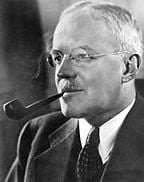|
|
| (32 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | {{Started}}{{Contracted}} | + | {{Images OK}}{{submitted}}{{approved}}{{Paid}}{{copyedited}} |
| − | {{redirect|CIA}} | + | |
| | {{Infobox Govt Agency | | {{Infobox Govt Agency |
| | | agency_name = Central Intelligence Agency | | | agency_name = Central Intelligence Agency |
| Line 12: |
Line 12: |
| | | seal_width = 125 px | | | seal_width = 125 px |
| | | seal_caption = Seal of the Central Intelligence Agency | | | seal_caption = Seal of the Central Intelligence Agency |
| − | | formed = 26 July, 1947 | + | | formed = July 26, 1947 |
| | | preceding1 = Central Intelligence Group | | | preceding1 = Central Intelligence Group |
| | | preceding2 = | | | preceding2 = |
| Line 36: |
Line 36: |
| | | website = [https://www.cia.gov/ www.cia.gov] | | | website = [https://www.cia.gov/ www.cia.gov] |
| | | footnotes = <ref>{{cite web | | | footnotes = <ref>{{cite web |
| − | | url=https://www.cia.gov/about-cia/faqs/index.html#employeenumbers
| |
| | | work=cia.gov | | | work=cia.gov |
| | | title=CIA Frequently Asked Questions | | | title=CIA Frequently Asked Questions |
| | | date=2006-07-28 | | | date=2006-07-28 |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| | }}</ref><ref name=faq>{{cite web | | }}</ref><ref name=faq>{{cite web |
| − | | url=https:https://www.cia.gov/about-cia/faqs/index.html#employeenumbers | + | | url=https://www.cia.gov/about-cia/faqs/index.html#employeenumbers |
| | | work=cia.gov | | | work=cia.gov |
| | | title=Public affairs FAQ | | | title=Public affairs FAQ |
| | | date=July 28, 2006 | | | date=July 28, 2006 |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15 | + | | accessdate=April 28, 2013 |
| − | }} However, it was made public for several years in the late 1990s. In 1997 it was of $26.6 billion and in 1998 it was $26.7 billion</ref><ref>{{cite web | + | }} However, it was made public for several years in the late 1990s. In 1997 it was of $26.6 billion and in 1998 it was $26.7 billion</ref><ref> {{cite web |
| − | | url=http://www.cato.org/dailys/7-28-97.html
| |
| − | | title=CIA Budget: An Unnecessary Secret
| |
| − | | author=[[Dave Kopel]]
| |
| − | | date=1997-07-28
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref><ref> {{cite web
| |
| | | url=http://www.fas.org/sgp/news/1999/11/wp112999.html | | | url=http://www.fas.org/sgp/news/1999/11/wp112999.html |
| | | title=Cloak Over the CIA Budget | | | title=Cloak Over the CIA Budget |
| | | date=1999-11-29 | | | date=1999-11-29 |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15 | + | | accessdate=April 28, 2013 |
| | }} </ref> | | }} </ref> |
| | }} | | }} |
| − | The''' Central Intelligence Agency'''('''CIA''') is an [[intelligence agency]] of the [[United States]] [[Federal government of the United States|government]]. Its first function is obtaining and analyzing information about foreign [[government]]s, [[corporation]]s, and persons. Its second function is [[propaganda]] and [[public relations]].<ref name="NSC10/2"/> Its third function is as the government's hidden hand via [[covert operation]]s at the direction of the [[President of the United States|President]] and under oversight by Congress.<ref name = "vision">{{cite web | + | The '''Central Intelligence Agency (CIA)''' is an intelligence-gathering agency of the United States government whose primary mission today is collecting secret [[information]] from abroad through human agents. Created in the aftermath of the [[Pearl Harbor]] attack to centralize all [[intelligence]]-gathering efforts by the [[U.S. government]], its three functions are divided according to intelligence collection, intelligence [[analysis]], and technical services. It also has the mandate to conduct covert action, semi-secret political, or [[paramilitary operations]] where the [[U.S. government]]'s hand is not directly visible. It also conducts [[counterintelligence]] against foreign-government intelligence services. The CIA's covert operations have caused much controversy for the agency, raising questions about the [[law|legality]], [[morality]], and effectiveness of such operations. |
| − | | title = CIA Vision, Mission, and Values
| + | |
| − | | work = cia.gov
| + | The CIA is restricted from operating inside the [[United States]], although it collects some intelligence from American visitors who return from overseas travel or individuals living in the U.S with access to foreign intelligence. The [[FBI]] is the lead domestic intelligence agency. |
| − | | url = https://www.cia.gov/about-cia/cia-vision-mission-values/index.html
| |
| − | | date= 2006-07-16
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-06-23
| |
| − | }}</ref> This last function has caused much controversy for the CIA — questions about the [[law|legality]], [[morality]], [[pragmatism|effectiveness]], and [[intelligence (trait)|intelligence]] of such operations.
| |
| | | | |
| − | Its headquarters is in the community of [[Langley, Virginia|Langley]] in the [[McLean, Virginia|McLean]] [[Census-designated place|CDP]] of [[Fairfax County, Virginia|Fairfax County]], [[Virginia]], a few miles northwest from downtown [[Washington, D.C.]] along the [[Potomac River]]. The CIA is part of the [[United States Intelligence Community|U.S. Intelligence Community]], led by the [[United States Director of National Intelligence|Director of National Intelligence]] (DNI). The role and functions of the CIA are roughly equivalent to those of the [[United Kingdom]]'s [[Secret Intelligence Service]] (MI6), the [[Canadian Security Intelligence Service]] (CSIS), the [[Australian Secret Intelligence Service]] (ASIS) and [[Israel]]'s [[Mossad]].
| + | The CIA's elite division is called the [[Directorate of Operations]] (DO), also known as the [[Clandestine Service]], that at its height in the 1980s, numbered around 10,000 specialists in [[espionage]], agent recruitment, and [[covert action]]. |
| | + | {{toc}} |
| | + | Until recently, the CIA director performed the dual functions of agency director and Director of Central Intelligence (DCI), the nominal head of all U.S. intelligence agencies. Under reform [[legislation]] passed in the aftermath of the September 11 attacks and failures related to [[Iraq]]’s weapons of mass destruction programs, the CIA was subsumed under the Office of the [[Director of National Intelligence]] and the CIA director no longer acts as DCI. The agency has been refocused as the primary human-intelligence gathering agency of the government. |
| | | | |
| − | The CIA is sometimes referred to [[euphemism|euphemistically]] in government and [[Military of the United States|military]] [[idiom#parlance|parlance]] as '''Other Government Agencies''' (or '''OGA'''), particularly when its operations in a particular area are an [[open secret]].<ref>{{cite web
| + | CIA headquarters is in the community of [[Langley, Virginia|Langley]] in the [[McLean, Virginia|McLean]], [[Virginia]], a few miles northwest from downtown [[Washington, D.C.]], along the [[Potomac River]]. |
| − | | url=http://www.post-gazette.com/pg/03236/214533.stm
| |
| − | | title=Unsavory allies stack CIA's deck
| |
| − | | author=Nir Rosen
| |
| − | | work=post-gazette.com
| |
| − | | accessdate=2003-08-24}}</ref><ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://www.yuricareport.com/PrisonerTortureDirectory/JordanLinksAbuGhraibToWhiteHouse.html
| |
| − | | work=Yurica Report
| |
| − | | title=Soldier Described White House Interest
| |
| − | | author=R. Jeffrey Smith
| |
| − | | date=2004-06-09
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref> Other terms include '''The Company''' and '''The Agency'''.
| |
| | | | |
| − | ==History== | + | ==History and operations== |
| | + | ===Creation=== |
| | + | [[Image:William Donovan.jpg|thumb|144px|William J. Donovan, widely credited as the "father" of the CIA]] |
| | [[Image:2430 E Street.png|thumb|144px|right|Original sign with seal from the CIA's first building on E Street in Washington, DC]] | | [[Image:2430 E Street.png|thumb|144px|right|Original sign with seal from the CIA's first building on E Street in Washington, DC]] |
| − | The Central Intelligence Agency was created by Congress with passage of the [[National Security Act of 1947]], signed into law by President [[Harry S. Truman]]. It is the descendant of the [[Office of Strategic Services]] (OSS) of [[World War II]], which was dissolved in October 1945 and its functions transferred to the State and War Departments. But the need for a centralized postwar intelligence-gathering operation was clearly recognized. Eleven months earlier, in 1944, [[William J. Donovan]] (a.k.a. Wild Bill Donovan), the OSS's creator, proposed to President [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]] creating a new espionage organization directly supervised by the President: "which will procure intelligence both by overt and [[covert]] methods and will at the same time provide intelligence guidance, determine national intelligence objectives, and correlate the intelligence material collected by all government agencies."<ref name=CIAfact>{{cite book | + | [[Image:Allen w dulles.jpg|thumb|144px|Allen Dulles]] |
| − | | title=Factbook on Intelligence
| + | The Central Intelligence Agency was created by Congress with passage of the [[National Security Act of 1947]], signed into law by President [[Harry S. Truman]]. It is the descendant of the [[Office of Strategic Services]] (OSS) of [[World War II]], which was dissolved in October 1945, and its functions transferred to the State and War Departments. However, the need for a centralized postwar intelligence-gathering operation was clearly recognized. |
| − | | publisher=Central Intelligence Agency
| |
| − | | year=1992
| |
| − | | month=December
| |
| − | | pages= p. 4-5
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref> Under his plan, a powerful, centralized civilian agency would have coordinated all the intelligence services. He also proposed that this agency have authority to conduct "subversive operations abroad," but "no police or law enforcement functions, either at home or abroad."<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=https://www.cia.gov/csi/kent_csi/docs/v20i1a02p_0006.htm
| |
| − | | work=cia.gov
| |
| − | | title=Truman on CIA
| |
| − | | author=[[Thomas F. Troy]]
| |
| − | | pages=p.6
| |
| − | | date=1993-09-22
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | Despite opposition from the military establishment, the [[State Department]] and the [[Federal Bureau of Investigation]] (FBI)<ref name=CIAfact/>, President Truman established the Central Intelligence Group in January 1946.<ref>{{cite web
| + | Eleven months earlier, in 1944, [[William J. Donovan]] (also known as Wild Bill Donovan), the OSS's creator, proposed to President [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]] creating a new [[espionage]] organization directly supervised by the President. Under Donovan's plan, a powerful, centralized civilian agency would coordinate all the intelligence services. He also proposed that this agency have authority to conduct "subversive operations abroad," but no police or law enforcement functions, either at home or abroad. |
| − | | url=https://www.cia.gov/csi/studies/96unclass/salvage.htm
| |
| − | | work=cia.gov
| |
| − | | title=The Creation of the Central Intelligence Group
| |
| − | | author=Michael Warner
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref> Later, under the [[National Security Act of 1947]] (effective September 18, 1947), the [[United States National Security Council|National Security Council]] and the Central Intelligence Agency were established. Rear Admiral [[Roscoe H. Hillenkoetter]] was appointed as the first [[Director of Central Intelligence]].
| |
| | | | |
| − | The now declassified National Security Council Directive on Office of Special Projects, June 18, 1948 (NSC 10/2) provided the operating instructions for the CIA:
| + | President [[Harry S. Truman]], established the [[Central Intelligence Group]] in January 1946, over objections from the State Department and the FBI, who saw the creation of the agency as a rival to their own functions. Later, under the [[National Security Act]] of 1947, the [[National Security Council]] and the Central Intelligence Agency were established. Rear Admiral [[Roscoe H. Hillenkoetter]] was appointed as the first [[Director of Central Intelligence]]. |
| | | | |
| − | {{cquote|Plan and conduct covert operations which are conducted or sponsored by this government against hostile foreign states or groups or in support of friendly foreign states or groups but which are so planned and conducted that any US Government responsibility for them is not evident to unauthorised persons and that if uncovered the US Government can [[plausible deniability|plausibly disclaim any responsibility]] for them. Covert action shall include any covert activities related to: propaganda; economic warfare; preventive direct action, including sabotage, anti-sabotage, demolition, and evacuation measures; subversion against hostile states, including assistance to underground resistance movements, guerrillas and refugee liberation groups, and support of indigenous anti-Communist elements in threatened countries of the free world.<ref name="NSC10/2">{{cite web
| + | The now declassified National Security Council Directive on the Office of Special Projects, June 18, 1948 (NSC 10/2), provided the operating instructions for the CIA's covert operations: |
| − | | url=http://www.state.gov/www/about_state/history/intel/290_300.html
| |
| − | | work=state.gov
| |
| − | | title=U.S. Department of State: Foreign Relations of the United States, 1945-1950, Emergence of the Intelligence Establishment
| |
| − | |pages=Document 292, Section 5
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref>}}
| |
| − | [[Image:Cia-lobby-seal.jpg|thumb|right|The 16-foot diameter granite CIA seal in the lobby of the Original Headquarters Building]]
| |
| − | In 1949, the [[Central Intelligence Agency Act]] ([[Public Law]] 81-110) was passed, permitting the agency to use confidential fiscal and administrative procedures, and exempting it from most of the usual limitations on the use of Federal funds. The act also exempted the CIA from having to disclose its "organization, functions, officials, titles, salaries, or numbers of personnel employed." It also created the program "PL-110," to handle defectors and other "essential aliens" who fall outside normal immigration procedures, as well as giving those persons [[Cover (intelligence)|cover stories]] and economic support.<ref name = "GEORGE"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =George Tenet v. John Doe
| |
| − | | work =Federation of American Scientists
| |
| − | | url =http://www.fas.org/sgp/jud/tenetvdoe-petresp.pdf
| |
| − | | date= 2006-07-16
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | | format=PDF}}</ref>
| |
| − | During the first years of its existence, other branches of government did not exercise much control over the Central Intelligence Agency; justified by the desire to match and defeat [[KGB]] actions throughout the globe, a task many believed could be accomplished only through an approach as equally ungentlemanly as the KGB's, consequently, few in government closely inquired about the CIA's activity. The rapid expansion of the CIA, and a developed sense of independence under the Director of Central Intelligence (DCI) [[Allen Dulles]] added to this trend.
| |
| | | | |
| − | Things came to a head in the early 1970s, around the time of the [[Watergate]] political burglary affair. A dominant feature of political life during that period were the attempts of [[United States Congress|Congress]] to assert oversight of U.S. Presidency, the executive branch of the U.S. Government. Revelations about past CIA activities, such as assassinations and attempted assassinations of foreign leaders, illegal domestic spying on U.S. citizens, provided the opportunities to execute Congressional oversight of U.S. intelligence operations. Hastening the Central Intelligence Agency's fall from grace were the burglary of the Watergate headquarters of the [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic Party]] by ex-CIA agents, and President [[Richard Nixon|Nixon's]] subsequent use of the CIA to impede the FBI's investigation of the burglary. In the famous "smoking gun" audio tape provoking President Nixon's resignation, Nixon ordered his chief of staff, [[H.R. Haldeman]], to tell the CIA that further investigation of Watergate would "open the whole can of worms" about the [[Bay of Pigs Invasion|Bay Of Pigs]] of Cuba, and, therefore, that the CIA should tell the FBI to cease investigating the Watergate burglary, due to reasons of "national security".<ref>{{cite web
| + | <blockquote>Plan and conduct covert operations which are conducted or sponsored by this government against hostile foreign states or groups or in support of friendly foreign states or groups but which are so planned and conducted that any U.S. Government responsibility for them is not evident to unauthorized persons and that if uncovered the U.S. Government can [[plausible deniability|plausibly disclaim any responsibility]] for them. Covert action shall include any covert activities related to: Propaganda; economic warfare; preventive direct action, including sabotage, anti-sabotage, demolition, and evacuation measures; subversion against hostile states, including assistance to underground resistance movements, guerrillas and refugee liberation groups, and support of indigenous anti-Communist elements in threatened countries of the free world.</blockquote> |
| − | | url=http://www.hpol.org/transcript.php?id=92
| |
| − | | work=hpol.org
| |
| − | | title= Transcript of a recording of a meeting between President Richard Nixon and H. R. Haldeman in the oval office
| |
| − | | date=1972-06-23
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | [[Image:CIA New HQ Entrance.jpg|thumb|The entrance of the CIA Headquarters.]] | + | ===Fighting communism=== |
| | + | The CIA was successful in limiting native Communist influence in [[France]] and [[Italy]], notably in the [[1948 Italian election]]. It also cooperated in a clandestine [[NATO]] "stay-behind" operation in Italy called [[Operation Gladio]], which was set up in Western Europe, intended to counter a [[Warsaw Pact]] invasion of Western Europe. In addition, the CIA managed to acquire the [[Rosenholz files]], containing the list of foreign spies of the [[Stasi]], in the former [[German Democratic Republic]] (East Germany). |
| | | | |
| − | In 1973, then-DCI [[James R. Schlesinger]] commissioned reports — known as the "[[Family jewels (Central Intelligence Agency)|Family Jewels]]" — on illegal activities by the Agency. In December 1974, [[Investigative journalist]] [[Seymour Hersh]] broke the news of the "Family Jewels" in a front-page article in the ''[[New York Times]]'', revealing that the CIA had assassinated foreign leaders, and had conducted surveillance on some seven thousand American citizens involved in the antiwar movement ([[Operation CHAOS]]).
