|
|
| (44 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | {{Started}}{{Contracted}} | + | {{Images OK}}{{submitted}}{{approved}}{{Paid}}{{Copyedited}} |
| | + | {{Infobox Settlement |
| | + | <!--See Template:Infobox settlement for additional fields that may be available—> |
| | + | <!--See the Table at Infobox settlement for all fields and descriptions of usage—> |
| | + | <!-- Basic info ----------------> |
| | + | |name=Manhattan<!-- at least one of the first two fields must be filled in —> |
| | + | |official_name=New York County |
| | + | |other_name= |
| | + | |native_name=<!-- if different from the English name —> |
| | + | |nickname= |
| | + | |settlement_type=[[Borough (New York City)|Borough]] of New York City <!-- e.g. Town, Village, City, etc.—> |
| | + | |total_type=<!-- to set a non-standard label for total area and population rows —> |
| | + | |motto= |
| | + | <!-- images and maps -----------> |
| | + | |image_skyline=NYC wideangle south from Top of the Rock.jpg |
| | + | |imagesize= |
| | + | |image_caption=[[Midtown Manhattan]] as seen from the [[GE Building]]. |
| | + | |image_flag= |
| | + | |flag_size= |
| | + | |image_sea= |
| | + | |seal_size= |
| | + | |image_shield= |
| | + | |shield_size= |
| | + | |image_blank_emblem= |
| | + | |blank_emblem_type= |
| | + | |blank_emblem_size= |
| | + | |image_map=Manhattan.gif |
| | + | |mapsize=175px |
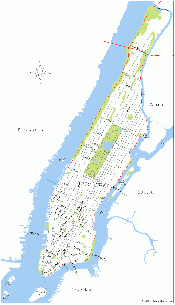
| | + | |map_caption=The Borough of Manhattan, highlighted in yellow, lies between the East River and the Hudson River. |
| | + | |pushpin_map=<!-- the name of a location map as per http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template:Location_map —> |
| | + | |pushpin_label_position=<!-- the position of the pushpin label: left, right, top, bottom, none —> |
| | + | |pushpin_map_caption= |
| | + | |pushpin_mapsize= |
| | + | <!-- Location ------------------> |
| | + | |coordinates_region=US-NY |
| | + | |subdivision_type=Country |
| | + | |subdivision_name=[[United States]] |
| | + | |subdivision_type1=State |
| | + | |subdivision_name1=[[New York]] |
| | + | |subdivision_type2=County |
| | + | |subdivision_name2=New York County |
| | + | |subdivision_type3=City |
| | + | |subdivision_name3=[[New York City]] |
| | + | <!-- Smaller parts (e.g. boroughs of a city) and seat of government —> |
| | + | |seat_type= |
| | + | |seat= |
| | + | |parts_type= |
| | + | |parts_style=<!--=list (for list), coll (for collapsed list), para (for paragraph format) |
| | + | Default is list if up to 5 items, coll if more than 5—> |
| | + | |parts=<!-- parts text, or header for parts list —> |
| | + | |p1= |
| | + | |p2=<!-- etc. up to p50: for separate parts to be listed—> |
| | + | <!-- Politics -----------------> |
| | + | |government_footnotes= |
| | + | |government_type= [[Borough (New York City)]] |
| | + | |leader_title=[[Borough President]] |
| | + | |leader_name=[[Scott Stringer]] (D)<br />— ''(Borough of Manhattan)'' |
| | + | |leader_title1=[[New York County District Attorney|District Attorney]] |
| | + | |leader_name1=[[Cyrus Vance, Jr.]]<br />— ''(New York County)'' |
| | + | |established_title=Settled |
| | + | |established_date=1624 |
| | + | <!-- Area ---------------------> |
| | + | |area_magnitude= |
| | + | |unit_pref= |
| | + | |area_footnotes= |
| | + | |area_total_sq_mi=33.77 |
| | + | |area_land_sq_mi=22.96 |
| | + | |area_water_sq_mi=10.81 |
| | + | |area_water_percent= |
| | + | <!-- Elevation --------------------------> |
| | + | |elevation_footnotes= |
| | + | |elevation_m= |
| | + | |elevation_ft= |
| | + | |elevation_max_m= |
| | + | |elevation_max_ft= |
| | + | |elevation_min_m= |
| | + | |elevation_min_ft= |
| | + | <!-- Population -----------------------> |
| | + | |population_as_of= 2010 |
| | + | |population_footnotes= |
| | + | |population_note= |
| | + | |population_total=1,585,873 |
| | + | |population_density_sq_mi=70951 |
| | + | |population_blank1_title = [[Demonym]] |
| | + | |population_blank1 = Manhattanite |
| | + | <!-- General information ---------------> |
| | + | |timezone= [[Eastern Standard Time Zone|EST]] |
| | + | |utc_offset= -5 |
| | + | |timezone_DST= [[Eastern Daylight Time Zone|EDT]] |
| | + | |utc_offset_DST= -4 |
| | + | |latd=40|latm=44|latNS=N |
| | + | |longd=73|longm=59|longEW=W |
| | + | <!-- Area/postal codes & others --------> |
| | + | |postal_code_type=<!-- enter ZIP code, Postcode, Post code, Postal code... —> |
| | + | |postal_code= |
| | + | |area_code= |
| | + | |website=[http://www.mbpo.org/ Official Website of the Manhattan Borough President] |
| | + | |footnotes= |
| | + | }} |
| | | | |
| − | {{otheruses}}
| + | '''Manhattan''' is a borough of [[New York City]], [[New York]], [[United States|USA]], coterminous with '''New York County'''. It is the most densely populated area in the United States. The Island of Manhattan is the largest section of the borough, which also includes several smaller islands and a small section of the mainland adjacent to [[The Bronx]]. The name ''Manhattan'' derives from the word ''Manna-hata,'' as written in the 1609 logbook of Robert Juet, an officer on [[Henry Hudson]]'s yacht ''Halve Maen'' (Half Moon). |
| − | {| class="toccolours" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" style="width: 250px; font-size: 90%; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; float: right;"
| + | {{toc}} |
| − | |+ style="margin-left: inherit; font-size: large;" |'''Manhattan'''
| + | A commercial, financial, and cultural center of the city, Manhattan has many famous landmarks, tourist attractions, museums, and universities. It is also home to the headquarters of the [[United Nations]] and the seat of city government. Manhattan has the largest central business district in the United States. It is the site of both the [[New York Stock Exchange]] and [[NASDAQ]], and is the home to the largest number of corporate headquarters in the nation. |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! colspan="2" bgcolor="#efefef" align="center"| Location
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | !colspan="2" align="center" | [[Image:Manhattan Highlight New York City Map Julius Schorzman.png|250px|]]
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |colspan="2" align="center" | <small>The Borough of Manhattan, highlighted in yellow, lies between the East River and the Hudson River.</small>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | !colspan="2" bgcolor="#efefef"|Government
| |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | |[[County]]:||New York
| |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | |[[Borough president]]:||[[Scott Stringer]]
| |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | !colspan="2" bgcolor="#efefef"|Demographics
| |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | |[[Population]]:||1,537,195
| |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | |[[Population density]]:||66,940/mi² (25,846/km²)
| |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | !colspan="2" bgcolor="#efefef"|Geography<ref name=NYCensusRankings/>
| |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | |[[Area]]:||33.77 mi² (87.46 km²)
| |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | |[[Land]]:||22.96 mi² (59.47 km²)
| |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | |[[Water]]:||10.81 mi² (28.00 km²)
| |
| − | |- style="vertical-align: top;"
| |
| − | |[[Geographic coordinate system|Coordinates]]:||40° 43′ 42″ N, 73° 59′ 39″ W
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | '''Manhattan''' is a borough of [[New York City]], [[New York]], [[United States|USA]], coterminous with '''New York County'''. With a United States Census, year 2000, of 1,537,195<ref name=NYCensusRankings>[http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/GCTTable?_bm=y&-geo_id=04000US36&-_box_head_nbr=GCT-PH1-R&-ds_name=DEC_2000_SF1_U&-_lang=en&-redoLog=false&-mt_name=PEP_2006_EST_GCTT1_ST2&-format=ST-7S&-_sse=on New York—Place and County Subdivision], [[United States Census Bureau]], accessed May 1, 2007.</ref> packed into a land area of 22.96 square miles (59.47 km²), it is the most densely populated county in the United States, with almost 67,000 residents per square mile (almost 26,000/km²).<ref>[http://www.ny.frb.org/regional/profile_nyc.html District Profile: New York City], [[Federal Reserve Bank of New York]]. Accessed September 4, 2006.</ref> The Island of Manhattan is the largest section of the borough, which also includes several smaller islands and a small section of the mainland adjacent to The Bronx. | |
| − | | |
| − | A commercial, financial, and cultural center of the city, Manhattan has many famous landmarks, tourist attractions, museums, and universities. It is also home to the headquarters of the [[United Nations]] and the seat of city government. Manhattan has the largest central business district in the United States. It is the site of both the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ, and is the home to the largest number of corporate headquarters in the nation. | |
| − | | |
| − | The name ''Manhattan'' derives from the word Manna-hata, as written in the 1609 logbook of Robert Juet, an officer on [[Henry Hudson]]'s yacht ''Halve Maen'' (Half Moon).<ref>[http://www.newsday.com/community/guide/lihistory/ny-history-hs216a1v,0,919043.story?coll=ny-lihistory-navigation Full Text of Robert Juet's Journal: From the collections of the New York Historical Society, Second Series, 1841 log book], ''[[Newsday]]''. Accessed May 16, 2007.</ref> A 1610 map depicts the name Manahata twice, on both the west and east sides of the Mauritius River (later named the [[Hudson River]]). The word "Manhattan" has been translated as "island of many hills" from the Lenape language.<ref name=Mannahatta>Holloway, Marguerite. [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9802E1D71F3CF935A25756C0A9629C8B63 "URBAN TACTICS; I'll Take Mannahatta"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', May 16, 2004, accessed April 30, 2007. "He could envision what Henry Hudson saw in 1609 as he sailed along Mannahatta, which in the Lenape dialect most likely meant ''island of many hills.'''</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| | ==History== | | ==History== |
| | ===Colonial=== | | ===Colonial=== |
| − | [[Image:CastelloMap.JPG|250px|right|thumb|Lower Manhattan in 1660, when it was part of New Amsterdam. The large structure toward the tip of the island is Fort Amsterdam.]] | + | [[Image:CastelloMap.JPG|250px|left|thumb|Lower Manhattan in 1660, when it was part of New Amsterdam. The large structure toward the tip of the island is Fort Amsterdam.]] |
| − | {{main|History of New York City}}
| |
| − | The area that is now Manhattan was long inhabited by the Lenape. In 1524, Lenape in canoes met Giovanni da Verrazzano, the first European explorer to pass New York Harbor, though he did not enter the harbor past the Narrows.<ref>Sullivan, Dr. James. [http://www.usgennet.org/usa/ny/state/his/bk1/ch3/pt1.html "The History of New York State: Book I, Chapter III"], USGenNet, accessed May 1, 2007. "There is satisfactory evidence that Giovanni da Verrazzano sailed into the outer harbor of New York in 1524.</ref> It was not until the voyage of [[Henry Hudson]], an Englishman who worked for the Dutch East India Company, that the area was mapped.<ref>{{cite book |title=New York: the World's Capital City, Its Development and Contributions to Progress |author=Rankin, Rebecca B., Cleveland Rodgers |publisher=Harper |year=1948}}</ref> Hudson discovered Manhattan Island on September 11, 1609, and continued up the river that bears his name, the [[Hudson River]], until he arrived at the site of present day Albany.<ref name=SciAm>[http://www.ulster.net/~hrmm/diglib/sciamer/hhudson/hhudson.htm "Henry Hudson and His Exploration"] ''[[Scientific American]]'', September 25, 1909, accessed May 1, 2007. "This was a vain hope, however, and the conviction must finally have come to the heart of the intrepid adventurer that once again he was foiled in his repeated quest for the northwest passage … On the following day the “Half Moon” let go her anchor inside of Sandy Hook. The week was spent in exploring the bay with a shallop, or small boat, and “they found a good entrance
| |
| − | between two headlands” (the Narrows) “and thus entered on the 11th of September into as fine a river as can be found.”"</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | A permanent European presence in New Netherland began in 1624 with the founding of a Dutch fur trading settlement on Governors Island. In 1625, construction was started on a citadel and a fort Amsterdam on Manhattan Island later called New Amsterdam (''Nieuw Amsterdam'').<ref>[http://www.cr.nps.gov/nr/travel/kingston/colonization.htm Dutch Colonies], [[National Park Service]]. Accessed May 19, 2007. "Sponsored by the West India Company, 30 families arrived in North America in 1624, establishing a settlement on present-day Manhattan."</ref><ref name=Tolerance>[http://tolerancepark.org/_wsn/page5.html Tolerance Park Historic New Amsterdam on Governors Island], Tolerance Park. Accessed May 12, 2007. See Legislative Resolutions Senate No. 5476 and Assembly No. 2708.</ref> Manhattan Island was chosen as the site of Fort Amsterdam, a citadel for the protection of the new arrivals; its 1625 establishment is recognized as the birth date of New York City.<ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/dcas/html/features/greenbook_seal_flag.shtml City Seal and Flag], [[New York City]], accessed May 13, 2007. "Date: Beneath the horizontal laurel branch the date 1625, being the year of the establishment of New Amsterdam."</ref> In 1626, Peter Minuit acquired Manhattan from native people in exchange for trade goods, often said to be worth $24.<ref>[http://teachpol.tcnj.edu/amer_pol_hist/fi/00000002.htm Letter of 1626 stating that Manhattan Island had been purchased for the value of 60 guilders], [[The College of New Jersey]]. Accessed April 26, 2007. The 60 guilders have been traditionally converted to about $24. If the money had been invested at anything above a 6.25% return (essentially a bond's current yield), it would be worth over $250 billion today, which exceeds Manhattan's estimated value of $200 billion. [http://oregonstate.edu/Dept/pol_sci/fac/sahr/infcf16652006.pdf Historical Inflation Data] (PDF), [[Oregon State University]]. It is virtually impossible to make a reasonable comparison of societies, values and price structures dated back to 1626, and 2006. The source warns that data of 1913 and earlier are highly approximative. Besides, the data, which had been tabulated, based on John J. McCusker's article ''How much is that in real money'' (Processing American Antiquarian Society 2001 ISBN 1-929545-01-0) started from 1665—40 years after the time, when the trade was settled. However, these numbers give the feeling of the price paid for Manhattan.</ref>
| + | The area that is now Manhattan was long inhabited by the [[Lenape]] tribe. In 1524, Lenape, in [[canoe]]s, met Giovanni da Verrazzano, the first European explorer to pass [[New York Harbor]]. <ref>Dr. James Sullivan, "The History of New York State: Book I, Chapter III", ''www.USGenNet.org''. "There is satisfactory evidence that [[Giovanni da Verrazzano]] sailed into the outer harbor of New York in 1524.</ref> It was not until the voyage of [[Henry Hudson]], an Englishman who worked for the [[Dutch East India Company]], that the area was [[cartography|mapped]].<ref>Rebecca B. Rankin, and Cleveland Rodgers. ''New York: the World's Capital City, Its Development and Contributions to Progress.'' (Harper, 1948).</ref> Hudson discovered Manhattan Island on September 11, 1609 and continued up the river that bears his name until he arrived at the site of present day [[Albany]].<ref>[http://www.ulster.net/~hrmm/diglib/sciamer/hhudson/hhudson.htm "Henry Hudson and His Exploration," ''[[Scientific American]]'', September 25, 1909]. ''www.ulster.net''. Retrieved May 1, 2007.</ref> |
| | | | |
| − | In 1647, Peter Stuyvesant was appointed as the last Dutch Director General of the colony.<ref>Williams, Jasmin K. [http://www.nypost.com/seven/11222006/news/cextra/new_york___the_empire_state_cextra_jasmin_k__williams.htm?page=0 "New York - The Empire States"], ''[[The New York Post]]'', November 22, 2006. Accessed May 19, 2007. "In 1647, Dutch leader Peter Stuyvesant arrived with an iron fist to put an end to the colony's rampant crime and restore order."</ref> The colony was granted self-government in 1652 and New Amsterdam was formally incorporated as a city on February 2, 1653.<ref>[http://www.nyccouncil.info/tools/about_council.cfm About the Council], [[New York City Council]]. Accessed May 18, 2007.</ref> In 1664, the British conquered the area and renamed it "New York" after the English [[James II of England|Duke of York and Albany]].<ref>[http://www.dos.state.ny.us/kidsroom/nysfacts/counties.html The Origins of New York State's County Names], [[New York]] Department of State, accessed April 27, 2007. "New York: in honor of the Duke of York.</ref> Stuyvesant and his council negotiated 24 articles of provisional transfer with the British which sought to guarantee New Netherlanders liberties, including [[freedom of religion]], under British rule.<ref>Griffis, William Elliot. [http://en.wikisource.org/wiki/The_Story_of_New_Netherland/Chapter_15 "The Story of New Netherland" Chapter XV: The Fall of New Netherland], ''[[Houghton Mifflin Company]]'', 1909. "In religious matters, Article VIII of the capitulation read, “The Dutch shall enjoy the liberty of their consciences in Divine worship and in Church government.”"</ref><ref>[http://tolerancepark.org/_wsn/page2.html Tolerance Park Historic New Amsterdam on Governors Island], Tolerance Park, accessed April 26, 2007.</ref>
| + | A permanent European presence in "New Netherland" began in 1624 with the founding of a Dutch fur trading settlement on Governors Island. In 1625, Manhattan Island was chosen as the site of Fort Amsterdam, a [[citadel]] for the protection of the new arrivals; establishment is recognized as the birth date of New York City.<ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/dcas/html/features/greenbook_seal_flag.shtml City Seal and Flag]. ''www.nyc.gov''. [[New York City]]. Retrieved May 13, 2007.</ref> In 1626, Peter Minuit acquired Manhattan from native people in exchange for trade goods, often said to be worth $24. |
| | | | |
| − | ===American Revolution and the early United States===
| + | In 1647, [[Peter Stuyvesant]] was appointed as the last Dutch Director General of the colony.<ref>Jasmin K. Williams, [http://www.nypost.com/seven/11222006/news/cextra/new_york___the_empire_state_cextra_jasmin_k__williams.htm?page=0 "New York - The Empire States," ''The New York Post'', November 22, 2006]. ''www.nypost.com''. Retrieved May 19, 2007.</ref> The colony was granted self-government in 1652 and New Amsterdam was formally incorporated as a city on February 2, 1653.<ref> About the Council, New York City Council. ''www.nycouncil.info''. </ref> In 1664, the British conquered the area and renamed it "New York" after the English [[James II of England|Duke of York and Albany]]. Stuyvesant and his council negotiated 24 articles of provisional transfer with the British which sought to guarantee New Netherlanders liberties, including [[freedom of religion]], under British rule.<ref> Tolerance Park Historic New Amsterdam on Governors Island. ''TolerancePark.org''.</ref> |
| − | Manhattan was at the heart of the New York Campaign, a series of major battles in the early [[American Revolutionary War]]. The Continental Army was forced to abandon Manhattan after the disastrous Battle of Fort Washington on November 16, 1776. The city became the British political and military center of operations in North America for the remainder of the war.<ref>[http://www.nycgovparks.org/sub_your_park/historical_signs/hs_historical_sign.php?id=8258 Fort Washington Park], [[New York City Department of Parks and Recreation]]. Accessed May 18, 2007.</ref> Manhattan was greatly damaged by the Great Fire of New York during the [[Great Britain|British]] military rule that followed. British occupation lasted until November 25, 1783, when [[George Washington]] returned to Manhattan, as the last British forces left the city.<ref>[http://www.nycgovparks.org/sub_newsroom/daily_plants/daily_plant_main.php?id=19733 "Happy Evacuation Day"], [[New York City Department of Parks and Recreation]], November 23, 2005. Accessed May 18, 2007.</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | [[Image:Federal Hall - Washington Statue.jpg|thumb|250px|left|John Quincy Adams Ward's statue of [[George Washington]] in front of Federal Hall, on the site where Washington was inaugurated as the first [[President of the United States|U.S. President]].]]
