Difference between revisions of "Comet" - New World Encyclopedia
(→Comet nomenclature: editing) |
(→Comet nomenclature: editing) |
||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
==Comet nomenclature== | ==Comet nomenclature== | ||
| − | The names given to comets have followed several different conventions over the past two centuries. Prior to the early twentieth century, most comets were simply referred to by the year in which they were observed, sometimes with adjectives to describe particularly bright comets. Examples are the "Great Comet of 1680" (Kirch's Comet, or C/1680 V1), the "Great September Comet of 1882" (C/1882 R1), and the "Daylight Comet of 1910" ("Great January Comet of 1910"). After [[Edmond Halley]]* demonstrated that the comets of 1531, 1607, and 1682 were the same body and successfully predicted its return in 1759, that comet became known as [[Comet Halley]]. Similarly, the second and third known periodic comets, Comet Encke and Comet Biela, were named after the astronomers who calculated their orbits rather than their original discoverers. Later, periodic comets were usually named after their discoverers, but comets that had appeared only once continued to be referred to by the year of their apparition. | + | The names given to comets have followed several different conventions over the past two centuries. Prior to the early twentieth century, most comets were simply referred to by the year in which they were observed, sometimes with adjectives to describe particularly bright comets. Examples are the "Great Comet of 1680" (Kirch's Comet, or C/1680 V1), the "Great September Comet of 1882" (C/1882 R1), and the "Daylight Comet of 1910" ("Great January Comet of 1910"). After [[Edmond Halley]]* demonstrated that the comets of 1531, 1607, and 1682 were the same body and successfully predicted its return in 1759, that comet became known as [[Comet Halley]]*. Similarly, the second and third known periodic comets, Comet Encke and Comet Biela, were named after the astronomers who calculated their orbits rather than their original discoverers. Later, periodic comets were usually named after their discoverers, but comets that had appeared only once continued to be referred to by the year of their apparition. |
| − | In the early twentieth century, the convention of naming comets after their discoverers became common, and | + | In the early twentieth century, the convention of naming comets after their discoverers became common, and that continues to be followed, up to a degree. A comet is named after up to three independent discoverers. In recent years, many comets have been discovered with the aid of instruments operated by large teams of astronomers—in this case, the name of the instrument may be included. For example, Comet IRAS-Araki-Alcock (C/1983 H1) was discovered independently by the [[IRAS]]* satellite and amateur astronomers Genichi Araki and George Alcock. |
| + | |||
| + | In the past, when multiple comets were discovered by the same individual, group of individuals, or team, the comets' names were distinguished by adding a numeral to the discoverers' names—for example, Comets Shoemaker-Levy 1–9. Today, the large numbers of comets discovered by some instruments has rendered this system impractical. For instance, in August 2005, [[SOHO]]* (the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory) discovered its 1000th comet<ref>[http://soho.nascom.nasa.gov/comet1000/ The SOHO 1000th Comet Contest] Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, 2005. Accessed on 2006-03-05.</ref>). Consequently, the comets' systematic designations are used to avoid confusion. | ||
Until 1994, comets were first given a provisional designation consisting of the year of their discovery followed by a lowercase letter indicating its order of discovery in that year (for example, C/1969 Y1|Comet Bennett 1969i was the 9th comet discovered in 1969). Once the comet had been observed through perihelion and its orbit had been established, the comet was given a permanent designation of the year of its perihelion, followed by a Roman numeral indicating its order of perihelion passage in that year, so that Comet Bennett 1969i became [[C/1969 Y1|Comet Bennett 1970 II]] (it was the second comet to pass perihelion in 1970)<ref name="arnett">[http://www.nineplanets.org/names.html Astronomical Names] Bill Arnett, 2000. Accessed on 2006-03-05.</ref> | Until 1994, comets were first given a provisional designation consisting of the year of their discovery followed by a lowercase letter indicating its order of discovery in that year (for example, C/1969 Y1|Comet Bennett 1969i was the 9th comet discovered in 1969). Once the comet had been observed through perihelion and its orbit had been established, the comet was given a permanent designation of the year of its perihelion, followed by a Roman numeral indicating its order of perihelion passage in that year, so that Comet Bennett 1969i became [[C/1969 Y1|Comet Bennett 1970 II]] (it was the second comet to pass perihelion in 1970)<ref name="arnett">[http://www.nineplanets.org/names.html Astronomical Names] Bill Arnett, 2000. Accessed on 2006-03-05.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 14:10, 7 July 2006
A comet is a small body in the solar system that orbits the Sun and at least occasionally exhibits a "coma" (or atmosphere) and a tail. The main body of the comet, called its nucleus, may be considered a minor planet and is composed of rock, dust, and ice. The coma and tail are primarily due to the effects of solar radiation on the comet's nucleus.