| + | The CIA also helped recruit many scientists who had worked in Nazi Germany to aid the United States. Several former Nazi operational agents were also reportedly recruited as United States' secret agents. |
| | | | |
| − | Congress responded to the disturbing charges in 1975, investigating the CIA in the Senate via the [[Church Committee]], chaired by Senator [[Frank Church]] (D-Idaho), and in the House of Representatives via the [[Pike Committee]], chaired by Congressman [[Otis Pike]] (D-NY). In addition, President [[Gerald Ford]] created the [[United States President's Commission on CIA activities within the United States|Rockefeller Commission]], and issued a directive prohibiting the assassination of foreign leaders.
| + | In 1949, the [[Central Intelligence Agency Act]] ([[Public Law]] 81-110) was passed, permitting the agency to use confidential fiscal and administrative procedures, and exempting it from most of the usual limitations on the use of federal funds. The act also exempted the CIA from having to disclose its "organization, functions, officials, titles, salaries, or numbers of personnel employed." The act also created the program "PL-110," to handle defectors and other "essential aliens" who fall outside normal immigration procedures, as well as giving those persons [[Cover (intelligence)|cover stories]] and economic support. |
| | | | |
| − | Repercussions from the [[Iran-Contra]] arms smuggling scandal included the creation of the [[Intelligence Authorization Act]] in 1991. It defined covert operations as secret missions in geopolitical areas where the U.S. is neither openly nor apparently engaged. This also required an authorizing chain of command, including an official, presidential finding report and the informing of the House and Senate Intelligence Committees, which, in emergencies, requires only "timely notification."
| + | In the 1950s, with Europe stabilizing along the [[Iron Curtain]], the CIA worked to limit the spread of Soviet influence elsewhere around the world, especially in the poor countries of the [[Third World]]. Encouraged by DCI [[Allen Dulles]], clandestine operations quickly dominated the organization's actions. |
| | | | |
| − | In 1988, President [[George H. W. Bush]] became the first former chief of the CIA to be elected [[President of the United States]].
| + | [[Image:Cuban missiles.jpg|thumb|This U-2 photo revealed Soviet missile installation in Cuba]] |
| | | | |
| − | Previously, the Director of Central Intelligence (DCI) oversaw the Intelligence Community, serving as the president's principal intelligence advisor, additionally serving as head of the Central Intelligence Agency. The DCI's title now is "Director of the Central Intelligence Agency" (DCIA), serving as head of the CIA.
| + | In 1950, the CIA organized the [[Pacific Corporation]], the first of many CIA private enterprises used effectively by the CIA both for intelligence gathering and covert operations. In 1951, the [[Columbia Broadcasting System]] began cooperating with the CIA, as did several other news-gathering groups in later years. It also pioneered the use of new technologies in intelligence work, including the famous [[U-2]] high altitude spy plane. |
| | | | |
| − | Currently, the Central Intelligence Agency reports to U.S. Congressional committees, but also answers directly to the President. The [[United States National Security Advisor|National Security Advisor]] is a permanent member of the [[cabinet]], responsible for briefing the President with pertinent information collected by all U.S. intelligence agencies, including the [[National Security Agency]], the [[Drug Enforcement Administration]], et cetera; all fifteen [[Intelligence Community]] agencies are under the authority of the [[Director of National Intelligence]].
| + | One of the CIA's major successes came during the [[Cuban Missile Crisis]], which began on October 16, 1962. On that day, President [[John F. Kennedy]] was informed that a U-2 mission flown over western [[Cuba]] two days before had taken [[photographs]] of Soviet-nuclear missile sites. The event was a watershed for the [[intelligence community]] and the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), in particular. It demonstrated that the technological collection capabilities so painstakingly constructed to monitor the [[Soviet Union]] had matured to give the U.S. intelligence community an unmatched ability to provide policymakers with sophisticated warning and situational awareness. The CIA took the lead in developing [[aerial]] and [[space]] photographic systems. |
| | | | |
| − | Many of the post-Watergate restrictions upon the Central Intelligence Agency were lifted after the [[September 11, 2001 attacks]] on the [[World Trade Center]] in New York City and the [[The Pentagon]]. 52 years earlier, in 1949, Congress and President Harry Truman had approved arrangements that CIA and national intelligence funding could be hidden in the U.S federal budget. Some critics charge this violates the requirement in the [[U.S. Constitution]] that the [[federal budget]] be openly published.
| + | Particularly during the [[Cold War]], the CIA supported numerous governments opposed to Communist insurgencies and Marxist political movements. Some of these were led by military [[dictator]]s friendly to perceived United States' geopolitical interests. In some cases, the CIA reportedly supported coups against elected governments. |
| | | | |
| − | ==Organization==
| + | The CIA also supported the [[Congress of Cultural Freedom]], which published literary and political journals such as ''[[Encounter (magazine)|Encounter]]'' (as well as ''Der Monat'' in [[Germany]] and ''Preuves'' in [[France]]), and hosted dozens of conferences bringing together some of the most eminent Western thinkers; it also gave assistance to intellectuals behind the [[Iron Curtain]]. |
| − | ===Agency seal===
| |
| − | [[Image:CIA.svg|thumb|right|150px]] | |
| − | The [[heraldic]] symbol of the CIA consists of 3 representative parts: the left-facing bald eagle head atop, the ''compass star'' (or compass rose), and the shield. The [[eagle]] is the national bird, standing for strength and alertness. The 16-point compass star represents the CIA's world-wide search for intelligence outside the United States, which is then reported to the headquarters for analysis, reporting, and re-distribution to policymakers. The compass rests upon a shield, symbolic of defense and intelligence.
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===Structure=== | + | ===Controversy mounts=== |
| − | * [[Director of the Central Intelligence Agency]] (DCIA) – The head of the CIA is given the title of the DCIA. The act that created the CIA in 1947 also created a [[Director of Central Intelligence]] (DCI) to serve as head of the United States intelligence community, act as the principal adviser to the President for intelligence matters related to the national security, and serve as head of the Central Intelligence Agency. The Intelligence Reform and Terrorism Prevention Act of 2004 amended the National Security Act to provide for a [[Director of National Intelligence]] who would assume some of the roles formerly fulfilled by the DCI, with a separate Director of the Central Intelligence Agency.
| + | [[Image:James Schlesinger official DoD photo.jpg|thumb|144px|James Schlesinger]] |
| − | * [[CIA Deputy Director|Deputy Director of the Central Intelligence Agency]] (DDCIA) – Assists the Director in his duties as head of the CIA and exercises the powers of the Director when the Director’s position is vacant or in the Director’s absence or disability.
| + | In the early 1970s, revelations about past CIA activities, such as assassinations of foreign leaders and illegal domestic spying on U.S. citizens, provided opportunities to execute Congressional oversight of U.S. intelligence operations. In 1973, then-DCI [[James R. Schlesinger]] had commissioned reports—known as the "[[Family jewels (Central Intelligence Agency)|Family Jewels]]"—on illegal activities by the Agency. In December 1974, [[Investigative journalist]] [[Seymour Hersh]] broke the news of the "Family Jewels" in a front-page article in the ''[[New York Times]],'' revealing that the CIA had assassinated foreign leaders, and had conducted surveillance on some 7,000 American citizens involved in the antiwar movement ([[Operation CHAOS]]). The CIA also suffered a major public relations setback when it was revealed that the infamous burglary of the Watergate headquarters of the [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic Party]] was conducted by ex-CIA agents. |
| − | * [[Associate Deputy Director of the Central Intelligence Agency]] (ADD) – Created July 5 2006, the ADD was delegated all authorities and responsibilities vested previously in the post of Executive Director. The post of Executive Director, which was responsible for managing the CIA on a day-to-day basis, was simultaneously abolished.<ref name = "statement"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =Statement by Director of the Central Intelligence Agency General Michael V. Hayden
| |
| − | | work =cia.gov
| |
| − | | url =https://www.cia.gov/cia/public_affairs/press_release/2006/pr07112006.htm
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-16
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | * [[Associate Director for Military Support]] (AD/MS) – The DCIA's principal adviser and representative on military issues. The AD/MS coordinates Intelligence Community efforts to provide Joint Force commanders with timely, accurate intelligence. The AD/MS also supports Department of Defense officials who oversee military intelligence training and the acquisition of intelligence systems and technology. A senior general officer, the AD/MS ensures coordination of Intelligence Community policies, plans and requirements relating to support to military forces in the intelligence budget.
| |
| | | | |
| − | ==== Directorates and other offices ====
| + | Congress responded in 1975, investigating the CIA in the Senate via the [[Church Committee]], chaired by Senator [[Frank Church]] (D-Idaho), and in the House of Representatives via the [[Pike Committee]], chaired by Congressman [[Otis Pike]] (D-NY). In addition, President [[Gerald Ford]] created the [[United States President's Commission on CIA activities within the United States|Rockefeller Commission]] to investigate CIA activities within the U.S. and issued a directive prohibiting the assassination of foreign leaders. |
| − | * The [[Directorate of Intelligence]], the analytical branch of the CIA, is responsible for the production and dissemination of all-source intelligence analysis on key foreign issues.<ref name = "fifty"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =Fifty Years of Service to the Nation
| |
| − | | work =cia.gov
| |
| − | | url =https://www.cia.gov/cia/di/index.html
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-16
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | * The [[National Clandestine Service]], a semi-independent service which was formerly the Directorate of Operations, is responsible for the clandestine collection of foreign intelligence and [[covert operation|covert action]].
| |
| − | * The [[Directorate of Science & Technology]] creates and applies innovative technology in support of the intelligence collection mission.<ref name = "Directorate"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =Directorate of Science & Technology
| |
| − | | work =cia.gov
| |
| − | | url =https://www.cia.gov/cia/dst/home.html
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-16
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | * The [[Directorate of Support]] provides the mission critical elements of the Agency's support foundation: people, security, information, property, and financial operations. Most of this Directorate is sub-structured into smaller offices based on role and purpose, such as the CIA [[Office of Security]].
| |
| − | * The [[Center for the Study of Intelligence]] maintains the Agency's historical materials and promotes the study of intelligence as a legitimate and serious discipline.<ref name = "study"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =Center for the Study of Intelligence
| |
| − | | work =cia.gov
| |
| − | | url =https://www.cia.gov/csi/index.html
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-16
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | * The Office of the [[General Counsel]] advises the Director of the Central Intelligence Agency on all legal matters relating to his role as CIA director and is the principal source of legal counsel for the CIA.<ref name = "GC"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =Office of the General Counsel | |
| − | | work =cia.gov
| |
| − | | url =https://www.cia.gov/ogc/index.htm
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-16
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | * The Office of [[Inspector General]] promotes efficiency, effectiveness, and accountability in the administration of Agency activities. OIG also seeks to prevent and detect fraud, waste, abuse, and mismanagement. The Inspector General is nominated by the President and confirmed by the Senate. The Inspector General, whose activities are independent of those of any other component in the Agency, reports directly to the Director of the Central Intelligence Agency. OIG conducts inspections, investigations, and audits at Headquarters and in the field, and oversees the Agency-wide grievance-handling system. The OIG provides a semiannual report to the Director of the Central Intelligence Agency which the Director is required by law to submit to the Intelligence Committees of Congress within 30 days.
| |
| − | * The Office of [[Public Affairs]] advises the Director of the Central Intelligence Agency on all media, public policy, and employee communications issues relating to his role as CIA director and is the CIA’s principal communications focal point for the media, the general public and Agency employees.<ref name = "PA"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =Office of Public Affairs
| |
| − | | work =cia.gov
| |
| − | | url =https://www.cia.gov/cia/public_affairs/pas.html
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-16
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | * The Office of [[Military Affairs]] provides intelligence and operational support to the US armed forces.<ref name = "OMA"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title = Office of Military Affairs
| |
| − | | work = cia.gov
| |
| − | | url = https://www.cia.gov/oma/oma.html
| |
| − | | date = 2007-03-24
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| | | | |
| | + | Under the [[Carter Administration]], CIA Director Adm. [[Stansfield Turner]] carried out what became known as the “Halloween Massacre,” firing large numbers of the agency’s most experienced operations officers with a terse note. The action was part of a shift in emphasis away from human-based [[spying]] operations to electronic spying. Today, the CIA is working to recover from the loss of its human spying capabilities, shortcomings that were highlighted by the failures related to the September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks. |
| | | | |
| | + | A high point for the CIA was its running, along with British intelligence, of a Soviet military spy inside the [[GRU]] military intelligence service, Colonel [[Oleg Penkovsky]]. Penkovsky provided documents on Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile capabilities that allowed the United States to understand the threat it was facing from [[Moscow]]’s nuclear missiles. It is an example today of the kind of intelligence that can only be provided by human spies. |
| | | | |
| − | ===Relationship with other agencies===
| + | [[Image:Angletn.jpg|thumb|144px|James Angleton]] |
| − | {{Unreferencedsection|date=June 2007}}
| |
| − | [[Image:Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird.jpg|thumb|175px|The USAF's [[SR-71 Blackbird]] was developed from the CIA's A-12 OXCART.]] | |
| − | | |
| − | The CIA acts as the primary American provider of central intelligence estimates. It is believed to make use of the product derived from surveillance [[satellite]]s of the [[National Reconnaissance Office]] (NRO) and the signal interception capabilities of the [[National Security Agency]] (NSA), including the [[ECHELON]] system, the surveillance aircraft of the various branches of the U.S. armed forces and the analysts of the [[State Department]] and [[United States Department of Energy|Department of Energy]]. At one point, the CIA even operated its own fleet of [[Lockheed U-2|U-2]] and [[A-12 OXCART]] surveillance aircraft. The agency has also operated alongside regular military forces, and also employs a group of clandestine officers with [[paramilitary]] skills in its [[Special Activities Division]]. [[Johnny Michael Spann|Johnny Michael "Mike" Spann]], a CIA officer killed in November 2001 during the [[War in Afghanistan (2001–present)|U.S. invasion of Afghanistan]], was one such individual. The CIA also has strong links with other foreign intelligence agencies such as the UK's [[MI6|Secret Intelligence Service]], the [[Canadian Security Intelligence Service]], Israel's [[Mossad]], and the [[Australian Secret Intelligence Service]]. Further, it is currently believed to be financing several [[Counterterrorist Intelligence Center]]s. One of these, known under the codename of [[Alliance Base]], was allegedly set up in [[Paris]] and jointly run in cooperation with France's [[DGSE]]. Although classified, the CIA may also be actively cooperating with India's [[Research and Analysis Wing]] and possibly Russia's [[Foreign Intelligence Service (Russia)|SVR]]. The CIA worked extensively with Pakistan's ISI throughout the Afghan-Soviet War, and works with this agency closely for the War on Terror.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Historical operations and controversies ==
| |
| − | {{see also|CIA sponsored regime change|Category:CIA operations}}
| |
| − | ===North America===
| |
| − | In 1950, the CIA organized the [[Pacific Corporation]], the first of many CIA private enterprises. In 1951, the [[Columbia Broadcasting System]] began co-operating with the CIA; President Truman created the [[Office of Current Intelligence]].