| + | ===American Revolution and early United States=== |
| − | From January 11, 1785 to Autumn 1788, New York City was the fifth of five capitals under the Articles of Confederation, with the Continental Congress residing at New York City Hall, then at Fraunces Tavern. New York was the first capital under the newly enacted [[United States Constitution|Constitution of the United States]], from March 4, 1789 to August 12, 1790 at Federal Hall.<ref>[http://www.senate.gov/reference/reference_item/Nine_Capitals_of_the_United_States.htm The Nine Capitals of the United States]. [[United States Senate]] Historical Office. Accessed June 9, 2005. Based on Fortenbaugh, Robert, ''The Nine Capitals of the United States'', York, PA: Maple Press, 1948.</ref>
| + | Manhattan was at the heart of the New York Campaign, a series of major battles in the early [[American Revolutionary War]]. The Continental Army was forced to abandon Manhattan after the disastrous Battle of Fort Washington on November 16, 1776. The city became the British political and military center of operations in North America for the remainder of the war.<ref>[http://www.nycgovparks.org/sub_your_park/historical_signs/hs_historical_sign.php?id=8258 Fort Washington Park]. ''www.nycgovparks.org''. Retrieved May 18, 2007.</ref> Manhattan was greatly damaged by the Great Fire of New York during the [[Great Britain|British]] military rule that followed. British occupation lasted until November 25, 1783, when [[George Washington]] returned to Manhattan, as the last British forces left the city. |
| | | | |
| − | ===19th century growth===
| + | [[Image:Federal Hall - Washington Statue.jpg|thumb|200px|left|Statue of [[George Washington]] in front of Federal Hall, on the site where Washington was inaugurated as the first [[President of the United States|U.S. President]].]] |
| − | New York grew as an economic center, first as a result of [[Alexander Hamilton]]'s policies and practices as the first [[Secretary of the Treasury]] and, later, with the opening of the [[Erie Canal]] in 1825, which connected the Atlantic port to the vast agricultural markets of the [[Mid-west]]ern United States and [[Canada]]. By 1835, New York City had surpassed [[Philadelphia]] as the largest city in the United States.
| + | From January 11, 1785 to Autumn 1788, New York City was the fifth of five U.S. capitals under the [[Articles of Confederation]], with the [[Continental Congress]] residing at New York City Hall, then at Fraunces Tavern. New York was the first capital under the newly enacted [[United States Constitution|Constitution of the United States]], from March 4, 1789 to August 12, 1790 at Federal Hall.<ref>[http://www.senate.gov/reference/reference_item/Nine_Capitals_of_the_United_States.htm The Nine Capitals of the United States, [[United States Senate]] Historical Office]. ''www.senate.gov''. Retrieved June 9, 2005. Based on Robert Fortenbaugh. ''The Nine Capitals of the United States.'' (York, PA: Maple Press, 1948).</ref> |
| | | | |
| − | [[Tammany Hall]] began to grow in influence with the support of many of the immigrant [[Irish people|Irish]], culminating in the election of the first Tammany mayor, [[Fernando Wood]], in 1854. Tammany Hall, a [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic Party]] [[political machine]] dominated local politics for decades. [[Central Park]], which opened to the public in 1858, became the first landscaped park in an American city and the nation's first public park.<ref>Blair, Cynthia. [http://www.newsday.com/about/ny-ihiny011405story,0,2798382.htmlstory "1858: Central Park Opens"], ''[[Newsday]]''. Accessed May 29, 2007. "Between 1853 and 1856, city commissioners purchased more than 700 acres from 59th Street to 106th Street between Fifth and Eighth Avenues to create Central Park, the nation’s first public park as well as its first landscaped park."</ref><ref>Rybczynski , Witold. [http://www.smithsonianmagazine.com/issues/2003/july/olmsteds.php "Olmsted's Triumph"], ''[[Smithsonian (magazine)]]'', July 2003. Accessed May 29, 2007. "By 1876, landscape designer Frederick Law Olmsted and architect Calvert Vaux had transformed the swampy, treeless 50 blocks between Harlem and midtown Manhattan into the first landscaped park in the United States."</ref> | + | ===Nineteenth century growth=== |
| | + | New York grew as an economic center, first as a result of [[Alexander Hamilton]]'s policies and practices as the first Secretary of the Treasury and, later, with the opening of the [[Erie Canal]] in 1825, which connected New York's Atlantic port to the vast [[agricultural]] producers of the mid-western United States and [[Canada]]. By 1835, New York City had surpassed [[Philadelphia]] as the largest city in the United States. |
| | | | |
| − | During the [[American Civil War]], the city's strong commercial ties to the [[American South|South]], its growing immigrant population, anger about [[conscription]] and resentment at those who could afford to pay $300 to avoid service, led to resentment against Lincoln's war policies, culminating in the three-day long [[New York Draft Riots]] of July 1863, one of the worst incidents of [[civil disorder]] in American history, with an estimated 119 participants and passersby killed.<ref>Ward, Geoffrey C. [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9404E3DA1139F935A35753C1A9649C8B63 "Gangs of New York"], a review of ''[[Paradise Alley]]'' by [[Kevin Baker]], ''[[The New York Times]]'', October 6, 2002. Accessed May 29, 2007. "The New York draft riots remain the worst civil disturbance in American history: according to the historian Adrian Cook, 119 people are known to have been killed, mostly rioters or onlookers who got too close when federal troops, brought back from the battlefield to restore order, started shooting."</ref>
| + | In politics, [[Tammany Hall]] began to grow in influence with the support of many of the immigrant Irish, culminating in the election of the first Tammany mayor, Fernando Wood, in 1854. The [[Democratic Party]] political machine dominated local politics for decades. Central Park, which opened to the public in 1858, became the first landscaped park in an American city and the nation's first public park.<ref>Witold Rybczynski, [http://www.smithsonianmagazine.com/issues/2003/july/olmsteds.php "Olmsted's Triumph," ''[[Smithsonian (magazine)]]'', July 2003]. Retrieved May 29, 2007.</ref> |
| | | | |
| − | [[Image:Nast-Tammany.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Thomas Nast]] denounces Tammany as a ferocious tiger killing democracy; the tiger image caught on.]] | + | During the [[American Civil War]], the city's strong commercial ties to the South, its growing immigrant population, anger about [[conscription]] and resentment at those who could afford to pay $300 to avoid service, led to resentment against Lincoln's war policies, culminating in the three-day long New York Draft Riots of July 1863, one of the worst incidents of civil disorder in American history, with an estimated 119 participants and passersby killed.<ref>Geoffrey C. Ward, [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9404E3DA1139F935A35753C1A9649C8B63 "Gangs of New York," a review of ''Paradise Alley'' by Kevin Baker, ''[[The New York Times]]'', October 6, 2002]. ''query.nytimes.com''.Retrieved May 29, 2007.</ref> |
| − | After the Civil War, the rate of immigration from Europe grew steeply, and New York became the first stop for millions seeking a new and better life in the United States, a role acknowledged by the dedication of the [[Statue of Liberty]] on October 28, 1886, a gift from the people of France.<ref>[http://www.nps.gov/archive/stli/prod02.htm Statue of Liberty], [[National Park Service]]. Accessed May 17, 2007.</ref><ref>[http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9B0DE3DE1E3FF935A35753C1A961948260&n=Top%2fReference%2fTimes%20Topics%2fSubjects%2fS%2fStatue%20of%20Liberty "New Jerseyans' Claim To Liberty I. Rejected"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', October 6, 1987. Accessed May 19, 2007. "The Supreme Court today refused to strip the Statue of Liberty of its status as a New Yorker. The Court, without comment, turned away a move by a two New Jerseyans to claim jurisdiction over the landmark for their state."</ref> The new European immigration brought further social upheaval. In a city of tenements packed with poorly paid laborers from dozens of nations, the city was a hotbed of [[revolution]], [[syndicalism]], [[racketeering]], and [[unionization]].
| |
| | | | |
| − | In 1874, the western portion of the present [[The Bronx|Bronx County]] was transferred to New York County, and in 1895 the remainder of the present Bronx County was annexed.<ref>Macy Jr., Harry. [http://www.newyorkfamilyhistory.org/modules.php?name=Sections&op=viewarticle&artid=45 Before the Five-Borough City: The Old Cities, Towns and Villages That Came Together to Form "Greater New York"], [[New York Genealogical and Biographical Society]] from ''The NYG&B Newsletter'', Winter 1998, accessed April 29, 2007. "In 1683, when the Province of New York was first divided into counties, the City of New York also became New York County... In 1874, to accommodate this growth, New York City and County annexed from Westchester County what is now the western Bronx... In 1895 New York City annexed the eastern Bronx."</ref> The [[City of Greater New York]] was formed in 1898, with Manhattan and the Bronx, though still one county, established as two separate [[borough (New York City)|boroughs]]. On January 1, 1914, the New York State Legislature created Bronx County, and New York County was reduced to its present boundaries.<ref>Hermalyn, Gary and Ultan, Lloyd. [http://www.nypl.org/branch/bronx/index2.cfm?Trg=1&d1=765&template=brgenhist Bronx History: A General Survey], [[New York Public Library]], accessed April 26, 2007.</ref>
| + | [[Image:Nast-Tammany.jpg|thumb|250px|Thomas Nast denounces Tammany as a ferocious tiger killing democracy; the tiger image caught on.]] |
| | + | After the [[American Civil War]], the rate of [[immigration]] from Europe grew steeply, and New York became the first stop for millions seeking a new and better life in the United States, a role acknowledged by the dedication of the [[Statue of Liberty]] on October 28, 1886, a gift from the people of [[France]]. The new European immigration brought further social upheaval. In a city of tenements packed with poorly paid laborers from dozens of nations, the city was a hotbed of socialist [[revolution]], racketeering, and unionization. |
| | | | |
| − | ===The 20th Century===
| + | In 1874, the western portion of the present Bronx was transferred to New York County, and in 1895, the remainder of the present Bronx County was annexed. The City of Greater New York was formed in 1898, with Manhattan and the Bronx, though still one county, established as two separate boroughs. On January 1, 1914, the New York State Legislature created Bronx County, and New York County was reduced to its present boundaries.<ref>Gary Hermalyn, and Lloyd Ultan, [http://www.nypl.org/branch/bronx/index2.cfm?Trg=1&d1=765&template=brgenhist Bronx History: A General Survey], [[New York Public Library]], ''www.nypl.org''. Retrieved April 26, 2007.</ref> |
| − | The construction of the [[New York City Subway]], first opened in 1904, helped bind the new city together. Starting in the 1920s, the city saw the influx of African Americans as part of the [[Great Migration (African American)|Great Migration]] from the [[U.S. Southern states|American South]], and the [[Harlem Renaissance]], part of a larger boom time in the [[Prohibition]] era that saw dueling skyscrapers in the skyline. New York City became the most populous city in the world in 1925, overtaking [[London]], which had reigned for a century.<ref>Chase-Dunn, Christopher and Manning, Susan. [http://www.irows.ucr.edu/research/citemp/ccr02/ccr02.htm "City systems and world-systems: Four millennia of city growth and decline"], [[University of California, Riverside]] Institute for Research on World-Systems. Accessed May 17, 2007. "New York, which became the largest city in the world by 1925, beating out London, is thus not included because we are studying constant regions."</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | On March 25, 1911, the [[Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire]] in [[Greenwich Village]] took the lives of 146 garment workers, which would eventually lead to great improvements in the city's fire department, building codes, and workplace regulations.<ref>Rosenberg, Jennifer. [http://history1900s.about.com/od/1910s/p/trianglefire.htm Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire], [[About.com]]. Accessed May 17, 2007.</ref>
| + | ===The twentieth century=== |
| | + | The construction of the [[New York City Subway]], first opened in 1904, helped bind the new city together. Tragedy struck the city on March 25, 1911, when the [[Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire]] in [[Greenwich Village]] took the lives of 146 garment workers, mostly young women, which would eventually lead to great improvements in the city's fire department, building codes, and workplace regulations.<ref>Jennifer Rosenberg,. [http://history1900s.about.com/od/1910s/p/trianglefire.htm Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire], ''history1900s.about.com''. Retrieved May 17, 2007.</ref> Starting in the 1920s, the city saw the influx of [[African Americans]] as part of the Great Migration from the U.S. Southern states and the [[Harlem Renaissance]], part of a larger boom time in the [[Prohibition]] era that saw dueling [[skyscraper]]s rise in the Manhattan skyline. New York City became the most populous city in the world in 1925, overtaking [[London]], which had reigned for a century.<ref>Chase-Dunn, Christopher and Manning, Susan. [http://www.irows.ucr.edu/research/citemp/ccr02/ccr02.htm "City systems and world-systems: Four millennia of city growth and decline," [[University of California, Riverside]] Institute for Research on World-Systems]. ''www.irows.ucr.edu''. Retrieved May 17, 2007.</ref> |
| | | | |
| − | [[Image:Manhattan1942.jpg|thumb|250px|right|[[Lower Manhattan]] in 1942]] | + | [[Image:Manhattan1942.jpg|thumb|250px|right|Lower Manhattan in 1942]] |
| | [[Image:Skyline Twin Towers photo by Sander Lamme.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Manhattan skyline with the [[World Trade Center|Twin Towers]].]] | | [[Image:Skyline Twin Towers photo by Sander Lamme.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Manhattan skyline with the [[World Trade Center|Twin Towers]].]] |
| − | The period between the World Wars saw the election of reformist mayor [[Fiorello LaGuardia]] and the fall of [[Tammany Hall]] after eighty years of political dominance.<ref>{{cite book|title=The Tiger – The Rise and Fall of Tammany Hall|first=Oliver E.|last=Allen|publisher=[[Addison-Wesley]] Publishing Company|url=http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=100781540|accessdate=2007-05-25|chapter=Chapter 9: The Decline|date=1993}}</ref> As the city's demographics stabilized, labor unionization brought new protections and affluence to the working class, the city's government and infrastructure underwent a dramatic overhaul under LaGuardia. Despite the effects of the [[Great Depression]], the 1930s saw the building of some of the world's tallest skyscrapers, including numerous [[Art Deco]] masterpieces that are still part of the city's skyline today. | + | The period between the World Wars saw the election of reformist mayor [[Fiorello LaGuardia]] and the fall of [[Tammany Hall]] after 80 years of political dominance.<ref>Oliver E. Allen. ''The Tiger – The Rise and Fall of Tammany Hall.'' (Addison-Wesley Publ. Co., 1993) [http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=100781540 ''Decline: Chapter 9]. ''questia.com''. Retrieved October 22, 2007.</ref> As the city's demographics stabilized, labor unionization brought new protections and affluence to the working class. The city's government and infrastructure underwent a dramatic overhaul under LaGuardia. Despite the effects of the [[Great Depression]], the 1930s saw the building of some of the world's tallest skyscrapers, including numerous [[Art Deco]] masterpieces, including the [[New Yorker Hotel]] that are still part of the city's skyline today. Much of the design of the city, its famous parks, and roadways was due to the genius of controversial power broker and builder [[Robert Moses]].<ref>Lee Gjertsen. "Robert Moses |
| | + | The controversial power broker who built New York" [http://politicians.suite101.com/article.cfm/robert_moses]. ''politicians.suite101.com''. Retrieved July 9, 2008.</ref> |
| | | | |
| − | Returning [[World War II]] veterans and immigrants from Europe created a postwar economic boom and led to the development of huge housing developments, targeted at returning veterans, including [[Peter Cooper Village—Stuyvesant Town]] which opened in 1947.<ref>"Stuyvesant Town to Get Its First Tenants Today," ''[[The New York Times]]'', August 1, 1947. p. 19</ref> In 1951, the [[United Nations]] relocated from its first headquarters in [[Queens]], to the East Side of Manhattan.<ref>Behrens, David. [http://www.newsday.com/community/guide/lihistory/ny-history-hs741a,0,7354306.story "The World Came to Long Island: The small Village of Lake Success played a big role in the launch of the United Nations"], ''[[Newsday]]''. Accessed May 29, 2007. "In the spring of 1951, the UN moved to its current home along Manhattan's East River."</ref> | + | Returning [[World War II]] veterans and immigrants from Europe created a postwar economic boom that led to the development of huge housing developments, targeted at returning veterans, including Peter Cooper Village—Stuyvesant Town, which opened in 1947.<ref>"Stuyvesant Town to Get Its First Tenants Today," ''[[The New York Times]]'', August 1, 1947, 19.</ref> In 1951, the [[United Nations]] relocated from its first headquarters in Queens to the East Side of Manhattan. |
| − | | |
| − | Like many major U.S. cities, New York suffered race riots and population and industrial decline in the 1960s. By the 1970s, the city had gained a reputation as a graffiti-covered, crime-ridden relic of history.<ref>[[Clyde Haberman|Haberman, Clyde]]. [http://www.nytimes.com/specials/nyc100/nyc100-8-haberman.html "Surviving Fiscal Crisis (and Disco)"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', January 25, 1998. Accessed May 29, 2007.</ref> In 1975, the city government faced imminent bankruptcy, and its appeals for assistance were initially rejected, summarized by the classic October 30, 1975 ''[[New York Daily News]]'' headline as "Ford to City: Drop Dead".<ref>Zeitz, Joshua. [http://www.americanheritage.com/articles/web/20051126-new-york-city-gerald-ford-labor-unions-municipal-assistance-corporation-emergency-financial-control-board.shtml "New York City on the Brink"], ''[[American Heritage (magazine)]]'', November 26, 2005. Accessed May 29, 2007.</ref> The fate was avoided through a federal loan and debt restructuring, and the city was forced to accept increased financial scrutiny by [[New York State]].<ref>Firestone, David. [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=990CEEDF1F3AF93BA25756C0A963958260 "This Time, New York City Is All Alone"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', May 18, 1995. Accessed May 29, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The 1980s saw a rebirth of [[Wall Street]], and the city reclaimed its role at the center of the world-wide financial industry. The 1980s also saw Manhattan at the heart of the [[AIDS]] crisis, with [[Greenwich Village, Manhattan|Greenwich Village]] at its epicenter. [[Gay Men's Health Crisis]] (GMHC) and [[AIDS Coalition to Unleash Power]] (ACT UP) were founded to advocate on behalf of those stricken with the disease.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Starting in the 1990s, crime rates dropped drastically and the outflow of population turned around, as the city once again became the destination not only of immigrants from around the world, but of many U.S. citizens seeking to live a cosmopolitan lifestyle that New York City can offer.
