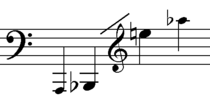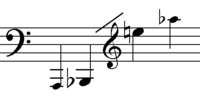Bassoon

| ||||||
|
The bassoon is a woodwind instrument in the double reed family that typically plays music written in the bass and tenor registers and occasionally even higher. It is called das Fagott in German, il fagotto in Italian, and le basson in French. Appearing in its modern form in the 1800s, the bassoon figures prominently in orchestral, concert band, and chamber music literature. The instrument is known for its distinctive tone color, wide range, variety of character, and agility. Its warm, dark, reedy timbre has often been compared to that of a male baritone voice. Due to the complicated fingering and the problem of reeds, the bassoon is an especially difficult instrument to learn; schoolchildren typically take up the bassoon only after starting on another woodwind instrument, such as the flute or clarinet. The spacing of keys and toneholes on the bassoon is large enough to be very difficult for a small child to manage. Some manufacturers make bassoons designed to be easier to play for those with small hands, such as younger players. The tenoroon may also be an option for younger players.
As music in the Christian Church in Europe evolved, the practice of four part harmonization became a defining characteristic of vocal and instrumental writing. In vocal music these four distinct parts were soprano, alto, tenor and bass. As the orchestra evolved, the woodwind, brass and string compliments also had four distinct voices ranging from high, mid-high, mid low and low registers. (Woodwinds: Flute, Oboe, Clarinet, Bassoon, Brass: Trumpet, Horn, Trombone, Tuba, and Strings: Violin, Viola, Cello, Bass.) The bassoon is the low voice in the woodwind choir.
Development
Early history
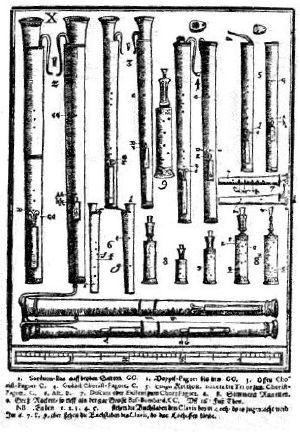
The dulcian is generally considered to be the forerunner of the modern bassoon, as it shares many characteristics with the latter, including a double reed fitted to a metal crook, obliquely drilled tone holes, and a conical bore that doubles back upon itself. The origins of the dulcian are obscure, but by the mid-sixteenth century it was available in as many as eight different sizes, from soprano to great bass. A full consort of dulcians was a rarity; its primary function seems to have been to provide the bass in the typical wind band of the time, either loud (shawms) or soft (recorders), indicating a remarkable ability to vary dynamics to suit the need. Otherwise, dulcian technique was rather primitive, with eight fingerholes and generally one key, indicating that it could play in only a limited number of key signatures.
About this time, the dulcian began to be known as fagotto in Italy. However, the usual etymology that equates fagotto with âbundle of sticksâ is somewhat misleading, as the latter term did not come into general use until somewhat later (Jansen 1978). A further discrepancy lies in the fact that the dulcian was usually carved out of a single block of wood, which is to say that it was a single "stick," and not a bundle.
It is tempting to say that the dulcian merged imperceptibly into the bassoon, but in fact there is circumstantial evidence to indicate that the baroque bassoon was a newly-invented instrument, with only a superficial resemblance to the old dulcian. Note that the dulcian was never entirely supplantedâit continued to be used well into the eighteenth century by Bach and others. The man most likely responsible for the development of the true bassoon was Martin Hotteterre (d. 1712), who may also have been the inventor of the three-piece flĂ»te traversiĂšre and the hautbois. Sometime in the 1650s, Hotteterre is believed to have conceived the bassoon in four sections (bell, bass joint, boot and wing joint), an arrangement which allowed far greater accuracy in machining the bore compared with the old dulcian. He also extended the compass downward to Bb with the addition of two keys (Lange and Thomson 1979). An alternate view holds that Hotteterre was but one of several craftsmen responsible for the development of the early bassoon; these may have included additional members of the Hotteterre family, as well as other French makers active around the same time (Kopp, 1999). No original French bassoon from this period survives, but if it did, it would most likely resemble the earliest extant bassoons of Johann Christoph Denner and Richard Haka from the 1680s. Sometime around 1700, a fourth key (G#) was added, and it was for this type of instrument that composers such as Vivaldi, Bach and Telemann wrote their demanding music. A fifth key, for the low Eb, was added during the first half of the eighteenth century. Notable makers of the 4-key and 5-key baroque bassoon include J.H. Eichentopf (c. 1678-1769), J. Poerschmann (1680-1757), Thomas Stanesby, Jr. (1668-1734), G.H. Scherer (1703-1778) and Prudent Thieriot (1732-1786).