Comets were formed in the outer solar system and later brought into the inner solar system by gravitational disturbance, forming highly elliptical orbits. Comets make relatively close approaches to the major planets, and their orbits are constantly changing. Some are moved into Sun-grazing orbits that destroy them when they near the Sun, while others are thrown out of the solar system forever.
Most comets are believed to originate in what is called the Oort cloud—a postulated spherical cloud of comets located about 50,000ndash;100,000 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun. The Oort cloud is thought to be a remnant of the original nebula that condensed to form the Sun and planets five billion years ago. The outer edges of such a nebula would be cool enough for water to exist in the solid state. Asteroids are formed by a different process, but very old comets that have lost all their volatile materials may come to resemble asteroids, such as the D-type asteroids.
History of comet study
Early observations and thought
Before the invention of the telescope, comets seemed to appear out of nowhere in the sky and gradually vanish out of sight. They were usually considered bad omens, portending the deaths of kings or noblemen, or upcoming catastrophes. In some cases, they were interpreted as attacks by heavenly beings against terrestrial inhabitants. Ancient sources, such as Chinese oracle bones, indicate that people have noticed the appearance of comets for millennia. One famous recording of Halley's Comet appears on the Bayeux Tapestry, which depicts the Norman conquest of England in 1066.[1]
In his book Meteorology (or Meteorologia), Aristotle propounded the view of comets that would hold sway in Western thought for nearly 2,000 years. He rejected the ideas of several earlier philosophers that comets were planets, or a phenomenon related to the planets, on the grounds that planets confined their motion to the circle of the zodiac, but comets could appear in any part of the sky.[2] According to him, comets were a phenomenon of the upper atmosphere, where hot, dry exhalations gathered and occasionally burst into flame. He used this mechanism to explain not only comets but also meteors, the aurora borealis, and even the Milky Way.
A few later classical philosophers did dispute this view of comets. Seneca the Younger, in his Natural Questions, observed that comets moved regularly through the sky and were undisturbed by the wind—behavior more typical of celestial phenomena than atmospheric ones. While conceding that other planets do not appear outside the Zodiac, he saw no reason why a planet-like object could not move through any part of the sky, given that humanity's knowledge of celestial things was very limited.[3] The Aristotelean viewpoint, however, proved more influential, and it was not until the sixteenth century that it was demonstrated that comets must exist outside the Earth's atmosphere.