| |
| | | | |
| − | Director [[Roscoe H. Hillenkoetter|Hillenkoetter]] approved [[Project BLUEBIRD]], later renamed [[Project ARTICHOKE]], which was the CIA's first mind control program. In the 1950s and 60s, the CIA ran a mind-control research program code-named [[Project MKULTRA]] in the United States and Canada. The project in Montreal included developing techniques used by Nazi scientists to wipe out the existing personalities of the victims.<ref>{{cite web
| + | Under CIA Counterintelligence Chief [[James Jesus Angleton]], the CIA imprisoned Soviet defector [[Yuri Nosenko]], whom Angleton believed to be an agent sent to provide disinformation to the CIA. Angleton had become close to another defector, [[Anatoli Golitsyn]], who reported that a secret unit within the [[Kremlin]] was engaged in strategic disinformation against the West. The dueling defectors set off an internal struggle within the CIA and led to Angleton’s "mole hunt," a search for Soviet penetration agents working within the CIA. |
| − | | url=http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/newspapers/sunday_times/scotland/article495413.ece
| |
| − | | work=The Sunday Times
| |
| − | | title=Brainwash victims win cash claims
| |
| − | | author= Karin Goodwin
| |
| − | | date=2004-11-17
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===Europe===
| + | Angleton had sought to reorient the CIA into a strategic counterintelligence agency, whose main goal would be targeting the [[Soviet]] [[KGB]] and its sister services with the initiative of bringing down the [[Soviet empire]]. Angleton, however, lost out in the power struggle to CIA Director [[William Colby]], who favored a more traditional intelligence and covert action approach. |
| − | {{see also|Strategy of tension}}
| |
| − | CIA was successful in limiting native Communist influence in [[France]] and [[Italy]], notably in the [[1948 Italian election]]. After WWII, a clandestine [[NATO]] "[[stay-behind]]" operation in Italy called [[Operation Gladio]], was set up in Western Europe, intended to counter a [[Warsaw Pact]] invasion of Western Europe. There are allegations that throughout the 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s, Gladio operatives were involved in a series of "[[false flag]]" fascist terrorist actions in Italy that were blamed on the "[[Red Brigades]]" and other Left-wing political groups in an attempt to politically discredit the Italian Left wing.<ref>{{cite journal | author= Charles Richards and Simon Jones | title= Skeletons start emerging from Europe's closet | journal= The Independent | year= November 16 1990 | pages= p. 11}}</ref> The US state department has denied involvement in terrorism and stated that some of the claims have been influenced by a Soviet forgery, [[US Army Field Manual 30-31B]].<ref name="StateDept">{{cite web|title=Misinformation about "Gladio/Stay Behind" Networks Resurfaces |publisher=United States Department of State |url=http://usinfo.state.gov/media/Archive/2006/Jan/20-127177.html}}</ref> | |
| | | | |
| − | In some unexplained way, the CIA managed to acquire the [[Rosenholz files]], containing the list of foreign spies of the [[Stasi]], in the former [[German Democratic Republic|GDR]].<ref>{{cite web
| + | The [[Farewell Dossier]]—a collection of documents containing intelligence gathered and handed over to NATO by the KGB defector Colonel Vladimir Vetrov (code-named "Farewell")—in 1981-82, revealed massive Soviet espionage on Western technology. The CIA created a successful counter-espionage program which involved giving defective technologies to Soviet agents. |
| − | | url=http://se2.isn.ch/serviceengine/FileContent?serviceID=12&fileid=612CAF70-74AC-5C75-C8BF-5A19D04ADEFB&lng=de
| |
| − | | work=Nowegian Institute for Defense Studies
| |
| − | | title=Stasi Files and GDR espionage Against the West
| |
| − | | author=Bernd Schafer
| |
| − | | format=PDF
| |
| − | | date=2007-03-13
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | === Nazi linkages ===
| + | In 1983, the CIA had more [[spies]] working inside the [[Soviet Union]] than at any time in its history. Infamous CIA operative [[Aldrich Ames]] would betray 25 active agents, some working at senior levels within the Soviet establishment. Many of these were taken to prison and then shot in the back of the head, so that the [[exit wound]] would render the face unrecognizable. In return, Ames received over $1.3 million in payments from the [[KGB]] from 1985-91. The total would eventually rise to $4 million. Ames was finally caught after a CIA mole-hunting team—with the assistance of the FBI—uncovered Ames's access to compromised cases and his suspect personal finances. |
| − | {{see also|Nazis in the CIA}}
| |
| − | After [[World War II]], many scientists who had worked in Nazi Germany were extracted from Germany in order to aid the U.S.; their recruitment was under aegis of [[Operation Paperclip]]. The CIA had also been aware of the location of some high-profile [[Nazi]] war criminals, including the whereabouts of [[Adolf Eichmann]] two years before he was captured by Israeli agents, but the agency did not publicize this information, as it did not have a policy of pursuing Nazi war criminals at the time.<ref>{{cite journal | author= Scott Shane | title= C.I.A. Knew Where Eichmann Was Hiding, Documents Show | journal= The New York Times | year= June 7 2006 | pages= p. 3}}</ref> Several former Nazi operational agents were recruited as U.S. secret agents, yet formed just a minor portion of the agents at that time; they were induced financially and promised exemption from criminal prosecution and trial for [[war crimes]] committed during World War II.<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://www.jstandard.com/articles/1159/1/Postwar-U.S.
| |
| − | | title=Postwar U.S.- Nazi link revealed
| |
| − | | author=Ron Kampeas
| |
| − | | date= 2006-08-06
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref> Some claim that these agents had a long-term corrosive effect on American intelligence agencies.<ref>{{cite book
| |
| − | | last = Simpson
| |
| − | | first = Christopher
| |
| − | | authorlink=Christopher Simpson
| |
| − | | year =August 1989
| |
| − | | title = Blowback: America's recruitment of Nazis and its effects on the Cold War
| |
| − | | publisher = Weidenfeld & Nicholson.
| |
| − | | location = New York
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 978-0020449959
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===Developing world===
| + | Repercussions from the [[Iran-Contra]] arms smuggling scandal included the creation of the [[Intelligence Authorization Act]] in 1991. It required an authorizing chain of command, including an official presidential report and the informing of the House and Senate Intelligence Committees. |
| − | In the 1950s, with Europe stabilizing along the [[Iron Curtain]], the CIA then tried limiting the spread of Soviet influence elsewhere around the world, especially in the poor countries of the [[Third World]]. Encouraged by DCI [[Allen Dulles]], clandestine operations quickly dominated the organization's actions.
| |
| | | | |
| − | Particularly during the [[Cold War]], the CIA supported many [[dictator]]s, including General [[Augusto Pinochet]] of Chile; dictators in [[Central America]], African Dictators like [[Mobutu Sese Seko]] and [[Jonas Savimbi]], the [[Mohammad Reza Pahlavi|Shah of Iran]], and the religious despots in [[Saudi Arabia]], [[Pakistan]], [[Kuwait]] and [[Indonesia]], who have been friendly to perceived U.S. geopolitical interests ([[anti-Communism]], natural resource access for petroleum companies and multinational corporations, and implementing neoliberal economics). In some cases the CIA supported coups against elected governments, partially because they were perceived, at the time, as turning into Communist dictatorships.
| + | In 1996, the [[U.S. House Permanent Select Committee on Intelligence]] issued a congressional report estimating that the [[clandestine service]] part of the [[intelligence community]] "easily" breaks "extremely serious laws" in countries around the world 100,000 times every year. |
| | | | |
| − | [[John Stockwell]], formerly a high-level CIA operative, claims that six million people have been killed by the United States in the Third World countries. This claim includes the deaths in the Korea and Vietnam wars that Stockwell feels should be blamed on the United States.<ref name = "stockwell"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =Americas Third World War How 6 million People Were killed in CIA secret wars against third world countries
| |
| − | | work =Information Clearing House
| |
| − | | url =http://www.informationclearinghouse.info/article4068.htm
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-11
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| | [[Image:Cia-memorial-wall.jpg|thumb|right|The lives of 83 fallen CIA officers are represented by 83 stars on the CIA memorial wall in the Old Headquarters building.]] | | [[Image:Cia-memorial-wall.jpg|thumb|right|The lives of 83 fallen CIA officers are represented by 83 stars on the CIA memorial wall in the Old Headquarters building.]] |
| | | | |
| − | ====Guatemala====
| + | Some of the post-Watergate restrictions upon the Central Intelligence Agency were lifted after the [[September 11, 2001 attacks]] on the [[World Trade Center]] in New York City and [[The Pentagon]]. Critics charge this violates the requirement in the [[U.S. Constitution]] that the [[federal budget]] be openly published. |
| − | {{main|1954 Guatemalan coup d'état}}
| |
| − | PBSUCCESS, authorized by [[Dwight Eisenhower|President Eisenhower]], is the codename for the CIA first covert operation in Latin America, carried out in Guatemala. According to most historians, the CIA-sponsored military coup in 1954 was “the poison arrow that pierced the heart of Guatemala's young democracy.”<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://consortiumnews.com/archive/story38.html
| |
| − | | work=The Consortium
| |
| − | | title=Guatemala – 1954: Behind the CIA’s Coup
| |
| − | | author=[[Kate Doyle]]
| |
| − | | date=1997
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref> The purpose of the operation was to overthrow [[Jacobo Arbenz Guzmán]], the [[democratically-elected]] [[President of Guatemala|President]] of [[Guatemala]].
| |
| − | The U.S. began to worry about the growth of Communism there because of policies set forth by Jacobo Arbenz. By recruiting a Guatemalan military force the CIA's operation succeeded in eliminating the democratic government and replacing it with a military junta headed by Colonel [[Carlos Castillo Armas]].
| |
| | | | |
| − | Some argue that a political and consequent social instability created in Guatemala 6 years later resulted in a very long civil war and its consequent, destructive impact upon the society, the economy, and the culture of Guatemala.
| + | In the findings of the independent [[National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States]] released on July 22, 2004, detailed several failures of the CIA in taking proper measures related to the September 11, 2001 attacks were called into account: |
| | | | |
| − | ====Iran====
| + | *"The CIA was limited in its effort to try to capture [[al Qaeda]] founder [[Osama bin Laden]] and his lieutenants in [[Afghanistan]] by the agency's use of proxies." |
| − | {{main|1953 Iranian coup d'état}}
| + | *"The failure of the CIA and [[FBI]] to communicate with each other… led to missed 'operational opportunities' to hinder or break the terror plot." |
| − | Britain, fearful of Iran’s plan to nationalize its oil industry, came up with the idea for the coup in 1952 and pressed the U.S. to mount a joint operation to remove the Prime Minister [[Mohammed Mossadegh]]<ref>{{cite book
| + | *"The CIA did not put 9/11 hijacker [[Khalid Almihdhar]] on a 'watch list' or notify the FBI when he had a U.S. visa in January 2000, or when he met with a key figure in the [[USS ''Cole'']] bombing. And the CIA failed to develop plans to track Almihdhar, or hijacker [[Nawaf Alhazmi]] when he obtained a U.S. visa and flew to Los Angeles." |
| − | | last =Wilber
| |
| − | | first =Donald N.
| |
| − | | authorlink =Donald N. Wilber
| |
| − | | coauthors = Emmanuel Andrew Maldonado
| |
| − | | year =April 16, 2000
| |
| − | | title =Overthrow of Premier Mossadeq of Iran
| |
| − | | publisher =The New York Times
| |
| − | | location =http://www.nytimes.com/library/world/mideast/iran-cia-intro.pdf
| |
| − | | id =
| |
| − | }}</ref> and allow the Shah [[Mohammed Reza Pahlavi]] to rule autocratically. Partially due to fear of a Communist overthrow due to increasing influence of the Communist [[Tudeh]] party, the US agreed. Brigadier General [[Norman Schwarzkopf, Sr.]] and CIA guru [[Kermit Roosevelt, Jr.]] were ordered to begin a covert operation. A complex plot, codenamed Operation Ajax, was conceived and executed from the US Embassy in [[Tehran]]. Ex CIA director Admiral Stansfield Turner had no intelligence of the Islamist revolution of 1979 in Iran as "It was a big gap in CIA coverage" and consequently the CIA engaged in numerous covert operations to maintain control. Currently, there has been no release of information from the CIA regarding any potential eminent threat from Iran and its nuclear ambitions.
| |
| | | | |
| − | ====Cuba====
| + | On November 5, 2002, newspapers reported that [[Al-Qaeda]] operatives in a car traveling through [[Yemen]] had been killed by a missile launched from a CIA-controlled [[RQ-1 Predator|Predator drone]]. On May 15, 2005, it was reported that another of these drones had been used to assassinate Al-Qaeda figure [[Haitham al-Yemeni]] inside [[Pakistan]]. |
| − | The limitations of large scale covert action became apparent during the CIA-organized [[Bay of Pigs Invasion]] of [[Cuba]] in 1961. The failed para-military invasion embarrassed the CIA and the United States world-wide. Recently de-classified documents show in written confirmation that President Kennedy had officially denied the CIA authorization to invade Cuba. Cuban leader [[Fidel Castro]] used the routed invasion to consolidate his power and strengthen Cuba's ties with the Soviet Union. Later, the CIA tried and failed several times to [[Fidel Castro#Assassination Attempts|assassinate]] Fidel Castro.