Modern history
Increasing demands on the capabilities of instruments and players in the 1800sâparticularly concert halls requiring louder tones and the rise of virtuoso composer-performersâspurred on the further refinement of the bassoon. Increased sophistication both in manufacturing techniques and acoustical knowledge made possible great improvements in the playability of the instrument.
The modern bassoon exists in two distinct primary forms, the Buffet system and the Heckel system. The Buffet system is played primarily in France but also in Belgium and parts of Latin America, while the Heckel system is played in the majority of the world.
Heckel (German) system
The design of the modern bassoon owes a great deal to the performer, teacher, and composer Carl AlmenrÀder, who, assisted by the German acoustic researcher Gottfried Weber developed the 17-key bassoon whose range spanned four octaves. AlmenrÀder's improvements to the bassoon began with an 1823 treatise in which he described ways of improving intonation, response, and technical ease of playing by means of augmenting and rearranging the keywork; subsequent articles further developed his ideas. Working at the Schott factory gave him the means to construct and test instruments according to these new designs, the results of which were published in Caecilia, Schott's house journal; AlmenrÀder continued publishing and building instruments until his death in 1846, and Ludwig van Beethoven himself requested one of the newly-made instruments after hearing of the papers. AlmenrÀder left Schott to start his own factory along with partner Johann Adam Heckel in 1831.
Heckel and two generations of descendants continued to refine the bassoon, and it is their instrument that has become the standard for other instrument makers to follow. Because of their superior singing tone quality (an improvement upon one of the main drawbacks of the AlmenrÀder instruments), the Heckel instruments competed for prominence with the reformed Wiener system, a Boehm-style bassoon, and a completely-keyed instrument devised by C. J. Sax, father of Adolphe Sax. One latecomer attempt, from 1893, with a logical reformed fingering system was implemented by F.W. Kruspe, but failed to catch on. Other attempts at improving the instrument included a 24-keyed model and a single-reeded mouthpiece, but both were found to have adverse effects on the bassoon's distinctive tone and were abandoned.
Coming into the twentieth century the Heckel-style German model of bassoon dominated the field; Heckel himself had made over 4,000 instruments by the turn of the century, and the English makers' instruments were no longer desirable for the changing pitch requirements of the symphony orchestra, remaining primarily in military band use.
Except for a brief 1940s wartime conversion to ball-bearing manufacture, the Heckel concern has produced instruments continuously to the present day. Heckel bassoons are considered by many the best, although a range of Heckel-style instruments is available from several other manufacturers, all with slightly different playing characteristics. Companies that manufacture Heckel-system bassoons include: Heckel, Yamaha, Fox Products, Schreiber, PĂŒchner, Selmer, Linton, Moosmann, Kohlert, Moennig/Adler, B.H. Bell and Guntram Wolf. In addition, several factories in mainland China are producing inexpensive instruments under such labels as Laval, Haydn and Lark, and these have been available in the West for some time now. However, they are generally of marginal quality and are usually avoided by serious players.
Because its mechanism is the most primitive of all the woodwinds, there have been occasional attempts at "reinventing" the bassoon. In the 1960s the Englishman Giles Brindley began development of what he called the "logical" bassoon, which aimed to improve intonation and evenness of tone through use of an electrically activated mechanism, making possible key combinations that were too complex for the human hand to manage. However, Brindley's "logical bassoon" was never marketed.
