Difference between revisions of "Watershed" - New World Encyclopedia
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Copyedited}}{{Paid}}{{Approved}}{{Images OK}}{{Submitted}} |
| − | '''Watershed''' | + | '''Watershed''' has traditionally designated the dividing line, or drainage divide, between two [[drainage basin]]s; that is, the ridge of high land or boundary separating regions that are drained by different river systems or bodies of water ([[lake]], [[sea]], etc.). Some uses of the term keep this meaning, but in [[North America]]n geographical usage watershed has come to be used interchangeably with the definition for drainage basin. In other words, watershed often refers to the entire region or area where all the waters drain into the same body of water, rather than just the elevation separating the waters flowing into different basins. Both are accepted definitions. |
| − | + | People live particular watersheds (in the sense of drainage basin), and each of these watersheds are unique, based on the specific size, terrain, [[soil]], land use, flora and fauna, climate, and so forth. [[Human]] activities impact watersheds, whether these activities be agricultural, residential, or commercial. For example, pesticides from [[agriculture|agricultural]] activities in the highlands may flow down to smaller rivers and then to major rivers or lakes. Today, there is a tendency to manage watershed areas in order to provide for human needs and for a healthy environment. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The concept of watersheds helps to promote an awareness of how our activities affect a wider group of humanity. Smaller watersheds are part of progressively larger watersheds. Ultimately, water in over 47 percent of the earth's land mass actually flows into the [[Atlantic Ocean]], and other areas flow into the Pacific, Arctic, and so forth. | |
| − | + | {{toc}} | |
| − | + | The term watershed comes from an old term ''shedding'', meaning "splitting" or "dividing." It is commonly used in the [[English language]] to refer to a turning point or a momentous event that marks a change of course, such as a "watershed moment in history." | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Terminology== |
| − | + | A ''drainage basin'' is a region of land where [[water]] from [[rain]] or [[snow]] melt drains downhill into a body of water, such as a [[river]], [[lake]], [[dam]], [[estuary]], [[wetland]], [[sea]] or [[ocean]]. The drainage basin includes both the streams and rivers that convey the water as well as the land surfaces from which water drains into those channels. The drainage basin acts like a funnel—collecting all the water within the area covered by the basin and channeling it into a waterway. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Other terms that can be used to describe the same concept are ''[[catchment]]'', ''catchment area'', ''catchment basin'', ''drainage area'', ''river basin'' and ''water basin''. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:Ohiorivermap.png|thumb|right|Map of the Ohio River Watershed (Drainage basin), part of the [[Mississippi River]] drainage basin.]] | |
| + | One can subdivide basins as well. The Upper Paraguay River Basin is the upper sub-basin of the Paraguay Basin, which is part of the 2.8 million square kilometer Parana Basin (or Parana-Paraguay Basin). The Parana Basin in turn is a sub-basin of the Rio de la Plata Basin (a region that includes the Uruguay Sub-Basin, draining the Uruguay River, and the Salado Sub-Basin). | ||
| − | + | Each drainage basin is separated topographically from adjacent basins by a ridge, hill, or mountain, which is known as a [[water divide]] or a ''watershed''. Water on one or the other side of that divide either flows toward or away from a particular basin. For example, there is a slightly pronounced rise in Brazil, the "Chapada dos Parecis," that divides the headwaters of the Paraguay River from the headwaters of some Amazon tributaries. Water on one side flows into the Paraguay Basin and the other side into the Amazon basin. Farther east, the Chapada dos Guimaraes forms another physical barrier between the Amazon and Paraguay River Basins. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Especially in North American usage, however, ''watershed'' refers to the drainage basin itself. For example, one college text defines watershed in this manner (Smith 1996): | |
| − | + | :"The land area contributing to the flow for any one stream is its ''basin''...These basins are also called watersheds. A ''watershed'' is a body of land bounded above by a ridge or water divide and below by the level at which the water drains from the basin." | |