| |
| | | | |
| − | ====Indochina==== | + | ===Reorganization=== |
| − | CIA operations became less visible after the Bay of Pigs, and shifted to being closely linked to aiding the U.S. military operation in [[Vietnam]]. Between 1962 and 1975, the CIA organized a [[Laos|Laotian]] group known as the Secret Army and ran a fleet of aircraft known as [[Air America]] to take part in the [[Secret War]] in Laos, part of the [[Vietnam War]]. | + | In the same year President [[George W. Bush]] appointed the CIA to be in charge of all human intelligence and manned spying operations. This was the culmination of a years-old turf war regarding influence, philosophy, and budget between the [[Defense Intelligence Agency]] of [[The Pentagon]] and the CIA. The Pentagon, through the DIA, wished to take control of the CIA's [[paramilitary]] operations and many of its human assets. The CIA, which has for years held that human intelligence is the core of the agency, successfully argued that the CIA's decades-long experience with human resources and civilian oversight made it, rather than the DIA, the ideal choice. Thus, the CIA was given charge of all United States' human intelligence, but as a compromise, The Pentagon was authorized to include increased paramilitary capabilities in future budget requests. Despite reforms which led it back to what the CIA considers its traditional principal capacities, the CIA Director's position has lost influence in the White House. For years, the Director of the CIA met regularly with the President to issue daily reports on ongoing operations. After the creation of the post of [[Director of National Intelligence]], the report is now given by the DNI, who oversees all United States' Intelligence activities. |
| | | | |
| − | The CIA's [[Phoenix Program]] during the [[Vietnam War]] was described by a former official as a "sterile depersonalized murder program." Quote: "I never knew an individual to be detained as a VC suspect who ever lived through an interrogation"<ref name = "bart"> {{cite web
| + | [[Image:Khalid Shaikh Mohammed after capture.jpg|thumb|Khalid Shaikh Mohammed]] |
| − | |url=http://homepage.ntlworld.com/jksonc/docs/phoenix-hcgo-19710802.html#kbo
| |
| − | |title=COMMITTEE ON GOVERNMENT OPERATIONS HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES - U.S. Assistance Programs in Vietnam - Statement of K. Barton Osborn
| |
| − | |accessdate=2007-06-25 | |
| − | |date=August 21971 | |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | In December 1978, three-and-a-half years after the withdrawal of U.S. military forces from Indochina, [[Cambodian-Vietnamese War|Vietnam invaded]] [[Cambodia]] and dislodged the genocidal regime of [[Pol Pot]]. According to socialist U.S. foreign policy critic [[William Blum]], the State Department continued to recognize the former government as the legitimate representative of Cambodia at the [[United Nations]], and the United States used a variety of means to give indirect support to the [[Khmer Rouge]], in an ongoing effort to thwart the Vietnamese-installed regime of [[Heng Samrin]]. Blum also claims that the CIA supplied arms directly to Khmer Rouge forces and also funneled more than $20 million/year of "non-lethal" aid to a coalition which included the Khmer Rouge, without Congressional approval.<ref name="Rogue State">{{cite web| title=Supporting Pol Pot — excerpted from the book [[Rogue State: A Guide to the World's Only Superpower|''Rogue State'']] | publisher=[[Third World Traveler]] | url=http://www.thirdworldtraveler.com/Blum/Support_PolPot_RS.html | accessdate=2007-07-08}}</ref>
| + | On July 9, 2004, the [[Senate Report of Pre-war Intelligence on Iraq]] of the [[Senate Intelligence Committee]] reported that the CIA exaggerated the danger presented by [[weapons of mass destruction]] in [[Iraq]], largely unsupported by the available intelligence. |
| | | | |
| − | ====Iraq====
| + | Earlier, in Novemeber 2002, the CIA successfully ended the life of Qaed Salim Sinan al-Harethi, a prominent member of Osama bin Laden’s [[al Qaeda]] terrorist network, through a Predator drone attack in Yemen. It has also been involved in identifying, capturing, and interrogating numerous terrorists, as well as in operations assisting troops fighting al Qaeda in [[Afghanistan]] and [[Iraq]]. In 2003, the CIA reportedly assisted in the capture of al Qaeda operations director [[Khalid Shaikh Mohammed]], who was later reported to have cooperated with CIA interrogators, providing valuable information on al Qaeda methods, plans, and personnel. On January 13, 2006, the CIA launched an [[Damadola airstrike|airstrike on Damadola]], a [[Pakistan]]i village near the Afghan border, where they believed [[Ayman al-Zawahiri]] was located. The airstrike killed a number of civilians, but al-Zawahiri escaped. Because al-Zawahiri is named as a terrorist enemy combatant by the United States, this and similar attacks are not covered under [[Executive Order 12333]], which banned assassinations. Many of the CIA's activities in the war on terror remain undisclosed for security reasons. |
| − | According to certain authors the CIA supported the 1963 military [[coup d'état]] in [[Iraq]] against the [[Qassim]] government and supported the subsequently installed government of [[Saddam Hussein]], until the 1990 Iraqi invasion of [[Kuwait]]. U.S. support for the invasion was predicated upon the notion that Iraq was a key buffer state in geopolitical relations with the [[Soviet Union]]. There are U.S. court records indicating the CIA militarily and monetarily assisted Iraq during the [[Iran-Iraq War]]. The CIA also was involved in the failed 1996 coup against Saddam Hussein.<ref name = "howthewest"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =How west helped Saddam gain power and decimate the Iraqi elite
| |
| − | | work =www.muslimedia.com
| |
| − | | url =http://www.muslimedia.com/archives/features98/saddam.htm
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-30
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref><ref name = "list"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =CIA Lists Provide Basis for Iraqi Bloodbath
| |
| − | | work =www.globalpolicy.org
| |
| − | | url =http://www.globalpolicy.org/security/issues/iraq/history/1963cialist.htm
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-30
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref><ref name = "why"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =The United States and Middle East: Why Do "They" Hate Us?
| |
| − | | work =zmag.org
| |
| − | | url =http://www.zmag.org/shalomhate.htm
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-30
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref><ref name = "key"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =Exclusive: Saddam Was key in early CIA plot
| |
| − | | work =www.informationclearinghouse.info
| |
| − | | url =http://www.informationclearinghouse.info/article2849.htm
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-30
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref><ref name = "carlos"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =United States of America v. Carlos Cardoen
| |
| − | | work =National Security Archive
| |
| − | | url =http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB82/iraq61.pdf
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-30
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | |format=PDF
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | The CIA also supported the [[Ba'ath Party]]'s 1968 coup d'état against the Government of Rahman Arif, with [[Saddam Husein]] eventually assuming power.<ref name = "tyrant"> {{cite journal
| + | ==Current organization== |
| − | | first =
| + | ===Agency seal=== |
| − | | last =
| + | [[Image:Cia-lobby-seal.jpg|thumb|right|The 16-foot diameter granite CIA seal in the lobby of the Original Headquarters Building]] |
| − | | authorlink =
| + | [[Image:CIA New HQ Entrance.jpg|thumb|The entrance of the CIA Headquarters]] |
| − | | coauthors =
| + | The [[heraldic]] symbol of the CIA consists of three representative parts: The left-facing bald eagle head atop, the ''compass star'' (or compass rose), and the shield. The [[eagle]] is the national bird, standing for strength and alertness. The 16-point compass star represents the CIA's world-wide search for intelligence outside the United States, which is then reported to the headquarters for analysis, reporting, and re-distribution to policymakers. The compass rests upon a shield, symbolic of defense and intelligence. |
| − | | year =2003 | |
| − | | month =March 14 | |
| − | | title =A Tyrant 40 Years in the Making | |
| − | | journal =New York Times
| |
| − | | volume = | |
| − | | issue = | |
| − | | pages =
| |
| − | | id =
| |
| − | | url =http://readthese.blogspot.com/2003_12_15_readthese_archive.html
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | According to former U.S. intelligence officials, the CIA orchestrated a bomb and sabotage campaign between 1992 and 1995 in Iraq via one of the resistance organizations, [[Iyad Allawi]]'s group, the man later installed as prime minister by the U.S.-led coalition after the U.S. invasion of Iraq in 2003. According to the Iraqi government at the time, and former CIA officer Robert Baer, the bombing campaign against [[Baghdad]] included both government and civilian targets. According to this former CIA official, the civilian targets included a movie theater and a bombing of a school bus and schoolchildren were killed. No public records of the secret bombing campaign are known to exist, and the former U.S. officials said their recollections were in many cases sketchy, and in some cases contradictory. "But whether the bombings actually killed any civilians could not be confirmed because, as a former C.I.A. official said, the United States had no significant intelligence sources in Iraq then."<ref name="common2">{{cite web
| + | ===Structure=== |
| − | | url=http://www.commondreams.org/headlines04/0609-02.htm
| + | * [[Director of the Central Intelligence Agency]] (DCIA)—The head of the CIA is given the title of the DCIA. The act that created the CIA in 1947, also created a [[Director of Central Intelligence]] (DCI) to serve as head of the United States intelligence community, act as the principal adviser to the President for intelligence matters related to the national security, and serve as head of the Central Intelligence Agency. The Intelligence Reform and Terrorism Prevention Act of 2004, amended the National Security Act to provide for a [[Director of National Intelligence]] who would assume some of the roles formerly fulfilled by the DCI, with a separate Director of the Central Intelligence Agency. |
| − | | work=The New York Times
| + | * [[CIA Deputy Director|Deputy Director of the Central Intelligence Agency]] (DDCIA)—Assists the Director in his duties as head of the CIA and exercises the powers of the Director when the Director’s position is vacant or in the Director’s absence or disability. |
| − | | title=Ex-C.I.A. Aides Say Iraq Leader Helped Agency in 90's Attacks
| + | * [[Associate Deputy Director of the Central Intelligence Agency]] (ADD)—Created July 5, 2006, the ADD was delegated all authorities and responsibilities vested previously in the post of Executive Director. The post of Executive Director, which was responsible for managing the CIA on a day-to-day basis, was simultaneously abolished. |
| − | | author=Joel Brinkley
| + | * [[Associate Director for Military Support]] (AD/MS)—The DCIA's principal adviser and representative on military issues. The AD/MS coordinates Intelligence Community efforts to provide Joint Force commanders with timely, accurate intelligence. The AD/MS also supports Department of Defense officials who oversee military intelligence training and the acquisition of intelligence systems and technology. A senior general officer, the AD/MS ensures coordination of Intelligence Community policies, plans, and requirements relating to support to military forces in the intelligence budget. |
| − | | date=2004-06-09
| |
| − | | date=2007-03-21
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | ====Chile==== | + | ===Relationship with other agencies=== |
| − | {{main|Project FUBELT}}
| + | The [[National Intelligence Council]], which oversees production of National Intelligence Estimates, was transferred under reform legislation to the Office of the [[Director of National Intelligence]]. It is believed to make use of the product derived from surveillance [[satellite]]s of the [[National Reconnaissance Office]] (NRO) and the signal interception capabilities of the [[National Security Agency]] (NSA), including the [[ECHELON]] system, the surveillance aircraft of the various branches of the U.S. armed forces and the analysts of the [[State Department]], and [[United States Department of Energy|Department of Energy]]. At one point, the CIA even operated its own fleet of [[Lockheed U-2|U-2]] and [[A-12 OXCART]] surveillance aircraft. |
| − | On September 4, 1970 [[Salvador Allende]] gained presidency after four elections and became the first socialist to be democratically elected in the Western Hemisphere in the 20<sup>th</sup> century.
| |
| − | Soon after, President [[Richard Nixon]] ordered a covert operation, [[Project FUBELT]], to undermine Allende's government and promote military coup in Chile. Joining the operations included [[Henry Kissinger]] (National Security Advisor), [[Richard Helms]] (CIA Director), and [[John N. Mitchell|Attorney General John Mitchell]]. Under the supervision of [[Thomas Karamessines]], a special task force was established and led by veteran [[David Atlee Phillips]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | On September 11, 1973 General [[Augusto Pinochet]], who had just 19 days prior become the commander in chief of the army, executed a bloody coup d'etat which resulted in the death of Allende and Pinochet's rise to military control of the state. Whether the US directly participated in the coup itself is disputed, see [[1973 Chilean coup d'état]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | ====Afghanistan====
| |
| − | {{seealso|Operation Cyclone}}
| |
| − | Often cited as one of the American intelligence community's biggest mistakes was the training, arming, supplying and supporting of the [[Mujahedeen]] (Islamist fighters) in [[Afghanistan]]{{Fact|date=June 2007}}, initiated under Carter and greatly expanded under Reagan, as American proxy soldiers against the [[Marxist]] regime and later the [[Soviet]] [[Soviet war in Afghanistan|intervention]]. Part of the Mujahedeen trained by the CIA later became the core cadre of [[Osama bin Laden]]'s [[Al Qaeda]] Islamist organization.<ref>http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/1670089.stm</ref> [[Zbigniew Brzezinski]], the National Security Advisor under President [[Jimmy Carter|Carter]], has [[Zbigniew Brzezinski#Afghanistan|discussed]] U.S. military involvement in Afghanistan in several magazines.<ref>http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/coldwar/interviews/episode-17/brzezinski1.html</ref> <ref>http://www.globalresearch.ca/articles/BRZ110A.html</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ====Sudan (Darfur)====
| |
| − | Democracy Now reported on June 5, 2005, "CIA Secretly Restores Ties to Sudan Despite Ongoing Human Rights Abuses in Darfur." The Los Angeles Times recently revealed that the U.S. has quietly forged a close intelligence partnership with Sudan despite the government's role in the mass killings in Darfur [http://www.democracynow.org/article.pl?sid=05/06/01/1440259]. Global Research, Canada reports early CIA involvement in Darfur and US involvement has gone unreported [http://www.globalresearch.ca/index.php?context=va&aid=4574].In 1978 oil was discovered in Southern Sudan. Rebellious war began five years later and was led by John Garang, who had taken military training at infamous Fort Benning, Georgia [[School of Americas]]. "The US government decided, in 1996, to send nearly $20 million of military equipment through the 'front-line' states of Ethiopia, Eritrea and Uganda to help the Sudanese opposition overthrow the Khartoum regime." [Federation of American Scientists fas.org]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Sudan’s interior minister accused Central Intelligence Agency of smuggling weapons into the troubled region of Darfur. Interior Minister Zubair Bashir Taha addressing a crowd consisting of youth organizations said that the CIA is seeking to “disrupt the demographics of Darfur.” The US special envoy to Darfur Andrew Natsios told reporters in Khartoum last week that Arab groups from neighboring countries were resettling in West Darfur and other lands traditionally belonging to local African tribes.Taha accused the US of being responsible for “prolonging the war in Darfur and the death of thousands of people after the Abuja peace agreement just like they did in Iraq”[[http://www.sudantribune.com/spip.php?article23023 Sudan Tribune 8/9/07]][http://coalitionfordarfur.blogspot.com/2007/07/darfur-sudan-accuses-cia-of-smuggling.html], [http://www.afrol.com/articles/26241].
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Cultural activities===
| |
| − | In 1967 it was revealed that the [[Congress of Cultural Freedom]] had been sponsored by the CIA. It published literary and political journals such as ''[[Encounter (magazine)|Encounter]]'' (as well as ''Der Monat'' in [[Germany]] and ''Preuves'' in [[France]]), and hosted dozens of conferences bringing together some of the most eminent Western thinkers; it also gave some assistance to intellectuals behind the [[Iron Curtain]]. The CIA states that, "Somehow this organization of scholars and artists — egotistical, free-thinking, and even anti-American in their politics — managed to reach out from its Paris headquarters to demonstrate that Communism, despite its blandishments, was a deadly foe of art and thought".<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=https://www.cia.gov/library/center-for-the-study-of-intelligence/kent-csi/docs/v38i5a10p.htm
| |
| − | | work=cia.gov
| |
| − | | title= Origins of the Congress for Cultural Freedom, 1949-50
| |
| − | | author=Michael Warner
| |
| − | | pages=1995 Edition — Volume 38, Number 5
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Drug trafficking===
| |
| − | {{main|CIA drug trafficking}}
| |
| − | <!--A writing of the Marine Col. Oliver North and Iran/Contra Arms transactions may contribute to this subject.—>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Numerous accusations have been made that the CIA has been involved in drug trafficking to fund illegal operations in Nicaragua during their civil war, Afghanistan during the Soviet invasion, and in Southeast Asia during the Vietnam War.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==== Contras ====
| |
| − | {{main|CIA and Contra's cocaine trafficking in the US}}
| |
| − | The [[Kerry Committee report]] in 1989 found that the U.S. State Department had paid drug traffickers. Some of these payments were after the traffickers had been indicted by federal law enforcement agencies on drug charges or while traffickers were under active investigation by these same agencies.<ref>{{cite web | |
| − | | author =Peter Kornbluh
| |
| − | | year =January/February 1997
| |
| − | | url =http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB2/storm.htm
| |
| − | | title =Anatomy of a Story, Crack the Contras and the CIA: The Storm Over Dark Alliance
| |
| − | | format =HTML
| |
| − | | work =
| |
| − | | publisher =Columbia Journalism Review
| |
| − | | accessdate =April 22
| |
| − | | accessyear =2006
| |
| − | }} ''Hosted on National Security Archives''</ref> The report declared, "It is clear that individuals who provided support for the Contras were involved in drug trafficking...and elements of the Contras themselves knowingly received financial and material assistance from drug traffickers." <ref name="white" />
| |
| − | | |
| − | Representative [[Maxine Waters]] testified to Congress:
| |
| − | {{cquote|Senator Kerry and his Senate investigation found drug traffickers had used the Contra war and tie to the Contra leadership to help this deadly trade. Among their devastating findings, the [[Kerry Committee report|Kerry committee investigators]] found that major drug lords used the Contra supply networks and the traffickers provided support for Contras in return. The CIA of course, created, trained, supported, and directed the Contras and were involved in every level of their war.<ref name = "water"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | author =
| |
| − | | year =1998
| |
| − | | url =http://www.csun.edu/CommunicationStudies/ben/news/cia/7May98/waters2.html
| |
| − | | title =Congressional Record (07 May 1998) [Page: H2970]
| |
| − | | format =HTML
| |
| − | | work =
| |
| − | | publisher =
| |
| − | | accessdate =April 22
| |
| − | | accessyear =2006
| |
| − | }} </ref>}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | In 1996, [[investigative journalist]] [[Gary Webb]] wrote a series of exposés for the ''[[San Jose Mercury News]]'' entitled, "Dark Alliance," in which he reported evidence that CIA aircraft, which had ferried arms to the [[Nicaragua]]n ''[[Contras]],'' had been used to ship [[cocaine]] to the United States on their return flights. Webb also alleged that [[Central American]] [[Illegal drug trade|narcotics traffickers]] could distribute cocaine in U.S. cities in the 1980s without the interference of normal law enforcement agencies, and that the CIA intervened to prevent the prosecution of drug dealers who were helping to fund the ''Contras''. He asserted that this led, in part, to the [[crack cocaine]] epidemic, especially in poor neighborhoods of [[Los Angeles]]. Faced with heavy Congressional and mainstream media criticism (especially from the ''[[Los Angeles Times]]''), the ''Mercury News'' ultimately retracted Webb's conclusions, and Webb was prevented from conducting any further investigative reporting. (Webb was transferred to cover non-controversial suburban stories and subsequently gave up journalism.)
