Difference between revisions of "Lake Baikal" - New World Encyclopedia
Keisuke Noda (talk | contribs) (import from wiki) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (75 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{approved}}{{submitted}}{{images OK}}{{ready}}{{Copyedited}} |
| − | {{ | + | {{Infobox lake |
|lake_name = Lake Baikal | |lake_name = Lake Baikal | ||
|image_lake = Olchon1.jpg | |image_lake = Olchon1.jpg | ||
| − | |caption_lake = | + | |caption_lake = [[Shaman]]-Stone of the [[Olkhon]] Island |
| − | |image_bathymetry = | + | |image_bathymetry = Karte baikal2.png |
|caption_bathymetry = | |caption_bathymetry = | ||
| − | |coords = {{ | + | |coords = {{coord|53.5|N|108.2|E}} |
| − | |type = [[Rift | + | |type = [[Rift lake|Continental rift lake]] |
| − | + | |inflow = [[Selenga]], [[Chikoy River|Chikoy]], [[Khilokh]], [[Uda River, Buryatia|Uda]], [[Barguzin (river)|Barguzin]], [[Upper Angara River|Upper Angara]] | |
|outflow = [[Angara River|Angara]] | |outflow = [[Angara River|Angara]] | ||
| − | |catchment = | + | |catchment = {{km2 to mi2|560000|precision=-3|abbr=yes}} |
| − | |basin_countries = | + | |basin_countries = Russia |
| − | |length = | + | |length = {{km to mi|636|abbr=yes}} |
| − | |width = | + | |width = {{km to mi|79|abbr=yes}} |
| − | |area = | + | |area = {{km2 to mi2|31494|abbr=yes}} |
| − | |depth = | + | |depth = {{m to ft|758|abbr=yes|precision=0}} |
| − | |residence_time = | + | |residence_time = 350 years |
| − | |max-depth = | + | |max-depth = {{m to ft|1637|abbr=yes|precision=0}} |
| − | |volume = | + | |volume = {{km3 to mi3|23600|abbr=yes|precision=-2}} |
| − | |shore = | + | |shore = {{km to mi|2100|abbr=yes|precision=-1}} |
| − | |elevation = | + | |elevation = {{m to ft|456|abbr=yes|precision=0}} |
|islands = 22 ([[Olkhon]]) | |islands = 22 ([[Olkhon]]) | ||
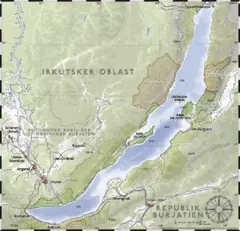
|cities = [[Irkutsk]] | |cities = [[Irkutsk]] | ||
| + | |frozen = January-May | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | '''Lake Baikal''' ({{lang-ru|о́зеро Байка́л ''Ozero Baykal''}}, {{pronounced|ˈozʲɪrə bʌjˈkɑl}}, {{lang-bxr|Байгал нуур ''Baygal nuur''}}) sits in Southern [[Siberia]] in [[Russia]], located between [[Irkutsk Oblast]] to the northwest and the [[Buryatia|Buryat Republic]] to the southeast, near the city of [[Irkutsk]]. Also known as the "Blue Eye of Siberia," it contains more water than all the North American [[Great Lakes]] combined. At {{m to ft|1637|precision=0}}, Lake Baikal constitutes the deepest lake in the world, and the [[List of lakes by volume|largest freshwater lake]] in the world by volume, holding approximately 20 percent of the world's total surface fresh water. | ||
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | Like [[Lake Tanganyika]], Lake Baikal formed in an ancient [[rift valley]] and therefore has a long, and crescent shape with a surface area (31,500 km²) less than half that of [[Lake Superior]] or [[Lake Victoria]]. Baikal serves as home to more than 1,700 species of plants and animals, two thirds found only in the lake zone. [[UNESCO]] designated Lake Baikal a [[World Heritage Site]] in 1996. At more than 25 million years old, it has been declared the oldest lake in the world. The successful dive of [[Mir-1]] and [[Mir-2]] [[mini-submarine]]s to the deepest place in Baikal on 29 July 2008, at over one mile, has opened the prospect of new discoveries of ancient lake life. | ||
| − | + | ==Geography and hydrography== | |
| − | + | [[Image:-26 swiatoinos.JPG.JPG|thumb|275px|left|The peninsula of [[Svyatoy Nos]].]] | |