Buffet (French) system
The Buffet system bassoon achieved its basic acoustical properties somewhat earlier than the Heckel; thereafter it continued to develop in a more conservative manner. While the early history of the Heckel bassoon included a complete overhaul of the instrument in both acoustics and keywork, the development of the Buffet system consisted primarily of incremental improvements to the keywork. This minimalist approach deprived the Buffet of the improved consistency, and thus the ease of operation and increased power found in the Heckel bassoons, but the Buffet is considered by some to have a more vocal and expressive quality. For example, the conductor John Foulds lamented in 1934 the dominance of the Heckel-style bassoon, considering them to be too homogeneous in sound with the horn.
Compared to the Heckel bassoon, Buffet system bassoons have a narrower bore and somewhat simplified mechanism, requiring different fingerings for many notes. It is not possible to switch from the Heckel to the Buffet, and vice versa, without extensive "retraining." Buffet instruments are known for a reedier sound and greater facility in the upper registers, reaching e''' and f''' with far greater ease and less air pressure. French woodwind tone in general exhibits a certain amount of "edge," with more of a vocal quality than is usual elsewhere, and the Buffet bassoon is no exception. This type of sound can be beneficial in music by French composers, but it also has drawn criticism for being too intrusive. As with all bassoons, the tone varies considerably depending on the individual instrument and performer. In the hands of a lesser player, the Heckel bassoon can sound rather flat and woody, but good players succeed in producing a vibrant, singing tone. Conversely, when poorly played the Buffet can sound buzzy and nasal, but good players succeed in producing a warm, expressive sound that approaches that of the Heckel.
Though the French system was once widely favored in England, Buffet-system instruments are no longer made there, and the last prominent English player of the French system retired in the 1980s. However, with its continued use in some regions and its distinctive tone, the Buffet continues to have a place in modern bassoon playing, particularly in France. Buffet-model bassoons are currently made in Paris by Buffet Crampon and Selmer. Some players, for example Gerald Corey in Canada, have learned to play both types and will alternate between them depending on the repertoire being played.
Construction and characteristics
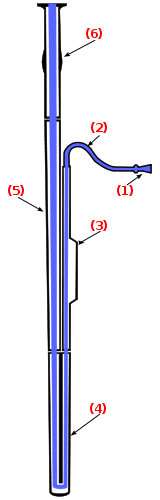
The bassoon disassembles into six main pieces, including the reed. The bell (6), extending upward; the long (or bass) joint (5), connecting the bell and the boot; the boot (or butt) (4), at the bottom of the instrument and folding over on itself; the wing (or tenor) joint (3), which extends from boot to bocal; and the bocal (or crook) (2), a crooked metal tube which attaches the wing joint to the reed, which is held in the mouth. (1) (listen â¶).
The modern bassoon is generally made of maple, with medium-hardness types such as sycamore maple (Bergahorn in German, Acer pseudoplantanus) and sugar maple (from North America) being preferred. Professional models are often made of Bergahorn (translates as "mountain maple," but distinct from the North American tree of that name). The most sought-after variety of Bergahorn for bassoons is the flamed "Riegel-Bergahorn" variety. Less-expensive models are made of materials such as polypropylene and ebonite, primarily for student and outdoor use; metal bassoons were made in the past but have not been in production by any major manufacturer since 1889.
The bore of the instrument is conical, like that of the oboe and the saxophone, and the parallel bores at the bottom of the instrument are connected by means of a u-shaped metal connector called the "U-tube." Both bore and holes are precision-machined, and each instrument is finished by hand for proper tuning. Since normal tone-hole placement on the bassoon would require a finger span much wider than that of the average adult, an expedient was developed whereby the vent holes are drilled at an oblique angle to the bore axis, making the spacing at the exterior manageable. Since the walls of the wing and boot joints are considerably thicker than that of other woodwinds, this means that the sound must travel a fair distance before reaching the outside, a feature that contributes in large part to the characteristic sound of the bassoon.