| |
| | | | |
| | + | Like many major U.S. cities, New York suffered [[race riots]] and population and industrial decline in the 1960s. By the 1970s, the city had gained a reputation as a graffiti-covered, crime-ridden relic of history. In 1975, the city government faced imminent [[bankruptcy]], and its appeals for assistance were initially rejected, summarized by the classic October 30, 1975 ''[[New York Daily News]]'' headline as "Ford to City: Drop Dead".<ref>Joshua Zeitz, [http://www.americanheritage.com/articles/web/20051126-new-york-city-gerald-ford-labor-unions-municipal-assistance-corporation-emergency-financial-control-board.shtml "New York City on the Brink" in ''[[American Heritage'' (magazine)]], November 26, 2005]. ''www.americanheritage.com''. Retrieved May 29, 2007.</ref> This fate was avoided through a federal loan and debt restructuring, and the city was forced to accept increased financial scrutiny by New York State. The 1980s saw a rebirth of [[Wall Street]], and the city reclaimed its role at the center of the world-wide financial industry. |
| | | | |
| | + | The 1980s also saw Manhattan at the heart of the [[AIDS]] crisis, with [[Greenwich Village]] at its epicenter. Gay Men's Health Crisis (GMHC) and AIDS Coalition to Unleash Power (ACT UP) were founded to advocate on behalf of those stricken with the disease. Starting in the 1990s, crime rates dropped drastically, and the outflow of population turned around as the city once again became the destination not only of immigrants from around the world but of many U.S. citizens seeking to live a cosmopolitan lifestyle that New York City can offer. |
| | | | |
| | ==Government== | | ==Government== |
| | {{main|Government of New York City}} | | {{main|Government of New York City}} |
| − | [[Image:Manhattan Municipal Building by David Shankbone edited-1.jpg|thumb|right|250px|[[Manhattan Municipal Building]]]] | + | [[Image:Manhattan Municipal Building by David Shankbone edited-1.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Manhattan Municipal Building]] |
| − | Since New York City's consolidation in 1898, Manhattan has been governed by the New York City Charter, which has provided for a "strong" [[Mayor-council government|mayor-council system]] since its revision in 1989.<ref>[http://www.abcny.org/pdf/Report%20on%20Ballot%20Proposals.pdf "Report on Ballot Proposals of the 2003 New York City Charter Revision Commission"] (PDF), [[Association of the Bar of the City of New York]]. Accessed May 11, 2007. "Unlike most cities that employ nonpartisan election systems, New York City has a very strong mayor system and, following the 1989 Charter Amendments, an increasingly powerful City Council."</ref> The centralized New York City government is responsible for public education, correctional institutions, libraries, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply, and welfare services in Manhattan. | + | [[Image:New York City Hall.jpg|thumb|right|175px|New York City Hall]] |
| | + | Since New York City's consolidation in 1898, Manhattan has been governed by the New York City Charter, which has provided for a "strong" mayor-council system since its revision in 1989. <ref>[http://www.abcny.org/pdf/Report%20on%20Ballot%20Proposals.pdf "Report on Ballot Proposals of the 2003 New York City Charter Revision Commission," Association of the Bar of the City of New York]. ''www.abcny.org''. Retrieved May 11, 2007.</ref> The centralized New York City government is responsible for public education, correctional institutions, libraries, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply, and welfare services in Manhattan. |
| | | | |
| − | The office of [[Borough President]] was created in the consolidation of 1898 to balance centralization with local authority. Each borough president had a powerful administrative role derived from having a vote on the [[New York City Board of Estimate]], which was responsible for creating and approving the city's budget and proposals for land use. In 1989 the [[Supreme Court of the United States]] declared the Board of Estimate unconstitutional on the grounds that Brooklyn, the most populous borough, had no greater effective representation on the Board than Staten Island, the least populous borough, a violation of the [[Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution|Fourteenth Amendment's]] [[Equal Protection Clause]] pursuant to the high court's 1964 "one man, one vote" decision.<ref>[http://www.law.cornell.edu/supct/html/historics/USSC_CR_0489_0688_ZS.html Cornell Law School Supreme Court Collection: Board of Estimate of City of New York v. Morris], [[Cornell Law School]]. Accessed June 12, 2006.</ref> | + | The office of Borough President was created in the consolidation of 1898 to balance centralization with local authority. Each borough president had a powerful administrative role derived from having a vote on the New York City Board of Estimate, which was responsible for creating and approving the city's budget and proposals for land use. In 1989, the [[Supreme Court of the United States]] declared the Board of Estimate system unconstitutional on the grounds that [[Brooklyn]], the most populous borough, had no greater effective representation on the Board than [[Staten Island]], the least populous borough, a violation of the Fourteenth Amendment's Equal Protection Clause pursuant to the high court's 1964 "one man, one vote" decision.<ref>[http://www.law.cornell.edu/supct/html/historics/USSC_CR_0489_0688_ZS.html Cornell Law School Supreme Court Collection: Board of Estimate of City of New York v. Morris, [[Cornell Law School]] ]. ''www.law.cornell.edu''. Retrieved June 12, 2006.</ref> |
| − | | |
| − | Since 1990, the largely-powerless Borough President has acted as an advocate for the borough at the mayoral agencies, the City Council, the New York state government, and corporations. Manhattan's [[Borough President]] is [[Scott Stringer]], elected as a [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democrat]] in 2005.<ref>[http://www.mbpo.org/about Manhattan Borough President Scott M. Stringer], Manhattan Borough President's Office. Accessed April 27, 2007. "Scott M. Stringer was sworn in as Manhattan’s 26th Borough President in January of 2006…"</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[Robert M. Morgenthau]], a Democrat, has been the District Attorney of New York County since 1974.<ref>[http://www.manhattanda.org/history/biography.htm Biography of Robert M. Morgenthau], New York County District Attorney's Office. Accessed April 27, 2007. "He returned to private life until 1974, when he made the first of eight successful bids for election as District Attorney of New York County."</ref> Manhattan has ten City Council members, the third largest contingent among the five boroughs. It also has 12 administrative districts, each served by a local Community Board. Community Boards are representative bodies that field complaints and serve as advocates for local residents.
| |
| − | As the host of the [[United Nations]], the borough is home to the world's largest international [[Consul (representative)|consular corps]], comprising 105 consulates, consulates general and honorary consulates.<ref>[http://www.consulsnewyork.com/about.htm Society of Foreign Consuls: About us]. Accessed July 19, 2006.</ref> It is also the home of [[New York City Hall]], the seat of New York City government housing the [[Mayor of New York City]] and the [[New York City Council]]. The mayor's staff and thirteen municipal agencies are located in the nearby [[Manhattan Municipal Building]], completed in 1916, one of the largest governmental buildings in the world.<ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/dcas/html/agencyinfo/municipal_building.shtml The Municipal Building], [[New York City]]. Accessed April 25, 2007. "But did you know that the Municipal Building is one of the largest government buildings in the world? Or that more than 28,000 New Yorkers are married here each year?"</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| | + | Since 1990, the largely-powerless Borough President has acted as an advocate for the borough at the mayoral agencies, the New York City Council, the New York state government, and corporations. Manhattan has ten City Council members, the third largest contingent among the five boroughs. It also has 12 administrative districts, each served by a local Community Board. Community Boards are representative bodies that field complaints and serve as advocates for local residents. |
| | | | |
| | + | As the host of the [[United Nations]], the borough is home to the world's largest international consular corps, comprising 105 consulates, consulates general, and honorary consulates.<ref>[http://www.consulsnewyork.com/about.htm Society of Foreign Consuls: About us]. ''www.consulsnewyork.com''. Retrieved July 19, 2006.</ref> It is also the home of New York City Hall, the seat of New York City government housing the Mayor of New York City and the New York City Council. The mayor's staff and 13 municipal agencies are located in the nearby Manhattan Municipal Building, completed in 1916, which was then known as one of the largest governmental buildings in the world.<ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/dcas/html/agencyinfo/municipal_building.shtml The Municipal Building], [[New York City]]. ''www.nyc.gov''. Retrieved April 25, 2007.</ref> |
| | | | |
| | ===Crime=== | | ===Crime=== |
| − | {{main|Crime in New York City}}
| |
| | [[Image:Leslie five points new york 1885 3c22660v.jpg|thumb|250px|Policeman leads upper class people through the Five Points in an 1885 sketch]] | | [[Image:Leslie five points new york 1885 3c22660v.jpg|thumb|250px|Policeman leads upper class people through the Five Points in an 1885 sketch]] |
| − | Starting in the mid-19th century, the United States became a magnet for immigrants seeking to escape poverty in their home countries. After arriving in New York, many new arrivals ended up living in squalor in the slums of the [[Five Points, Manhattan|Five Points]] neighborhood, an area between [[Broadway (New York City)|Broadway]] and the [[Bowery, Manhattan|Bowery]], northeast of [[New York City Hall]]. By the 1820s, the area was home to many gambling dens and [[Brothel|"houses of ill repute"]], and was known as a dangerous place to go to. In 1842, [[Charles Dickens]] visited the area and was appalled at the horrendous living conditions he had seen.<ref>Christiano, Gregory. [http://urbanography.com/5_points/ "The Five Points"], Urbanography. Accessed May 16, 2007.</ref> The area was so notorious at the time that it even caught the attention of [[Abraham Lincoln]], who visited the area before his [[Cooper Union Address]] in 1860.<ref>Walsh, John, [http://www.irish-society.org/Hedgemaster%20Archives/five_points.htm "The Five Points"], Irish Cultural Society of the Garden City Area, September 1994. Accessed May 16, 2007. "The Five Points slum was so notorious that it attracted the attention of candidate Abraham Lincoln who visited the area before his Cooper Union Address."</ref> The predominantly Irish [[Five Points Gang]] was one of the country's first major [[organized crime]] entities. | + | Starting in the mid-nineteenth century, the United States became a magnet for immigrants seeking to escape poverty in their home countries. After arriving in New York, many new arrivals ended up living in squalor in the slums of the [[Five Points]] neighborhood, an area between Broadway and the Bowery, northeast of New York City Hall. By the 1820s, the area was home to many gambling dens and [[brothel]]s and was known as a dangerous place to go to. The area was so notorious at the time that it even caught the attention of [[Abraham Lincoln]], who visited the area before his Cooper Union Address in 1860.<ref>John Walsh, [http://www.irish-society.org/Hedgemaster%20Archives/five_points.htm "The Five Points," Irish Cultural Society of the Garden City Area, September 1994]. ''www.irish-society.org''. Retrieved May 16, 2007.</ref> The predominantly Irish Five Points Gang was one of the country's first major [[organized crime]] entities. |
| − | | |
| − | As Italian immigration grew in the early 1900s, many joined the Irish gangs. [[Al Capone]] got his start in crime with the Five Points Gang,<ref>[http://www.chicagohs.org/history/capone.html Al Capone], [[Chicago History Museum]]. Accessed May 16, 2007. "Capone was born on January 17, 1899, in Brooklyn, New York.... He became part of the notorious Five Points gang in Manhattan and worked in gangster Frankie Yale's Brooklyn dive, the Harvard Inn, as a bouncer and bartender."</ref> as did [[Lucky Luciano]].<ref>[http://www.crimelibrary.com/gangsters_outlaws/mob_bosses/luciano/born_2.html A Gangster is Born], [[Court TV]]. Accessed May 16, 2007. "By 1916, Luciano was a leading member of the notorious Five Points Gang and named by police as the prime suspect in a number of murders."</ref> The [[Mafia]] (also known as ''Cosa Nostra'') first developed in the mid-19th century in [[Sicily]] and spread to the [[East Coast of the United States]] during the late 19th century following waves of Sicilian and Southern Italian [[emigration]]. Lucky Luciano established La Cosa Nostra in Manhattan, forming alliances with other criminal enterprises, including the Jewish mob, led by [[Meyer Lansky]], the leading Jewish gangster of that period.<ref name=Smithsonian>Jaffe, Eric. [http://www.smithsonianmagazine.com/issues/2007/april/mob.php "Talking to the Feds: The chief of the FBI's organized crime unit on the history of La Cosa Nostra"], ''[[Smithsonian (magazine)]]'', April 2007. Accessed May 16, 2007.</ref> from 1920–1933, [[Prohibition in the United States|Prohibition]] helped create a thriving [[black market]] in liquor, which the Mafia was quick to capitalize on.<ref name=Smithsonian/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | New York City experienced a sharp increase in crime during the 1960s and 1970s, with a near fivefold jump in the violent crime rate, from 21.09 per thousand in 1960 to a peak of 102.66 in 1981. Homicides continued to increase in the city as a whole for another decade, with murders recorded by the [[New York City Police Department|NYPD]] jumping from 390 in 1960, to 1,117 in 1970, 1,812 in 1980 and reaching its peak of 2,262 in 1990. Starting circa 1990, New York City saw record declines in homicide, rape, robbery, aggravated assault, violent crime, burglary, larceny, motor vehicle theft and property crime, a trend that has continued to today.<ref>Langan, Patrick A. and Durose, Matthew R. [http://samoa.istat.it/Eventi/sicurezza/relazioni/Langan_rel.pdf "The Remarkable Drop in Crime in New York City"] (PDF). [[United States Department of Justice]], October 21, 2004. Accessed May 16, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Based on 2005 data, New York City has the lowest crime rate among the ten largest cities in the United States.<ref name=Bloomberg>Zeranski, Todd. [http://www.bloomberg.com/apps/news?pid=10000103&sid=aHWGwSJjpbOU&refer=us NYC Is Safest City as Crime Rises in U.S., FBI Say"]. ''[[Bloomberg Television|Bloomberg News]]'', June 12, 2006. Accessed May 16, 2007.</ref> The city as a whole ranked fourth nationwide in the 13th annual [[Morgan Quitno]] survey of the 32 cities surveyed with a population above 500,000.<ref>[http://www.morganquitno.com/cit07pop.htm 13th Annual Safest (and Most Dangerous) Cities: Top and Bottom 25 Cities Overall], accessed May 16, 2007.</ref> The [[New York Police Department]], with 36,400 officers, is larger than the next four largest U.S. departments combined. The NYPD's counter-terrorism division, with 1,000 officers assigned, is larger than the [[FBI]]'s.<ref name=Bloomberg/> The NYPD's [[CompStat]] system of crime tracking, reporting and monitoring has been credited with a drop in crime in New York City that has far surpassed the drop elsewhere in the United States.<ref>MacDonald, Heather. [http://www.city-journal.org/html/16_3_ny_cops.html "New York Cops: Still the Finest - Bucking a national trend, Gotham’s crime rate keeps dropping. Here’s why."], ''[[City Journal (New York)]]'', Summer 2006. Accessed May 16, 2007. "But to his immense credit (and that of Mayor Michael Bloomberg, who has backed him), Kelly has maintained the heart of New York’s policing revolution—the now-famous accountability mechanism known as Compstat, a weekly crime-control meeting where top brass grill precinct bosses about every last detail of their command—even as he has refined the department’s ability to analyze and respond to crime trends."</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Since 1990, crime in Manhattan has plummeted in all categories tracked by the CompStat profile. A borough that saw 503 murders in 1990 has seen a drop of nearly 78% to 111 in 2006. Robbery and burglary are down by more than 80% during the period, and auto theft has been reduced by more than 90%. Overall crime has declined by more than 75% since 1990 in the seven major crime categories tracked by the system, and year-to-date statistics through May 2007 show continuing declines.<ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/nypd/pdf/chfdept/cspbms.pdf Patrol Borough Manhattan South — Report Covering the Week of 04/30/2007 Through 05/06/2007] (PDF), [[New York City Police Department]] [[CompStat]], May 6, 2007. Accessed May 16, 2007.</ref><ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/nypd/pdf/chfdept/cspbms.pdf Patrol Borough Manhattan North — Report Covering the Week of 04/30/2007 Through 05/06/2007] (PDF), [[New York City Police Department]] [[CompStat]], May 6, 2007. Accessed May 16, 2007.</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| | + | As Italian immigration grew in the early 1900s, many joined the Irish gangs. Gangster [[Al Capone]] got his start in crime with the Five Points Gang, <ref> Al Capone, [[Chicago History Museum]]. ''www.chicagohs.org''.</ref> as did Lucky Luciano. The [[Mafia]] (also known as ''Cosa Nostra'') first developed in the mid-nineteenth century in [[Sicily]] and spread to the East Coast of the United States, following waves of Sicilian and Southern Italian emigration. Lucky Luciano established '''La Cosa Nostra''' in Manhattan, forming alliances with other criminal enterprises, including the Jewish mob, led by [[Meyer Lansky]], the leading Jewish gangster of that period.<ref>Eric Jaffe, [http://www.smithsonianmagazine.com/issues/2007/april/mob.php "Talking to the Feds: The chief of the FBI's organized crime unit on the history of La Cosa Nostra," ''[[Smithsonian (magazine)]]'', April 2007]. ''www.smithsonianmagazine.com''. Retrieved May 16, 2007.</ref> From 1920–1933, [[Prohibition in the United States|Prohibition]] helped create a thriving [[black market]] in [[alcoholic beverage|liquor]], which the Mafia was quick to exploit. |