| − | + | While known as the "North Sea" in historical Chinese texts, Lake Baikal had been located in the then Xionu territory. Lake Baikal had been out of the public eye until the Russian government built the [[Trans-Siberian railway]] between 1896 and 1902. The scenic loop encircling Lake Baikal needed 200 bridges and 33 tunnels. As under construction, [[Fedor Kirillovich Drizhenko|F.K. Drizhenko]] headed a hydrogeographical expedition that produced the first detailed atlas of the contours of Baikal's depths. The atlas demonstrated that Lake Baikal has more water than all of [[North America]]'s [[Great Lakes]] combined—{{km3 to mi3|23600}}, about one fifth of the total fresh water on the earth.<ref name=facts>[https://lakebaikal.org/lake-baikal-facts/ Lake Baikal Facts] ''Lake Baikal''. Retrieved January 28, 2020.</ref> In surface area, the much shallower Great Lakes [[Lake Superior|Superior]], [[Lake Huron|Huron]] and [[Lake Michigan|Michigan]] in North America, as well as by the relatively shallow [[Lake Victoria]] in [[East Africa]] exceeded it. Known as the "[[Galápagos Islands|Galápagos]] of Russia," its age and isolation have produced some of the world's richest and most unusual [[fish|freshwater fauna]] of exceptional value to [[evolution|evolutionary science]].<ref>[https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/754/ Lake Baikal] ''UNESCO World Heritage Center''. Retrieved January 28, 2020.</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Lake Baikal | + | Lake Baikal lies in a [[rift valley]] created by the [[Baikal Rift Zone]] where the crust of the earth pulls apart.<ref name="oddities"> Carla Helfferich, [https://www.gi.alaska.edu/alaska-science-forum/oddities-lake-baikal The Oddities of Lake Baikal]. ''Alaska Science Forum'', July 12, 1990. Retrieved January 28, 2020.</ref> |
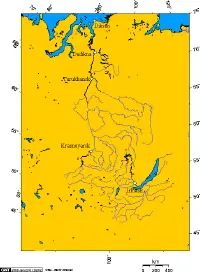
| − | + | [[Image:Yenisei basin 7.png|thumb|200px|The [[Yenisei River]] basin, Lake Baikal, and the settlements of [[Dikson (urban-type settlement)|Dikson]], [[Dudinka]], [[Turukhansk]], [[Krasnoyarsk]], [[Irkutsk]].|left]] | |
| − | | | + | At {{km to mi|636}} long and {{km to mi|79}} wide, Lake Baikal has the largest surface area of any freshwater lake in [[Asia]] ([[1 E10 m²|31,494 km²]]), constituting the deepest lake in the world (1,637 meters, previously measured at 1,620 meters). The bottom of the lake measures 1,285 meters below sea level, but below that lies some {{km to mi|7|precision=1}} of [[sediment]], placing the rift floor some 8–9 kilometers (more than 5 miles) below the surface: the deepest continental [[rift]] on [[Earth]].<ref name="oddities"/> In geological terms, the rift, young and active, widens about two centimeters per year. The [[fault zone]] experiences frequent [[seismic activity]]. New [[hot springs]] appear in the area and notable [[earthquake]]s happen every few years. It drains into the [[Angara]] tributary of the [[Yenisei]]. |
| − | + | {{readout||right|250px|Lake Baikal in Southern Siberia, [[Russia]] is the deepest lake in the world}} | |
| − | + | Its age, estimated at [[1 E14 s|25–30 million years]], makes it one of the most ancient lakes in [[geology|geological]] history. Unique among large, high-latitude lakes, its [[sediment]]s have been unscoured by overriding continental ice sheets. U.S. and Russian studies of core sediment in the 1990s provide a detailed record of climatic variation over the past 250,000 years. Geologists expect longer and deeper sediment cores in the near future. Lake Baikal has been confirmed as the only fresh water lake with direct and indirect evidence of [[gas hydrate]]s existing.<ref>T. V. Matveeva, et al., [https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00367-003-0144-z Gas hydrate accumulation in the subsurface sediments of Lake Baikal (Eastern Siberia)] ''Geo-Marine Letters'' 23(3-4) (2003): 289. Retrieved January 28, 2020.</ref> | |
| − | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The lake is completely surrounded by mountains, with the [[Baikal Mountains]] on the north shore and the [[taiga]] technically protected as a national park. It contains 22 islands; the largest, [[Olkhon]], measures {{km to mi|72}} long. The lake has as many as three hundred and thirty inflowing [[river]]s, the main ones draining directly into Baikal include the [[Selenga River]], the [[Barguzin River]], the [[Upper Angara River]], the [[Turka River]], the [[Sarma River]] and the [[Snezhnaya River]]. The [[Angara River]] serves as its single drainage outlet.<ref name=facts/> Despite its great depth, the lake's waters have excellent oxygenation throughout the water column compared to the [[Stratification (water)|stratification]] that occurs in such bodies of water as [[Lake Tanganyika]] and the [[Black Sea]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Olkhon]], the largest island in Lake Baikal, constitutes the fourth-largest [[List of islands in lakes|lake-bound island in the world]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Wildlife== | |
| + | [[Image:Omul Fish.jpg|thumb|250px|Omul Fish at the [[Listvyanka]] market.]] | ||
| − | The | + | The extent of [[biodiversity]] present in Lake Baikal surpasses all except a few lakes. Lake Baikal hosts over 2,500 species of plants and varieties of animals, with over 80 percent of animals [[Endemic (ecology)|endemic]]. The [[Baikal Seal]] or [[nerpa]] ''(Phoca sibirica)'', found throughout Lake Baikal, constitutes one of only three entirely freshwater [[phocid|seal]] species in the world, the other being the two subspecies of freshwater [[Ringed Seal]]. The [[omul]] ''(Coregonus autumnalis migratorius),'' a smallish endemic [[salmonid]], may be the most important local species.<ref>Deborah Byrd, Lake Baikal: Earth’s deepest, oldest lake ''EarthSky'', June 4, 2019.</ref> Local people catch and [[Smoking (food)|smoke]] the salmonid, selling it widely in markets around the lake. |
| − | + | The two species of [[golomyanka]] or Baikal oil fish (''Comephorus baicalensis'' and ''C. dybowskii'') have earned special note. Those long-finned, translucent fish, living in depths of 700 to 1600 feet, serve as the primary prey for the Baikal seal, representing the largest fish biomass in the lake. The Baikal oil fish have become famous for disintegrating into a pool of oil and bones when withdrawn rapidly from the high pressures of the deep water. The Baikal [[Grayling (genus)|grayling]] ''(Thymallus arcticus baicalensis),'' a fast swimming [[salmonid]] popular among anglers, and the [[Baikal sturgeon]] ''(Asipenser baerri baicalensis)'' both constitute important endemic species with commercial value. | |
| − | + | Hunters commonly track and shoot [[bear]] and [[deer]] along Baikal shores. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Research== |
| − | [[ | + | [[File:Baikal lake Crack in the ice.jpg|thumb|200px|Ice cover survey on the lake]] |
| − | + | Several organizations have been conducting natural research projects on Lake Baikal, mostly governmental or groups associated with governmental organizations. | |
| − | + | In July 2008, Russia sent two small submersibles, Mir-1 and Mir-2, to descend 1,592 m (5,223 ft) to the bottom of Lake Baikal to conduct geological and biological tests on its unique ecosystem. Russian scientist and federal politician [[Artur Chilingarov]], the leader of the mission, took part in the Mir dives.<ref>[https://sputniknews.com/russia/20080729115171121/ Russian mini-subs surface after record dive in Siberian lake] ''Novosti'', July 29, 2008 (in English) Retrieved January 28, 2020.</ref> | |
| − | [[ | + | ==Environmental concerns== |
| + | [[Image:Lakebaikalwinter.jpg|thumb|250px|The lake in the winter, as seen from the tourist resort of [[Listvyanka]]. The ice becomes thick enough to support pedestrians and snowmobiles.]] | ||
| − | == | + | ===Baykalsk pulp and paper mill=== |