| − | + | In defining watershed, Langbein and Iseri (1995) of the United States Geological Survey note these dual meanings of watershed and the potential problem of ambiguity: | |
| + | :"Watershed. The divide separating one drainage basin from another and in the past has generally been used to convey this meaning. However, over the years, use of the term to signify drainage basin or catchment area has come to predominate, although drainage basin is preferred. Drainage divide, or just divide, is used to denote the boundary between one drainage area and another. Used alone, the term "watershed" is ambiguous and should not be used unless the intended meaning is clear." | ||
| − | + | Watersheds, as drainage basins, can be large or small, such as the small pond on a person's property or the Amazon River Basin. The [[Atlantic Ocean]] drains approximately 47 percent of all land in the world. The [[Pacific Ocean]] drains just over 13 percent of the land in the world. The [[Indian Ocean]] drains around 13 percent of the Earth's land. The basin of the Arctic Sea drains most of northern Canada and Russia. The [[Southern Ocean]] drains [[Antarctica]], which is about eight percent of the Earth's land. [[Endorheic basin|Endorheic drainage basins]] are inland basins that do not drain into an ocean; around 18 percent of all land drains to endorheic lakes or seas. The largest of these consists of much of the interior of [[Asia]], and drains into the [[Caspian Sea]] and the [[Aral Sea]]. | |
| − | + | == Importance of watersheds == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Watersheds, as drainage basins, have been important historically in determining boundaries, particularly in regions where trade by water has been important. For example, the [[England|English]] crown gave the [[Hudson's Bay Company]] a monopoly on the [[Indian Trade]] in the entire [[Hudson Bay]] watershed, an area called [[Rupert's Land]]. The company later acquired the North American watershed of the [[Arctic Ocean]] (the [[North-Western Territory]]). These lands later became part of [[Canada]] as the [[Northwest Territories]], making up the vast majority of Canada's land area. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | [[Image:Mississippi River basin.jpg|thumb|300px|The [[Mississippi River]] drains the largest area of any [[United States|U.S.]] river, much of it [[agriculture|agricultural]] regions. Agricultural runoff and other water pollution that flows to the outlet is the cause of the [[dead zone (ecology)|dead zone]] in the [[Gulf of Mexico]].]] | ||
In [[hydrology]], the drainage basin is a logical unit of focus for studying the movement of water within the [[hydrological cycle]], because the majority of water that discharges from the basin outlet originated as [[Precipitation (meteorology)|precipitation]] falling on the basin. A portion of the water that enters the groundwater system beneath the drainage basin may flow towards the outlet of another drainage basin because groundwater flow directions do not always match those of their overlying drainage network. Measurement of the discharge of water from a basin may be made by a [[stream gauge]] located at the basin's outlet. | In [[hydrology]], the drainage basin is a logical unit of focus for studying the movement of water within the [[hydrological cycle]], because the majority of water that discharges from the basin outlet originated as [[Precipitation (meteorology)|precipitation]] falling on the basin. A portion of the water that enters the groundwater system beneath the drainage basin may flow towards the outlet of another drainage basin because groundwater flow directions do not always match those of their overlying drainage network. Measurement of the discharge of water from a basin may be made by a [[stream gauge]] located at the basin's outlet. | ||
| − | + | In [[ecology]], watersheds (as drainage basins) are important units. As water flows over the ground and along rivers it can pick up nutrients, sediment, and [[water pollution|pollutants]]. Like the water, they get transported towards the outlet of the basin, and can affect the ecological processes along the way as well as in the receiving water body. Modern usage of artificial [[fertilizer]]s, containing [[nitrogen]], [[phosphorus]], and [[potassium]], has affected the mouths of watersheds. The [[mineral]]s will be carried by the watershed to the mouth and accumulate there, disturbing the natural mineral balance. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | ||