| | | | |
| | + | New York City experienced a sharp increase in crime during the 1960s and 1970s, with a near fivefold jump in the [[violent crime]] rate, from 21.09 per thousand in 1960 to a peak of 102.66 in 1981. Homicides continued to increase in the city as a whole for another decade, with murders recorded by the New York City Police Department, jumping from 390 in 1960 to 1,117 in 1970, 1,812 in 1980, and reaching its peak of 2,262 in 1990. Starting about 1990, New York City saw record declines in [[homicide]], rape, [[robbery]], aggravated assault, violent crime, burglary, larceny, motor vehicle theft and property crime, a trend that has continued, as funds were invested in improved housing and living conditions in the poorest neighborhoods. |
| | | | |
| | ==Economy== | | ==Economy== |
| | [[Image:6thAvenuefrom49th.JPG|thumb|right|250px|Skyscrapers along Sixth Avenue.]] | | [[Image:6thAvenuefrom49th.JPG|thumb|right|250px|Skyscrapers along Sixth Avenue.]] |
| − | Manhattan is the economic engine of New York City, with its 2.3 million workers drawn from the entire [[New York metropolitan area]] accounting for almost ⅔ of all jobs in New York City.<ref name=BLSManhattanLabor/> Manhattan's daytime population swells to 2.874 million, with commuters adding a net 1.337 million people to the population. This commuter influx of 1.459 million workers coming into Manhattan was the largest of any other county or city in the country, and was more than triple the 481,000 commuters who headed into second-ranked [[Washington, D.C.]].<ref>[http://www.usatoday.com/news/2003-03-06-commute.htm "Commuting shifts in top 10 metro areas"], ''[[USA Today]]'', May 20, 2005. Accessed June 25, 2007.</ref><ref>[http://www.census.gov/population/socdemo/daytime/2000/tab02.csv Estimated Daytime Population and Employment-Residence Ratios: 2000], [[United States Census, 2000]]. Accessed June 25, 2007.</ref> | + | Manhattan is the economic engine of New York City, with its 2.3 million workers drawn from the entire New York metropolitan area, accounting for almost ⅔ of all jobs in New York City. Its most important economic sector is the finance industry, whose 280,000 workers earned more than half of all the wages paid in the borough. Wall Street is frequently used to represent the entire financial industry. New York City is home to the most corporate headquarters of any city in the nation, the overwhelming majority based in Manhattan. Midtown Manhattan is the largest central business district in the United States.<ref>Patricia Noonan, Testimony on Moynihan Station Draft EIS, Partnership for New York City, testimony dated May 31, 2000. ''www.nycp.org''.</ref> Lower Manhattan is home to both the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ and is the nation's third-largest central business district (after Chicago's Loop).<ref>[http://www.fta.dot.gov/about/offices/about_FTA_927.html Lower Manhattan Recovery Office, [[Federal Transit Administration]] ]. ''www.fta.dot.gov''. Retrieved April 26, 2007.</ref> |
| − | | |
| − | Its most important economic sector is the finance industry, whose 280,000 workers earned more than half of all the wages paid in the borough. [[Wall Street]] is frequently used to represent the entire financial industry. In 2006, those in the Manhattan financial industry earned an average weekly pay about $8,300 (including bonuses), while the average weekly pay was about $2,500. The health care sector represented 11.3% of the borough's jobs and 4% of total compensation, with workers taking home about $900 per week.<ref>McGeehan, Patrick. [http://www.nytimes.com/2006/11/23/nyregion/23income.html?ref=nyregion Income Soars on Wall St., Widening Gap], ''[[The New York Times]]'', March 23, 2006. Accessed May 1, 2007.</ref> | |
| − | | |
| − | New York City is home to the most corporate headquarters of any city in the nation, the overwhelming majority based in Manhattan.<ref>[http://www.empire.state.ny.us/press/press_display.asp?id=575 Fortune Magazine: New York State and City Home to Most Fortune 500 Companies], [[Empire State Development Corporation]], press release dated April 8, 2005, accessed April 26, 2007. "New York City is also still home to more Fortune 500 headquarters than any other city in the country."</ref> Midtown Manhattan is the largest central business district in the United States.<ref>Noonan, Patrica. [http://www.nycp.org/testimonies/2006/tst_053106_moynihan.html Testimony on Moynihan Station Draft EIS], Partnership for New York City, testimony dated May 31, 2006, accessed April 26, 2007. "Combined with the expansion of the Jacob K. Javits Convention Center, the Far West Side promises to become the logical extension of the largest central business district in the country."</ref> Lower Manhattan is home to both the [[New York Stock Exchange]] and [[NASDAQ]], and is the nation's third-largest central business district (after [[Chicago]]'s [[Chicago Loop|Loop]]).<ref>[http://www.fta.dot.gov/about/offices/about_FTA_927.html Lower Manhattan Recovery Office], [[Federal Transit Administration]], accessed April 26, 2007. "Lower Manhattan is the third largest business district in the nation. Prior to September 11th more than 385,000 people were employed there and 85% of those employees used public transportation to commute to work."</ref> | |
| − | | |
| − | Seven of the world's top eight global [[advertising agency]] networks are headquartered in Manhattan.<ref>[http://adage.com/datacenter/datapopup.php?article_id=116384 Top 10 Consolidated Agency Networs: Ranked by 2006 Worldwide Network Revenue], ''[[Advertising Age]]'' Agency Report 2007 Index, published April 25, 2007. Accessed June 8, 2007.</ref> "Madison Avenue" is often used [[metonymy|metonymously]] to refer to the entire advertising field, after [[Madison Avenue (Manhattan)|Madison Avenue]] became identified with the advertising industry after the explosive growth in the area in the 1920s.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2006 statistics showed that the average weekly wages paid to Manhattan workers is $1,453 (excluding bonuses), the highest in the country's 325 largest counties, and the salary growth of 7.8% was the highest among the ten largest counties. Pay in the borough was 85% higher than the $784 pay earned weekly nationwide and nearly double the amount earned by workers in the outer boroughs. Manhattan's workforce is overwhelmingly focused on white collar professions, with manufacturing (39,800 workers) and construction (31,600) accounting for a small fraction of the borough's employment.<ref name=BLSManhattanLabor>[http://www.bls.gov/ro2/fax/qcew9310.pdf Average Weekly Wage in Manhattan at $1,453 in Second Quarter 2006] (PDF), [[Bureau of Labor Statistics]], [[United States Department of Labor]], February 20, 2007. Accessed February 21, 2007.</ref><ref name=NYPost>Geller, Andy. [http://www.nypost.com/seven/02212007/news/regionalnews/n_y__hits_paydirt_regionalnews_andy_geller.htm "N.Y. Hits 'Pay'dirt: Manhattan No. 1 in Nat'l Salary Surge], ''[[New York Post]]'', February 21, 2007. Accessed May 18, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Historically, this corporate presence has been complemented by many independent retailers, though a recent influx of national chain stores has caused many to lament the creeping homogenization of Manhattan.<ref>Stasi, Linda. [http://www.villagevoice.com/news/9739,stasi,470,4.html NY, OH: It's Cleaner, Whiter, Brighter], ''[[The Village Voice]]'', September 24, 1997. Accessed June 20, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Culture==
| |
| − | [[Image:Times Square (Tall).jpg|thumb|right|250px|[[Times Square]] is the center of the city's theater district.]]
| |
| − | [[Image:Guggenheim museum exterior.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The exterior of Frank Lloyd Wright's Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum]]
| |
| − | {{seealso|Culture of New York City}}
| |
| − | Manhattan has been the scene of many important American cultural movements. In 1912, about 20,000 workers, a quarter of them women, marched on [[Washington Square Park]] to commemorate the [[Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire]], which killed 146 workers on March 25, 1911. Many of the women wore fitted tucked-front blouses like those manufactured by the Triangle Shirtwaist Company, a clothing style that became the working woman's uniform and a symbol of female independence, reflecting the alliance of labor and suffrage movements.<ref>[http://www.ilr.cornell.edu/trianglefire/ The Triangle Factory Fire], [[Cornell University School of Industrial and Labor Relations]], accessed April 25, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − | The [[Harlem Renaissance]] in the 1920s established the African-American literary canon in the United States. Manhattan's vibrant visual art scene in the 1950s and 1960s was a center of the American [[pop art]] movement, which gave birth to such giants as [[Jasper Johns]] and [[Roy Lichtenstein]]. Perhaps no other artist is as associated with the downtown pop art movement of the late 1970s as [[Andy Warhol]], who socialized at clubs like [[Serendipity 3]] and [[Studio 54]] and was shot in the chest in 1968 by the radical feminist [[Valerie Solanas]], founder of the group "Society for Cutting Up Men" (S.C.U.M.) and author of the [[SCUM Manifesto]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | A popular haven for art, the downtown neighborhood of [[Chelsea, Manhattan|Chelsea]] is widely known for its galleries and cultural events, with more than 200 art galleries that are home to modern art from upcoming artists and respected artists as well.<ref>[http://www.travelandleisure.com/articles/stylish-traveler-chelsea-girls-september-2005 "Stylish Traveler: Chelsea Girls"], ''[[Travel + Leisure]]'', September 2005. Accessed May 14, 2007. "With more than 200 galleries, Chelsea has plenty of variety."</ref><ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/dcp/html/about/pr122004.shtml "City Planning Begins Public Review for West Chelsea Rezoning to Permit Housing Development and Create Mechanism for Preserving and Creating Access to the High Line"], [[New York City]] Department of City Planning press release dated December 20, 2004. Accessed May 29, 2007. "Some 200 galleries have opened their doors in recent years, making West Chelsea a destination for art lovers from around the City and the world."</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[Broadway theatre]] is often considered the highest professional form of theatre in the United States. [[Play]]s and [[musical theater|musicals]] are staged in one of the 39 larger professional theatres with at least 500 seats, almost all in and around Times Square.<ref>Weber, Bruce. [http://theater2.nytimes.com/mem/theater/treview.html?_r=1&res=9C02E0DB123AF931A35754C0A9659C8B63&oref=slogin "Critic's Notebook: Theater's Promise? Look Off Broadway"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', July 2, 2003. Accessed May 29, 2007. "It's also true that what constitutes Broadway is easy to delineate; it's a universe of 39 specified theaters, which all have at least 500 seats. Off Broadway is generally considered to comprise theaters from 99 to 499 seats (anything less is thought of as Off Off), which ostensibly determines the union contracts for actors, directors and press agents."</ref> [[Off-Broadway]] theatres feature productions in venues with 100-500 seats.<ref>[http://www.tdf.org/tdf_servicepage.aspx?id=103 Theatre 101], [[Theatre Development Fund]]. Accessed May 29, 2007.</ref> A little more than a mile from Times Square is the [[Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts|Lincoln Center]], home to one of the world's most prestigious opera houses, that of the [[Metropolitan Opera]].<ref>[http://www.abc.net.au/classic/daily/stories/s630189.htm Music Details for Sunday 5 January 1997], [[ABC Classic FM]]. Accessed June 19, 2007. "James Levine made his Metropolitan Opera debut at the age of 27, conducting Tosca.... Since the mid eighties he has held the role of Artistic Director, and it is under his tenure that the Met has become the most prestigious opera house in the world."</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Manhattan is also home to some of the most extensive art collections, both contemporary and historical, in the world including the [[Metropolitan Museum of Art]], the [[Museum of Modern Art]] (MoMA), the [[Whitney Museum of American Art]], and the [[Frank Lloyd Wright]]-designed [[Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum|Guggenheim Museum]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | Manhattan is the borough most closely associated with New York City by non-residents; even some natives of New York City's outer boroughs will describe a trip to Manhattan as "going to the city".<ref>Purdum, Todd S. [http://select.nytimes.com/search/restricted/article?res=F1061EFC3A5E0C718EDDAB0894DA494D81 " POLITICAL MEMO; An Embattled City Hall Moves to Brooklyn"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', February 22, 1992. Accessed May 9, 2007. ""Leaders in all of them fear that recent changes in the City Charter that shifted power from the borough presidents to the City Council have diminished government's recognition of the sense of identity that leads people to say they live in the Bronx, and to describe visiting Manhattan as 'going to the city.'"</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The borough has a place in several American [[idiom]]s. The phrase ''"[[New York minute (time)|a New York minute]]"'' is meant to convey a very short period of time, sometimes in hyperbolic form, as in "perhaps faster than you would believe is possible." It refers to the rapid pace of life in Manhattan.<ref>{{cite web | author =|title = New York Minute| work = [[Dictionary of American Regional English]] |date = 1984-01-01| url = http://www.worldwidewords.org/qa/qa-new1.htm| accessdate = 2006-09-05}}</ref> The term "[[melting pot]]" was first popularly coined to describe the densely populated immigrant neighborhoods on the [[Lower East Side]] in [[Israel Zangwill]]'s play ''[[The Melting Pot]]'', which was an adaptation of [[William Shakespeare]]'s ''[[Romeo and Juliet]]'' set by Zangwill in New York City in 1908.<ref>[http://www.pbs.org/fmc/timeline/emeltpot.htm "The Melting Pot"], ''The First Measured Century'', [[Public Broadcasting Service]]. Accessed April 25, 2007.</ref> The iconic [[Flatiron Building]] is said to have been the source of the phrase "[[23 skidoo]]" or scram, from what cops would shout at men who tried to get glimpses of women's dresses being blown up by the winds created by the triangular building.<ref>Dolkart, Andrew S. [http://ci.columbia.edu/0240s/0242_2/0242_2_s5_text.html "The Architecture and Development of New York City: The Birth of the Skyscraper - Romantic Symbols"], [[Columbia University]], accessed May 15, 2007. "It is at a triangular site where Broadway and Fifth Avenue—the two most important streets of New York—meet at Madison Square, and because of the juxtaposition of the streets and the park across the street, there was a wind-tunnel effect here. In the early twentieth century, men would hang out on the corner here on Twenty-third Street and watch the wind blowing women's dresses up so that they could catch a little bit of ankle. This entered into popular culture and there are hundreds of postcards and illustrations of women with their dresses blowing up in front of the Flatiron Building. And it supposedly is where the slang expression "23 skidoo" comes from because the police would come and give the voyeurs the 23 skidoo to tell them to get out of the area."</ref> The "[[Big Apple]]" dates back to the 1920s, when a reporter heard the term used by [[New Orleans, Louisiana|New Orleans]] stablehands to refer to New York City's racetracks and named his racing column "Around The Big Apple." Jazz musicians adopted the term to refer to the city as the world's jazz capital, and a 1970s ad campaign by the New York Convention and Visitors Bureau helped popularize the term.<ref>[http://www.ci.nyc.ny.us/html/om/html/97/sp082-97.html "MAYOR GIULIANI SIGNS LEGISLATION CREATING "BIG APPLE CORNER" IN MANHATTAN"], [[New York City]] press release dated February 12, 1997.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Sports===
| |
| − | [[Image:Msg2005d.JPG|thumb|right|250px|[[Madison Square Garden]] is home to the Knicks, Rangers and Liberty.]]
| |
| − | [[Image:Pologrounds5.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The [[Polo Grounds]] was home to the baseball Giants, Yankees and Mets, and both the football Giants and Jets.]]