In 1577, a bright comet was visible for several months. The Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe used measurements of the comet's position taken by him and other (geographically separated) observers to conclude that the comet must be at least four times more distant from the Earth than the Moon.[4]
Orbital studies
Once comets had been demonstrated to be objects in the heavens, the question of how they moved through the heavens was debated during most of the next century. Even after Johannes Kepler had determined in 1609 that the planets moved about the Sun in elliptical orbits, he was reluctant to believe that the laws that governed the motions of the planets would also describe the motion of other bodies. He thought that comets traveled among the planets along straight lines. Galileo Galilei, although a staunch Copernicanist, rejected Tycho's measurements and held to the Aristotelean notion of comets moving along straight lines through the upper atmosphere.[5]
The first suggestion that Kepler's laws of planetary motion should also apply to the comets was made by William Lower in 1610. In the following decades, other astronomers—including Pierre Petit, Giovanni Borelli, Adrien Auzout, Robert Hooke, Johann Baptist Cysat, and Giovanni Domenico Cassini—argued that comets curve about the Sun on elliptical or parabolic paths. Yet others, such as Christian Huygens and Johannes Hevelius, supported the idea of the linear motion of comets.[5]
The matter was resolved by the bright comet (C/1680 V1) discovered by Gottfried Kirch on November 14, 1680. Astronomers throughout Europe tracked its position for several months. In 1681, the Saxon pastor Georg Samuel Doerfel set forth his proofs that comets are heavenly bodies moving in parabolas, with the Sun at the focus. Then Isaac Newton, in his Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (1687), showed that if an object moves under the influence of his inverse square law of gravity, it would trace out an orbit shaped like one of the conic sections. Using the comet of 1680 as an example, he demonstrated how a comet's path through the sky could fit a parabolic orbit.[6]
In 1705, Edmond Halley applied Newton's method to 24 cometary apparitions that had occurred between 1337 and 1698. He noted that three of these—the comets of 1531, 1607, and 1682—had very similar orbital elements, and he could further account for the slight differences in their orbits in terms of gravitational influences of Jupiter and Saturn. Confident that these three apparitions had been three appearances of the same comet, he predicted that it would reappear in 1758-9.[7] (Earlier, Robert Hooke had identified the comet of 1664 with that of 1618,[8] while Jean-Dominique Cassini had suspected the identity of the comets of 1577, 1665, and 1680. Both were incorrect.) Halley's predicted return date was later refined by a team of three French mathematicians—Alexis Clairaut, Joseph Lalande, and Nicole-Reine Lepaute, who predicted the date of the comet's 1759 perihelion to within one month's accuracy. When the comet returned as predicted, it became known as Comet Halley or Halley's Comet (its official designation is 1P/Halley). Its next appearance is due in 2061.
Among the comets with short enough periods to have been observed several times in the historical record, Comet Halley is unique in consistently being bright enough to be visible to the naked eye. Since the confirmation of Comet Halley's periodicity, many other periodic comets have been discovered by telescopic observations.
The second comet to be discovered to have a periodic orbit was Comet Encke (official designation 2P/Encke). Over the period 1819–1821, the German mathematician and physicist Johann Franz Encke computed orbits for a series of cometary apparitions observed in 1786, 1795, 1805, and 1818. He concluded they were same comet and successfully predicted its return in 1822. By 1900, 17 comets had been observed at more than one perihelion passage and recognized as periodic comets. As of April 2006, 175 comets have achieved this distinction, though several have since been destroyed or lost.
Studies of physical characteristics
Newton described comets as compact, solid, and durable bodies. In other words, he thought of a comet as a planet-like object that moved in a very oblique orbit, with the greatest freedom, persevering in its motion even against the course and direction of the regular planets. He described the comet's tail as a thin, slender vapor emitted by the comet's head (or nucleus), ignited or heated by the Sun.
In Newton's view, comets were absolutely necessary for the conservation of water on our planet. He thought that the Earth is in a continual process of drying up, especially through the uptake of moisture by vegetation, and inferred that the planet needed to be resupplied with water. According to him, the spirit that makes the finest, subtlest, and best part of our air, and which is absolutely requisite for the life and being of all things, came principally from the comets.
As early as the eighteenth century, some scientists and thinkers made correct hypotheses about the physical composition of comets. In 1755, Immanuel Kant hypothesized that comets are composed of some volatile substance that, when vaporized, produced their brilliant displays near perihelion—that is, when the comet's orbit brought it closest to the Sun. German mathematician Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel, after observing streams of vapor in the 1835 apparition of Comet Halley, proposed in 1836 that the jet forces of evaporating material could be great enough to significantly alter a comet's orbit, and he argued that the non-gravitational movements of Comet Encke resulted from this mechanism.