| |
| − | | |
| − | After the "Dark Alliance" reports in the ''Mercury News'', CIA [[Inspector General]] [[Frederick Hitz]] was assigned to investigate these allegations. In 1998 the new CIA director, [[George Tenet]] declared that he was releasing the report.<ref name="white"> {{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Cockburn
| |
| − | | first =Alexander
| |
| − | | authorlink =
| |
| − | | coauthors =Jeffrey St Clair
| |
| − | | year =October 1 1999
| |
| − | | title =Whiteout: The CIA, Drugs and the Press
| |
| − | | publisher =Verso
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 1-85984-258-5
| |
| − | }}</ref> The report and Hitz's testimony showed that the "CIA did not 'expeditiously' cut off relations with alleged drug traffickers" and "the CIA was aware of allegations that 'dozens of people and a number of companies connected in some fashion to the contra program' were involved in drug trafficking"<ref name="white" /><ref name = "WP"> {{cite journal
| |
| − | | first =Walter
| |
| − | | last =Pincus
| |
| − | | authorlink =
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =1998
| |
| − | | month =March 17
| |
| − | | title =Inspector: CIA Kept Ties With Alleged Traffickers
| |
| − | | journal =The Washington Post
| |
| − | | volume =
| |
| − | | issue =
| |
| − | | pages =p. A12
| |
| − | | id =
| |
| − | | url =http://www.anomalous-images.com/news/news181.html
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref> Hitz also said that under an agreement in 1982 between [[Ronald Reagan]]'s Attorney General [[William French Smith]] and the CIA, agency officers were not required to report allegations of drug trafficking involving non-employees, which was defined as meaning paid and non-paid "assets [meaning agents], pilots who ferried supplies to the contras, as well as contra officials and others.<ref name = "WP" /> This agreement, which had not previously been revealed, came at a time when there were allegations that the CIA was using drug dealers in its controversial covert operation to bring down the leftist Sandinista government in Nicaragua.<ref name = "WP" /> Only after Congressional funds were restored in 1986 was the agreement modified to require the CIA to stop paying agents whom it believed were involved in the drug trade.<ref name="white" />
| |
| − | | |
| − | ====Drugs in Asia====
| |
| − | It has also been alleged that the CIA was involved in the opium/heroin trade in Asia during the [[Vietnam War]] and later, which was the focus of [[Alfred W. McCoy|Alfred W. McCoy's]] book, ''[[The Politics of Heroin in Southeast Asia|The Politics of Heroin: CIA Complicity in the Global Drug Trade]],'' an earlier edition of which had already been subjected to attempted suppression by the CIA.<ref name = "mccoy"> {{cite book
| |
| − | | last = McCoy
| |
| − | | first = Alfred W.
| |
| − | | authorlink =Alfred W. McCoy
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =May 1 2003
| |
| − | | title =[[The Politics of Heroin in Southeast Asia|The Politics of Heroin: CIA Complicity in the Global Drug Trade]]
| |
| − | | publisher =Lawrence Hill Books
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 1-55652-483-8
| |
| − | }}</ref><ref name = "goofy"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | author =
| |
| − | | year =
| |
| − | | url =http://www.serendipity.li/cia.html#cia_drug_trafficking
| |
| − | | title =The CIA's Drug-Trafficking Activities
| |
| − | | format =HTML
| |
| − | | work =
| |
| − | | publisher =
| |
| − | | accessdate =April 22
| |
| − | | accessyear =2006
| |
| − | }} </ref><ref name = "amazon"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | author =
| |
| − | | year =
| |
| − | | url =http://www.amazon.com/gp/product/1556524838/sr=1-1/qid=1145699061/ref=pd_bbs_1/103-4696757-3275842?%5Fencoding=UTF8&s=books
| |
| − | | title =The Politics of Heroin: CIA Complicity in the Global Drug Trade, Library Journal book review
| |
| − | | format = HTML
| |
| − | | work =
| |
| − | | publisher =Library Journal
| |
| − | | accessdate =April 22
| |
| − | | accessyear =2006
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | The CIA's air cargo operation, [[Air America]], has also been accused of transporting drugs.<ref>Dale Scott, Peter. Drugs, Oil, and War: The United States in Afghanistan, Columbia and Indochina (Rowman and Littlefield, 2003) ISBN 0-7425-2522-8</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Mafia connections and assassination plots===
| |
| − | {{further|[[Plausible denial]], [[Cuba Project]], [[G. Robert Blakey]], [[Church Committee]]}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | The United States government has conspired with organized crime figures to assassinate foreign heads of state. The CIA has been linked to several assassination attempts on foreign leaders, including first democratically elected prime minister of the Democratic Republic of Congo [[Patrice Lumumba]], former leader of Panama [[Omar Torrijos]]<ref> {{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://web.mit.edu/activities/thistle/v9/9.07/2CIA.html
| |
| − | | title=How Will John's Special Talents Be Put to Use in the CIA?
| |
| − | | author=Mark Zepezauer
| |
| − | }}</ref> and the President of Cuba, [[Fidel Castro]]. Between August 1960, and April 1961, the CIA with the help of the Mafia assassins pursued a series of plots to poison or shoot Castro according to the assassination plots proposed by Colonel Sheffield Edwards, director of the CIA's Office of Security.<ref name="NYC_use_refs_tags_dammnit">{{cite web
| |
| − | | title = Bay of Pigs 40 years after.
| |
| − | | work = National Security Archive
| |
| − | | url = http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/bayofpigs/chron.html
| |
| − | | accessdate= 2007-07-16
| |
| − | }} p. 3, 14 ''CIA, Inspector General's Report on Efforts to Assassinate Fidel Castro.''</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Notre Dame law professor [[G. Robert Blakey]], counsel for the [[House Select Committee on Assassinations]], states that the CIA withheld information from the [[Warren Commission]] and frustrated the efforts of the Congressional Committee he represented.<ref name = "rob"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =G. Robert Blakey's 2003 Addendum to this Interview
| |
| − | | work =PBS Frontline
| |
| − | | url =http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/shows/oswald/interviews/blakey.html#addendum
| |
| − | | date=2006-09-05
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | According to a 1997 ''New York Times'' article, the CIA conducted a covert propaganda campaign to squelch criticism of the Warren Report. The CIA urged its field stations to use their "propaganda assets" to attack those who didn't agree with the Warren Report. In a dispatch from CIA headquarters, the Agency instructed its stations around the world to:
| |
| − | | |
| − | # counteract the "new wave of books and articles criticizing the [Warren] Commission's findings...[and] conspiracy theories ...[that] have frequently thrown suspicion on our organization";
| |
| − | # "discuss the publicity problem with liaison and friendly elite contacts, especially politicians and editors;" and
| |
| − | # "employ propaganda assets to answer and refute the attacks of the critics. ... Book reviews and feature articles are particularly appropriate for this purpose. ... The aim of this dispatch is to provide material for countering and discrediting the claims of the conspiracy theorists..."<ref name = "cable"> {{cite journal
| |
| − | | first =
| |
| − | | last =
| |
| − | | authorlink =
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year = 1977
| |
| − | | month =December 26
| |
| − | | title =Cable Sought to Discredit Critics of [[Warren Commission|Warren Report]]
| |
| − | | journal =New York Times
| |
| − | | volume =
| |
| − | | issue =
| |
| − | | pages = A3
| |
| − | | id =
| |
| − | | url =
| |
| − | | accessdate=2006-04-22
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | === Philip Agee ===
| |
| − | Former case officer [[Philip Agee]], who later worked with the Soviet [[KGB]] [citation needed] and the Cuban intelligence service [citation needed], has argued that CIA covert action is extraordinarily widespread, extending to [[propaganda]] campaigns within countries allied to the United States.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Declassified CIA torture manuals===
| |
| − | {{Further|[[U.S. Army and CIA interrogation manuals]]}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | In 1984, a CIA manual for training the Nicaraguan contras in psychological operations was discovered, entitled "[[Psychological Operations in Guerrilla War]]".<ref name = "manual"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =Declassified Army and CIA Manuals
| |
| − | | work =Latin American Working Group
| |
| − | | url =http://www.lawg.org/misc/Publications-manuals.htm
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-30
| |
| − | | accessdate=2006-04-26
| |
| − | }} </ref> The manual recommended “selective use of violence for propagandistic effects” and to “neutralize” (i.e., kill) government officials. Nicaraguan Contras were taught to lead:
| |
| − | | |
| − | {{cquote|...demonstrators into clashes with the authorities, to provoke riots or shootings, which lead to the killing of one or more persons, who will be seen as the martyrs; this situation should be taken advantage of immediately against the Government to create even bigger conflicts.}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | The manual also recommended:
| |
| − | | |
| − | {{cquote|...selective use of armed force for PSYOP [psychological operations] effect.... Carefully selected, planned targets — judges, police officials, tax collectors, etc. — may be removed for PSYOP effect in a UWOA [unconventional warfare operations area], but extensive precautions must insure that the people “concur” in such an act by thorough explanatory canvassing among the affected populace before and after conduct of the mission.<ref name = " "> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =Terrorism Debacles in the Reagan Administration
| |
| − | | work =The Future of Freedom Foundation
| |
| − | | url =http://www.fff.org/freedom/fd0406c.asp
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-30
| |
| − | | accessdate=2006-04-27
| |
| − | }} </ref>}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | The CIA claimed that the purpose of the manual was to "moderate" activities already being done by the Contras.<ref name = "middle"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =International Law PSCI 0236 > International Law PSCI 0236 > Introduction
| |
| − | | work =middlebury.edu
| |
| − | | url =https://segue.middlebury.edu/index.php?action=site&site=psci0236a-f06
| |
| − | | accessdate=2006-09-05
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | On January 24 1997, two new manuals were declassified in response to a Freedom of Information Act ([[FOIA]]) request filed by the [[Baltimore Sun]] in 1994. The first manual, "[[KUBARK Counterintelligence Interrogation]]," dated July 1963, is the source of much of the material in the second manual. The second manual, "[[Human Resource Exploitation Training Manual - 1983]]," was used in at least seven U.S. training courses conducted in Latin American countries, including [[Honduras]], between 1982 and 1987.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Both manuals deal exclusively with interrogation and have an entire chapter devoted to "coercive techniques."<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://www.gwu.edu/%7Ensarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB122/index.htm#hre
| |
| − | | work=The National Security Archive
| |
| − | | title=CIA, Human Resource Exploitation Training Manual - 1983
| |
| − | | pages=part I (pp. 1-67) - part II (pp. 68-124)
| |
| − | | author=
| |
| − | | | accessdate=2006-05-12
| |
| − | }}</ref> <ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://www.gwu.edu/%7Ensarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB122/index.htm#kubark
| |
| − | | work=The National Security Archive
| |
| − | | title=CIA, KUBARK Counterintelligence Interrogation, July 1963
| |
| − | | pages=part 1 (pp. 1-60) - part II (pp. 61-112) - part III (pp. 113-128)
| |
| − | | accessdate=2006-04-26
| |
| − | }}</ref> These manuals recommend arresting suspects early in the morning by surprise, blindfolding them, and stripping them naked. Interrogation rooms should be windowless, soundproof, dark and without toilets. Suspects should be held incommunicado and should be deprived of any kind of normal routine in eating and sleeping. The manuals describe coercive techniques to be used "to induce psychological regression in the subject by bringing a superior outside force to bear on his will to resist."<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://www.lawg.org/misc/Publications-manuals.htm
| |
| − | | work= Latin America Working Group
| |
| − | | title=Declassified Army and CIA Manuals Used in Latin America: An Analysis of Their Content
| |
| − | | author=Lisa Haugaard
| |
| − | | date=1997-02-18
| |
| − | | accessdate=2006-04-26
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===UFOs and Robertson Panel===
| |
| − | {{further|[[Robertson Panel]]}}
| |
| − | In 1951 the US Air Force revitalized [[Project Grudge]], a program investigating UFOs between 1948-1949. Captain [[Edward J. Ruppelt]] ran the program and recommended that the [[Battelle Memorial Institute]], a Columbus, Ohio think tank, do a statistical analysis of existing UFO reports. The think tank released its report in late 1953. Before the final Battelle report was ready however, the CIA became interested in the UFO issue as a national security and arranged to have a secret official committee, the Robertson Panel, look into the compiled UFO data.<ref name = "UFO"> {{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Denzler
| |
| − | | first =Brenda
| |
| − | | authorlink =Brenda Denzler
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =2003
| |
| − | | title =The Lure of the Edge: Scientific Passions, Religious Beliefs, and the Pursuit of UFOs
| |
| − | | publisher =University of California Press
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 0-520-23905-9
| |
| − | }}p. 12-14 </ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The Robertson Panel began in January 1953, and met for a total of twelve hours, studying twenty-three alleged UFO sighting cases. The CIA concluded that UFOs presented little or no interesting scientific data and were only a threat to the United States if sighting reports clogged communications facilities and created a climate of fear among the population which the enemy could exploit before launching an attack. The Robertson Panel therefore suggested, first, an active campaign of public education, perhaps using TV and radio celebrities and the services of [[Walt Disney Productions]]; second, an active debunking of sightings in order to de-mystify UFOs in the public mind. Implicit in this education campaign was increased air force secrecy about sighting reports so as not to support public interest. The committee also recommended covert surveillance of civilian UFO groups, in order to monitor those who could promote public interest in UFOs.<ref name = "UFO" />
| |
| − | | |
| − | The recommendations of the Robertson Panel were implemented by a series of special military regulations. Joint-Army-Navy-Air Force Publication 147 ([[JANAP 146]]) of December 1953 made reprinting of any UFO sighting to the public a crime under the Espionage Act, with fines of up to ten thousand dollars and imprisonment ranging from one to ten years. This act was considered binding on all who knew of the act's existence, including commercial airline pilots. A 1954 revision of Air Force Regulation 200-2 ([[AFR 200-2]]) made all sighting reports submitted to the air force classified material and prohibited the release of any information about UFO sightings ''unless'' the sighting was able to be positively identified. In February 1958 a revision of AFR 200-2 allowed the military to give the FBI the names of people who were "illegally or deceptively bringing the subject [of UFOs] to public attention." Because of the [[Robertson Panel]] the air force's [[Project Blue Book]]'s procedures of investigating UFOs also changed, attempting to find a quick explanation and then file them away. Project Blue Book was a successor of [[Project Grudge]].<ref name = "UFO" />
| |
| − | | |
| − | In 1956 retired Marine Major [[Donald Keyhoe]] founded the [[National Investigations Committee on Aerial Phenomena]] (NICAP), a UFO investigations organization. By 1969 Keyhoe turned his focus on the CIA as the source of the UFO cover up. NICAP's board, headed by Colonel [[Jospeph Bryan III]], forced Keyhoe to retire as NICAP chief. Bryan was actually a former covert CIA agent who had served the agency as founder and head of its psychological warfare division. Under Bryan's leadership, the NICAP disbanded its local and state affiliate groups, and by 1973 it had been completely closed.<ref name = "UFO2">Denzler, p. 17</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | After the [[Freedom of Information Act]] was made law in 1974, [[Ufologists]] involved in making FOIA requests reported that more than nine hundred pages of information released for the CIA indicated that the organization was collecting and analyzing sighting reports from as early as 1949. In 1997 the CIA came forward to admit its historical interest in UFOs.<ref name = "UFO3">Denzler, p. 21</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | === Farewell dossier ===
| |
| − | {{main|Farewell Dossier}}
| |
| − | The [[Farewell Dossier]] in 1981 revealed massive Soviet espionage on Western technology. A successful counter-espionage program was created which involved giving defective technologies to Soviet agents.<ref name=hoffman>{{cite web