| |
| − | [[Image:Hilltoppark1903.jpg|300px|thumb|[[Hilltop Park]], former home of the New York Yankees]]
| |
| − | Manhattan is home of the [[NBA]]'s [[New York Knicks]] and [[NHL]]'s [[New York Rangers]], who play their home games at [[Madison Square Garden]], the only major professional sports arena in the borough. The [[New York Jets]] proposed a [[West Side Stadium]] for their home field, but the proposal was eventually defeated in June 2005, leaving them at [[Giants Stadium]] in [[East Rutherford, New Jersey]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | Today, Manhattan is the only borough in New York City that does not have a pro baseball franchise. Yet three of the four major league teams to play in New York City played in Manhattan. The [[San Francisco Giants|New York Giants]] played in the various incarnations of the [[Polo Grounds]] at [[155th Street (Manhattan)|155th Street]] and [[Eighth Avenue (Manhattan)|Eighth Avenue]] from their inception in 1883 — except for 1889, when they split their time between [[Jersey City, New Jersey|Jersey City]] and Staten Island, and when they played in Hilltop Park in 1911 — until they headed west with the [[Los Angeles Dodgers|Brooklyn Dodgers]] after the 1957 season.<ref>[http://sanfrancisco.giants.mlb.com/sf/history/ballparks.jsp Giants Ballparks: 1883–Present], [[MLB.com]]. Accessed May 8, 2007.</ref> The New York Yankees began their franchise as the Hilltoppers, named for [[Hilltop Park]], where they played from their creation in 1903 until 1912. The team moved to the Polo Grounds with the 1913 season, where they were officially christened the ''New York Yankees'', remaining there until they moved across the [[Harlem River]] in 1923 to [[Yankee Stadium]].<ref>[http://newyork.yankees.mlb.com/nyy/history/ballparks.jsp Yankee Ballparks: 1903–Present], [[MLB.com]]. Accessed May 8, 2007.</ref> The New York Mets played in the Polo Grounds in 1962 and 1963, their first two seasons, before [[Shea Stadium]] was completed in 1964.<ref>[http://newyork.mets.mlb.com/nym/history/ballparks.jsp Mets Ballparks: 1962–Present], [[MLB.com]]. Accessed May 8, 2007.</ref> After the Mets departed, the Polo Grounds was demolished in April 1964, replaced by public housing.<ref>Drebinger, John. "The Polo Grounds, 1889–1964: A Lifetime of Memories; Ball Park in Harlem Was Scene of Many Sports Thrills," ''[[The New York Times]]'', January 5, 1964. p. S3.</ref><ref>Arnold, Martin. "Ah, Polo Grounds, The Game is Over; Wreckers Begin Demolition for Housing Project," ''[[The New York Times]]'', April 11, 1964. p. 27.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The first national college-level basketball championship, the [[National Invitation Tournament]], was held in New York in 1938 and remains in the city.<ref>[http://www.nit.org/history/nit-history.html History of the National Invitation Tournament], [[National Invitation Tournament]]. Accessed May 8, 2007. "Tradition. The NIT is steeped in it. The nation's oldest postseason collegiate basketball tournament was founded in 1938."</ref> The [[New York Knicks]] started play in 1946 as one of the [[National Basketball Association]]'s original teams, playing their first home games at the [[69th Regiment Armory]], before making Madison Square Garden their permanent home.<ref>[http://www.nba.com/knicks/history/new_knicks_history.html History of the New York Knicks], [[NBA.com]]. Accessed May 8, 2007.</ref> The [[New York Liberty]] of the [[Women's National Basketball Association|WNBA]] have shared the Garden with the Knicks since their creation in 1997 as one of the league's original eight teams.<ref>[http://www.wnba.com/liberty/news/history_timeline.html The New York Liberty Story], [[Women's National Basketball Association]]. Accessed May 8, 2007.</ref> [[Rucker Park]] in [[Harlem]] is a playground court, famed for its ''[[street ball]]'' style of play, where many NBA athletes have played in the summer league.<ref>[http://www.tqnyc.org/NYC00157/BestBasketballPlayers/Rucker%20Park.htm Rucker Park], ThinkQuest New York City. Accessed May 8, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Though both of New York City's football teams play today across the [[Hudson River]] in [[Giants Stadium]] in [[East Rutherford, New Jersey]], both teams started out playing in the Polo Grounds. The [[New York Giants]] played side-by-side with their baseball namesakes from the time they entered the [[National Football League]] in 1925, until crossing over to Yankee Stadium in 1956.<ref>[http://www.giants.com/history/TheGiantsStadiums.asp The Giants Stadiums: Where the Giants have called home from their inception in 1925 to the present], [[New York Giants]], dated November 7, 2002. Accessed May 8, 2007. "The Giants shared the Polo Grounds with the New York Baseball Giants from the time they entered the league in 1925 until they moved to the larger Yankee Stadium for the start of the 1956 season."</ref> The [[New York Jets]], originally known as the ''Titans'', started out in 1960 at the Polo Grounds, staying there for four seasons before joining the Mets in Queens in 1964.<ref>[http://www.stadiumsofnfl.com/past/SheaStadium.htm Stadiums of The NFL: Shea Stadium], Stadiums of the NFL. Accessed May 8, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The [[New York Rangers]] of the [[National Hockey League]] have played in the various locations of Madison Square Garden since their founding in the 1926–1927 season. The Rangers were predated by the [[New York Americans]], who started play in the Garden the previous season, lasting until the team folded after the 1941–1942 NHL season, a season in which it played in the Garden as the ''Brooklyn Americans''.<ref>[http://www.sportsecyclopedia.com/nhl/nya/nyamericans.html New York Americans], Sports Encyclopedia. Accessed May 8, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Media===
| |
| − | Manhattan is served by the major New York City dailies, including ''[[The New York Times]]'', ''[[New York Daily News]]'', and ''[[New York Post]]'', which are all headquartered in the borough. The nation's largest financial newspaper, ''[[The Wall Street Journal]]'', is also based here. Other daily newspapers include ''[[AM New York]]'', ''The Greenwich Village Gazette'' and ''The Villager''. ''[[The New York Amsterdam News]]'', based in Harlem, is one of the leading African American weekly newspapers in the United States. ''[[The Village Voice]]'' is a leading alternative weekly based in the borough.<ref>[http://www.abyznewslinks.com/unitenyny.htm New York City Newspapers and News Media], ABYZ News Links. Accessed May 1, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The television industry developed in New York and is a significant employer in the city's economy. The four major American broadcast networks, [[American Broadcasting Company|ABC]], [[CBS]], [[Fox Broadcasting Company|FOX]] and [[NBC]], are all headquartered in Manhattan, as are many cable channels are based in the city as well, including [[MTV]], [[Fox News]], [[HBO]] and [[Comedy Central]]. In 1971, [[WLIB]] became New York's first black-owned radio station and the crown jewel of [[Inner City Broadcasting Corporation]]. A co-founder of Inner City was [[Percy Sutton]], a former Manhattan borough president and long one of the city’s most powerful black leaders.<ref>Jaker, Bill; Sulek, Frank; and Kanze, Peter[http://books.google.com/books?id=QwQfaS521mkC&pg=PA113&lpg=PA113&dq=wlib+%22inner+city+broadcasting+corporation%22&source=web&ots=lD0A5elcij&sig=HGLxbcoLEtXhsyp1cWqEvo_z9SY "The Airwaves of New York: Illustrated Histories of 156 AM Stations in the Metropolitan Area"], [[Google Book Search]], p. 113. Accessed April 25, 2007.</ref> WLIB began broadcasts for the African-American community in 1949 and regularly interviewed civil rights leaders like [[Malcolm X]] and aired live broadcasts from conferences of the [[National Association for the Advancement of Colored People|NAACP]]. Influential [[WQHT]], also known as ''Hot 97'', claims to be the premier hip-hop station in the United States. [[WNYC]], comprising an AM and FM signal, has the largest public radio audience in the nation and is the most-listened to commercial or non-commercial radio station in Manhattan.<ref>[http://www.wnyc.org/about/bio_pres.html President's Bio], [[WNYC]], accessed May 1, 2007. "Heard by over 1.2 million listeners each week, WNYC radio is the largest public radio station in the country and is dedicated to producing broadcasting which extends New York City’s cultural riches to public radio stations nationwide."</ref> [[WBAI]], with news and information programming, is one of the few socialist radio stations operating in the United States.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The oldest [[public-access television]] channel in the United States is the [[Manhattan Neighborhood Network]], founded in 1971, offers eclectic local programming that ranges from a jazz hour to discussion of labor issues to foreign language and religious programming.<ref>[http://www.mnn.org/en/community-celebrates-public-access-tvs-35th-annive Community Celebrates Public Access TV's 35th Anniversary], [[Manhattan Neighborhood Network]] press release dated August 6, 2006, accessed April 28, 2007. "Public access TV was created in the 1970s to allow ordinary members of the public to make and air their own TV shows—and thereby exercise their free speech. It was first launched in the U.S. in Manhattan July 1st 1971, on the Teleprompter and Sterling Cable systems, now Time Warner Cable."</ref> [[NY1]], [[Time Warner Cable]]'s local news channel, is known for its beat coverage of City Hall and state politics.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Landmarks and architecture===
| |
| − | [[Image:New-York-Jan2005.jpg|thumb|right|250px|View of Midtown from the [[Empire State Building]].]]
| |
| − | The [[skyscraper]], which has shaped Manhattan's distinctive skyline, has been closely associated with New York City's identity since the end of the 19th century. From 1890–1973, the [[List of tallest buildings and structures in the world#Tallest buildings|world's tallest building]] was in Manhattan, with nine different buildings holding the title.<ref>McKinley, Jesse. "F.Y.I.: Tall, Taller. Tallest," ''[[The New York Times]]'', November 5, 1995. p. CY2.</ref> The [[New York World Building]] on [[Park Row (Manhattan)|Park Row]], was the first to take the title, standing 309 feet (91 m) until 1955, when it was demolished to construct a new ramp to the [[Brooklyn Bridge]].<ref>"Big Span Project Initiated by City; Manhattan Plaza of Brooklyn Bridge Would Be Rebuilt to Cope With Traffic Increase COST IS PUT AT $6,910,000 Demolition Program is Set — Street System in the Area Also Faces Rearranging," ''[[The New York Times]], ''July 24, 1954. p. 15.</ref> The nearby [[Park Row Building]], with its 29 stories standing 391 feet high (119 m) took the title in 1899.<ref>Gray, Christopher. [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9A03E6DB1F38F931A25750C0A9669C8B63 " Streetscapes/The Park Row Building, 15 Park Row; An 1899 'Monster' That Reigned High Over the City"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', March 12, 2000. Accessed May 15, 2007.</ref> The 41-story [[Singer Building]], constructed in 1908 as the headquarters of the eponymous sewing machine manufacturer, stood 612 feet high (187 m) until 1967, when it became the tallest building ever demolished.<ref>Gray, Christopher. [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9F0CE4DA1739F931A35752C0A9639C8B63&sec=&spon=&pagewanted=print " STREETSCAPES/Singer Building; Once the Tallest Building, But Since 1967 a Ghost"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', January 2, 2005. Accessed May 15, 2007. "The 41-story Singer Building, the tallest in the world in 1908 when it was completed at Broadway and Liberty Street, was until Sept. 11, 2001, the tallest structure ever to be demolished. The building, an elegant Beaux-Arts tower, was one of the most painful losses of the early preservation movement when it was razed in 1967.... Begun in 1906, the Singer Building incorporated Flagg's model for ''a city of towers,'' with the 1896 structure reconstructed as the base, and a 65-foot-square shaft rising 612 feet high, culminating in a bulbous mansard and giant lantern at the peak."</ref> The [[Metropolitan Life Insurance Company Tower]], standing 700 feet (213 m) at the foot of [[Madison Avenue (Manhattan)|Madison Avenue]], wrested the title in 1909, with a tower reminiscent of [[St Mark's Campanile]] in [[Venice]].<ref>Gray, Christopher. [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9A00E5DA1139F935A15756C0A960958260 " Streetscapes/Metropolitan Life at 1 Madison Avenue;For a Brief Moment, the Tallest Building in the World"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', May 26, 1996. Accessed May 15, 2007.</ref> The [[Woolworth Building]], and its distinctive [[Gothic architecture]], took the title in 1913, topping off at 792 feet (241 m).<ref>Dunlap, David W. [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=990DEFD61030F931A35752C1A9669C8B63 " Condos to Top Vaunted Tower Of Woolworth"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', November 2, 2000. Accessed May 15, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The [[Roaring Twenties]] saw a race to the sky, with three separate buildings pursuing the world's tallest title in the span of a year. As the stock market soared in the days before the [[Wall Street Crash of 1929]], two developers publicly competed for the crown.<ref>"Denies Altering Plans for Tallest Building; Starrett Says Height of Bank of Manhattan Structure Was Not Increased to Beat Chrysler.," ''[[The New York Times]]'', October 20, 1929. p. 14.</ref> At 927 feet (282 m), [[40 Wall Street]], completed in May 1930 in an astonishing 11 months as the headquarters of the [[Bank of Manhattan]], seemed to have secured the title.<ref>"Bank of Manhattan Built in Record Time; Structure 927 Feet High, Second Tallest in World, Is Erected in Year of Work.," ''[[The New York Times]]'', May 6, 1930. p. 53.</ref> At [[Lexington Avenue (Manhattan)|Lexington Avenue]] and [[42nd Street (Manhattan)|42nd Street]], auto executive [[Walter Chrysler]] and his architect [[William Van Alen]] developed plans to build the structure's trademark 185 foot-high (56 m) spire in secret, pushing the [[Chrysler Building]] to 1,046 feet (319 m) and making it the tallest in the world when it was completed in 1929.<ref>Gray, Christopher. [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9C02E3D91739F934A25751C1A963958260 " Streetscapes: The Chrysler Building; Skyscraper's Place in the Sun"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', December 17, 1995. Accessed May 15, 2007. "Then Chrysler and Van Alen again revised the design, this time in order to win a height competition with the 921-foot tower then rising at 40 Wall Street. This was done in secret, using as a staging area the huge square fire-tower shaft, intended to vent smoke from the stairways. Inside the shaft, Van Alen had teams of workers assemble the framework for a 185-foot-high spire that, when lifted into place in the fall of 1929, made the Chrysler building, at 1,046 feet, 4.75 inches high, the tallest in the world."</ref> Both buildings were soon surpassed, with the May 1931 completion of the 86-story [[Empire State Building]] and its [[Art Deco]] spire soaring 1,250 feet (381 m) in the air.<ref>"Rivalry for Height is Seen as Ended; Empire State's Record to Stand for Many Years, Builders and Realty Men Say. Practical Limit Reached; Its Top Rises 1,250 Feet, but Staff Carrying Instruments Extends Pinnacle to 1,265.5 Feet.," ''[[The New York Times]]'', May 2, 1931. p. 7.</ref><ref>Gray, Christopher. [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9E0CE7DE1730F937A25755C0A964958260&n=Top%2FReference%2FTimes%20Topics%2FSubjects%2FE%2FEmpire%20State%20Building "Streetscapes: The Empire State Building; A Red Reprise for a '31 Wonder"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', June 14, 1992. Accessed May 15, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The former Twin Towers of the [[World Trade Center]], once an iconic symbol of the City, were located in [[Lower Manhattan]]. At 1,368 feet (417&m), the 110-story buildings were the world's tallest from 1972, until they were surpassed by the construction of the [[Sears Tower]] in 1974.<ref>Barss, Karen. [http://www.infoplease.com/spot/skyscraperhistory.html "The History of Skyscrapers: A race to the top"], Information Please. Accessed May 17, 2007. "The Empire State Building would reign supreme among skyscrapers for 41 years until 1972, when it was surpassed by the World Trade Center (1,368 feet, 110 stories). Two years later, New York City lost the distinction of housing the tallest building when the Sears Tower was constructed in Chicago (1450 feet, 110 stories)."</ref> By the end of the 20th century the Twin Towers of the World Trade Center were arguably among the world's most famous and recognizable buildings until their destruction in the [[September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks]]. The [[Freedom Tower]], a replacement for the Twin Towers of the World Trade Center, is currently under construction and is slated to be ready for occupancy in 2011.<ref>[http://www.wtc.com/inner_page.aspx?id=14 World Trade Center: Frequently Asked Questions], [[World Trade Center]]. Accessed May 27, 2007. See "Project Information" tab for construction schedule.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | In 1961, [[Penn Central Transportation|Penn Central]] unveiled plans to tear down the old [[Pennsylvania Station (New York City)|Penn Station]] and replace it with a new [[Madison Square Garden]] and [[One Penn Plaza|office building]] complex. Organized protests were aimed at preserving the [[McKim, Mead, and White]]-designed structure completed in 1910, widely considered a masterpiece of the [[Beaux-Arts architecture|Beaux-Arts]] style and one of the architectural jewels of New York City.<ref>Gray, Christopher. [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9902E5D6123AF933A15756C0A9679C8B63 " Streetscapes/'The Destruction of Penn Station'; A 1960's Protest That Tried to Save a Piece of the Past"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', May 20, 2001. Accessed May 17, 2007.</ref> Despite these efforts, demolition of the structure began in October 1963. The loss of Penn Station—called “an act of irresponsible public vandalism” by historian [[Lewis Mumford]]—led directly to the enactment in 1965 of a local law establishing the [[New York City Landmarks Preservation Commission]], which is responsible to preserve the "city's historic, aesthetic, and cultural heritage".<ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/lpc/html/faqs/faq_about.shtml About the Landmarks Preservation Commission], [[New York City Landmarks Preservation Commission]]. Accessed May 17, 2007.</ref> The [[historic preservation]] movement triggered by Penn Station's demise has been credited with the retention of some one million structures nationwide, including nearly 1,000 in New York City.<ref>[http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2002/10/11/sunday/main525288.shtml "Requiem For Penn Station"], [[CBS News]], October 13, 2002. Accessed May 17, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The theatre district around [[Broadway (New York City)|Broadway]] at [[Times Square]], [[New York University]], [[Columbia University]], [[Flatiron Building]], the [[Financial District, Manhattan|Financial District]] around [[Wall Street]], [[Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts]], [[Little Italy]], [[Harlem, Manhattan|Harlem]], the [[American Museum of Natural History]], [[Chinatown, Manhattan|Chinatown]], and [[Central Park]] are all located on this densely populated island.