| − | + | [[Image:Baikal south.jpg|thumb|250px|The lake in the summer, as seen from [[Bolshiye Koty]] on the southwest shore.]] | |
| − | [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Industrialists constructed the Baykalsk Pulp and Paper Mill (BPPM) in 1966 on the shore line. The BPPM [[bleach]]es its paper with [[chlorine]], discharging the waste into Baikal. Despite numerous protests, the BPPM still operates. [[Environmentalist|Environmental activists]] endeavor to make the pollution less harmful rather than end BPPM's production, since a plant shutdown would end jobs vital to the local economy. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ===East Siberia-Pacific Ocean Oil Pipeline=== |
| − | < | + | Russian oil pipelines state company [[Transneft]] planned to build a trunk pipeline that would have come within {{m to ft|800|precision=-1}} of the lake shore in a zone of substantial seismic activity. Environmental activists in Russia, Greenpeace, Baikal pipeline opposition, and local citizens strongly opposed these plans, because an accidental oil spill would cause significant damage to the fragile lake environment. Russian president [[Vladimir Putin]] intervened, ordering the company to consider an alternative route {{km to mi|40}} to the north to avoid such ecological risks. <ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/4945998.stm Putin orders oil pipeline shifted] ''BBC News'', April 26, 2006. Retrieved January 28, 2020.</ref> Transneft agreed to alter its plans, moving the pipeline away from Lake Baikal. Work began on the pipeline two days after President Putin agreed to changing the route away from Lake Baikal.<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/4954554.stm Work starts on Russian pipeline]. ''BBC News'' April 28, 2006. Retrieved January 28, 2020. </ref> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | < | ||
| − | |||
| − | </ | + | ===Uranium Enrichment Center=== |
| + | In 2006, the Russian Government announced plans to build the world's first International Uranium Enrichment Center at an existing nuclear facility in Angarsk, 95 kilometers from the lake's shores. Critics argue that could lead to a disaster for the region, urging the Government to reconsider.<ref>[http://www.newint.org/columns/currents/2008/05/01/environment/ Saving the Sacred Sea] ''New Internationalist'', May 2, 2008. Retrieved January 28, 2020.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Uranium Enrichment Center was opened in Angarsk in December, 2010.<ref>[https://www.iaea.org/newscenter/news/russia-inaugurates-worlds-first-low-enriched-uranium-reserve Russia Inaugurates World's First Low Enriched Uranium Reserve] ''International Atomic Energy Agency'', December 17, 2010. Retrieved January 28, 2020.</ref> | ||
| − | == | + | ===Tourism=== |
| − | + | Investors from the [[tourism|tourist industry]] have been drawn to Lake Baikal since energy revenues sparked an economic boom. That represents an economic benefit to local residents but potential harm to the Lake Baikal site. Viktor Grigorov, owner of the Grand Baikal in [[Irkutsk]], a city with a population of about 600.000, numbers among the [[investors]] who planned to build three hotels, creating 570 jobs. In 2007, the Russian government declared the Baikal region a [[special economic zone]]. The popular [[resort]] of Listvyanka has a seven-story Hotel Mayak. ''[[Rosatom]]'' plans to build a [[laboratory]] in Baikal, in conjunction with an international [[uranium]] plant and to invest $2.5bn in the region and create 2,000 jobs in the city of [[Angarsk]].<ref>Tom Esslemont, [http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/6982271.stm 'Pearl of Siberia' draws investors] ''BBC News'', September 7, 2007. Retrieved January 28, 2020.</ref> The harmful toll of hotels in the World Heritage site, Lake Baikal, looms as an environmental threat. | |