| − | + | Because drainage basins are coherent entities in a hydrological sense, it has become common to manage water resources on the basis of individual basins. In the [[U.S. state]] of [[Minnesota]], governmental entities that perform this function are called [[watershed district]]s. In [[New Zealand]], they are called catchment boards. Comparable community groups based in Ontario, [[Canada]], are called [[Conservation Authority|conservation authorities]]. In North America this function is referred to as [[watershed management]]. | |
| − | + | ==References== | |
| − | + | * DeBarry, P. A. 2004. ''Watersheds: Processes, Assessment and Management.'' John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0471264237. | |
| − | + | * Langbein, W. B., and K. T. Iseri. 1995. [http://water.usgs.gov/wsc/glossary.html General introduction and hydrologic definitions. Manual of hydrology: Part 1. General surface-water techniques. Watershed] ''Washington, D.C. United States Government Printing Office, Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper 1541-A''. Retrieved December 19, 2007. | |
| − | + | * McCammon, B. P. 1994. [http://watershed.org/news/fall_94/terminology.html Recommended watershed terminology] ''Watershed Management Council''. Retrieved December 19, 2007. | |
| − | + | * Smith, R. L. 1996. ''Ecology and Field Biology'', 5th edition. New York: HarperCollins College Publishers. ISBN 0065009762. | |
| − | == | + | ==External links== |
| − | + | All links retrieved May 3, 2023. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * [http://water.usgs.gov/wsc ''Science in Your Watershed''] USGS. | |
| − | |||
| − | * [http://water.usgs.gov/wsc ''Science in Your Watershed''] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Life sciences]] | [[Category:Life sciences]] | ||
| − | [[Category:Geography]] | + | [[Category:Geography]][[Category:Ecology]] |
{{credit|Watershed|171231180|Drainage_basin|172064197}} | {{credit|Watershed|171231180|Drainage_basin|172064197}} | ||
Latest revision as of 23:19, 3 May 2023
Watershed has traditionally designated the dividing line, or drainage divide, between two drainage basins; that is, the ridge of high land or boundary separating regions that are drained by different river systems or bodies of water (lake, sea, etc.). Some uses of the term keep this meaning, but in North American geographical usage watershed has come to be used interchangeably with the definition for drainage basin. In other words, watershed often refers to the entire region or area where all the waters drain into the same body of water, rather than just the elevation separating the waters flowing into different basins. Both are accepted definitions.
People live particular watersheds (in the sense of drainage basin), and each of these watersheds are unique, based on the specific size, terrain, soil, land use, flora and fauna, climate, and so forth. Human activities impact watersheds, whether these activities be agricultural, residential, or commercial. For example, pesticides from agricultural activities in the highlands may flow down to smaller rivers and then to major rivers or lakes. Today, there is a tendency to manage watershed areas in order to provide for human needs and for a healthy environment.
The concept of watersheds helps to promote an awareness of how our activities affect a wider group of humanity. Smaller watersheds are part of progressively larger watersheds. Ultimately, water in over 47 percent of the earth's land mass actually flows into the Atlantic Ocean, and other areas flow into the Pacific, Arctic, and so forth.
The term watershed comes from an old term shedding, meaning "splitting" or "dividing." It is commonly used in the English language to refer to a turning point or a momentous event that marks a change of course, such as a "watershed moment in history."
Terminology
A drainage basin is a region of land where water from rain or snow melt drains downhill into a body of water, such as a river, lake, dam, estuary, wetland, sea or ocean. The drainage basin includes both the streams and rivers that convey the water as well as the land surfaces from which water drains into those channels. The drainage basin acts like a funnel—collecting all the water within the area covered by the basin and channeling it into a waterway.
Other terms that can be used to describe the same concept are catchment, catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin and water basin.
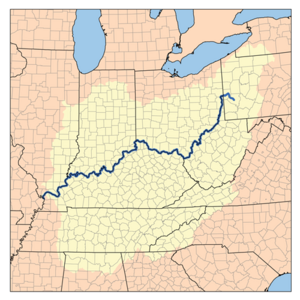
One can subdivide basins as well. The Upper Paraguay River Basin is the upper sub-basin of the Paraguay Basin, which is part of the 2.8 million square kilometer Parana Basin (or Parana-Paraguay Basin). The Parana Basin in turn is a sub-basin of the Rio de la Plata Basin (a region that includes the Uruguay Sub-Basin, draining the Uruguay River, and the Salado Sub-Basin).