| |
| | | | |
| − | The city is a leader in energy-efficient "green" office buildings, such as [[Hearst Tower (New York City)|Hearst Tower]] and the rebuilt [[7 World Trade Center]].<ref name="greenbuilding">Pogrebin, Robin. [http://www.nytimes.com/2006/04/16/arts/design/16gree.html "7 World Trade Center and Hearst Building: New York's Test Cases for Environmentally Aware Office Towers"], ''[[The New York Times]], April 16, 2006. Accessed July 19, 2006.</ref>
| + | Seven of the world's top eight global advertising agency networks are headquartered in Manhattan. The term "Madison Avenue" is often used to refer to the entire advertising field, after Sixth Avenue, renamed "Madison Avenue", became identified with the lucrative [[advertising industry]] after the explosive growth in the area in the 1920s. Historically, this corporate presence has been complemented by many independent retailers, though a recent influx of national chain stores has caused many to lament the creeping homogenization of Manhattan. |
| − | | |
| − | [[Central Park]] is bordered on the north by West [[110th Street (Manhattan)|110th Street]], on the west by [[Eighth Avenue (Manhattan)|Eighth Avenue]], on the south by West [[59th Street (Manhattan)|59th Street]], and on the east by [[Fifth Avenue (Manhattan)|Fifth Avenue]]. Along the park's borders, these streets are usually referred to as [[Central Park North]], [[Central Park West]], and [[Central Park South]], respectively. (Fifth Avenue retains its name along the eastern border.) The park was designed by [[Frederick Law Olmsted]] and [[Calvert Vaux]]. The 843 acre (3.4 km²) park offers extensive [[walking track]]s, two [[ice-skating]] rinks, a wildlife sanctuary, and grassy areas used for various sporting pursuits, as well as playgrounds for children. The park is a popular oasis for migrating birds, and thus is popular with bird watchers. The 6 mile (10 km) road circling the park is popular with joggers, bicyclists and inline skaters, especially on weekends and in the evenings after 7:00 p.m., when automobile traffic is banned.<ref name=CentralPark>[http://www.centralpark.com/pages/general-info.html Central Park General Information], Central Park Conservancy. Accessed September 21, 2006.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | While much of the park looks natural, it is almost entirely landscaped and contains several artificial lakes. The construction of Central Park in the 1850s was one of the era's most massive public works projects. Some 20,000 workers crafted the topography to create the English-style pastoral landscape Olmsted and Vaux sought to create. Workers moved nearly 3 million cubic yards of soil and planted more than 270,000 trees and shrubs.<ref>[http://www.centralpark.com/pages/history_2.html Central Park History], Central Park Conservancy. Accessed September 21, 2006.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | 17.8% of the borough, a total of 2,686 acres (10.9 km²), are devoted to parkland. Almost 70% of Manhattan's space devoted to parks is located outside of Central Park, including 204 playgrounds, 251 Greenstreets, 371 basketball courts and many other amenities.<ref name=MBPOEnvironment/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | '''360° Panorama of Manhattan seen from the Empire State Building'''
| |
| − | <div style="height: 295px; width: 95%; overflow: auto; padding: 3px;text-align: left; border:solid 1px;" title="braglist - zum scrollen"; >
| |
| − | [[Image:Skyline-New-York-City.jpg|3000px|360° Panorama of Manhattan seen from the Empire State Building]] </div> <br style="clear:both;"/>
| |
| | | | |
| | ==Housing== | | ==Housing== |
| − | In the early days of Manhattan, wood construction and poor access to water supplies left the city vulnerable to fires. In 1776, shortly after the [[Continental Army]] evacuated Manhattan and left it to the British, a massive fire broke out destroying one-third of the city and some 500 houses.<ref>[http://www.virtualny.cuny.edu/FIRE/greatfire1776.html Great Fire of 1776], [[City University of New York]]. Accessed April 30, 2007. "Some of Washington's advisors suggested burning New York City so that the British would gain little from its capture. This idea was abandoned and Washington withdrew his forces from the city on September 12, 1776. Three days later the British occupied the city and on September 21st, a fire broke out in the Fighting Cocks Tavern. Without the city's firemen present and on duty, the fire quickly spread. A third of the city burnt and 493 houses destroyed."</ref> | + | In the early days of Manhattan, wood construction and poor access to water supplies left the city vulnerable to fires. In 1776, shortly after the [[Continental Army]] evacuated Manhattan and left it to the British, a massive fire broke out, destroying one-third of the city and some 500 houses.<ref>[http://www.virtualny.cuny.edu/FIRE/greatfire1776.html Great Fire of 1776, [[City University of New York]] ]. ''www.virtualny.cuny.edu''. Retrieved April 30, 2007. "Some of Washington's advisers suggested burning New York City so that the British would gain little from its capture. This idea was abandoned, and Washington withdrew his forces from the city on September 12, 1776. Three days later, the British occupied the city, and on September 21, a fire broke out in the Fighting Cocks Tavern. Without the city's firemen present and on duty, the fire quickly spread. A third of the city burnt and 493 houses destroyed."</ref> |
| | | | |
| − | The rise of immigration near the turn of the century left major portions of Manhattan, especially the [[Lower East Side]], densely packed with recent arrivals, crammed into unhealthy and unsanitary housing. Tenements were usually five-stories high, constructed on the then-typical 25x100 lots, with "cockroach landlords" exploiting the new immigrants.<ref>[http://www.upress.umn.edu/sles/Chapter2/ch2-3.html Building the Lower East Side Ghetto], accessed April 30, 2007.</ref><ref name=NYTTenements>Peterson, Iver. [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=940DE3D8163BF930A35752C0A96E948260 "Tenements of 1880's Adapt to 1980's"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', January 3, 1988, accessed April 30, 2007. "Usually five stories tall and built on a 25-foot lot, their exteriors are hung with fire escapes and the interiors are laid out long and narrow—in fact, the apartments were dubbed railroad flats."</ref> By 1929, stricter fire codes and the increased use of elevators in residential buildings, were the impetus behind a new housing code that effectively ended the tenement as a form of new construction, though many tenement buildings survive today on the East Side of the borough.<ref name=NYTTenements/> | + | The rise of immigration near the turn of the century left major portions of Manhattan, especially the Lower East Side, densely packed with recent arrivals, crammed into unhealthy and unsanitary housing. Tenements were usually five-stories high, constructed on the then-typical 25x100 lots, with landlords exploiting the new immigrants.<ref>[http://www.upress.umn.edu/sles/Chapter2/ch2-3.html Building the Lower East Side Ghetto]. ''www.upress.umn.edu''. Retrieved April 30, 2007.</ref> By 1929, stricter fire codes and the increased use of elevators in residential buildings were the impetus behind a new housing code that effectively ended the tenement as a form of new construction, though many tenement buildings survive today on the East Side of the borough. |
| | | | |
| − | Today, Manhattan offers a wide array of public and private housing options. There were 798,144 housing units in Manhattan as of the 2000 Census, at an average density of 34,756.7/mi² (13,421.8/km²).<ref name=NYCensusRankings/> Only 20.3% of Manhattan residents lived in owner-occupied housing, the second-lowest rate of all counties in the nation, behind [[The Bronx]].<ref name=OwnerOccupied/> | + | Today, Manhattan offers a wide array of public and private housing options. There were 798,144 housing units in Manhattan as of the 2000 Census, at an average density of 34,756.7/mi² (13,421.8/km²). Only 20.3 percent of Manhattan residents lived in owner-occupied housing, the second-lowest rate of all counties in the nation, behind The Bronx. |
| | | | |
| − | ==Infrastructure== | + | ==Notes== |
| − | ===Transportation===
| + | <references/> |
| − | [[Image:Grand Central test.jpg|thumb|right|250px|[[Grand Central Terminal]]]]
| |
| − | [[Image:Mta station wall.jpg|thumb|250px|The [[New York City Subway]] is the primary means of travel in Manhattan.]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | {{seealso|Transportation in New York City}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | Manhattan is unique in the United States for its intense use of [[public transportation]] and lack of private car ownership. While 88% of Americans nationwide drive to their jobs and only 5% use public transportation, mass transit is the dominant form of travel for residents of Manhattan, with 72% of borough resident using public transportation and only 18% driving to work.<ref name=2001summary>[http://www.bts.gov/publications/highlights_of_the_2001_national_household_travel_survey/html/executive_summary.html Highlights of the 2001 National Household Travel Survey], [[Bureau of Transportation Statistics]], [[United States Department of Transportation]]. Accessed May 21, 2006.</ref><ref>[http://home2.nyc.gov/html/dcp/pdf/transportation/td_fullpedlosb.pdf "New York City Pedestrian Level of Service Study - Phase I, 2006"], [[New York City]] Department of City Planning, April 2006, p. 4. Accessed May 17, 2007. "In the year 2000, 88% of workers over 16 years old in the U.S. used a car, truck or van to commute to work, while approximately 5% used public transportation and 3% walked to work.... In Manhattan, the borough with the highest population density (66,940 people/sq mi. in year 2000; 1,564,798 inhabitants) and concentration of business and tourist destinations, only 18% of the working population drove to work in 2000, while 72% used public transportation and 8% walked."</ref> According to the [[United States Census, 2000|2000 U.S. Census]], more than 75% of Manhattan households do not own a car.<ref name=2001summary />
| |
| − | | |
| − | In 2007, Mayor Bloomberg [[New York congestion pricing|proposed]] a [[congestion pricing]] system that would charge drivers entering Manhattan below [[86th Street (Manhattan)|86th Street]] between 6 a.m. and 6 p.m. weekdays a fee of $8 per car or $21 per truck, with lower fees for travel within the pricing zone. The plan would be modeled on a similar system in [[London]], and is intended to improve air quality and traffic flow, with funds raised used for mass transit improvements throughout the city.<ref>Hakim, Dan and Rivera, Ray. [http://www.nytimes.com/2007/06/08/nyregion/08congestion.html?_r=1&ref=nyregion&oref=slogin "City Traffic Pricing Wins U.S. and Spitzer’s Favor"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', June 8, 2007. Accessed June 12, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The [[New York City Subway]], the largest [[Rapid transit|subway]] system in the world by track mileage, is the primary means of travel within the city, connecting to every borough except Staten Island. A second subway, the [[Port Authority Trans-Hudson]] (PATH) system, connects Manhattan to northern [[New Jersey]]. Transit passengers tender their fares with pay-per-ride [[MetroCard (New York City)|MetroCard]]s, which are valid on all city buses and subways, as well as on PATH trains. A one-way fare on the bus or subway is $2.00,<ref>[http://www.mta.info/nyct/subway/howto_sub.htm How to Ride the Subway], [[Metropolitan Transportation Authority (New York)]]. Accessed May 11, 2007.</ref> and PATH costs $1.50.<ref>[http://www.panynj.gov/CommutingTravel/path/html/fares.html PATH Rapid-Transit System: Fares and QuickCard], [[Port Authority of New York and New Jersey]]. Accessed September 10, 2006.</ref> There are daily, 7-day, and 30-day MetroCards that allow unlimited trips on all subways (except PATH) and MTA bus routes (except for express buses).<ref>[http://www.mta.info/metrocard/index.html Metrocard], [[Metropolitan Transportation Authority (New York)]]. Accessed May 11, 2007.</ref> The PATH QuickCard is being phased out, and both PATH and the MTA are testing "smart card" payment systems to replace the MetroCard.<ref>[http://www.panynj.gov/CommutingTravel/path/html/faq.html PATH Frequently Asked Questions], [[Port Authority of New York and New Jersey]], accessed April 28, 2007. "PATH will phase out QuickCard once the SmartLink Fare Card is introduced."</ref> [[regional rail|Commuter rail]] services operating to and from Manhattan are the [[Long Island Rail Road]] (which connects Manhattan and other [[New York City]] boroughs to [[Long Island]]), the [[Metro-North Railroad]] (which connects Manhattan to [[Westchester County]] and Southwestern Connecticut) and [[New Jersey Transit]] trains to various points in New Jersey.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The [[New York City Transit buses|MTA New York City Bus]] offers a wide variety of local buses within Manhattan. An extensive network of express bus routes serves commuters and other travelers heading into Manhattan. The bus system served 740 million riders in 2004, ranking first in the nation, more than double the ridership in second-ranked [[Los Angeles, California|Los Angeles]].<ref>[http://www.mta.info/nyct/facts/ffbus.htm Bus Facts], [[Metropolitan Transportation Authority (New York)]], accessed May 11, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | New York's iconic yellow cabs, which number 13,087 city-wide and must have the requisite medallion authorizing the pick up of street hails, are ubiquitous in the borough.<ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/tlc/html/about/about.shtml About the NYC Taxi and Limousine Commission], accessed September 4, 2006.</ref> Manhattan also sees tens of thousands of bicycle commuters. The [[Roosevelt Island Tramway]], the only commuter cable car in North America, whisks commuters between [[Roosevelt Island]] and Manhattan in less than five minutes, and has been servicing the island since 1978.<ref>[http://www.rioc.com/thetram.htm The Roosevelt Island Tram], [[Roosevelt Island Operating Corporation]], accessed April 30, 2007.</ref> The [[Staten Island Ferry]], which runs 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, annually carries over 19 million passengers on the 5.2 mile (8.4 km) run between Manhattan and Staten Island. Each weekday five vessels are used to transport almost 65,000 passengers on 110 boat trips.<ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/dot/html/masstran/ferries/statfery.html#facts Facts About the Ferry], [[New York City Department of Transportation]], accessed April 28, 2007. "A typical weekday schedule involves the use of five boats to transport approximately 65,000 passengers daily (110 daily trips). A four-boat (15 minute headway) rush hour schedule is maintained."</ref><ref>[http://www.nyccouncil.info/pdf_files/reports/siferry.pdf An Assessment of Staten Island Ferry Service and Recommendations for Improvement] (PDF), [[New York City Council]], November 2004, accessed April 28, 2007. ""Of the current fleet of seven vessels, five boats make 104 trips on a typical weekday schedule".</ref> The ferry has been fare-free since 1997, when the then-50-cent fare was eliminated.<ref>Holloway, Lynette. [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9402E2DF1331F93AA15757C0A961958260 "Mayor to End 50-Cent Fare On S.I. Ferry"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', April 29, 1997, accessed April 28, 2007. "Mayor Rudolph W. Giuliani said yesterday that he would eliminate the 50-cent fare on the Staten Island Ferry starting July 4, saying people who live outside Manhattan should not have to pay extra to travel."</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The metro region's commuter rail lines converge at [[Pennsylvania Station (New York City)|Penn Station]] and [[Grand Central Terminal]], on the west and east sides of Midtown Manhattan, respectively. They are the two busiest rail stations in the United States. About one in every three users of mass transit in the country and two-thirds of the nation's rail riders live in New York and its suburbs.<ref>[http://mta.info/mta/network.htm The MTA Network], [[Metropolitan Transportation Authority (New York)|Metropolitan Transportation Authority]], accessed May 17, 2006.</ref> [[Amtrak]] provides inter-city passenger rail service from Penn Station to [[Boston, Massachusetts|Boston]], [[Philadelphia, Pennsylvania|Philadelphia]], [[Baltimore, Maryland|Baltimore]] and [[Washington, D.C.]]; [[Upstate New York]], [[New England]]; cross-border service to [[Toronto]] and [[Montreal]]; and destinations in the South and Midwest.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The [[Lincoln Tunnel]], which carries 120,000 vehicles per day under the Hudson River between New Jersey and Manhattan, is the world's busiest vehicular tunnel.<ref>[http://www.nycroads.com/crossings/lincoln/ Lincoln Tunnel Historic Overview], NYCRoads.com. Accessed April 28, 2007. "According to the Port Authority, the Lincoln Tunnel carries approximately 120,000 vehicles per day (AADT), making it the busiest vehicular tunnel in the world."</ref> It was built instead of a bridge to allow for unfettered passage of large passenger and cargo ships that sailed through [[New York Harbor]] and up the Hudson to Manhattan's piers. The [[Queens Midtown Tunnel]], built to relieve congestion on the bridges connecting Manhattan with Queens and Brooklyn, was the largest non-Federal project of its time when it was completed in 1940.<ref>[http://www.nycroads.com/crossings/queens-midtown/ Queens-Midtown Tunnel], NYCRoads.com. Accessed April 27, 2007. "The twin-tube tunnel was completed on November 15, 1940. When it opened, it was the largest non-Federal project of its time."</ref> President [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]] was the first person to drive through it.<ref>"President the 'First' to Use Midtown Tube; Precedence at Opening Denied Hundreds of Motorists," ''[[The New York Times]]'', November 9, 1940. p. 19.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The [[Franklin D. Roosevelt East River Drive|FDR Drive]] and [[Harlem River Drive]] are two limited-access routes that skirt the East Side of Manhattan along the East River, designed by controversial New York master planner [[Robert Moses]].<ref>Kennicott, Philip. [http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/03/09/AR2007030900449.html "A Builder Who Went to Town: Robert Moses Shaped Modern New York, for Better and for Worse"], ''[[The Washington Post]]'', March 11, 2007, accessed April 30, 2007. "The list of his accomplishments is astonishing: seven bridges, 15 expressways, 16 parkways, the West Side Highway and the Harlem River Drive…"</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Manhattan has three public heliports. [[US Helicopter]] offers regularly scheduled helicopter service connecting the [[Downtown Manhattan Heliport]] with [[John F. Kennedy International Airport]] in Queens and [[Newark Liberty International Airport]] in [[New Jersey]].<ref>Yu, Roger. [http://www.usatoday.com/money/biztravel/2006-12-10-check-in-copter_x.htm Airport Check-in: Speedy service from Newark to Manhattan coming], ''[[USA Today]]'', December 10, 2006. Accessed April 28, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | New York has the largest clean-air diesel-[[hybrid vehicle|hybrid]] and [[compressed natural gas]] bus fleet in the country, and some of the first hybrid taxis, most of which operate in Manhattan.<ref>[http://www.sierraclub.org/pressroom/releases/pr2005-07-01a.asp "New York City’s Yellow Cabs Go Green"] [[Sierra Club]] press release dated July 1, 2005. Accessed July 19, 2006.</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Utilities===