A different comet-related discovery overshadowed these ideas for nearly a century. Over the period 1864–1866, the Italian astronomer Giovanni Schiaparelli computed the orbit of the Perseid meteors and, based on orbital similarities, correctly deduced that the Perseids were fragments of Comet Swift-Tuttle. The link between comets and meteor showers was dramatically underscored in 1872, when a major meteor shower occurred from the orbit of Comet Biela, which had been observed to split into two pieces during its 1846 apparition and had never been seen again after 1852. This led to a "gravel bank" model of comet structure, according to which comets consist of loose piles of small rocky objects coated with an icy layer.
By the middle of the twentieth century, this model's shortcomings became clear. In particular, the model failed to explain how a body that contained only a little ice could continue to put on a brilliant display of evaporating vapor after several perihelion passages. In 1950, Fred Lawrence Whipple proposed that rather than being rocky objects containing some ice, comets were icy objects containing some dust and rock.[9] This "dirty snowball" model was soon accepted. It was confirmed when an armada of spacecraft (including the European Space Agency's Giotto probe and the Soviet Union's Vega 1 and Vega 2) flew through the coma of Halley's comet in 1986 to photograph the nucleus and observed the jets of evaporating material. The American probe Deep Space 1 flew past the nucleus of Comet Borrelly on September 21, 2001, and confirmed that the characteristics of Comet Halley are also found on other comets.
The Stardust spacecraft, launched in February 1999, collected particles from the coma of Comet Wild 2 in January 2004 and returned the samples to Earth in a capsule in January 2006. Claudia Alexander, a program scientist for Rosetta from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory has modeled comets for years. In her report to space.com, she expressed her astonishment at the number of jets, their appearance on the dark side of the comet as well as on the light side, their ability to lift large chunks of rock from the surface of the comet, and the fact that comet Wild 2 is not some loosely cemented rubble pile.[10]
Forthcoming space missions will add greater detail to our understanding of what comets are made of. In July 2005, the Deep Impact probe blasted a crater on Comet Tempel 1 to study its interior. In 2014, the European Rosetta probe will orbit comet Comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko and place a small lander on its surface.
Rosetta, equipped with highly sensitive instruments, observed Tempel 1 before, during, and after the impact caused by the Deep Impact probe. At a distance of about 80 million kilometers from the comet, Rosetta was in the most privileged position to observe the event. Rosetta measured the water vapor content and cross-section of the dust created by the impact. European scientists then calculated that the dust/ice mass ratio was greater than one, suggesting that comets are better described as dust held together by ice rather than ice comtaminated with dust. Hence, they are now "icy dirtballs" rather than "dirty snowballs" as previously believed.
Debate over comet composition
As late as 2002, there is conflict on how much ice is in a comet. NASA's Deep Space 1 team, working at NASA's Jet Propulsion Lab, obtained high-resolution images of the surface of comet Borrelly. They announced that comet Borrelly exhibits distinct jets, yet has a hot, dry surface. In the words of Dr. Laurence Soderblom of the U.S. Geological Survey, "The spectrum suggests that the surface is hot and dry. It is surprising that we saw no traces of water ice." He, however, went on to suggest that the ice may be hidden below the crust, as "either the surface has been dried out by solar heating and maturation, or perhaps the very dark soot-like material that covers Borrelly's surface masks any trace of surface ice."[11]
The recent Deep Impact probe has also yielded preliminary results suggesting there is less ice in comets than originally predicted.
Physical characteristics
- Most comets are too faint to be visible without the aid of a telescope, but in each decade, a few become bright enough to be visible with the naked eye.