The wing joint and the small bore of the boot joint of wooden bassoons are lined with hard rubber to prevent damage from moisture; wooden instruments are also stained and varnished. The wood of professional bassoons, such as Heckel and Fox, may also be decorated with so-called "tiger stripes" prior to finishing to simulate the look of flamed maple. The top of the bell is completed with either a French style metal ring, or a German style plastic or ivory ring. The connection between joints consists of a tenon that fits into a socket; the tenons are wrapped either in cork or waxed string to provide a tight air seal. The bocal, one end of which is wrapped in cork for sealing and inserted into a socket at the top of the wing joint, complements and enhances the playing characteristics of the instrument. Bocals are available in several different lengths; a bassoonist chooses the length needed in order to achieve a certain pitch level.
Folded upon itself, the bassoon stands 134 cm (4.4 ft) tall, but the total length is 254 cm (roughly 8.3 ft). Playing is facilitated by doubling the tube back on itself and by closing the distance between the widely-spaced holes with a complex system of keywork, which extends throughout nearly the entire length of the instrument. There are also short-reach bassoons made for the benefit of young or petite players.
Bassoon players must learn three different clefs: primarily bass, but also tenor and treble. The range of the bassoon begins at B-flat1 (the first one below the bass staff) and extends upward over three octaves. Higher notes are possible but difficult to produce and rarely called for; orchestral parts rarely go higher than the C or D, with even Stravinsky's famously difficult opening solo in The Rite of Spring only ascending to the D. The low A at the bottom of the range first appeared in Wagnerâs Tristan (1865) and is only possible with a special extension to the instrument. This extension can take the form of an extra, longer replacement bell (with additional keywork on the long joint) or a paper tube, English horn bell, or similar extension placed in the bassoon's Bb bell. Wagner frequently used low A in his operas and encouraged Heckel to construct instruments with low A capability and the A bell still exists as an option. While the extra bell preserves chromatic possibilities, the simpler alternatives make the bottom B-flat impossible to play and affect the intonation of the lower notes. The last chord of the 1922 Quintet for Winds by Carl Nielsen includes an optional low A, and Gustav Mahler occasionally uses it in his symphonies.
Usage in ensembles
Earlier ensembles
The bassoon was first used in the orchestra to reinforce the bass line, and to act as the bass of the double reed choir (oboes, taille). Baroque composer Jean-Baptiste Lully and his Les Petits Violons included oboes and bassoons along with the strings in the 16-piece (later 21-piece) ensemble, as one of the first orchestras to include the newly-invented double reeds. Antonio Cesti included a bassoon in his 1668 opera Pomo d'oro. However, the use of the bassoon in the concert orchestra was sporadic until the late seventeenth century when double reeds began to make their way into the standard instrumentation, largely due to the spread of the hautbois to countries outside of France. Increasing use of the bassoon as a basso continuo instrument meant that it began to be included in opera orchestras, first in France and later in Italy, Germany and England. Meanwhile, composers such as Boismortier, Corrette, Galliard, Zelenka, Fasch and Telemann wrote demanding solo and ensemble music for the instrument. Antonio Vivaldi brought the bassoon to prominence by featuring it in 37 concerti for the instrument.
By mid-century, the bassoon's function in the orchestra was still mostly limited to that of a continuo instrumentâsince scores often made no specific mention of the bassoon, its use was implied, particularly if there were parts for oboes or other winds. Beginning in the early Rococo era, composers such as Haydn, J.C. Bach, Sammartini and Stamitz included parts that exploited the bassoon for its unique color, rather than for its perfunctory ability to double the bass line. Orchestral works with fully-independent parts for the bassoon would not become commonplace until the Classical era. Mozart's "Jupiter" symphony is a prime example, with its famous bassoon solos in the first movement. The bassoons were generally paired, as in current practice, though the famed Mannheim Orchestra boasted four.
