or private residences. Due to the religious affiliation of the university, most instruction focused on teaching the Qur'an, although broader instruction in fields such as logic, astronomy, and history also took place. As part of their education, students were expected to write books based on their research, the profits of which were second only to the gold-salt trade. The most famous scholar of Sanhore was Ahmed Baba &ndash, a highly distinguished historian frequently quoted in the Tarikh-es-Sudan and other works.
The Libraries of Timbuktu
The historical importance of Timbuktu has preserved for posterity through a system of libraries that cross the city and West Africa in general. Among the libraries that play a vital role in preserving the history of Timbuktu are: Institute des Hautes Etudes et de Recherche Islamique — Ahmed Baba, Timbuktu, Mamma Haidara Library, Fondo Kati Library, Al-Wangari Library, and Mohamed Tahar Library. Considered part of the African Ink Road that connects West Africa to North Africa and East Africa, these libraries are just a few of the 120 libraries that previously existed in Timbuktu and the surrounding areas.
The manuscripts housed in Timbuktu libraries document all aspects of daily life and cover all aspects of human endeavor. As a historical source, the Timbuktu manuscripts have proven particularly valuable due to their detailed historical documents. Over one million objects have been preserved through the library system, most of which are found in Sokoto, Nigeria. The complete extent of the collections is not known, however, as many documents and artifacts were hidden after colonialists removed complete libraries to Paris, London and other parts of Europe. Many of the hidden libraries have not been discovered to this day.
Timbuktu as a Mythical City
Tales of Timbuktu's fabulous wealth helped prompt European exploration of the west coast of Africa. Exploration of Timbuktu was often motivated by outrageous tales of wealth that glossed over the reality of the city and cemented its reputation as a mythical land of wealth. Among the earliest descriptions of Timbuktu are those of Leo Africanus and Shabeni.
Leo Africanus
Leo Africanus is possibly the most famous author to describe life in the fabled city of Timbuktu. He first came to Timbuktu in 1512, while the Songhai Empire was at its peak and exercised control over the city.
He described the wealth of the city by saying:
The rich king of Tombuto hath many plates and sceptres of gold, some whereof weigh 1300 pounds. ... He hath always 3000 horsemen ... (and) a great store of doctors, judges, priests, and other learned men, that are bountifully maintained at the king's expense. [4]
Shabeni
Shabeni visited Timbuktu as a 14 year old around 1787 with his father. Growing up to be a merchant in Tetuan, he was captured and led out his adult life in England.
A version of his story is related by James Grey Jackson in his book An Account of Timbuctoo and Hausa, 1820:
On the east side of the city of Timbuctoo, there is a large forest, in which are a great many elephants. The timber here is very large. The trees on the outside of the forest are remarkable...they are of such a size that the largest cannot be girded by two men. They bear a kind of berry about the size of a walnut, in clusters consisting of from ten to twenty berries. Shabeeny cannot say what is the extent of this forest, but it is very large.
Decline of Timbuktu
The decline of Timbuktu began began with the influx of Portuguese traders, who undercut the importance of Timbuktu on the Niger River by using the mouth of the river as a trading location. The destruction of Timbuktu was cemented with the invasion of Morisco mercenaries armed with European-style guns in the service of the Moroccan sultan in 1591. The military invasion was the final blow to an already deteriorated nation.
Timbuktu today
Despite its history of auspicious wealth, modern day Timbuktu is a deeply impoverished city. While the city offers few economic attractions it still attracts visitors based on its mythical status and the fabled existence. Tourists to Timbuktu wishing to explore the truth behind the myth can reach the city through its international airport. However, he image of the city as mysterious or mythical has survived to the present day in other countries: a poll among young Britons in 2006 found 34% did not believe the town existed, while the other 66% considered it "a mythical place".[5]
Timbuktu is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, listed since 1988. In 1990, it was added to the list of world heritage sites in danger due to the threat of desert sands and desertification. A program was set up to preserve the historical sites of Timbuktu. In 2005, it was taken off the list of endangered sites.
Timbuktu is currently (beginning 2007) a candidate in a competition to choose the New Seven Wonders of the World.[6]
Timbuktu was one of the major stops during Henry Louis Gates' PBS special "Wonders of the African World". Gates visited with Abdel Kadir Haidara, curator of the Mamma Haidara Library together with Ali Ould Sidi from the Cultural Mission of Mali. It is thanks to Gates that an Andrew Mellon Foundation grant was obtained to finance the construction of the library's facilities, later inspiring the work of the Timbuktu Manuscripts Project. The town is home to an institute dedicated to preserving historic documents from the region, in addition to two small museums (one of them the house in which the great German explorer Heinrich Barth spent six months in 1853-54), and the symbolic Flame of Peace monument commemorating the reconciliation between the Tuareg and the government of Mali.