| − | + | ==Notes== | |
| − | + | <references/> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | * Kozhov, M. M. ''Lake Baikal and Its Life. Monographiae biologicae, v. 11.'' The Hague: W. Junk, 1963. {{OCLC|660805}} | ||
| + | * Matthiessen, Peter, and Boyd Norton. ''Baikal: Sacred Sea of Siberia.'' San Francisco: Sierra Club Books, 1992. ISBN 0871565846 | ||
| + | * Thomson, Peter. ''Sacred Sea: A Journey to Lake Baikal.'' Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2007. ISBN 0195170512 | ||
| + | * Van Rensbergen, P., et al., 2002. Sub-lacustrine mud volcanoes and cold seeps caused by dissociation of gas hydrates in Lake Baikal. ''Geology'' 30(7): 631-634. | ||
| − | [ | + | == External links == |
| − | [ | + | All links retrieved October 21, 2022. |
| − | + | * [https://www.livescience.com/57653-lake-baikal-facts.html Lake Baikal: World's Largest, Deepest Lake] ''Live Science'' | |
| − | [ | + | * [https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/754/ Lake Baikal] ''UNESCO World Heritage Center'' |
| − | + | * [https://lakebaikal.org/ Lake Baikal: World's Deepest Lake] | |
| − | [ | + | * [https://earthsky.org/earth/what-is-the-worlds-deepest-lake Lake Baikal: Earth’s deepest, oldest lake] ''Earth Sky'' |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {{World Heritage Sites in Russia}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Landmarks]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Geography]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Bodies of water]] | ||
| + | [[Category:World Heritage Sites]] | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{credits|227047719}} |
Latest revision as of 05:36, 4 March 2023
| Lake Baikal | |
|---|---|
| | |
| Coordinates | |
| Lake type | Continental rift lake |
| Primary sources | Selenga, Chikoy, Khilokh, Uda, Barguzin, Upper Angara |
| Primary outflows | Angara |
| Catchment area | 560,000 km² (216,000 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | Russia |
| Max length | 636 km (395.2 mi) |
| Max width | 79 km (49.1 mi) |
| Surface area | 31,494 km² (12,159.9 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 758 m (2,487 ft) |
| Max depth | 1,637 m (5,371 ft) |
| Water volume | 23,600 km3 (5,700 cu mi) |
| Residence time (of lake water) | 350 years |
| Shore length1 | 2,100 km (1,300 mi) |
| Surface elevation | 456 m (1,496 ft) |
| Islands | 22 (Olkhon) |
| Settlements | Irkutsk |
| 1 Shore length is an imprecise measure which may not be standardized for this article. | |
Lake Baikal (Russian: о́зеро Байка́л Ozero Baykal, pronounced [ˈozʲɪrə bʌjˈkɑl], Buryat: Байгал нуур Baygal nuur) sits in Southern Siberia in Russia, located between Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Buryat Republic to the southeast, near the city of Irkutsk. Also known as the "Blue Eye of Siberia," it contains more water than all the North American Great Lakes combined. At 1,637 meters (5,371 ft), Lake Baikal constitutes the deepest lake in the world, and the largest freshwater lake in the world by volume, holding approximately 20 percent of the world's total surface fresh water.
Like Lake Tanganyika, Lake Baikal formed in an ancient rift valley and therefore has a long, and crescent shape with a surface area (31,500 km²) less than half that of Lake Superior or Lake Victoria. Baikal serves as home to more than 1,700 species of plants and animals, two thirds found only in the lake zone. UNESCO designated Lake Baikal a World Heritage Site in 1996. At more than 25 million years old, it has been declared the oldest lake in the world. The successful dive of Mir-1 and Mir-2 mini-submarines to the deepest place in Baikal on 29 July 2008, at over one mile, has opened the prospect of new discoveries of ancient lake life.