- Long-period comets are believed to originate in a distant cloud known as the Oort cloud (after the astronomer Jan Hendrik Oort who hypothesised its existence). They are sometimes perturbed from their distant orbits by gravitational interactions, falling into extremely elliptical orbits that can bring them very close to the Sun. One theory says that as a comet approaches the inner solar system, solar radiation causes part of its outer layers, composed of ice and other materials, to melt and evaporate.
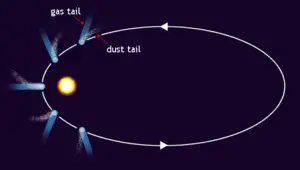
The streams of dust and gas released by this process form a large, tenuous atmosphere around the comet called the coma, and the forces exerted on the coma by the Sun's radiation pressure and solar wind produce enormous tails. The dust and gas streams form their own distinct tails that point in slightly different directions. The coma and tails are illuminated by the Sun and may become visible from the Earth when a comet passes through the inner solar system—the dust reflects sunlight directly and the gases glow due to ionization.
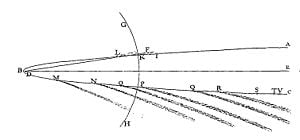
The tail of dust is usually in or close to the comet's orbit, and it is often curved. The tail of gases, called the ion tail, always points directly away from the Sun, as the gases are more strongly affected by the solar wind than dust is, and they follow the magnetic field lines rather than an orbital trajectory. The solid body (nucleus) of a comet is generally less than 50 km across, but the coma may be larger than the Sun, and ion tails have been observed to extend 150 million km or more.
Cometary nuclei are among the blackest objects known to exist in the solar system. The Giotto probe found that Comet Halley's nucleus reflects approximately 4% of the light that falls on it, and Deep Space 1 discovered that Comet Borrelly's surface reflects only 2.4–3% of the light that falls on it. By comparison, asphalt reflects 7% of the light that falls on it. The Tagish Lake meteorite, believed to have come from a D-type asteroid or comet, is also one of the darkest meteorites.[12] The dark surface material is thought to be made up of complex organic compounds and other carbon-containing materials. Solar heat drives off volatile compounds, leaving behind heavy long-chain organics that tend to be very dark, such as tar or crude oil. The darkness of cometary surfaces allows them to absorb the heat necessary to drive their outgassing.
In 1996, researchers were surprised to find that comets emit X rays—a phenomenon that had not been predicted.[13] The X rays are thought to be generated by the interaction between comets and the solar wind: when highly charged ions fly through a cometary atmosphere, they collide with cometary atoms and molecules. In these collisions, the ions capture one or more electrons, leading to the emission of X rays and radiation in the far ultraviolet region.[14]
Orbital characteristics
Comets are classified according to their orbital periods. Short-period comets have orbits of less than 200 years, while long-period comets have longer orbits but remain gravitationally bound to the Sun. Main-belt comets are those that orbit within the asteroid belt, and single-apparition comets have parabolic or hyperbolic orbits, so that they permanently exit the solar system after just one pass by the Sun. Modern observations have revealed a few genuinely hyperbolic orbits, but no more than could be accounted for by perturbations from Jupiter.
While long-period comets are thought to originate in the Oort cloud, short-period comets are thought to be formed in the Kuiper belt. The short-period Comet Encke has an orbit that never places it farther from the Sun than Jupiter.
A variety of mechanisms have been proposed to explain why comets have come to develop highly elliptical orbits, including close approaches to other stars, as the Sun follows its orbit through the Milky Way. In addition, it appears that the orbits of comets coming from the Oort cloud are often strongly influenced by the gravity of giant planets, based on their close encounters. Jupiter exerts the greatest influence, being more than twice as massive as all the other planets combined, as well as the swiftest of the giant planets.