| |
| − | |url=http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/4394002
| |
| − | |work=msnbc.msn.com
| |
| − | |title=CIA slipped bugs to Soviets - Memoir recounts Cold War technological sabotage
| |
| − | |author=David E. Hoffman
| |
| − | |date=February 27, 2004
| |
| − | |accessdate=2007-07-20}}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | === CIA on Technology ===
| |
| − | | |
| − | CIA was not only keeping a tab on enemy agents and spies but was all the time, looking at how to solve these vexed issues through the use of technology and IT. Its obsession with technology was twofold: one for its own use and second what the Soviets might be using it for. Right from the onset, the agency has been making confidential reports and assessing technology. The big push for the same came in fifties with the launch of Sputnik satellite by erstwhile USSR.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The agency did not miss the irrepressible computer either, the miracle machine that was also evolving more or less around the same time. There are around 517 declassified documents on computers, from the oldest on German textile industry using computers as a tool published in August 1945 to the latest on WMD search in Iraq dating from September, 2004. In one document, the author, late Joseph Becker, referred to the computer as a 'competent mechanical slave'.[http://shashwatdc.blogspot.com/2007/07/feature-cias-take-on-computer-it.html]
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Recent controversies==
| |
| − | ===War on terror===
| |
| − | {{further|[[War on Terrorism]]}}
| |
| − | On November 5 2002, newspapers reported that [[Al-Qaeda]] operatives in a car travelling through [[Yemen]] had been killed by a missile launched from a CIA-controlled [[RQ-1 Predator|Predator drone]] (a medium-altitude, remote-controlled aircraft). On May 15, 2005, it was reported that another of these drones had been used to assassinate Al-Qaeda figure [[Haitham al-Yemeni]] inside [[Pakistan]].<ref name = "Surv"> {{cite journal
| |
| − | | first =Dana
| |
| − | | last =Priest
| |
| − | | authorlink = Dana Priest
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year = 2005
| |
| − | | month =May 15
| |
| − | | title =Surveillance Operation in Pakistan Located and Killed Al Qaeda Official
| |
| − | | journal =Washington Post
| |
| − | | volume =
| |
| − | | issue =
| |
| − | | pages =A25
| |
| − | | id =
| |
| − | | url =http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2005/05/14/AR2005051401121.html
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Soon after, President Bush appointed the CIA to be in charge of all human intelligence and manned spying operations. This was the culmination of a years old turf war regarding influence, philosophy and budget between the [[Defense Intelligence Agency|DIA]] of [[The Pentagon]] and the CIA. The Pentagon, through the DIA, wanted to take control of the CIA's [[paramilitary]] operations and many of its human assets. The CIA, which has for years held that human intelligence is the core of the agency, successfully argued that the CIA's decades long experience with human resources and civilian oversight made it the ideal choice. Thus, the CIA was given charge of all US human intelligence, but as a compromise, the Pentagon was authorized to include increased paramilitary capabilities in future budget requests.{{Fact|date=July 2007}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | Despite reforms which have led back to what the CIA considers its traditional principal capacities, the CIA Director position has lost influence in the White House. For years, the Director of the CIA met regularly with the President to issue daily reports on ongoing operations. After the creation of the post of [[Director of National Intelligence]], currently occupied by [[John Michael McConnell|Mike McConnell]], the report is now given by the DNI—who oversees all US Intelligence activities, including DIA operations outside of CIA jurisdiction. Former CIA Director [[Porter Goss]], himself also a former CIA officer, denies this has had a diminishing effect on morale, in favor of promoting his singular mission to reform the CIA into the lean and agile counter-terrorism focused force he believes it should be.{{Fact|date=July 2007}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | On January 13 2006, the CIA launched an [[Damadola airstrike|airstrike on Damadola]], a [[Pakistan]]i village near the Afghan border, where they believed [[Ayman al-Zawahiri]] was located. The airstrike killed a number of civilians but al-Zawahiri apparently was not among them.<ref name = "WP"> {{cite journal
| |
| − | | first =Dafna
| |
| − | | last =Linzer
| |
| − | | authorlink =
| |
| − | | coauthors =Griff Witte
| |
| − | | year =2006
| |
| − | | month =January 14
| |
| − | | title =U.S. Airstrike Targets Al Qaeda's Zawahiri
| |
| − | | journal =
| |
| − | | volume =
| |
| − | | issue =
| |
| − | | pages =A09
| |
| − | | id =
| |
| − | | url =http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/01/13/AR2006011302260.html
| |
| − | | accessdate=2006-04-22
| |
| − | }}</ref> The Pakistani government issued a [http://www.cnn.com/2006/WORLD/meast/01/14/alqaeda.strike/ strong protest] against the US attack, considered a violation of Pakistan's sovereignty. However, several legal experts argue that this cannot be considered an assassination attempt as al-Zawahiri is named as terrorist and an enemy combatant by the United States, and therefore this targeted killing is not covered under [[Executive Order 12333]], which banned assassinations.<ref name = "UPI"> {{cite journal
| |
| − | | first =Pamela
| |
| − | | last =Hess
| |
| − | | authorlink =
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =2006
| |
| − | | month =November 8
| |
| − | | title = Experts: Yemen strike not assassination
| |
| − | | journal =UPI
| |
| − | | volume =
| |
| − | | issue =
| |
| − | | pages =
| |
| − | | id =
| |
| − | | url =www.upi.com/view.cfm?StoryID=20021107-042725-6586r
| |
| − | | accessdate=2006-04-22
| |
| − | }}</ref> <ref name = "Bazan"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | author =Elizabeth B. Bazan
| |
| − | | year =January 4 2002
| |
| − | | url =http://www.fas.org/irp/crs/RS21037.pdf
| |
| − | | title =Assassination Ban and E.O. 12333:A Brief Summary
| |
| − | | format =HTML
| |
| − | | work =
| |
| − | | publisher =CRS Report for Congress
| |
| − | | accessdate =April 26
| |
| − | | accessyear =2006
| |
| − | }} </ref><ref name = "Tom"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | author =Tom O'Connor, Mark Stevens
| |
| − | | year =November 2005
| |
| − | | url =http://faculty.ncwc.edu/toconnor/430/430lect16.htm
| |
| − | | title =The Handling of Illegal Enemy Combatants
| |
| − | | format =HTML
| |
| − | | work =
| |
| − | | publisher =
| |
| − | | accessdate =April 26
| |
| − | | accessyear =2006
| |
| − | }} </ref> <ref name = "parks"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | author =
| |
| − | | year =
| |
| − | | url =http://www.ksg.harvard.edu/cchrp/Use%20of%20Force/October%202002/Parks_final.pdf
| |
| − | | title =Memorandum on Executive Order 12333 and Assassination
| |
| − | | format =PDF
| |
| − | | work =
| |
| − | | publisher =
| |
| − | | accessdate =April 26
| |
| − | | accessyear =2006
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | <ref name = "Addicott"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | author =Jeffrey Addicott
| |
| − | | year =November 7 2002
| |
| − | | url =http://jurist.law.pitt.edu/forum/forumnew68.php
| |
| − | | title =The Yemen Attack: Illegal Assassination or Lawful Killing?
| |
| − | | format =
| |
| − | | work =HTML
| |
| − | | publisher =
| |
| − | | accessdate =April 26
| |
| − | | accessyear =2006
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===The 2003 War in Iraq===
| |
| − | {{Further|[[Iraq War]]}}
| |
| − | In 2002 an anonymous source, quoted in the [[Washington Post]], says the CIA was authorized to execute a covert operation, if necessary with help of the [[United States Army Special Forces|Special Forces]], that could serve as a preparation for a full military attack against Iraq.<ref name = "All"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =CIA-Hussein report: Support, condemnation Lawmakers back proposal to oust Hussein; Baghdad sneers
| |
| − | | work =CNN.com
| |
| − | | url =http://www.cnn.com/2002/ALLPOLITICS/06/16/iraq.congress/
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-30
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | U.S. intelligence on Iraqi [[weapons of mass destruction]] have been focus of intense scrutiny in the U.S. In 2004, the continuing armed resistance against the U.S. military occupation of Iraq, and the widely-perceived need for a [[systematic review]] of the respective roles of the CIA, the [[FBI]], and the [[Defense Intelligence Agency]] are prominent themes.
| |
| − | On July 9, 2004, the [[Senate Report of Pre-war Intelligence on Iraq]] of the [[Senate Intelligence Committee]] reported that the CIA exaggerated the danger presented by [[weapons of mass destruction]] in [[Iraq]], largely unsupported by the available intelligence.<ref name = "report"> {{cite journal
| |
| − | | first =Douglas | |
| − | | last =Jehl
| |
| − | | authorlink = Douglas Jehl
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =2004
| |
| − | | month =July 9
| |
| − | | title =Report Says Key Assertions Leading to War Were Wrong
| |
| − | | journal =New York Times
| |
| − | | volume =
| |
| − | | issue =
| |
| − | | pages =
| |
| − | | id =
| |
| − | | url =http://www.nytimes.com/2004/07/09/national/09CND-INTEL.html?ei=5090&en=f0e09ebc88477493&ex=1247198400&partner=rssuserland&pagewanted=all
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Secret CIA prisons===
| |
| − | A report by the [[human rights]] organisation [[Human Rights Watch]], entitled [[Enduring Freedom - Abuses by US Forces in Afghanistan]], claims that the CIA has operated in Afghanistan since September, 2001<ref>http://www.hrw.org/reports/2004/afghanistan0304/</ref>; maintaining a large facility in the Ariana Chowk neighborhood of [[Kabul]] and a detention and interrogation facility at the [[Bagram airbase]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | A story by reporter [[Dana Priest]] published in ''[[The Washington Post]]'' of November 2 2005, reported: "The CIA has been hiding and interrogating some of its most important alleged al Qaeda captives at a Soviet-era compound in Eastern Europe, according to U.S. and foreign officials familiar with the arrangement."<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2005/11/01/AR2005110101644_pf.html
| |
| − | | work=The Washington Post
| |
| − | | title=CIA Holds Terror Suspects in Secret Prisons
| |
| − | | author=Dana Priest
| |
| − | | date=2005-11-01
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref> The reporting of the secret prisons was heavily criticized by members and former members of the Bush Administration. However, Dana Priest states no one in the administration requested that the Washington Post not print the story. Rather they asked they not publish the names of the countries in which the prisons are located.<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://msnbc.msn.com/id/13615446/page/6/
| |
| − | | work=MSNBC
| |
| − | | title=Transcript of interview of [[Andrea Mitchell]], [[Mitch McConnell]], [[Chuck Schumer]], [[Bill Bennett]], [[John Harwood]], [[Dana Priest]] and [[William Safire]]
| |
| − | | date= 2006-06-02
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref> "The Post has not identified the East European countries involved in the secret program at the request of senior U.S. officials who argued that the disclosure could disrupt counter-terrorism efforts".<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | |url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2005/11/03/AR2005110300422.html?nav=hcmodule
| |
| − | | work=The Washington Post
| |
| − | | title=U.S. Faces Scrutiny Over Secret Prisons
| |
| − | | author=[[Craig Whitlock]]
| |
| − | | date=2005-11-03
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref> While it was maintained that these prisons did not exist, recently the Bush administration has come forward and admitted their existence.<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/5321606.stm
| |
| − | | work= BBC News
| |
| − | | title=Bush admits to CIA secret prisons
| |
| − | | author=
| |
| − | | date=2006-09-07
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | An August 13, 2007 story by [[Jane Mayer]] in [[The New Yorker]] reports that the CIA has operated "black site" secret prisons by the direct Presidential order of [[George W. Bush]] since shortly after 9/11, and that extreme psychological interrogation measures based at least partially on the Vietnam-era [[Phoenix Program]] were used on detainees. These included sensory deprivation, sleep deprivation, keeping prisoners naked indefinitely and photographing them naked to degrade and humiliate them, and forcibly administering drugs by suppositories to further break down their dignity. According to Mayer's report, CIA officers have taken out professional liability insurance, fearing that they could be criminally prosecuted if what they have already done became public knowledge. <ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://www.newyorker.com/reporting/2007/08/13/070813fa_fact_mayer?currentPage=1
| |
| − | | work=The New Yorker
| |
| − | | title=The Black Sites; A rare look inside the C.I.A.’s secret interrogation program
| |
| − | | author=Jane Mayer
| |
| − | | date=2007-08-13
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-08-13
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | In December 2005, [[ABC News]] reported that former agents claimed the CIA used [[waterboarding]], along with five other "Enhanced Interrogation Techniques," against detainees held in the secret prisons.<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://abcnews.go.com/WNT/Investigation/story?id=1375123
| |
| − | | work=ABC News
| |
| − | | title=Sources Tell ABC News Top Al Qaeda Figures Held in Secret CIA Prisons
| |
| − | | author=[[Brian Ross]] and Richard Esposito
| |
| − | | date=2005-12-05
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref><ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://abcnews.go.com/WNT/Investigation/story?id=1322866&page=1
| |
| − | | work=ABC News
| |
| − | | title=CIA's Harsh Interrogation Techniques Described
| |
| − | | author=[[Brian Ross]] and Richard Esposito
| |
| − | | date=2005-11-18
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref> Waterboarding is widely regarded as a form of [[torture]], though there are reports that President Bush signed a secret "finding" that it is not, authorizing its use.
| |
| − | | |
| − | After a media and public outcry in Europe concerning headlines about "secret CIA prisons" in Poland and other US allies, the EU through its Committee on Legal Affairs investigated whether any of its members, especially Poland, the Czech Republic or Romania had any of these "secret CIA prisons." After an investigation by the EU Committee on Legal Affairs and Human Rights, the EU determined that it could not find any of these prisons. In fact, they could not prove if they had ever existed at all. To quote the report, "At this stage of the investigations, there is no formal, irrefutable evidence of the existence of secret CIA detention centres in [[Romania]], [[Poland]] or any other country. Nevertheless, there are many indications from various sources which must be considered reliable, justifying the continuation of the analytical and investigative work."<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://assembly.coe.int/Main.asp?link=/CommitteeDocs/2006/20060124_Jdoc032006_E.htm
| |
| − | | work=Council of Europe
| |
| − | | title=Alleged secret detentions in Council of Europe member states
| |
| − | | author=Dick Marty
| |
| − | | pages=chapter E: Preliminary analysis of the information already obtained, part C: Secret detention centres
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | On 28 December 2006, the BBC reported that during 2003, a well-known CIA Gulfstream aircraft implicated in extraordinary renditions, N379P, had on several occasions landed at the Polish airbase of [[Szczytno-Szymany_International_Airport|Szymany]]. The airport manager reported that airport officials were told to keep away from the aircraft, which parked at the far end of the runway and frequently kept their engines running. Vans from a nearby intelligence base ([[Stare Kiejkuty (base)|Stare Kiejkuty]]) met the aircraft, stayed for a short while and then drove off. Landing fees were paid in cash, with the invoices made out to "probably fake" American companies. <ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/6212843.stm
| |
| − | | work=BBC
| |
| − | | title=Hunt for CIA 'black site' in Poland
| |
| − | | author=Nick Hawton
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-08-01
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | On 13 December 2005 [[Dick Marty]], investigating illegal CIA activity in Europe on behalf of the [[Council of Europe]], reported evidence that "individuals had been abducted and transferred to other countries without respect for any legal standards." His investigation has found that no evidence exists establishing the existence of secret CIA prisons in Europe, but added that it was "highly unlikely" that European governments were unaware of the American program of renditions. However, Marty's interim report, which was based largely on a compendium of press clippings has been harshly criticised by the governments of various EU member states. <ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2005/12/13/world/main1121577.shtml?cmp=EM8706
| |
| − | | work=CBS News
| |
| − | | title=CIA Prisons Moved To North Africa?