Geography and hydrography
While known as the "North Sea" in historical Chinese texts, Lake Baikal had been located in the then Xionu territory. Lake Baikal had been out of the public eye until the Russian government built the Trans-Siberian railway between 1896 and 1902. The scenic loop encircling Lake Baikal needed 200 bridges and 33 tunnels. As under construction, F.K. Drizhenko headed a hydrogeographical expedition that produced the first detailed atlas of the contours of Baikal's depths. The atlas demonstrated that Lake Baikal has more water than all of North America's Great Lakes combined—23,600 cubic kilometers (5,662.4 cu mi), about one fifth of the total fresh water on the earth.[1] In surface area, the much shallower Great Lakes Superior, Huron and Michigan in North America, as well as by the relatively shallow Lake Victoria in East Africa exceeded it. Known as the "Galápagos of Russia," its age and isolation have produced some of the world's richest and most unusual freshwater fauna of exceptional value to evolutionary science.[2]
Lake Baikal lies in a rift valley created by the Baikal Rift Zone where the crust of the earth pulls apart.[3]
At 636 kilometers (395.2 mi) long and 79 kilometers (49.1 mi) wide, Lake Baikal has the largest surface area of any freshwater lake in Asia (31,494 km²), constituting the deepest lake in the world (1,637 meters, previously measured at 1,620 meters). The bottom of the lake measures 1,285 meters below sea level, but below that lies some 7 kilometers (4.3 mi) of sediment, placing the rift floor some 8–9 kilometers (more than 5 miles) below the surface: the deepest continental rift on Earth.[3] In geological terms, the rift, young and active, widens about two centimeters per year. The fault zone experiences frequent seismic activity. New hot springs appear in the area and notable earthquakes happen every few years. It drains into the Angara tributary of the Yenisei.
Its age, estimated at 25–30 million years, makes it one of the most ancient lakes in geological history. Unique among large, high-latitude lakes, its sediments have been unscoured by overriding continental ice sheets. U.S. and Russian studies of core sediment in the 1990s provide a detailed record of climatic variation over the past 250,000 years. Geologists expect longer and deeper sediment cores in the near future. Lake Baikal has been confirmed as the only fresh water lake with direct and indirect evidence of gas hydrates existing.[4]
The lake is completely surrounded by mountains, with the Baikal Mountains on the north shore and the taiga technically protected as a national park. It contains 22 islands; the largest, Olkhon, measures 72 kilometers (44.7 mi) long. The lake has as many as three hundred and thirty inflowing rivers, the main ones draining directly into Baikal include the Selenga River, the Barguzin River, the Upper Angara River, the Turka River, the Sarma River and the Snezhnaya River. The Angara River serves as its single drainage outlet.[1] Despite its great depth, the lake's waters have excellent oxygenation throughout the water column compared to the stratification that occurs in such bodies of water as Lake Tanganyika and the Black Sea.
Olkhon, the largest island in Lake Baikal, constitutes the fourth-largest lake-bound island in the world.
Wildlife
The extent of biodiversity present in Lake Baikal surpasses all except a few lakes. Lake Baikal hosts over 2,500 species of plants and varieties of animals, with over 80 percent of animals endemic. The Baikal Seal or nerpa (Phoca sibirica), found throughout Lake Baikal, constitutes one of only three entirely freshwater seal species in the world, the other being the two subspecies of freshwater Ringed Seal. The omul (Coregonus autumnalis migratorius), a smallish endemic salmonid, may be the most important local species.[5] Local people catch and smoke the salmonid, selling it widely in markets around the lake.
The two species of golomyanka or Baikal oil fish (Comephorus baicalensis and C. dybowskii) have earned special note. Those long-finned, translucent fish, living in depths of 700 to 1600 feet, serve as the primary prey for the Baikal seal, representing the largest fish biomass in the lake. The Baikal oil fish have become famous for disintegrating into a pool of oil and bones when withdrawn rapidly from the high pressures of the deep water. The Baikal grayling (Thymallus arcticus baicalensis), a fast swimming salmonid popular among anglers, and the Baikal sturgeon (Asipenser baerri baicalensis) both constitute important endemic species with commercial value.
Hunters commonly track and shoot bear and deer along Baikal shores.
Research
Several organizations have been conducting natural research projects on Lake Baikal, mostly governmental or groups associated with governmental organizations.
In July 2008, Russia sent two small submersibles, Mir-1 and Mir-2, to descend 1,592 m (5,223 ft) to the bottom of Lake Baikal to conduct geological and biological tests on its unique ecosystem. Russian scientist and federal politician Artur Chilingarov, the leader of the mission, took part in the Mir dives.[6]
Environmental concerns
Baykalsk pulp and paper mill
Industrialists constructed the Baykalsk Pulp and Paper Mill (BPPM) in 1966 on the shore line. The BPPM bleaches its paper with chlorine, discharging the waste into Baikal. Despite numerous protests, the BPPM still operates. Environmental activists endeavor to make the pollution less harmful rather than end BPPM's production, since a plant shutdown would end jobs vital to the local economy.