A number of periodic comets discovered in earlier decades or centuries are now "lost." Their orbits were never known well enough to predict future appearances. Occasionally, however, a newly discovered comet is found to have an orbit identical to that of an earlier, "lost" comet. For example, Comet 11P/Tempel-Swift-LINEAR was discovered in 1869 but became unobservable after 1908 due to perturbations by Jupiter. It was not found again until accidentally rediscovered in 2001 by LINEAR, a project that monitors near-Earth asteroids.[15]
Comet nomenclature
The names given to comets have followed several different conventions over the past two centuries. Prior to the early twentieth century, most comets were simply referred to by the year in which they were observed, sometimes with adjectives to describe particularly bright comets. Examples are the "Great Comet of 1680" (Kirch's Comet, or C/1680 V1), the "Great September Comet of 1882" (C/1882 R1), and the "Daylight Comet of 1910" ("Great January Comet of 1910"). After Edmond Halley demonstrated that the comets of 1531, 1607, and 1682 were the same body and successfully predicted its return in 1759, that comet became known as Comet Halley. Similarly, the second and third known periodic comets, Comet Encke and Comet Biela, were named after the astronomers who calculated their orbits rather than their original discoverers. Later, periodic comets were usually named after their discoverers, but comets that had appeared only once continued to be referred to by the year of their apparition.
In the early twentieth century, the convention of naming comets after their discoverers became common, and that continues to be followed, up to a degree. A comet is named after up to three independent discoverers. In recent years, many comets have been discovered with the aid of instruments operated by large teams of astronomers—in this case, the name of the instrument may be included. For example, Comet IRAS-Araki-Alcock (C/1983 H1) was discovered independently by the IRAS satellite and amateur astronomers Genichi Araki and George Alcock.
In the past, when multiple comets were discovered by the same individual, group of individuals, or team, the comets' names were distinguished by adding a numeral to the discoverers' names—for example, Comets Shoemaker-Levy 1–9. Today, the large numbers of comets discovered by some instruments has rendered this system impractical. For instance, in August 2005, SOHO (the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory) discovered its 1000th comet[16]). Consequently, the comets' systematic designations are used to avoid confusion.
Until 1994, comets were first given a provisional designation consisting of the year of their discovery followed by a lowercase letter indicating its order of discovery in that year (for example, C/1969 Y1|Comet Bennett 1969i was the 9th comet discovered in 1969). Once the comet had been observed through perihelion and its orbit had been established, the comet was given a permanent designation of the year of its perihelion, followed by a Roman numeral indicating its order of perihelion passage in that year, so that Comet Bennett 1969i became Comet Bennett 1970 II (it was the second comet to pass perihelion in 1970)[17]
Increasing numbers of comet discoveries made this procedure awkward, and in 1994 the International Astronomical Union approved a new naming system. Comets are now designated by the year of their discovery followed by a letter indicating the half-month of the discovery and a number indicating the order of discovery (a system similar to that already used for asteroids), so that the fourth comet discovered in the second half of February 2006 would be designated 2006 D4. Prefixes are also added to indicate the nature of the comet, with P/ indicating a periodic comet, C/ indicating a non-periodic comet, X/ indicating a comet for which no reliable orbit could be calculated, D/ indicating a comet which has broken up or been lost, and A/ indicating an object that was mistakenly identified as a comet, but is actually a minor planet. After their second observed perihelion passage, periodic comets are also assigned a number indicating the order of their discovery.[18] So Halley's Comet, the first comet to be identified as periodic, has the systematic designation 1P/1682 Q1. Comet Hale-Bopp's designation is C/1995 O1.
There are only four objects that are cross-listed as both comets and asteroids: 2060 Chiron (95P/Chiron), 133P/Elst-Pizarro (7968 Elst-Pizarro), 60558 Echeclus (174P/Echeclus) and 4015 Wilson-Harrington (107P/Wilson-Harrington).