Another important use of the bassoon during the Classical era was in the Harmonie, a chamber ensemble consisting of pairs of oboes, horns and bassoons; later, two clarinets would be added to form an octet. The Harmonie was an ensemble maintained by German and Austrian noblemen for private music-making, and was a cost-effective alternative to a full orchestra. Haydn, Mozart, Beethoven and Krommer all wrote considerable amounts of music for the Harmonie.
Modern ensembles
The modern symphony orchestra typically calls for two bassoons, often with a third playing the contrabassoon. Some works call for four or more players. The first player is frequently called upon to perform solo passages. The bassoon's distinctive tone suits it for both plaintive, lyrical solos such as Ravel's Boléro and more comical ones, such as the grandfather's theme in Peter and the Wolf. Its agility suits it for passages such as the famous running line (doubled in the violas and cellos) in the overture to The Marriage of Figaro. In addition to its solo role, the bassoon is an effective bass to a woodwind choir, a bass line along with the cellos and double basses, and harmonic support along with the French horns.
A wind ensemble will usually also include two bassoons and sometimes contra, each with independent parts; other types of concert wind ensembles will often have larger sections, with many players on each of first or second parts; in simpler arrangements there will be only one bassoon part and no contra. The bassoon's role in the wind band is similar to its role in the orchestra, though when scoring is thick it often cannot be heard above the brass instruments also in its range. La Fiesta Mexicana, by H. Owen Reed, features the instrument prominently, as does the transcription of Malcolm Arnold's Four Scottish Dances which has become a staple of the concert band repertoire.
The bassoon is also part of the standard wind quintet instrumentation, along with the flute, oboe, clarinet, and horn; it is also frequently combined in various ways with other woodwinds. Richard Strauss's "Duet-Concertino" pairs it with the clarinet as concertante instruments, with string orchestra in support.
The bassoon quartet has also gained favor in recent times, with the Neo Bubonic Bassoon Quartet being one of the more notable groups. The bassoon's wide range and variety of tone colors make it ideally suited to grouping in like-instrument ensembles. Peter Schickele's "Last Tango in Bayreuth" (after themes from Tristan and Isolde) is a popular work; Schickele's fictional alter ego P. D. Q. Bach exploits the more humorous aspects with his quartet "Lip My Reeds," which at one point calls for players to perform on the reed alone. It also calls for a low A at the very end by the first bassoon. The ending is written so that the fourth bassoon does not play in the final chord; instead, his or her role is to place an extension in the bell of the first bassoon so that the note can be played.
Technique
The bassoon is held diagonally in front of the player and cannot easily be supported by the player's hands alone. The most common means of support are 1) a neck-strap or shoulder-harness attached to the top of the boot joint, or 2) a seat strap attached to the base of the boot joint and either directly to the chair or resting on the chair seat, stabilized by the player's weight. Occasionally a spike similar to those used for the cello or the bass clarinet is attached to the bottom of the boot joint and rests on the floor. It is possible to play while standing up if the player uses a neck strap or similar harness, or wraps the seat strap around the trousers belt.
The Heckel-system bassoon is played with both hands in a stationary position, the left above the right, with five main finger holes on the front of the instrument plus a sixth that is key-activated. Five additional keys on the front are controlled by the little fingers of each hand. The back of the instrument has twelve or more keys to be controlled by the thumbs (the exact number varies depending on model).
An aspect of bassoon technique not found on any other woodwind is called flicking. It involves the momentary pressing, or "flicking," of the high A, C and D keys by the left hand thumb at the beginning of certain notes in the middle octave in order to eliminate the "cracking" or brief microphonic that happens without the use of the key. "Flicking" is not universal amongst bassoonists; some American players, principally on the East Coast, use it sparingly, if at all. The rest use it virtually 100% of the timeâit has become in essence "part of the fingering." European players in general are "flickers," but some hold down the appropriate key for the duration of the note, rather than just at the beginning.
