Leucine
| |
Leucine | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| (S)-2-amino-4-methyl-pentanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 61-90-5 |
| PubChem | 6106 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C6H13NO2 |
| Mol. weight | 131.18 |
| SMILES | CC(C)C[C@H](N)C(O)=O |
| Complete data | |
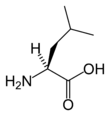
Leucine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH2CH(CH3)2. Its three letter code is leu, its one letter code is L, and its codons are UUA, UUG, CUU, and CUC. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesise it. With a hydrocarbon side chain, leucine is classified as a hydrophobic amino acid. It is an isomer of isoleucine.
Biosynthesis
As an essential amino acid, leucine is not synthesized in animals, hence it must be ingested, usually as a component of proteins. It is synthesized in plants and microorganisms via several steps starting from pyruvic acid. The initial part of the pathway also leads to valine. The intermediate α-ketovalerate is converted to α-isopropylmalate and then β-isopropylmalate, which is dehydrogenated to α-ketoisocaproate, which in the final step undergoes reductive amination. Enzymes involved in a typical biosynthesis include:[1]
- acetolactate synthase
- acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase
- dihydroxyacid dehydratase
- α-isopropylmalate synthase
- α-isopropylmalate isomerase
- leucine aminotransferase
Dietary aspects
Major food sources of leucine include whole grains, milk products, eggs (~1 g/100g), pork, beef, chicken, pulses (such as soybeans (~3 g/100g), chick peas and lentils) and leaf vegetables.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ Nelson, D. L.; Cox, M. M. "Lehninger, Principles of Biochemistry" 3rd Ed. Worth Publishing: New York, 2000. ISNB 1-57259-153-6.
External links
- Leucine biosynthesis
- Leucine content in food
- Computational Chemistry Wiki
- Leucine prevents muscle loss in rats
- Leucine helps regulate appetite in rats
Template:ChemicalSources
| Major families of biochemicals | ||
| Peptides | Amino acids | Nucleic acids | Carbohydrates | Nucleotide sugars | Lipids | Terpenes | Carotenoids | Tetrapyrroles | Enzyme cofactors | Steroids | Flavonoids | Alkaloids | Polyketides | Glycosides | ||
| Analogues of nucleic acids: | The 20 Common Amino Acids | Analogues of nucleic acids: |
| Alanine (dp) | Arginine (dp) | Asparagine (dp) | Aspartic acid (dp) | Cysteine (dp) | Glutamic acid (dp) | Glutamine (dp) | Glycine (dp) | Histidine (dp) | Isoleucine (dp) | Leucine (dp) | Lysine (dp) | Methionine (dp) | Phenylalanine (dp) | Proline (dp) | Serine (dp) | Threonine (dp) | Tryptophan (dp) | Tyrosine (dp) | Valine (dp) | ||
Template:Organic-compound-stub Template:Molecular-cell-biology-stub
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.