Peculiar comets
Of the thousands of known comets, some are very unusual. Comet Encke orbits from inside the orbit of Jupiter to inside the orbit of Mercury while Comet 29P/Schwassmann-Wachmann orbits in a nearly circular orbit entirely between Jupiter and Saturn. 2060 Chiron, whose unstable orbit keeps it between Saturn and Uranus, was originally classified as an asteroid until a faint coma was noticed. Similarly, Comet Shoemaker-Levy 2 was originally designated asteroid 1990 UL3. Some near-Earth asteroids are thought to be extinct nuclei of comets which no longer experience outgassing.
Some comets have been observed to break up. Comet Biela was one significant example, breaking into two during its 1846 perihelion passage. The two comets were seen separately in 1852, but never again after that. Instead, spectacular meteor showers were seen in 1872 and 1885 when the comet should have been visible. A lesser meteor shower, the Andromedids, occurs annually in November, and is caused by the Earth crossing Biela's orbit.[19]
Several other comets have been seen to break up during their perihelion passage, including great comets West and Comet Ikeya-Seki. Some comets, such as the Kreutz Sungrazers, orbit in groups and are thought to be pieces of a single object that has previously broken apart.
Another very significant cometary disruption was that of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9, which was discovered in 1993. At the time of its discovery, the comet was in orbit around Jupiter, having been captured by the planet during a very close approach in 1992. This close approach had already broken the comet into hundreds of pieces, and over a period of 6 days in July 1994, these pieces slammed into Jupiter's atmosphere — the first time astronomers had observed a collision between two objects in the solar system. However, it has been suggested that the object responsible for the Tunguska event in 1908 was a fragment of Comet Encke.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ "Britain's Bayeux Tapestry, scene 1," Reading Museum Service, 2000-2004, Accessed on 2005-03-22.
- ↑ Meteorologia l.1.c.6., Aristotle, 350 B.C.E.
- ↑ Sagan, Carl, and Druyan, Ann, Comet, New York: Random House, 1985, pp. 23-24. ISBN 0-394-54908-2.
- ↑ A Brief History of Comets, part I European Southern Observatory, 2003.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Prasar, V. (2001) Development of Cometary Thought, Part II
- ↑ Newton, I.S. (1687) Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, Josephi Streater, London.
- ↑ Halleio, E. (1705) Astronomiæ Cometicæ Synopsis, Philosophical Transactions 24, 1882–1899
- ↑ Pepys, S. (1893) The Diary of Samuel Pepys, M.A., F.R.S., George Bell & Sons, London.
- ↑ Whipple, F.L. (1950) A Comet Model I. The Acceleration of Comet Encke, Astrophysical Journal 111, 375–394.
- ↑ Strange Comet Unlike Anything Known
- ↑ NASA Spacecraft Finds Comet Has Hot, Dry Surface
- ↑ Hiroi, T., Zolensky, M.E., and Pieters, C.M. (2001) "The Tagish Lake meteorite: A possible sample from a D-type asteroid." Science 293, 2234-2236.
- ↑ First X-Rays from a Comet Discovered Accessed on 2006-03-05.
- ↑ Probing space weather with comets Accessed on 2006-03-05.
- ↑ "Cometography" Gary W. Kronk, '11P/Tempel-Swift-LINEAR', 2001–2005 Accessed on 2006-03-05.
- ↑ The SOHO 1000th Comet Contest Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, 2005. Accessed on 2006-03-05.
- ↑ Astronomical Names Bill Arnett, 2000. Accessed on 2006-03-05.
- ↑ Cometary Designation System Committee on Small Body Nomenclature, 1994. Accessed on 2006-03-05.
- ↑ The Andromedids ("Bielids")
External links
- A Brief History of Comets: Part I, Part II
- Development of Cometary Thought: Part I, Part II
- Cometography.com
- David Jewitt overview of the comets
- Listing of newly discovered comets
- Everything you wanted to know about comets and asteroids — Provided by New Scientist.
- Source of useful comet-related material on the Web
- Open Directory Project: Comets
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.