There exists an ingenious "no-flick" octave key system invented by Arthur Weisberg, available as an add-on. Only a few years old, it has yet to be offered as "standard equipment" by any of the major bassoon manufacturers.
While bassoons are usually critically tuned at the factory, the player nonetheless has a great degree of flexibility of pitch control through the use of breath support and embouchure. Players can also use alternate fingerings to adjust the pitch of many notes.
Extended techniques
Many extended techniques can be performed on the bassoon, such as multiphonics, flutter tonguing, circular breathing, double tonguing, and harmonics.
Also, using certain fingerings, notes may be produced on the instrument that sound lower pitches than the actual range of the instrument. These "impossible notes" tend to sound very gravelly and out of tune, but technically sound below the low B flat. Alternatively, lower notes can be produced by inserting a small paper or rubber tube into the end of the bell, which converts the lower B flat into a lower note such as an A natural, but this affects the tuning of other notes in the lower register.
Reeds and reed construction
The modern reed
Bassoon reeds, made of Arundo donax cane, are often made by the players themselves, although beginner bassoonists tend to buy their reeds from professional reed makers. Reeds begin with a length of tube cane that is split into three or four pieces. The cane is then trimmed and gouged to the desired thickness, leaving the bark attached. After soaking, the gouged cane is cut to the proper shape and milled to the desired thickness, or profile, by removing material from the bark side. This can be done by hand with a file; more frequently it is done with a machine or tool designed for the purpose. After the profiled cane has soaked once again it is folded over in the middle. Prior to soaking, the reedmaker will have lightly scored the bark with parallel lines with a knife; this insures that the cane will assume a cylindrical shape during the forming stage. On the bark portion, the reedmaker binds on three coils or loops of brass wire to aid in the final forming process. The exact placement of these loops can vary somewhat depending on the reedmaker. The bound reed blank is then wrapped with thick cotton or linen thread to protect it, and a conical steel mandrel which has been heated in a flame is quickly inserted in between the blades. Using a special pair of pliers, the reedmaker presses down the cane, making it conform to the shape of the mandrel; the steam generated by the heated mandrel causes the cane to permanently assume the shape of the mandrel. The upper portion of the cavity thus created is called the "throat," and its shape has an influence on the final playing characteristics of the reed. The lower, mostly cylindrical portion will be reamed out with a special tool, allowing the reed to fit on the bocal.
After the reed has dried, the wires are tightened around the reed, which has shrunk after drying. The lower part is sealed (generally with a nitrocellulose-based cement such as Duco) and then wrapped with string to ensure both that no air leaks out through the bottom of the reed and that the reed maintains its shape.
To finish the reed, the end of the reed blank, originally at the center of the unfolded piece of cane, is cut off, creating an opening. The blades above the first wire are now roughly 27-30 mm long. In order for the reed to play, a slight bevel must be created at the tip with a knife, although there is also a machine that can perform this function. Other adjustments with the knife may be necessary, depending on the hardness and profile of the cane and the requirements of the player. The reed opening may also need to be adjusted by squeezing either the first or second wire with the pliers. Additional material may be removed from the sides (the "channels") or tip to balance the reed. Additionally, if the "e" in the staff is sagging in pitch, it may be necessary to "clip" the reed by removing 1-2 mm from its length.
Playing styles of individual bassoonists vary greatly; because of this, most advanced players will make their own reeds, in the process customizing them to their individual playing requirements. Many companies and individuals do offer reeds for sale, but even with store-bought reeds, the player must know how to make adjustments to suit his particular playing style.
The early reed
Little is known about the early construction of the bassoon reed, as few examples survive, and much of what is known is only what can be gathered from artistic representations. The earliest known written instructions date from the middle of the seventeenth century, describing the reed as being held together by wire or resined thread; the earliest actual reeds that survive are more than a century younger, a collection of 21 reeds from the late eighteenth century Spanish bajon.