| |
| − | | author=[[Associated Press]]
| |
| − | | date=2005-12-13
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-05-23
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ====Khaled el-Masri ====
| |
| − | {{main|Khalid El-Masri}}
| |
| − | Khalid El-Masri is a [[Germany|German]] citizen who was detained, flown to [[Afghanistan]], and interrogated and allegedly tortured by the CIA for several months, and then released without charge. This was apparently due to a misunderstanding that arose concerning the similarity of the spelling of El-Masri's name with the spelling of suspected terrorist [[Khalid al-Masri]]. Germany has issued warrants for 13 people suspected to be involved with the abduction.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ====Imam Rapito ====
| |
| − | {{Main|Imam Rapito}}
| |
| − | The Imam Rapito affair refers to the alleged abduction and transfer by the CIA to Egypt of the Imam of Milan, and alleged terrorist, [[Hassan Mustafa Osama Nasr]], also known as Abu Omar, and tortured and abused. Hassan Nasr was released by Egyptian justice in February 2007, who considered his detention "unfounded," and has not been indicted for any alleged crime in Italy. Ultimately, twenty-six Americans and nine Italians have been indicted with a trial pending.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Supporting warlords in Somalia===
| |
| − | The CIA supported [[warlord]]s in Somalia in order to prevent [[Al-Qaeda]] members hiding in the war-torn country.<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://news.scotsman.com/latest.cfm?id=831732006
| |
| − | | work= Scotsman Reuters
| |
| − | | title=U.S. funding Somali warlords - intelligence experts
| |
| − | | author=David Morgan
| |
| − | | date=2006-06-05
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref> The US supported the Ethiopian intervention to restore the UN recognized government. The US also carried out reconnaissance flights and air attacks targeting the 1998 Embassy terrorists.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Clandestine service===
| |
| − | In 1996, the [[U.S. House Permanent Select Committee on Intelligence]] issued a congressional report estimating that the [[clandestine service]] part of the [[intelligence community]] "easily" breaks "extremely serious laws" in countries around the world, 100,000 times every year.
| |
| − | <ref name = "memoryhole"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =The CIA Commits Over 100,000 Serious Crimes Per Year
| |
| − | | work =www.thememoryhole.org
| |
| − | | url =http://www.thememoryhole.org/ciacrimes.htm
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-16
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | <ref name="government_printing_office"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title=IC21: The Intelligence Community in the 21st Century
| |
| − | | work=www.access.gpo.gov
| |
| − | | url=http://www.access.gpo.gov/congress/house/intel/ic21/ic21_toc.html
| |
| − | | date=1996-06-05
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | According to the report, DO (Directorate of Operations) officers who engage in highly illegal activities not only risk political embarrassment to his or her country and President, but also endanger the freedom of the clandestine officer him- or herself. Regarded the facts and recent history, the case officers are held accountable for overseeing the Clandestine Service (CS) and the Director's of Central Intelligence (DCI) must work closely with the Director of the CS and directly responsible for him.<ref name = "congress"> {{cite web
| |
| − | | title =The Intelligence Community in the 21st Century, Staff Study, Permanent Select Committee on Intelligence, House of Representatives, One Hundred Fourth Congress
| |
| − | | work =One Hundred Fourth Congress
| |
| − | | url =http://www.loyola.edu/dept/politics/intel/ic21_files/ic21009.html
| |
| − | | date=2006-07-16
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Criticism for ineffectiveness===
| |
| − | The agency has also been criticized for ineffectiveness as an intelligence gathering agency. These criticisms included allowing a [[double agent]], [[Aldrich Ames]], to gain high position within the organization, and for focusing on finding informants with information of dubious value rather than on processing the vast amount of [[open source intelligence]]. On October 13, 1950, the CIA had assured President Truman that the Chinese would not send troops to Korea. Six days later, over one million Chinese troops arrived.<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://www.historians.org/Perspectives/NewsBriefs/2006/0605/KerberArticle.cfm
| |
| − | | work=American Historical Association
| |
| − | | title=Protecting the Nation's Memory
| |
| − | | author=Linda K. Kerber
| |
| − | | date=2006-05-15
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }} </ref> In addition, the CIA has come under particular criticism for failing to predict the [[collapse of the Soviet Union]] and [[Operation Shakti|India's nuclear tests]] or to forestall the [[September 11, 2001 attacks]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | Proponents of the CIA respond by stating that only the failures become known to the public, whereas the successes usually cannot be known until decades have passed because release of successful operations would reveal operational methods to foreign intelligence, which could affect future and ongoing missions. Some successes for the CIA include the [[Lockheed U-2|U-2]] and [[SR-71]] programs, and anti-[[Soviet Union|Soviet]] operations in [[Afghanistan]] in the mid-1980s, although critics charge that these helped foster the genesis of today's terrorist groups.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==="The Family Jewels" ===
| |
| − | On 27 June 2007 the CIA released two collections of previously classified documents which outlined various activities of doubtful legality.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The first collection, the "[[Family jewels (Central Intelligence Agency)|Family Jewels]]," consists of almost 700 pages of responses from CIA employees to a 1973 directive from Director of Central Intelligence [[James Schlesinger]] requesting information about activities inconsistent with the Agency's charter.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The second collection, the [[CAESAR-POLO-ESAU papers]], consists of 147 documents and 11,000 pages of research from 1953 to 1973 relating to Soviet and Chinese leadership hierarchies, and Sino-Soviet relations.<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | |url=http://www.foia.cia.gov/
| |
| − | |work=cia.gov
| |
| − | |title=CIA Releases Two Significant Collections of Historical Documents
| |
| − | |accessdate=2007-06-02
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Other controversies===
| |
| − | In a briefing held September 15 2001, [[George Tenet]] presented the [[Worldwide Attack Matrix]]: A "top-secret" document describing covert CIA anti-terror operations in eighty countries in [[Asia]], the [[Middle East]], and [[Africa]]. The actions, underway or being recommended, would range from "routine propaganda to lethal covert action in preparation for military attacks." The plans, if carried out, "would give the CIA the broadest and most lethal authority in its history."<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/ac2/wp-dyn/A64802-2002Jan30?language=printer
| |
| − | | work=The Washington Post
| |
| − | | title=At Camp David, Advise and Dissent
| |
| − | | author=Bob Woodward and Dan Balz
| |
| − | | date=2002-01-30
| |
| − | | accessdate=2006-04-26
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | In a trend some find disturbing, many of its former duties and functions are being "outsourced" and "privatized."[http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/07/06/AR2007070601993_pf.html]
| + | The agency has also operated alongside regular military forces, and also employs a group of clandestine officers with [[paramilitary]] skills in its [[Special Activities Division]]. The CIA also has strong links with other foreign intelligence agencies such as the UK's [[MI6|Secret Intelligence Service]], the [[Canadian Security Intelligence Service]], Israel's [[Mossad]], and the [[Australian Secret Intelligence Service]]. |
| − | [http://select.nytimes.com/search/restricted/article?res=FA0C14F8355B0C768EDDAF0894DF404482] | |
| | | | |
| − | ====Propaganda====
| + | Further, the CIA is currently believed to be financing several [[Counter-terrorist Intelligence Center]]s. |
| − | Various media outlets have reported that the CIA may have used Wikipedia as a propaganda tool.<ref name="Elsworth">Elsworth,Catherine. "[http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=/news/2007/08/16/wiki116.xml Wikipedia Slueth's tool reveals entry fiddling]." ''[[Telegraph]].'' April 16, 2007. </ref> Allegedly, employees of the intelligence agency altered biographical information contained in Wikipedia entries on former presidents including Ronald Reagan and Richard Nixon.
| |
| − | When asked by the BBC whether it could confirm whether the changes had been made by a person using a CIA computer, an agency spokesperson responded: 'I cannot confirm that the traffic you cite came from agency computers.
| |
| − | "I'd like in any case to underscore a far larger and more significant point that no one should doubt or forget: The CIA has a vital mission in protecting the United States, and the focus of this agency is there, on that decisive work.' <ref name="Fildes">Fildes, Jonathan. "[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/technology/6947532.stm Wikipedia shows CIA page edits]." ''[[BBC]].'' August 15, 2007. </ref> Nevertheless, [[Wikipedia Scanner]] allegedly shows that workers on the agency's computers made edits to the page of Iran's president. While other changes that have been made are more innocuous, and include tweaks to the profile of former CIA chief Porter Goss and celebrities such as [[Oprah Winfrey]].
| |
| | | | |
| | ==Publications== | | ==Publications== |
| − | One of the CIA's best-known publications, ''[[The World Factbook]]'', is in the [[public domain]] and is made freely available without [[copyright]] restrictions because it is a work of the United States federal government. | + | [[Image:Wfbcover.jpg|thumb|144px|The CIA's ''World Factbook'']] |
| − | | + | One of the CIA's best-known publications, ''[[The World Factbook]],'' is in the [[public domain]] and is made freely available without [[copyright]] restrictions because it is a work of the United States federal government. |
| − | The CIA since 1955 has published an in-house professional journal known as ''Studies in Intelligence'' that addresses historical, operational, doctrinal, and theoretical aspects of the intelligence profession. Unclassified and declassified ''Studies'' articles, as well as other books and [[monographs]], are made available by CIA's [[Center for the Study of Intelligence]] on a limited basis through Internet and other publishing mechanisms.<ref name="Studies in Intelligence">{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=https://www.cia.gov/csi/index.html
| |
| − | | work=CIA.gov
| |
| − | | title=Center for the Study of Intelligence website
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref> A further annotated collection of ''Studies'' articles was published through [[Yale University Press]] under the title ''Inside CIA's Private World: Declassified Articles from the Agency's Internal Journal, 1955-1992''.<ref name="Yale University Press">{{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Westerfield
| |
| − | | first =H. Bradford
| |
| − | | authorlink =H. Bradford Westerfield
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year = August 1997
| |
| − | | title =Inside CIA's Private World: Declassified Articles from the Agency's Internal Journal, 1955-1992
| |
| − | | publisher =Yale University Press
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 0-3000-7264-3
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | In 2002, CIA's [[Sherman Kent School for Intelligence Analysis]] began publishing the unclassified ''Kent Center Occasional Papers'', aiming to offer "an opportunity for intelligence professionals and interested colleagues—in an unofficial and unfettered vehicle—to debate and advance the theory and practice of intelligence analysis."<ref name="Kent Center papers">{{cite web
| |
| − | | url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications//Kent_Papers/index.html
| |
| − | | work=cia.gov
| |
| − | | title=Kent Center Occasional Papers
| |
| − | | accessdate=2007-04-15
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | ==See also==
| + | Since 1955, the CIA has published an in-house professional journal known as ''Studies in Intelligence'' that addresses historical, operational, doctrinal, and theoretical aspects of the intelligence profession. Unclassified and declassified ''Studies'' articles, as well as other books and [[monographs]], are made available by the CIA's [[Center for the Study of Intelligence]] on a limited basis through Internet and other publishing mechanisms. |
| − | <!--alphabetize your entries!!!--->
| |
| − | {{col-begin}}
| |
| − | {{col-2}}
| |
| − | '''Books''' | |
| − | * ''[[At the Center of the Storm: My Years at the CIA]]'', [[George Tenet]]'s memoir
| |
| − | * ''[[The CIA and September 11 (book)|The CIA and September 11]]'', a controversial book about the CIA and the events of [[September 11, 2001 attacks|11 September 2001]]
| |
| − | * ''[[Gary Webb#Dark Alliance|Dark Alliance]],'' by [[investigative journalist]] [[Gary Webb]], about the CIA-[[Contra]]-crack cocaine connection
| |
| | | | |
| − | '''CIA's operations'''
| + | In 2002, the CIA's [[Sherman Kent School for Intelligence Analysis]] began publishing the unclassified ''Kent Center Occasional Papers,'' aiming to offer "an opportunity for intelligence professionals and interested colleagues-—in an unofficial and unfettered vehicle-—to debate and advance the theory and practice of intelligence analysis." |
| − | * [[Acoustic Kitty]]
| |
| − | * [[Allegations of state terrorism by United States of America]]
| |
| − | * [[Church Committee]] - 1976 Senate committee investigation
| |
| − | *[[Pike Committee]] - 1976 House committee investigation
| |
| − | *[[United States President's Commission on CIA activities within the United States|Rockefeller Commission]]
| |
| − | *[[Family jewels (Central Intelligence Agency)]]
| |
| − | *[[CIA sponsored regime change]]
| |
| − | *[[Kerry Committee report]] - looked into charges of drug trafficking
| |
| − | *[[CIA drug trafficking]]
| |
| − | *[[CIA and Contra's cocaine trafficking in the US]]
| |
| | | | |
| − | '''CIA-related terms'''
| + | ==Notes== |
| − | * [[Numbers station]]
| + | <references/> |
| − | * [[Blowback (intelligence)|Blowback]]
| |
| − | * [[CIA cryptonym]]
| |
| − | * [[Extraordinary rendition]]
| |
| − | * [[HUMINT]]
| |
| − | * [[Z-Division]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | '''CIA's components'''
| |
| − | * [[Bin Laden Issue Station]] - The CIA's bin Laden tracking unit, 1996-2005
| |
| − | * [[In-Q-Tel]] - venture capital arm of the CIA
| |
| − | * [[Harvey Point]] - an operating base for blimps conducting anti-submarine surveillance of the Atlantic coast.
| |
| − | * [[National Clandestine Service]] (formerly the Directorate of Operations)
| |
| − | * [[Special Activities Division]] - paramilitary section of the CIA
| |
| − | * [[Technical Services Staff]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | {{col-2}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | '''CIA insiders and "whistleblowers"'''
| |
| − | <!--alphabetize please. Note: If some IPs try to add Mohammad Reza Aghaei Laghaei to this list, please remove it immediately. Thanks.—> | |
| − | * [[Theodore Shackley]] - former [[CIA]] [[espionage|agent]] involved with the [[Phoenix Program]]
| |
| − | *[[Philip Agee]]
| |
| − | *[[Robert Baer]]
| |
| − | *[[A.B. "Buzzy" Krongard]]
| |
| − | *[[Mary O. McCarthy]]
| |
| − | *[[Ralph McGehee]]
| |
| − | *[[Victor Marchetti]]
| |
| − | *[[Lindsay Moran]]
| |
| − | *[[L. Fletcher Prouty]]
| |
| − | *[[Frank Snepp]]
| |
| − | *[[John Stockwell]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | '''Conspiracy theories'''
| |
| − | * [[9/11 conspiracy theories]]
| |
| − | * [[Kennedy assassination theories]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | '''Media'''
| |
| − | * [[Vince Flynn]] - author of government fiction with major characters who work for the [[CIA]]
| |
| − | * [[R J Hillhouse]] - author of political fiction about the outsourcing of the [[CIA]]
| |
| − | * ''[[The Agency (TV series)|The Agency]]'', a [[CBS]] television series about the CIA
| |
| − | * ''[[Alias (TV series)|Alias]]'', an [[American Broadcasting Company|ABC]] television series about the CIA
| |
| − | *''[[American Dad]]'', an animated comedy series that spoofs the CIA.
| |
| − | *''[[24 (TV series)|24]]'', a television series about a fictional branch of the CIA.