The city continues to face political threats, however, and in the 1990s Timbuktu came under attack from Tuareg people hoping to build their own state. The Tuareg Rebellion was symbolically ended with a burning of weapons in the town in 1996.
Attractions
Timbuktu's main attractions are the intellectual and religious centers that have existed in the cities for centuries. The most prominent of the Islamic sites are the proliferate mud mosques, which are said to have inspired Antoni Gaudí. These include:
- Djinguereber Mosque, built in 1327 by El Saheli
- Sankore Mosque, also known as Sankore University, built in the early fifteenth century
- Sidi Yahya mosque, built in the 1441 by Mohamed Naddah.
- From 2008, NUON will set up their EDM headquarters in Timbuktu, to be headed by André Koelewijn. [citation needed]
Other attractions include a museum, terraced gardens and a water tower.
- Sahara Desert Tribal Camp.jpg
Sahara Desert Tribal Camp
Language
The main language of Timbuktu is Koyra Chiini, a variety of Songhay spoken by over 80% of residents. Some smaller population groups speak Hassaniya Arabic and Tamashek.
Famous people connected with Timbuktu
- Ali Farka Toure (1939–2006) Born in Timbuktu.[7]
- Heinrich Barth (1821-1865) German traveler and scholar and the first European to investigate into African history
- Bernard Peter de Neumann, GM (1917–1972) "The Man From Timbuctoo".[8] Held prisoner of war there along with other members of the crew of the Criton during 1941-1942.
Sister cities
 - Chemnitz, Germany
- Chemnitz, Germany - Y Gelli Gandryll (Hay-on-Wye), Wales
- Y Gelli Gandryll (Hay-on-Wye), Wales - Kairouan, Tunisia
- Kairouan, Tunisia - Marrakech, Morocco
- Marrakech, Morocco- Liopolis
 - Saintes, France
- Saintes, France -
-  - Tempe, Arizona, United States[9]
- Tempe, Arizona, United States[9]
See also
- Timbuktu Manuscripts Project
Sources and Further reading
- Braudel, Fernand. 1984. The perspective of the world. New York: Harper & Row. ISBN 0060153172 and ISBN 9780060153175
- Auster, Paul. 1999. Timbuktu: a novel. New York: Henry Holt. ISBN 0805054073 and ISBN 9780805054071
- Smith, David N. 1983. Timbuktu. New York: Dodd, Mead. ISBN 0396082327 and ISBN 9780396082323
- Jenkins, Mark. 1997. To Timbuktu. New York: W. Morrow. ISBN 0688115853 and ISBN 9780688115852
- Davidson, Basil. 1998. West Africa Before the Colonial Era: A History to 1850. Essex: Pearson Education Limited. ISBN 0582318521 and ISBN 9780582318526
External links
- Leo Africanus: Description of Timbuktu. Washington State University. Retrieved June 21, 2007.
- Shabeni's Description of Timbuktu. The 153 Club. Retrieved June 21, 2007.
- Trekking to Timbuktu—Student Version. National Endowment for the Humanities. Retrieved June 21, 2007.
- Wonders: Sankore Mosque. The Road to Timbuktu. Retrieved June 21, 2007.
- Rashidi, Runoko. The Great University of Sankore at Timbuktu a Brief Note. The Global African Presence. Retrieved June 21, 2007.
- The Timbuktu Libraries. Libraries of Timbuktu. Retrieved June 21, 2007.
- Pearce, Justin. October 3, 2005. Saving Mali's written treasures. British Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved June 21, 2007.
- Ancient Manuscripts from the Desert Libraries of Timbuktu. Library of Congress. Retrieved June 21, 2007.
- Hammer, Joshua. The Treasures of Timbuktu. Smithsonian. Retrieved June 21, 2007.
-
- Mapping from Multimap or GlobalGuide or Google Maps
- Satellite image from WikiMapia
- Mapping from OpenStreetMap
Notes and references
- ↑ http://news.yahoo.com/s/nm/20061110/sc_nm/mali_manuscripts_dc_1
- ↑ http://news.yahoo.com/s/nm/20061110/sc_nm/mali_manuscripts_dc_1
- ↑ Timbuktu — World Heritage (Unesco.org)
- ↑ "Ibn Battuta and his Saharan Travels" 153 Club
- ↑ "Search on for Timbuktu's twin" BBC News, 18 October 2006. Retrieved 28 March 2007
- ↑ From Machu Picchu to Timbuktu — The Search for the World's Seven New Wonders. Der Spiegel. Retrieved 2006-12-29.
- ↑ "African star Ali Farka Toure dies" BBC News, 7 March 2006. Retrieved 7 March 2006
- ↑ The Daily Express, 10 February 1943. Front Page: The Man From Timbuctoo
- ↑ "Search on for Timbuktu's twin" BBC News, 18 October 2006. Retrieved 28 March 2007
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.