The bassoon in jazz and rock
The bassoon is infrequently used as a jazz instrument and rarely seen in a jazz ensemble. It first began appearing at all in the 1920s, including specific calls for its use in Paul Whiteman's group and a few other session appearances. The next few decades saw the instrument used only sporadically, as symphonic jazz fell out of favor, but the 1960s saw artists such as Yusef Lateef and Chick Corea incorporate bassoon into their recordings; Lateef's diverse and eclectic instrumentation saw the bassoon as a natural addition, while Corea employed the bassoon in combination with flautist Hubert Laws.
The bassoon plays a prominent part in the Motown Records 1970 number one hit The Tears of a Clown performed by Smokey Robinson and The Miracles, with instrumentation by The Funk Brothers.
More recently, Illinois Jacquet and Frank Tiberi have both doubled on bassoon in addition to their usual saxophone performances. Bassoonist Karen Borca, a performer of free jazz, is one of the few jazz musicians to play only bassoon; Michael Rabinowitz, the Spanish bassoonist Javier Abad, and James Lassen, an American resident in Bergen, Norway, are others. Lindsay Cooper, Paul Hanson, and Daniel Smith are also currently using the bassoon in jazz. French bassoonists Jean-Jacques Decreux and Alexandre Ouzounoff have both recorded jazz, exploiting the flexibility of the Buffet system instrument to good effect.
In the genre of rock music, Lindsay Cooper used the bassoon in the art rock band Henry Cow, and Brian Gulland played bassoon in the Medieval-influenced progressive rock band Gryphon; both bands were most active during the 1970s. In the 1990s, Aimee DeFoe played bassoon in the Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania indie rock band Blogurt.
Also, Otsuka Ai's song LOVE MUSIC features a bassoon.
The bassoon in art and literature

Much of the early history of the bassoon is known through its representation in painting; the only source of description for the early bassoon reed, for example, is in paintings from late 16th century Spain.
There was also a painting made by Edgar Degas in 1870, called "L'orchestre de l'opéra" ("The Orchestra of the Opera," also known as "In the Orchestra Pit"), features a bassoon player in the orchestra amongst several other orchestra members.
Audio examples
Technical examplesA collection of samples demonstrating the bassoon's range, abilities, and tone.
|
Concerti and other orchestral literature
Baroque
- Antonio Vivaldi wrote 39 concerti for bassoon, 37 of which exist in their entirety today
- Georg Philipp Telemann Sonata in F minor
Classical
- Johann Christian Bach, Bassoon Concerto in B flat, Bassoon Concerto in E-flat major
- Johann Nepomuk Hummel, Bassoon Concerto in F, W75
- Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Bassoon Concerto in B flat, K191
- Carl Stamitz, Bassoon Concerto in F Major
- Johann Baptist Vanhal, Bassoon in C Major, Concerto in F Major for two bassoons and orchestra
- Anselm Viola, Bassoon Concerto in F major (1791)
Romantic
- Edward Elgar, Romance for Bassoon and Orchestra, op. 62
- Carl Maria von Weber, Andante e rondo ungarese in C minor, op. 35; Bassoon Concerto in F, op. 75
- Camille Saint-Saëns, Sonata for bassoon and piano in G Major, op. 168
Contemporary
- Luciano Berio, Sequenza XII for Bassoon (1995)
- Henri Dutilleux, Sarabande et CortĂšge for bassoon and piano (1942)
- Alvin Etler, Sonata for Bassoon and Piano
- Sofia Gubaidulina, Concerto for bassoon and low strings (1975)
- Paul Hindemith, Sonata for Bassoon and Piano (1938)
- Gordon Jacob, Concerto for Bassoon, Strings and Percussion, Four Sketches for Bassoon, Partita for Bassoon
- Francisco Mignone, Double Bassoon Sonata, 16 valses for Bassoon
- Willson Osborne, Rhapsody for Bassoon
- Andrzej Panufnik, Concerto for Bassoon and small orchestra (1985)
- John Steinmetz, Sonata for Bassoon and Piano
- Richard Strauss, Duet Concertino for Clarinet and Bassoon with strings and harp (1948)
- John Williams, The Five Sacred Trees: Concerto for Bassoon and Orchestra (1997)
- Marcus Tristan Heathcock, Sinfonia Concertante for Bassoon and orchestra (2007)
Famous orchestral passages
- Béla Bartók : Concerto for Orchestra; the second movement features woodwind instruments in pairs, beginning with the bassoons, and the recapitulation of their duet adds a third instrument playing a staccato counter-melody.