East Siberia-Pacific Ocean Oil Pipeline
Russian oil pipelines state company Transneft planned to build a trunk pipeline that would have come within 800 meters (2,620 ft) of the lake shore in a zone of substantial seismic activity. Environmental activists in Russia, Greenpeace, Baikal pipeline opposition, and local citizens strongly opposed these plans, because an accidental oil spill would cause significant damage to the fragile lake environment. Russian president Vladimir Putin intervened, ordering the company to consider an alternative route 40 kilometers (24.9 mi) to the north to avoid such ecological risks. [7] Transneft agreed to alter its plans, moving the pipeline away from Lake Baikal. Work began on the pipeline two days after President Putin agreed to changing the route away from Lake Baikal.[8]
Uranium Enrichment Center
In 2006, the Russian Government announced plans to build the world's first International Uranium Enrichment Center at an existing nuclear facility in Angarsk, 95 kilometers from the lake's shores. Critics argue that could lead to a disaster for the region, urging the Government to reconsider.[9]
The Uranium Enrichment Center was opened in Angarsk in December, 2010.[10]
Tourism
Investors from the tourist industry have been drawn to Lake Baikal since energy revenues sparked an economic boom. That represents an economic benefit to local residents but potential harm to the Lake Baikal site. Viktor Grigorov, owner of the Grand Baikal in Irkutsk, a city with a population of about 600.000, numbers among the investors who planned to build three hotels, creating 570 jobs. In 2007, the Russian government declared the Baikal region a special economic zone. The popular resort of Listvyanka has a seven-story Hotel Mayak. Rosatom plans to build a laboratory in Baikal, in conjunction with an international uranium plant and to invest $2.5bn in the region and create 2,000 jobs in the city of Angarsk.[11] The harmful toll of hotels in the World Heritage site, Lake Baikal, looms as an environmental threat.
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Lake Baikal Facts Lake Baikal. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ↑ Lake Baikal UNESCO World Heritage Center. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Carla Helfferich, The Oddities of Lake Baikal. Alaska Science Forum, July 12, 1990. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ↑ T. V. Matveeva, et al., Gas hydrate accumulation in the subsurface sediments of Lake Baikal (Eastern Siberia) Geo-Marine Letters 23(3-4) (2003): 289. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ↑ Deborah Byrd, Lake Baikal: Earth’s deepest, oldest lake EarthSky, June 4, 2019.
- ↑ Russian mini-subs surface after record dive in Siberian lake Novosti, July 29, 2008 (in English) Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ↑ Putin orders oil pipeline shifted BBC News, April 26, 2006. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ↑ Work starts on Russian pipeline. BBC News April 28, 2006. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ↑ Saving the Sacred Sea New Internationalist, May 2, 2008. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ↑ Russia Inaugurates World's First Low Enriched Uranium Reserve International Atomic Energy Agency, December 17, 2010. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
- ↑ Tom Esslemont, 'Pearl of Siberia' draws investors BBC News, September 7, 2007. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Kozhov, M. M. Lake Baikal and Its Life. Monographiae biologicae, v. 11. The Hague: W. Junk, 1963. OCLC 660805
- Matthiessen, Peter, and Boyd Norton. Baikal: Sacred Sea of Siberia. San Francisco: Sierra Club Books, 1992. ISBN 0871565846
- Thomson, Peter. Sacred Sea: A Journey to Lake Baikal. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2007. ISBN 0195170512
- Van Rensbergen, P., et al., 2002. Sub-lacustrine mud volcanoes and cold seeps caused by dissociation of gas hydrates in Lake Baikal. Geology 30(7): 631-634.
External links
All links retrieved October 21, 2022.
- Lake Baikal: World's Largest, Deepest Lake Live Science
- Lake Baikal UNESCO World Heritage Center
- Lake Baikal: World's Deepest Lake
- Lake Baikal: Earth’s deepest, oldest lake Earth Sky
| |||||||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.