| |
| − | Gas and electric service is provided by [[Consolidated Edison]] to all of Manhattan. Con Edison's electric business traces its roots back to [[Thomas Edison]]'s [[Edison Illuminating Company|Edison Electric Illuminating Company]], the first investor-owned electric utility. The company started service on September 4, 1882, using one generator to provide 110 [[volt]]s [[direct current]] (DC) to 59 customers with 800 light bulbs, in a one-square-mile area of [[Lower Manhattan]] from his [[Pearl Street Station]].<ref>[http://www.eei.org/industry_issues/industry_overview_and_statistics/history/index.htm "History of the Electric Power Industry"], [[Edison Electric Institute]]. Accessed May 16, 2007.</ref> Con Edison operates the world's largest [[District heating|district steam]] system, which consists of 105 miles (169 km) of steam pipes, providing steam for heating, hot water, and air conditioning<ref>Ray, C. Claiborne. [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9E0CEEDE1530F931A25756C0A964958260 "Q&A"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', May 12, 1992. Accessed May 16, 2007. "In a steam-powered system, the whole cycle of compression, cooling, expansion and evaporation takes place in a closed system, like that in a refrigerator or electrical air-conditioner. The difference, Mr. Sarno said, is that the mechanical power to run the compressor comes from steam-powered turbines, not electrical motors."</ref> by some 1,800 Manhattan customers.<ref>[http://www.coned.com/history/steam.asp A brief history of con edison: steam], [[Consolidated Edison]]. Accessed May 16, 2007.</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | Manhattan, surrounded by two brackish rivers, had a limited supply of fresh water available on the island, which dwindled as the city grew rapidly after the [[American Revolutionary War]]. To supply the needs of the growing population, the city acquired land in [[Westchester County, New York|Westchester County]] and constructed the [[Croton Aqueduct]] system, which went into service in 1842. The system took water from a dam at the [[Croton River]], and sent it down through [[the Bronx]], over the [[Harlem River]] via the [[High Bridge (New York City)|High Bridge]], to storage reservoirs in [[Central Park]] and at [[42nd Street (Manhattan)|42nd Street]] and [[Fifth Avenue (Manhattan)|Fifth Avenue]], and through a network of cast iron pipes on to consumer's faucets.<ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/dep/html/history.html New York City's Water Supply System: History], [[New York City Department of Environmental Protection]]. Accessed September 5, 2006.</ref>
| + | ==References== |
| | + | * Burrows, Edwin G., and Mike Wallace. ''Gotham: A History of New York City to 1898'' (The History of NYC Series). Oxford University Press, 1998. ISBN 0195116348 |
| | + | *Ellis, Edward Robb. ''The Epic of New York City: A Narrative History.'' Reprint. Carroll & Graf, 2005. ISBN 0786714360 |
| | + | *Fortenbaugh, Robert. ''The Nine Capitals of the United States.'' York, PA: Maple Press, 1948. |
| | + | *Jackson, Kenneth T. ''The Encyclopedia of New York City.'' Yale University Press, 1995. ISBN 0300055366 |
| | + | *Hamill, Pete. ''Downtown: My Manhattan''. New York: Little, Brown, 2004. ISBN 9780316734516 |
| | + | *Shorto, Russell. ''The Island at the Center of the World: The Epic Story of Dutch Manhattan and the Forgotten Colony That Shaped America''. New York: Doubleday, 2004. ISBN 9780385503495 |
| | + | *Mackay, Donald A. ''The Building of Manhattan''. New York: Harper & Row, 1987. ISBN 9780060157883 |
| | + | *Sullivan, Dr. James. ''The History of New York State.'' Lewis Historical Publishing Company, Inc., 1927. |
| | | | |
| − | Today, the [[New York City Department of Environmental Protection]] provides water to residents fed by a 2,000 square mile (5,180 km²) [[drainage basin|watershed]] in the [[Catskill Mountains]]. Because the watershed is in one of the largest protected wilderness areas in the United States, the natural water filtration process remains intact. As a result, New York is one of only five major cities in the United States with drinking water pure enough to require only chlorination to ensure its purity at the tap under normal conditions.<ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/dep/html/news/tokyo2.html "Maintaining Water Quality that Satisfies Customers: New York City Watershed Agricultural Program."], [[New York City Department of Environmental Protection]], November 20, 1998. Accessed May 16, 2007.</ref><ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/dep/html/wsstate.html "2005 Drinking Water Supply and Quality Report"], [[New York City Department of Environmental Protection]]. Accessed July 19, 2006.</ref> Water comes to Manhattan through [[New York City Water Tunnel No. 1]] and [[New York City Water Tunnel No. 2|Tunnel No. 2]], completed in 1917 and 1936, respectively. Construction started in 1970 continues on [[New York City Water Tunnel No. 3]], which will double the system's exisiting 1.2 billion gallon-a-day capacity while and provide a much-needed backup to the two other tunnels.<ref>Chan, Sewell. [http://www.nytimes.com/2006/08/10/nyregion/10tunnel.html?ex=1312862400&en=d8d98e5d189bd599&ei=5088&partner=rssnyt&emc=rss "Tunnelers Hit Something Big: A Milestone"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', August 10, 2006. Accessed May 16, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The [[New York City Department of Sanitation]] is responsible for garbage removal.<ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/dsny/html/about/about.shtml About DSNY], [[New York City Department of Sanitation]], Accessed May 16, 2007.</ref> Trash is disposed at dumps in New Jersey, since the 2001 closure of the [[Fresh Kills Landfill]] on [[Staten Island]].<ref>Burger, Michael and Stewart, Christopher. [http://www.gothamgazette.com/iotw/garbage/ "Garbage After Fresh Kills"], ''[[Gotham Gazette]]'', January 28, 2001. Accessed May 16, 2007. "To make up for the loss of Fresh Kills, the city plans to ship much of its garbage out of town by way of a mega-transfer site in Linden, New Jersey"</ref><ref name=MBPOEnvironment>[http://www.mbpo.org/policy/environment Environment], Manhattan Borough President's Office. Accessed May 16, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==Education==
| |
| − | {{seealso|Education in New York City|List of colleges and universities in New York City}}
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Image:New York Public Library 030616.jpg|250px|thumb|New York Public Library, central block, built 1897–1911, [[Carrère and Hastings]], architects (June 2003)]]
| |
| − | Education in Manhattan is provided by a vast number of public and private institutions. Public schools in the borough are operated by the [[New York City Department of Education]], the largest public school system in the United States,<ref>[http://www.city-data.com/us-cities/The-Northeast/New-York-Education-and-Research.html New York: Education and Research], City Data. Accessed September 10, 2006.</ref> serving 1.1 million students.<ref>Gootman, Elissa. [http://www.nytimes.com/2006/09/05/nyregion/05schools.html "Back to School in a System Being Remade"], ''[[The New York Times]], September 5, 2006. Accessed May 11, 2007.</ref>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Some of the best-known New York City public high schools, such as [[Stuyvesant High School]], [[Fiorello H. LaGuardia High School of Music & Art and Performing Arts|Fiorello H. LaGuardia High School]], [[High School of Fashion Industries]], [[Murry Bergtraum High School]], [[Manhattan Center for Science and Mathematics]] and [[Hunter College High School]], are located in Manhattan. The city also hosts a new hybrid school, [[Bard High School Early College]], which serves students from around the city.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Manhattan is home to many of the most prestigious private prep schools in the nation, the most well-known are the elite [[Brearley School]], [[Chapin School]], [[Collegiate School]], [[Dalton School]], and [[Spence School]]. The borough is also home to two private schools that are known for being the most diverse in the nation, they are [[Manhattan Country School]] and [[United Nations International School]].
| |
| − |
| |
| − | As of 2003, 52.3% of Manhattan residents over age 25 have a bachelor's degree, the fifth highest of all counties in the country.<ref>[http://www.census.gov/acs/www/Products/Ranking/2003/R02T050.htm Percent of People 25 Years and Over Who Have Completed a Bachelor's Degree], [[United States Census Bureau]], accessed April 28, 2007.</ref> By 2005, about 60% of residents were college graduates and some 25% had earned advanced degrees, giving Manhattan one of the nation's densest concentrations of highly educated people.<ref>McGeehan, Patrick. [http://select.nytimes.com/gst/abstract.html?res=FB0E16FF3F5A0C758DDDA10894DE404482 "New York Area Is a Magnet For Graduates"], ''[[The New York Times]]'', August 16, 2006. Accessed June 6, 2007. "In Manhattan, nearly three out of five residents were college graduates and one out of four had advanced degrees, forming one of the highest concentrations of highly educated people in any American city."</ref>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Manhattan has various colleges and universities including [[Columbia University]], [[New York University]] (NYU) and [[Fordham University]]. Other schools include [[The Juilliard School]], [[New York Institute of Technology]], [[Pace University]], [[Yeshiva University]], [[Cooper Union]], [[The New School]], and the [[Fashion Institute of Technology]], part of the [[State University of New York]].
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The [[City University of New York]] (CUNY), the municipal college system of New York City, is the largest urban university system in the United States, serving more than 226,000 degree students and a roughly equal number of adult, continuing and professional education students.<ref>[http://www1.cuny.edu/about/index.html The City University of New York is the nation's largest urban public university], [[City University of New York]], accessed April 27, 2007. "The City University of New York is the nation's largest urban public university…"</ref> A third of college graduates in New York City graduate from CUNY, with the institution enrolling about half of all college students in New York City. CUNY senior colleges located in Manhattan include: [[Baruch College]], [[City College of New York]], [[Hunter College]], [[John Jay College of Criminal Justice]], and the [[CUNY Graduate Center]] (graduate studies and doctoral granting institution). The only CUNY community college located in Manhattan is the [[Borough of Manhattan Community College]].
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Manhattan is a world center for training and education in medicine and the life sciences.<ref>{{cite news|title=Mayor Michael R. Bloomberg and Economic Development Corporation President Andrew M. Alper Unveil Plans to Develop Commercial Bioscience Center in Manhattan|author=New York City Economic Development Corporation|url=http://home2.nyc.gov/portal/site/nycgov/menuitem.c0935b9a57bb4ef3daf2f1c701c789a0/index.jsp?pageID=mayor_press_release&catID=1194&doc_name=http%3A%2F%2Fhome2.nyc.gov%2Fhtml%2Fom%2Fhtml%2F2004b%2Fpr310-04.html&cc=unused1978&rc=1194&ndi=1|date=2004-11-18|accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> The city as a whole receives the second-highest amount of annual funding from the [[National Institutes of Health]] among all U.S. cities<ref>{{cite web|title=NIH Domestic Institutions Awards Ranked by City, Fiscal Year 2003|author=National Institutes of Health|date=2003|url=http://grants.nih.gov/grants/award/trends/top100fy03.htm|accessdate=2007-03-26}}</ref>, the bulk of which goes to Manhattan's research institutions, including [[Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center]], [[Rockefeller University]], [[Mount Sinai School of Medicine]] and [[Weill Cornell Medical College]].
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Manhattan is served by the [[New York Public Library]], which has the largest collection of any public library system in the country.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.libraryspot.com/lists/listlargestlibs.htm |title=Nation's Largest Libraries |publisher=LibrarySpot |accessdate=2007-06-06}}</ref> The five units of the Central Library—Mid-Manhattan Library, Donnell Library Center, The New York Public Library for the Performing Arts, Andrew Heiskell Braille and Talking Book Library and the Science, Industry and Business Library—are all located in Manhattan.<ref>[http://www.nypl.org/branch/central/ The Central Libraries], [[New York Public Library]]. Accessed June 6, 2007.</ref> More than 35 other branch libraries are located in the borough.<ref>[http://www.nypl.org/hours/index.cfm?Trg=1&b=mn Manhattan Map], [[New York Public Library]]. Accessed June 6, 2006.</ref>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == See also ==
| |
| − | * [[Midtown (Manhattan)|Midtown]]
| |
| − | * [[Lower Manhattan]]
| |
| − | * [[Sawing off of Manhattan Island]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==Notes==
| |
| − | {{reflist|2}}
| |
| | | | |
| | ==External links== | | ==External links== |
| − | {{commons|Manhattan}}
| + | All links retrieved November 5, 2022. |
| − | ;Manhattan local government and services
| + | * [http://manhattanbp.nyc.gov/html/home/home.shtml Manhattan Borough President official site]. |
| − | * [http://www.mbpo.org/ Manhattan Borough President official site] | + | * [http://www.manhattanda.org/ Manhattan District Attorney official site]. ''www.manhattanda.org''. |
| − | * [http://www.manhattanda.org/ Manhattan District Attorney official site] | + | * [http://newyorkbirds.free.fr/bridges%20of%20New%20York/Manhattan%20Bridges/index.php Aerial view of all bridges in Manhattan]. ''newyorkbirds.free.fr''. |
| − | | + | * Maps of [http://www.radicalcartography.net/?manhattan-heights Building Heights], and [http://www.radicalcartography.net/?manhattan-value Land Value], plus [http://www.radicalcartography.net/?manhattan-dev theoretical] and [http://www.radicalcartography.net/?manhattan-far zoning-based] maps of underdevelopment, all from ''www.radicalcartography.net''. |
| − | ;Maps, streets, and neighborhoods
| |
| − | * [http://newyorkbirds.free.fr/bridges%20of%20New%20York/Manhattan%20Bridges/index.php Aerial view of all bridges in Manhattan] | |
| − | * Maps of [http://www.radicalcartography.net/?manhattan-heights Building Heights] and [http://www.radicalcartography.net/?manhattan-value Land Value], plus [http://www.radicalcartography.net/?manhattan-dev theoretical] and [http://www.radicalcartography.net/?manhattan-far zoning-based] maps of underdevelopment, all from www.radicalcartography.net | |
| − | * [http://www.gentrify.us/manhattan.html Gentrification in Manhattan (Harlem, Lower East Side and Washington Heights neighborhoods are profiled. Contains photos, links and an interactive map]
| |
| − | * [http://manhattan.mobi Manhattan's Mobile Internet for cell phone users]
| |
| − | | |
| − | ;Historical references
| |
| − | * [http://teachpol.tcnj.edu/amer_pol_hist/fi/00000006.htm Map of Mannados or Manhattan in 1661 (PD)]
| |
| − | * [http://bklyn-genealogy-info.com/Map/NY.1729.html 1729 map of Manhattan]
| |
| − | | |
| − | {{New York City}}
| |
| − | {{Manhattan}}
| |
| − | {{New York City Islands}}
| |
| | | | |
| − | {{coor title dms|40|43|42|N|73|59|39|W|Type:City}}
| + | [[Category:Geography]] |
| | + | [[Category:Cities]] |
| | + | [[Category:United States]] |
| | | | |
| − | [[Category:nations and places]]
| + | {{Credits|141079400}} |
| − | {{Credit|141079400}} | |
| Manhattan |
| — Borough of New York City — |
| New York County |
|
Midtown Manhattan as seen from the GE Building.
|
| The Borough of Manhattan, highlighted in yellow, lies between the East River and the Hudson River.
|
| Coordinates: 40°44′N 73°59′W |
| Country
| United States
|
| State
| New York
|
| County
| New York County
|
| City
| New York City
|
| Settled |
1624 |
| Government |
| - Type |
Borough (New York City) |
| - Borough President
| Scott Stringer (D)
— (Borough of Manhattan) |
| - District Attorney
| Cyrus Vance, Jr.
— (New York County) |
| Area |
| - Total
|
33.77 sq mi (87.5 km²) |
| - Land |
22.96 sq mi (59.5 km²) |
| - Water |
10.81 sq mi (28 km²) |
| Population (2010) |
| - Total |
1,585,873 |
| - Density |
70,951/sq mi (27,394.3/km²) |
| - Demonym |
Manhattanite |
| Time zone |
EST (UTC-5)
|
| - Summer (DST) |
EDT (UTC-4) |
| Website: Official Website of the Manhattan Borough President
|
Manhattan is a borough of New York City, New York, USA, coterminous with New York County. It is the most densely populated area in the United States. The Island of Manhattan is the largest section of the borough, which also includes several smaller islands and a small section of the mainland adjacent to The Bronx. The name Manhattan derives from the word Manna-hata, as written in the 1609 logbook of Robert Juet, an officer on Henry Hudson's yacht Halve Maen (Half Moon).
A commercial, financial, and cultural center of the city, Manhattan has many famous landmarks, tourist attractions, museums, and universities. It is also home to the headquarters of the United Nations and the seat of city government. Manhattan has the largest central business district in the United States. It is the site of both the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ, and is the home to the largest number of corporate headquarters in the nation.
History
Colonial

Lower Manhattan in 1660, when it was part of New Amsterdam. The large structure toward the tip of the island is Fort Amsterdam.