- Ludwig van Beethoven : Symphony 4 in B flat major, Symphony 9 in D minor, last movement
- Hector Berlioz : Symphonie Fantastique (In the fourth movement, there are several solo and tutti bassoon-featuring passages. This piece calls for four bassoons.)
- Paul Dukas : The Sorcerer's Apprentice, widely recognized as used in the movie Fantasia
- Edvard Grieg : In the Hall of the Mountain King
- Carl Orff : Carmina Burana
- Sergei Prokofiev : Peter and the Wolf (possibly the most-recognized bassoon theme, the part of the grandfather)
- Maurice Ravel : Rapsodie Espagnole (features a fast, lengthy dual cadenza at the end of the first movement), Boléro (the bassoon has a high descending solo passage near the beginning), Piano Concerto in G Major
- Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov : Scheherazade, second movement
- Dmitri Shostakovich : several symphonies including #1, 4, 5 : 8, & 9, Symphony 5 in Eb major
- Igor Stravinsky : The Rite of Spring (opens with a famously unorthodox bassoon solo), lullaby from The Firebird
- Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky : Symphony 4 in F minor, Symphony 5 in E minor, Symphony 6 in B minor
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Camden, Archie. Bassoon technique. London; NY: Oxford University Press, 1962. OCLC 670790
- Jansen, Will. The Bassoon: Its History, Construction, Makers, Players, and Music. Uitgeverij F. Knuf, 1978. 5 Volumes
- Langwill, Lyndesay Graham. The bassoon and controbassoon. London: E. Benn; NY: W.W. Norton, 1965. OCLC 480742
- Waterhouse, William. Bassoon. London: Kahn & Averill, 2003. ISBN 1871082684
Additional reading
- The Double Reed (currently three issues per year), I.D.R.S. Publications (see www.idrs.org)
- Journal of the International Double Reed Society (annual since about 1972), I.D.R.S. Publications
- Baines, Anthony (ed.), Musical Instruments Through the Ages. Penguin Books, 1961.
- Jansen, Will. The Bassoon: Its History, Construction, Makers, Players, and Music. Uitgeverij F. Knuf, 1978. 5 Volumes
- Kopp, James B., "The Emergence of the Late Baroque Bassoon," in The Double Reed 22 (4) (1999).
- Lange, H.J. and Thomson, J.M., "The Baroque Bassoon," Early Music (July 1979).
- Popkin, Mark and Glickman, Loren, Bassoon Reed Making, The Instrumentalist Publishing Company, 2nd ed., 1987
- Sadie, Stanley, (ed.), The New Grove Dictionary of Musical Instruments. s.v. "Bassoon," 2001
- Spencer, William (rev. Mueller, Frederick), The Art of Bassoon Playing. Summy-Birchard Inc., 1958
- Stauffer, George B. (1986). "The Modern Orchestra: A Creation of the Late Eighteenth Century." In Joan Peyser (Ed.) The Orchestra: Origins and Transformations Charles Scribner's Sons, 41-72.
- Weaver, Robert L. (1986). "The Consolidation of the Main Elements of the Orchestra: 1470-1768." In Joan Peyser (Ed.) The Orchestra: Origins and Transformations Charles Scribner's Sons, 7-40.
External links
All links retrieved September 20, 2023.
- International Double Reed Society
- British Double Reed Society
- Bassoon Fingering Charts
- Curtal, Dulcian, BajĂłn - A History of the Precursor to the Bassoon Maggie Kilbey's comprehensive book.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.