Impala
- For other uses, see Impala (disambiguation).
| Impala | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 A Black-faced Impala in Etosha National Park, Namibia
| ||||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Aepyceros melampus (Lichtenstein, 1812) | ||||||||||||||||
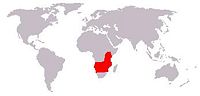 Range map
| ||||||||||||||||
|
Impala is the common name for a light-built, swift-running, powerful-jumping African antelope, Aepyceros melampus, characterized by a reddish brown fur with white on underside, chin, and tail, and long, ridged, lyre-shaped horns in the males.
renowned for leaping ability
Overview and description
Impalas are a type of antelope, a diverse group of typically hollow-horned, slender-built, and swift bovids native to Africa and Asia. Antelope species do not form a taxonomic group but are spread throughout the subfamilies of the Bovidae family (bovids) of the order Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates). All antelopes have long, slender legs and powerful muscles where the upper legs meet the body, providing leverage and increasing leg stride and speed.
Impalas are medium-sized antelopes and are lightly built. They range from 40 to 80 kilograms (88-176 pounds), with a body length of 120 to 160 centimeters (4-5.3 feet), a shoulder height of 75-95 centimeters (2.5-3.1 feet), and a tail from 30-45 centimeters (12-18 inches) long (Grzimek et al. 2004). Males are larger than females.
Impalas are reddish-brown in color, have lighter flanks and white underbellies with a characteristic "M" marking on its rear. There are black stripes down the forehead, ear tips, tail, and thighs (Grzimek et al. 2004).
The horns are long and curved (lyre-shaped) in males and can reach up to 90 centimeters (36 inches) in length. In general, the horns range from 45 to 92 centimeters (18-37 inches) (Grzimek et al. 2004).
Antelopes are known as fast runners that are good at quick, precise turns, and they can run very fast for extended periods of time. The impala exhibits this characteristic, but in particular is renowned fro being a powerful jumper that can lead three meters (10 feet) into the air and a length of 9 meters (30 feet).
Impalas, as with other antelopes, are ruminants. Like other ruminants, such as cattle and goats, they have well-developed cheek teeth or molars, which grind cud into a pulp. They have no upper incisors or canines; in order to tear grass stems and leaves, their lower incisors press against a hard upper gum pad when they bite.
The scientific name, Aepyceros melampus, comes from the Greek αιπος or aipos, meaning "high"; κερος or ceros meaning "horn"; melas, meaning "black"; and pous meaning "foot." The name impala comes from the Zulu language.
Distribution and habitat
Impalas are found in savannas and thick bushveld in Kenya, Tanzania, Mozambique, northern Namibia, Botswana, Zambia, Zimbabwe, southern Angola, northeastern South Africa, and Uganda (where they are the source of that country's capital city's name, Kampala).
Impalas generally prefer ecotones between open grassland and woodland. They require cover and surface water (Grzimek et al. 2004).
Ecology
Impala are among the dominant species in many savannas. They can adapt to different environment by being grazers in some areas and browsers in others. They graze when the grass is green and growing and browse at other times. They will browse on shoots, seedpods and foliage.
Herds will use specific areas for their excrement. Impala are active during both day and night and are dependent on water. A herd is normally an indicator of water close by. Impala can thrive in areas where pure grazers can not survive.
When frightened or startled the whole impala herd starts leaping about in order to confuse their predator. They can jump distances more than 9 meters (30 ft) and 2.5 meters (8 ft) high. Leopards, cheetah, Nile crocodiles, lions, spotted hyenas and wild dogs prey on impala.
Social structure and reproduction
Females and young form herds of up to two hundred individuals. When food is plentiful, adult males will establish territories and round up any female herd that enter their grounds and will chase away bachelor males that follow. They will even chase away recently weaned males. A male impala tries to prevent any female from leaving its territory. During the dry seasons, territories are abandoned as herds must travel farther to find food. Large, mixed tranquil herds of females and males form.
Young male impala who have been made to leave their previous herd form bachelor herds of around thirty individuals. Males that are able to dominate their herd are contenders for assuming control of their territory.

The breeding season of impala, also called rutting, begins toward the end of the wet season in May. The entire affair typically lasts approximately three weeks. While young are born after seven months, the mother has the ability to prolong giving birth for an additional month if conditions are harsh. When giving birth a female impala will isolate herself from the herd despite numerous attempts by the male to keep her in his territory. The impala mother will keep the fawn in an isolated spot for a few days or even leave it lying out in hiding for a couple days, weeks, or more before returning to the herd. There the fawn will join a nursery group and will go to its mother only to nurse and when predators are near. Fawns are suckled for 4 to 6 months. Males who mature are forced out of the group and will join bachelor herds.
Taxonomy
In the past, taxonomists have put the impala in the same tribe as gazelles, kobs and hartebeests. However it was found that the impala was so different from any of these tribes that it was put in its own tribe, Aepycerotini respectively.
Usually two subspecies are distinguished, which is supported by mitochondrial DNA analysisCite error: Invalid <ref> tag; invalid names, e.g. too many:
- Black-faced Impala Aepyceros melampus petersi
- Common Impala Aepyceros melampus melampus
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Grzimek, B., D. G. Kleiman, V. Geist, and M. C. McDade. 2004. Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia. Detroit: Thomson-Gale. ISBN 0307394913.
- Antelope Specialist Group 1996. [1]. 2006 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species., World Conservation Union. Retrieved on 11 May 2006.
- Estes, R. (1991). The Behavior Guide to African Mammals, Including Hoofed Mammals, Carnivores, Primates. Los Angeles, The University of California Press
- African Wildlife Fundation - Impala
- Arkive - Impala
External links
A group of impala in South Africa
- Aepyceros melampus.png
Impala in Zambia
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.