The area that is now Manhattan was long inhabited by the Lenape tribe. In 1524, Lenape, in canoes, met Giovanni da Verrazzano, the first European explorer to pass New York Harbor. [1] It was not until the voyage of Henry Hudson, an Englishman who worked for the Dutch East India Company, that the area was mapped.[2] Hudson discovered Manhattan Island on September 11, 1609 and continued up the river that bears his name until he arrived at the site of present day Albany.[3]
A permanent European presence in "New Netherland" began in 1624 with the founding of a Dutch fur trading settlement on Governors Island. In 1625, Manhattan Island was chosen as the site of Fort Amsterdam, a citadel for the protection of the new arrivals; establishment is recognized as the birth date of New York City.[4] In 1626, Peter Minuit acquired Manhattan from native people in exchange for trade goods, often said to be worth $24.
In 1647, Peter Stuyvesant was appointed as the last Dutch Director General of the colony.[5] The colony was granted self-government in 1652 and New Amsterdam was formally incorporated as a city on February 2, 1653.[6] In 1664, the British conquered the area and renamed it "New York" after the English Duke of York and Albany. Stuyvesant and his council negotiated 24 articles of provisional transfer with the British which sought to guarantee New Netherlanders liberties, including freedom of religion, under British rule.[7]
American Revolution and early United States
Manhattan was at the heart of the New York Campaign, a series of major battles in the early American Revolutionary War. The Continental Army was forced to abandon Manhattan after the disastrous Battle of Fort Washington on November 16, 1776. The city became the British political and military center of operations in North America for the remainder of the war.[8] Manhattan was greatly damaged by the Great Fire of New York during the British military rule that followed. British occupation lasted until November 25, 1783, when George Washington returned to Manhattan, as the last British forces left the city.

Statue of
George Washington in front of Federal Hall, on the site where Washington was inaugurated as the first U.S. President.
From January 11, 1785 to Autumn 1788, New York City was the fifth of five U.S. capitals under the Articles of Confederation, with the Continental Congress residing at New York City Hall, then at Fraunces Tavern. New York was the first capital under the newly enacted Constitution of the United States, from March 4, 1789 to August 12, 1790 at Federal Hall.[9]
Nineteenth century growth
New York grew as an economic center, first as a result of Alexander Hamilton's policies and practices as the first Secretary of the Treasury and, later, with the opening of the Erie Canal in 1825, which connected New York's Atlantic port to the vast agricultural producers of the mid-western United States and Canada. By 1835, New York City had surpassed Philadelphia as the largest city in the United States.
In politics, Tammany Hall began to grow in influence with the support of many of the immigrant Irish, culminating in the election of the first Tammany mayor, Fernando Wood, in 1854. The Democratic Party political machine dominated local politics for decades. Central Park, which opened to the public in 1858, became the first landscaped park in an American city and the nation's first public park.[10]
During the American Civil War, the city's strong commercial ties to the South, its growing immigrant population, anger about conscription and resentment at those who could afford to pay $300 to avoid service, led to resentment against Lincoln's war policies, culminating in the three-day long New York Draft Riots of July 1863, one of the worst incidents of civil disorder in American history, with an estimated 119 participants and passersby killed.[11]

Thomas Nast denounces Tammany as a ferocious tiger killing democracy; the tiger image caught on.
After the American Civil War, the rate of immigration from Europe grew steeply, and New York became the first stop for millions seeking a new and better life in the United States, a role acknowledged by the dedication of the Statue of Liberty on October 28, 1886, a gift from the people of France. The new European immigration brought further social upheaval. In a city of tenements packed with poorly paid laborers from dozens of nations, the city was a hotbed of socialist revolution, racketeering, and unionization.
In 1874, the western portion of the present Bronx was transferred to New York County, and in 1895, the remainder of the present Bronx County was annexed. The City of Greater New York was formed in 1898, with Manhattan and the Bronx, though still one county, established as two separate boroughs. On January 1, 1914, the New York State Legislature created Bronx County, and New York County was reduced to its present boundaries.[12]
The twentieth century
The construction of the New York City Subway, first opened in 1904, helped bind the new city together. Tragedy struck the city on March 25, 1911, when the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire in Greenwich Village took the lives of 146 garment workers, mostly young women, which would eventually lead to great improvements in the city's fire department, building codes, and workplace regulations.[13] Starting in the 1920s, the city saw the influx of African Americans as part of the Great Migration from the U.S. Southern states and the Harlem Renaissance, part of a larger boom time in the Prohibition era that saw dueling skyscrapers rise in the Manhattan skyline. New York City became the most populous city in the world in 1925, overtaking London, which had reigned for a century.[14]
The period between the World Wars saw the election of reformist mayor Fiorello LaGuardia and the fall of Tammany Hall after 80 years of political dominance.[15] As the city's demographics stabilized, labor unionization brought new protections and affluence to the working class. The city's government and infrastructure underwent a dramatic overhaul under LaGuardia. Despite the effects of the Great Depression, the 1930s saw the building of some of the world's tallest skyscrapers, including numerous Art Deco masterpieces, including the New Yorker Hotel that are still part of the city's skyline today. Much of the design of the city, its famous parks, and roadways was due to the genius of controversial power broker and builder Robert Moses.[16]
Returning World War II veterans and immigrants from Europe created a postwar economic boom that led to the development of huge housing developments, targeted at returning veterans, including Peter Cooper Village—Stuyvesant Town, which opened in 1947.[17] In 1951, the United Nations relocated from its first headquarters in Queens to the East Side of Manhattan.
Like many major U.S. cities, New York suffered race riots and population and industrial decline in the 1960s. By the 1970s, the city had gained a reputation as a graffiti-covered, crime-ridden relic of history. In 1975, the city government faced imminent bankruptcy, and its appeals for assistance were initially rejected, summarized by the classic October 30, 1975 New York Daily News headline as "Ford to City: Drop Dead".[18] This fate was avoided through a federal loan and debt restructuring, and the city was forced to accept increased financial scrutiny by New York State. The 1980s saw a rebirth of Wall Street, and the city reclaimed its role at the center of the world-wide financial industry.
The 1980s also saw Manhattan at the heart of the AIDS crisis, with Greenwich Village at its epicenter. Gay Men's Health Crisis (GMHC) and AIDS Coalition to Unleash Power (ACT UP) were founded to advocate on behalf of those stricken with the disease. Starting in the 1990s, crime rates dropped drastically, and the outflow of population turned around as the city once again became the destination not only of immigrants from around the world but of many U.S. citizens seeking to live a cosmopolitan lifestyle that New York City can offer.
Government

Manhattan Municipal Building
Since New York City's consolidation in 1898, Manhattan has been governed by the New York City Charter, which has provided for a "strong" mayor-council system since its revision in 1989. [19] The centralized New York City government is responsible for public education, correctional institutions, libraries, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply, and welfare services in Manhattan.
The office of Borough President was created in the consolidation of 1898 to balance centralization with local authority. Each borough president had a powerful administrative role derived from having a vote on the New York City Board of Estimate, which was responsible for creating and approving the city's budget and proposals for land use. In 1989, the Supreme Court of the United States declared the Board of Estimate system unconstitutional on the grounds that Brooklyn, the most populous borough, had no greater effective representation on the Board than Staten Island, the least populous borough, a violation of the Fourteenth Amendment's Equal Protection Clause pursuant to the high court's 1964 "one man, one vote" decision.[20]
Since 1990, the largely-powerless Borough President has acted as an advocate for the borough at the mayoral agencies, the New York City Council, the New York state government, and corporations. Manhattan has ten City Council members, the third largest contingent among the five boroughs. It also has 12 administrative districts, each served by a local Community Board. Community Boards are representative bodies that field complaints and serve as advocates for local residents.
As the host of the United Nations, the borough is home to the world's largest international consular corps, comprising 105 consulates, consulates general, and honorary consulates.[21] It is also the home of New York City Hall, the seat of New York City government housing the Mayor of New York City and the New York City Council. The mayor's staff and 13 municipal agencies are located in the nearby Manhattan Municipal Building, completed in 1916, which was then known as one of the largest governmental buildings in the world.[22]
Crime

Policeman leads upper class people through the Five Points in an 1885 sketch
Starting in the mid-nineteenth century, the United States became a magnet for immigrants seeking to escape poverty in their home countries. After arriving in New York, many new arrivals ended up living in squalor in the slums of the Five Points neighborhood, an area between Broadway and the Bowery, northeast of New York City Hall. By the 1820s, the area was home to many gambling dens and brothels and was known as a dangerous place to go to. The area was so notorious at the time that it even caught the attention of Abraham Lincoln, who visited the area before his Cooper Union Address in 1860.[23] The predominantly Irish Five Points Gang was one of the country's first major organized crime entities.
As Italian immigration grew in the early 1900s, many joined the Irish gangs. Gangster Al Capone got his start in crime with the Five Points Gang, [24] as did Lucky Luciano. The Mafia (also known as Cosa Nostra) first developed in the mid-nineteenth century in Sicily and spread to the East Coast of the United States, following waves of Sicilian and Southern Italian emigration. Lucky Luciano established La Cosa Nostra in Manhattan, forming alliances with other criminal enterprises, including the Jewish mob, led by Meyer Lansky, the leading Jewish gangster of that period.[25] From 1920–1933, Prohibition helped create a thriving black market in liquor, which the Mafia was quick to exploit.
New York City experienced a sharp increase in crime during the 1960s and 1970s, with a near fivefold jump in the violent crime rate, from 21.09 per thousand in 1960 to a peak of 102.66 in 1981. Homicides continued to increase in the city as a whole for another decade, with murders recorded by the New York City Police Department, jumping from 390 in 1960 to 1,117 in 1970, 1,812 in 1980, and reaching its peak of 2,262 in 1990. Starting about 1990, New York City saw record declines in homicide, rape, robbery, aggravated assault, violent crime, burglary, larceny, motor vehicle theft and property crime, a trend that has continued, as funds were invested in improved housing and living conditions in the poorest neighborhoods.
Economy

Skyscrapers along Sixth Avenue.
Manhattan is the economic engine of New York City, with its 2.3 million workers drawn from the entire New York metropolitan area, accounting for almost ⅔ of all jobs in New York City. Its most important economic sector is the finance industry, whose 280,000 workers earned more than half of all the wages paid in the borough. Wall Street is frequently used to represent the entire financial industry. New York City is home to the most corporate headquarters of any city in the nation, the overwhelming majority based in Manhattan. Midtown Manhattan is the largest central business district in the United States.[26] Lower Manhattan is home to both the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ and is the nation's third-largest central business district (after Chicago's Loop).[27]
Seven of the world's top eight global advertising agency networks are headquartered in Manhattan. The term "Madison Avenue" is often used to refer to the entire advertising field, after Sixth Avenue, renamed "Madison Avenue", became identified with the lucrative advertising industry after the explosive growth in the area in the 1920s. Historically, this corporate presence has been complemented by many independent retailers, though a recent influx of national chain stores has caused many to lament the creeping homogenization of Manhattan.
Housing
In the early days of Manhattan, wood construction and poor access to water supplies left the city vulnerable to fires. In 1776, shortly after the Continental Army evacuated Manhattan and left it to the British, a massive fire broke out, destroying one-third of the city and some 500 houses.[28]
The rise of immigration near the turn of the century left major portions of Manhattan, especially the Lower East Side, densely packed with recent arrivals, crammed into unhealthy and unsanitary housing. Tenements were usually five-stories high, constructed on the then-typical 25x100 lots, with landlords exploiting the new immigrants.[29] By 1929, stricter fire codes and the increased use of elevators in residential buildings were the impetus behind a new housing code that effectively ended the tenement as a form of new construction, though many tenement buildings survive today on the East Side of the borough.
Today, Manhattan offers a wide array of public and private housing options. There were 798,144 housing units in Manhattan as of the 2000 Census, at an average density of 34,756.7/mi² (13,421.8/km²). Only 20.3 percent of Manhattan residents lived in owner-occupied housing, the second-lowest rate of all counties in the nation, behind The Bronx.
Notes
- ↑ Dr. James Sullivan, "The History of New York State: Book I, Chapter III", www.USGenNet.org. "There is satisfactory evidence that Giovanni da Verrazzano sailed into the outer harbor of New York in 1524.
- ↑ Rebecca B. Rankin, and Cleveland Rodgers. New York: the World's Capital City, Its Development and Contributions to Progress. (Harper, 1948).
- ↑ "Henry Hudson and His Exploration," Scientific American, September 25, 1909. www.ulster.net. Retrieved May 1, 2007.
- ↑ City Seal and Flag. www.nyc.gov. New York City. Retrieved May 13, 2007.
- ↑ Jasmin K. Williams, "New York - The Empire States," The New York Post, November 22, 2006. www.nypost.com. Retrieved May 19, 2007.
- ↑ About the Council, New York City Council. www.nycouncil.info.
- ↑ Tolerance Park Historic New Amsterdam on Governors Island. TolerancePark.org.
- ↑ Fort Washington Park. www.nycgovparks.org. Retrieved May 18, 2007.
- ↑ The Nine Capitals of the United States, United States Senate Historical Office. www.senate.gov. Retrieved June 9, 2005. Based on Robert Fortenbaugh. The Nine Capitals of the United States. (York, PA: Maple Press, 1948).
- ↑ Witold Rybczynski, "Olmsted's Triumph," Smithsonian (magazine), July 2003. Retrieved May 29, 2007.
- ↑ Geoffrey C. Ward, "Gangs of New York," a review of Paradise Alley by Kevin Baker, The New York Times, October 6, 2002. query.nytimes.com.Retrieved May 29, 2007.
- ↑ Gary Hermalyn, and Lloyd Ultan, Bronx History: A General Survey, New York Public Library, www.nypl.org. Retrieved April 26, 2007.
- ↑ Jennifer Rosenberg,. Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire, history1900s.about.com. Retrieved May 17, 2007.
- ↑ Chase-Dunn, Christopher and Manning, Susan. "City systems and world-systems: Four millennia of city growth and decline," University of California, Riverside Institute for Research on World-Systems. www.irows.ucr.edu. Retrieved May 17, 2007.
- ↑ Oliver E. Allen. The Tiger – The Rise and Fall of Tammany Hall. (Addison-Wesley Publ. Co., 1993) Decline: Chapter 9. questia.com. Retrieved October 22, 2007.
- ↑ Lee Gjertsen. "Robert Moses
The controversial power broker who built New York" [1]. politicians.suite101.com. Retrieved July 9, 2008.
- ↑ "Stuyvesant Town to Get Its First Tenants Today," The New York Times, August 1, 1947, 19.
- ↑ Joshua Zeitz, "New York City on the Brink" in American Heritage'' (magazine), November 26, 2005. www.americanheritage.com. Retrieved May 29, 2007.
- ↑ "Report on Ballot Proposals of the 2003 New York City Charter Revision Commission," Association of the Bar of the City of New York. www.abcny.org. Retrieved May 11, 2007.
- ↑ Cornell Law School Supreme Court Collection: Board of Estimate of City of New York v. Morris, Cornell Law School . www.law.cornell.edu. Retrieved June 12, 2006.
- ↑ Society of Foreign Consuls: About us. www.consulsnewyork.com. Retrieved July 19, 2006.
- ↑ The Municipal Building, New York City. www.nyc.gov. Retrieved April 25, 2007.
- ↑ John Walsh, "The Five Points," Irish Cultural Society of the Garden City Area, September 1994. www.irish-society.org. Retrieved May 16, 2007.
- ↑ Al Capone, Chicago History Museum. www.chicagohs.org.
- ↑ Eric Jaffe, "Talking to the Feds: The chief of the FBI's organized crime unit on the history of La Cosa Nostra," Smithsonian (magazine), April 2007. www.smithsonianmagazine.com. Retrieved May 16, 2007.
- ↑ Patricia Noonan, Testimony on Moynihan Station Draft EIS, Partnership for New York City, testimony dated May 31, 2000. www.nycp.org.
- ↑ Lower Manhattan Recovery Office, Federal Transit Administration . www.fta.dot.gov. Retrieved April 26, 2007.
- ↑ Great Fire of 1776, City University of New York . www.virtualny.cuny.edu. Retrieved April 30, 2007. "Some of Washington's advisers suggested burning New York City so that the British would gain little from its capture. This idea was abandoned, and Washington withdrew his forces from the city on September 12, 1776. Three days later, the British occupied the city, and on September 21, a fire broke out in the Fighting Cocks Tavern. Without the city's firemen present and on duty, the fire quickly spread. A third of the city burnt and 493 houses destroyed."
- ↑ Building the Lower East Side Ghetto. www.upress.umn.edu. Retrieved April 30, 2007.
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Burrows, Edwin G., and Mike Wallace. Gotham: A History of New York City to 1898 (The History of NYC Series). Oxford University Press, 1998. ISBN 0195116348
- Ellis, Edward Robb. The Epic of New York City: A Narrative History. Reprint. Carroll & Graf, 2005. ISBN 0786714360
- Fortenbaugh, Robert. The Nine Capitals of the United States. York, PA: Maple Press, 1948.
- Jackson, Kenneth T. The Encyclopedia of New York City. Yale University Press, 1995. ISBN 0300055366
- Hamill, Pete. Downtown: My Manhattan. New York: Little, Brown, 2004. ISBN 9780316734516
- Shorto, Russell. The Island at the Center of the World: The Epic Story of Dutch Manhattan and the Forgotten Colony That Shaped America. New York: Doubleday, 2004. ISBN 9780385503495
- Mackay, Donald A. The Building of Manhattan. New York: Harper & Row, 1987. ISBN 9780060157883
- Sullivan, Dr. James. The History of New York State. Lewis Historical Publishing Company, Inc., 1927.
External links
All links retrieved November 5, 2022.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article
in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.