Each drainage basin is separated topographically from adjacent basins by a ridge, hill, or mountain, which is known as a water divide or a watershed. Water on one or the other side of that divide either flows toward or away from a particular basin. For example, there is a slightly pronounced rise in Brazil, the "Chapada dos Parecis," that divides the headwaters of the Paraguay River from the headwaters of some Amazon tributaries. Water on one side flows into the Paraguay Basin and the other side into the Amazon basin. Farther east, the Chapada dos Guimaraes forms another physical barrier between the Amazon and Paraguay River Basins.
Especially in North American usage, however, watershed refers to the drainage basin itself. For example, one college text defines watershed in this manner (Smith 1996):
- "The land area contributing to the flow for any one stream is its basin...These basins are also called watersheds. A watershed is a body of land bounded above by a ridge or water divide and below by the level at which the water drains from the basin."
In defining watershed, Langbein and Iseri (1995) of the United States Geological Survey note these dual meanings of watershed and the potential problem of ambiguity:
- "Watershed. The divide separating one drainage basin from another and in the past has generally been used to convey this meaning. However, over the years, use of the term to signify drainage basin or catchment area has come to predominate, although drainage basin is preferred. Drainage divide, or just divide, is used to denote the boundary between one drainage area and another. Used alone, the term "watershed" is ambiguous and should not be used unless the intended meaning is clear."
Watersheds, as drainage basins, can be large or small, such as the small pond on a person's property or the Amazon River Basin. The Atlantic Ocean drains approximately 47 percent of all land in the world. The Pacific Ocean drains just over 13 percent of the land in the world. The Indian Ocean drains around 13 percent of the Earth's land. The basin of the Arctic Sea drains most of northern Canada and Russia. The Southern Ocean drains Antarctica, which is about eight percent of the Earth's land. Endorheic drainage basins are inland basins that do not drain into an ocean; around 18 percent of all land drains to endorheic lakes or seas. The largest of these consists of much of the interior of Asia, and drains into the Caspian Sea and the Aral Sea.
Importance of watersheds
Watersheds, as drainage basins, have been important historically in determining boundaries, particularly in regions where trade by water has been important. For example, the English crown gave the Hudson's Bay Company a monopoly on the Indian Trade in the entire Hudson Bay watershed, an area called Rupert's Land. The company later acquired the North American watershed of the Arctic Ocean (the North-Western Territory). These lands later became part of Canada as the Northwest Territories, making up the vast majority of Canada's land area.

In hydrology, the drainage basin is a logical unit of focus for studying the movement of water within the hydrological cycle, because the majority of water that discharges from the basin outlet originated as precipitation falling on the basin. A portion of the water that enters the groundwater system beneath the drainage basin may flow towards the outlet of another drainage basin because groundwater flow directions do not always match those of their overlying drainage network. Measurement of the discharge of water from a basin may be made by a stream gauge located at the basin's outlet.
In ecology, watersheds (as drainage basins) are important units. As water flows over the ground and along rivers it can pick up nutrients, sediment, and pollutants. Like the water, they get transported towards the outlet of the basin, and can affect the ecological processes along the way as well as in the receiving water body. Modern usage of artificial fertilizers, containing nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, has affected the mouths of watersheds. The minerals will be carried by the watershed to the mouth and accumulate there, disturbing the natural mineral balance.
Because drainage basins are coherent entities in a hydrological sense, it has become common to manage water resources on the basis of individual basins. In the U.S. state of Minnesota, governmental entities that perform this function are called watershed districts. In New Zealand, they are called catchment boards. Comparable community groups based in Ontario, Canada, are called conservation authorities. In North America this function is referred to as watershed management.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- DeBarry, P. A. 2004. Watersheds: Processes, Assessment and Management. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0471264237.
- Langbein, W. B., and K. T. Iseri. 1995. General introduction and hydrologic definitions. Manual of hydrology: Part 1. General surface-water techniques. Watershed Washington, D.C. United States Government Printing Office, Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper 1541-A. Retrieved December 19, 2007.
- McCammon, B. P. 1994. Recommended watershed terminology Watershed Management Council. Retrieved December 19, 2007.
- Smith, R. L. 1996. Ecology and Field Biology, 5th edition. New York: HarperCollins College Publishers. ISBN 0065009762.
External links
All links retrieved May 3, 2023.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.