| |
| − | | |
| − | '''Other national and international agencies'''
| |
| − | * [[List of intelligence agencies]]
| |
| − | * [[Defense Intelligence Agency]]
| |
| − | * [[Federal Bureau of Investigation]] (FBI)
| |
| − | ** [[COINTELPRO]]
| |
| − | * [[National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency]]
| |
| − | * [[National Security Agency]]
| |
| − | * [[Private intelligence agencies]]
| |
| − | * [[Secret Intelligence Service|Secret Intelligence Service (MI6)]]
| |
| − | * [[Mossad]], [[Israel]]'s Intelligence agency
| |
| − | | |
| − | '''Unclassified'''
| |
| − | *[[McCarthy Era]]
| |
| − | *[[Pinkerton Agency]]
| |
| − | *[[Red Scare]]
| |
| − | {{col-end}}
| |
| | | | |
| | ==References== | | ==References== |
| − | <div class="reflist4" style="height: 200px; overflow: auto; padding: 3px; border: 1px solid #ababab">{{reflist|2}}</div>
| + | * Andrew, Christopher. ''For the President's Eyes Only''. HarperCollins, 1996. ISBN 0-00-638071-9 |
| − | | + | * Baer, Robert. ''See No Evil: The True Story of a Ground Soldier in the CIA's War on Terrorism''. Three Rivers Press, 2003. ISBN 1-4000-4684-X |
| − | ==Further reading==
| + | * Bearden, Milton, & Risen, James. ''The Main Enemy: The Inside Story of the CIA's Final Showdown With the KGB''. Random House, 2003. ISBN 0-679-46309-7 |
| − | * {{cite book | + | * Blum, William. ''Killing Hope: U.S. Military and CIA Interventions Since World War II''. Common Courage Press, 2003. ISBN 1-56751-252-6 |
| − | | last =Andrew
| + | * Ranelagh, John. ''The Agency, the Rise and Decline of the CIA''. Touchstone Books, 1987. ISBN 978-0671639945 |
| − | | first =Christopher
| + | * Westerfield, H. Bradford. ''Inside CIA's Private World: Declassified Articles from the Agency's Internal Journal, 1955-1992''. Yale University Press, 1997. ISBN 0-300-07264-3 |
| − | | authorlink =Christopher Andrew
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =1996
| |
| − | | title =For the President's Eyes Only
| |
| − | | publisher =[[HarperCollins]]
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 0-00-638071-9
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | *{{cite book | |
| − | | last =Baer
| |
| − | | first =Robert
| |
| − | | authorlink =Robert Baer
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =2003
| |
| − | | title = [[See No Evil (book)|See No Evil]]: The True Story of a Ground Soldier in the CIA's War on Terrorism
| |
| − | | publisher =[[Three Rivers Press]]
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 1-4000-4684-X
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | *{{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Baer
| |
| − | | first =Robert
| |
| − | | authorlink =Robert Baer
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =2003
| |
| − | | title =[[Sleeping With the Devil]]: How Washington Sold Our Soul for Saudi Crude
| |
| − | | publisher =Crown
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 1-4000-5021-9
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | *{{cite book | |
| − | | last =Bearden
| |
| − | | first =Milton
| |
| − | | authorlink =Milton Bearden
| |
| − | | coauthors =James Risen
| |
| − | | year = 2003
| |
| − | | title =The Main Enemy: The Inside Story of the CIA's Final Showdown With the KGB
| |
| − | | publisher =Random House
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 0-679-46309-7
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | *{{cite book | |
| − | | last =Blum
| |
| − | | first =William
| |
| − | | authorlink =William Blum
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =2003
| |
| − | | title =[http://www.thirdworldtraveler.com/Blum/KillingHope_page.html Killing Hope: U.S. Military and CIA Interventions Since World War II]
| |
| − | | publisher =Common Courage Press
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 1-56751-252-6
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | *{{cite web | |
| − | | title =Chile and the United States: Declassified Documents relating to the Military Coup, 1970-1976
| |
| − | | work =National Security Archives Online
| |
| − | | url =http://www.gwu.edu/%7Ensarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB8/nsaebb8.htm
| |
| − | | accessdate=September 11, 1998
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | *{{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Chomsky
| |
| − | | first =Noam
| |
| − | | authorlink =Noam Chomsky
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year = 2003
| |
| − | | title =[[Hegemony or Survival]]
| |
| − | | publisher =Henry Holt & Co.
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 0-8050-7688-3
| |
| − | }} Also ''Deterring Democracy'', also ''9/11''
| |
| − | * {{cite book| last =Cockburn| first =Alexander | authorlink =Jeffrey St. Clair| coauthors =| year =October 1999| title =Whiteout: The CIA, Drugs and the Press | publisher =Verso | location =| id =ISBN 1-8598-4258-5 }}
| |
| − | *{{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Grey
| |
| − | | first =Stephen
| |
| − | | authorlink =Stephen Grey
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year = 2006
| |
| − | | title =[[Ghost Plane: The True Story of the CIA Torture Program]]
| |
| − | | publisher =St. Martin's Press
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 978-0312360238
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | *{{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Johnson
| |
| − | | first =Loch K.
| |
| − | | authorlink =Loch K. Johnson
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =1991
| |
| − | | title =America's Secret Power: The CIA in a Democratic Society
| |
| − | | publisher =Oxford University Press
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | *{{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Kessler
| |
| − | | first =Ronald
| |
| − | | authorlink =Ronald Kessler
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =1992, reissue 1994
| |
| − | | title =Inside the CIA
| |
| − | | publisher =Pocket Books
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 0-671-73458-X
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | * {{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Littell
| |
| − | | first =Robert
| |
| − | | authorlink =Robert Littell
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =2002
| |
| − | | title =The Company: A Novel of the CIA
| |
| − | | publisher =[[Overlook Press]]
| |
| − | | location = New York
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 978-1585671977
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | *{{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Mahle
| |
| − | | first =Melissa Boyle
| |
| − | | authorlink =
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year = 2004
| |
| − | | title =Denial and Deception: An Insider's View of the CIA from Iran-Contra to 9/11
| |
| − | | publisher =Nation Books
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 1-56025-649-4
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | * {{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Marchetti
| |
| − | | first =Victor
| |
| − | | authorlink = Victor Marchetti
| |
| − | | coauthors =John D. Marks
| |
| − | | year =1975 reissue 1989
| |
| − | | title =The CIA and the Cult of Intelligence
| |
| − | | publisher =Dell
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 978-0440203360
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | *{{cite book| last =McCoy| first =Alfred W.| authorlink =Alfred W. McCoy| coauthors =| year =2003 | title =The Politics of Heroin: CIA Complicity in the Global Drug Trade| publisher =Lawrence Hill Books| location =| id =1556524838 }} CIA involvement with the drug trade since World War 2 to present day.
| |
| − | *{{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Mendez
| |
| − | | first =Antonio J.
| |
| − | | authorlink =Antonio J. Mendez
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =1999
| |
| − | | title =Master of Disguise: My Secret Life in the CIA
| |
| − | | publisher =William Morrow and Company, Inc
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 0-06-095791-3
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | *{{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Moran
| |
| − | | first =Lindsay
| |
| − | | authorlink =Lindsay Moran
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =2005
| |
| − | | title =Blowing My Cover: My Life as a CIA Spy and Other Misadventures
| |
| − | | publisher =[[Berkley Books]]
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 0-425-20562-2
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | * {{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Prouty
| |
| − | | first =L. Fletcher
| |
| − | | authorlink =L. Fletcher Prouty
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =April 1973
| |
| − | | title =[[The Secret Team]]: The CIA and Its Allies in Control of the United States and the World
| |
| − | | publisher =Prentice Hall
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 0-13-798173-2
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | *{{cite book| last =Scott | first =Peter Dale | authorlink =Peter Dale Scott| coauthors =Jonathan Marshall| year =April 1998| title =Cocaine Politics: Drugs, Armies, and the CIA in Central America| publisher =University of California Press| location =| id =0520214498 }} ''CIA involvement in the drug trade during the US backed Contra war with Nicaragua.''
| |
| − | *{{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Saunders
| |
| − | | first =Frances Stonor
| |
| − | | authorlink =Frances Stonor Saunders
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =1999
| |
| − | | title =The Cultural Cold War: The CIA and the World of Arts and Letters
| |
| − | | publisher =[[New Press]]
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 1-56584-664-8
| |
| − | }} (AKA, ''Who Paid the Piper?: CIA and the Cultural Cold War'' 1999 Granta [UK edition])
| |
| − | *{{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Smith, Jr.
| |
| − | | first =W. Thomas
| |
| − | | authorlink =W. Thomas Smith, Jr.
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =2003
| |
| − | | title =Encyclopedia of the Central Intelligence Agency
| |
| − | | publisher =[[Facts on File]]
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 0-8160-4667-0
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | * {{cite book| last =Webb | first =Gary | authorlink =Gary Webb| coauthors =| year =May 1999| title =Dark Alliance: The CIA, the Contras, and the Crack Cocaine Explosion | publisher =Seven Stories Press | location =| id =1888363932 }}
| |
| − | * {{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Weiner
| |
| − | | first =Tim
| |
| − | | authorlink =Tim Weiner
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =2007
| |
| − | | title =Legacy of Ashes
| |
| − | | publisher =[[Doubleday]]
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 978-0-385-51445-3
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | *{{cite book | |
| − | | last =Westerfield
| |
| − | | first =H. Bradford
| |
| − | | authorlink =H. Bradford Westerfield
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =1997
| |
| − | | title =Inside CIA's Private World: Declassified Articles from the Agency's Internal Journal, 1955-1992
| |
| − | | publisher =Yale University Press
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 0-300-07264-3
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | *{{cite book
| |
| − | | last =Woodward
| |
| − | | first =Bob
| |
| − | | authorlink =Bob Woodward
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | year =1988
| |
| − | | title =Veil
| |
| − | | publisher =[[Pocket Books]]
| |
| − | | location =
| |
| − | | id =ISBN 0-671-66159-0
| |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | ==External links== | | ==External links== |
| − | {{Commons|Central Intelligence Agency}}
| + | All links retrieved December 3, 2023. |
| − | {{wikinewscat|CIA}}
| + | * [https://www.cia.gov/ CIA official site]. ''www.cia.gov''. |
| − | | + | * [http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/index.html George Washington University National Security Archive]. ''www.gwu.edu''. |
| − | ===Official websites and documents===
| |
| − | * [https://www.cia.gov/ CIA official site] | |
| − | * [http://www.foia.cia.gov/ CIA official Freedom of Information Act (foia) site]
| |
| − | * [http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/index.html George Washington University National Security Archive]: | |
| − | ** [http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/news/20000919/ Documents on CIA involvement with Pinochet]
| |
| − | ** [http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB4/index.html On CIA involvement in Guatemala]
| |
| − | ** [http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB146/ On CIA involvement with Nazi War Criminals (especially the Gehlen organization)]
| |
| − | * [http://www.archives.gov/iwg/index.html U.S. National Archive's Nazi War Crimes and Japanese Imperial Government Records Interagency Working Group.]
| |
| − | ** [http://www.archives.gov/iwg/declassified_records/rg_263_cia_records/rg_263_report.html Summary of newly acquired CIA name files (including Klaus Barbie)]
| |
| − | * [http://www.parascope.com/articles/0397/kubark06.htm CIA manual on coercive questioning]
| |
| − | *[https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html CIA World Factbook]
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===Other links===
| |
| − | *[http://shashwatdc.blogspot.com A Tech Journalist's Blog] Here the journalist has done extensive research on how CIA was keeping a tab on technology and how it was using computer systems itself.
| |
| − | *[http://www.rca5600.be www.rca5600.be] about the action of the Agency in Cultural field
| |
| − | *[http://www.thespywhobilledme.com/ The Spy Who Billed Me] author Dr.[[Raelynn Hillhouse|R.J. Hillhouse's]] national security blog, focusing upon the outsourcing of the War on Terror and regularly covering the latest developments with the CIA outsourcing to private intelligence corporations.
| |
| − | *{{cite web
| |
| − | | title =CIA Sourcewatch
| |
| − | | work =www.sourcewatch.org
| |
| − | | url =http://www.sourcewatch.org/index.php?title=CIA Sourcewatch
| |
| − | | accessdate=2006-07-11
| |
| − | }} Explains CIA operation methods
| |
| − | * [http://nobelprize.org/literature/laureates/2005/pinter-lecture-e.html ''Art, Truth and Politics'': Harold Pinter's Nobel Prize Lecture]. Online posting. 8 December 2005. 9 December 2005.
| |
| − | * [http://www.rotten.com/library/conspiracy/cia/ CIA information at Rotten.com].
| |
| − | * [http://www.copvcia.com Cop vs. CIA]. Online posting. From the Wilderness (mirror site) /
| |
| − | * ''[http://www.csun.edu/CommunicationStudies/ben/news/cia/ Cocaine Import Agency]''. Online posting. ''San José Mercury News''. (On alleged drug-smuggling by the CIA.)
| |
| − | * ''[http://www.libcom.org/history/articles/cultural-cold-war/ The Cultural Cold War]'', by Nathaniel Catchpole.
| |
| − | * [http://www.in-q-tel.com/ In-Q-Tel official site].
| |
| − | * ''[http://www.thirdworldtraveler.com/CIA/CIA_Diary_Agee.html Inside the Company: CIA Diary]''. Online posting. Third World Traveler: Excerpt from a book by leading whistleblower [[Philip Agee]].
| |
| − | * ''[http://members.aol.com/bblum6/American_holocaust.htm Killing Hope]'', by [[William Blum]].
| |
| − | * [http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/ National Security Archive (George Washington University)].
| |
| − | * [http://montages.blogspot.com/2005/01/outsourcing-intelligence.html "Outsourcing Intelligence"]. Online blogpost. ''Montage'' 5 January 2005.
| |
| − | * ''[http://www.isria.com/en/free/0000026.php The Relations between the CIA and the Executive Power since 2001]''. Online posting (HTML file). ISRIA. 5 February 2006.
| |
| − | * ''[http://www.isria.com/en/free/File1_NOMIKOS_15jan06.pdf The Role of Open Sources in Intelligence]''. Online posting (Pdf file). 31 31 December 2005.
| |
| − | * [http://www.janes.com/security/international_security/news/jid/jid060511_1_n.shtml "Yet more turmoil at the CIA"]. Online posting. Janes. (On implications of the "departure" of [[Porter Goss]].
| |
| − | * [http://www.specialforcesroh.com/browse.php?mode=viewc&catid=53 CIA] roll of honour, awards and images.
| |
| − | * [http://thefederalregister.com/b.p/department/CENTRAL_INTELLIGENCE_AGENCY/ Central Intelligence Agency Meeting Notices and Rule Changes] from The Federal Register [http://thefederalregister.com/rss/department/CENTRAL_INTELLIGENCE_AGENCY/ RSS Feed]
| |
| − | *[http://freepressinternational.com/category/cia/ Video's and Info]
| |
| − | *[http://www.nachrichtendienste.ch/THESIS_BY_MARCEL_STUESSI_SECRET_PERSONAL_DATA_GATHERING_.pdf Proposal for a Privacy Protection Guideline on Secret Personal Data Gathering and Transborder Flows of Such Data in the Fight against Terrorism and Serious Crime by Marcel Stuessi]
| |
| − | *[http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB222/ CIA "Family Jewels" documents]
| |
| | | | |
| − | {{Intelligence agencies of USA}}
| |
| − | {{intelorgofwor}}
| |
| − | {{Cold War}}
| |
| − | [[Category:history and biography]]
| |
| | {{Credit|151888725}} | | {{Credit|151888725}} |
| | + | [[Category:History]] |
Central Intelligence Agency
CIA
|

Seal of the Central Intelligence Agency
|
| Agency overview
|
| Formed |
July 26, 1947
|
| Preceding Agency |
Central Intelligence Group
|
| Headquarters |
Langley, Virginia, United States
|
| Employees |
Classified
|
| Annual Budget |
Classified
|
| Minister Responsible |
John Michael McConnell, Director of National Intelligence
|
| Agency Executives |
General Michael Hayden USAF, Director
Stephen Kappes, Deputy Director
Michael Morell, Associate Deputy Director
|
| Website
|
| www.cia.gov
|
| Footnotes
|
| [1][2][3]
|
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) is an intelligence-gathering agency of the United States government whose primary mission today is collecting secret information from abroad through human agents. Created in the aftermath of the Pearl Harbor attack to centralize all intelligence-gathering efforts by the U.S. government, its three functions are divided according to intelligence collection, intelligence analysis, and technical services. It also has the mandate to conduct covert action, semi-secret political, or paramilitary operations where the U.S. government's hand is not directly visible. It also conducts counterintelligence against foreign-government intelligence services. The CIA's covert operations have caused much controversy for the agency, raising questions about the legality, morality, and effectiveness of such operations.
The CIA is restricted from operating inside the United States, although it collects some intelligence from American visitors who return from overseas travel or individuals living in the U.S with access to foreign intelligence. The FBI is the lead domestic intelligence agency.
The CIA's elite division is called the Directorate of Operations (DO), also known as the Clandestine Service, that at its height in the 1980s, numbered around 10,000 specialists in espionage, agent recruitment, and covert action.
Until recently, the CIA director performed the dual functions of agency director and Director of Central Intelligence (DCI), the nominal head of all U.S. intelligence agencies. Under reform legislation passed in the aftermath of the September 11 attacks and failures related to Iraq’s weapons of mass destruction programs, the CIA was subsumed under the Office of the Director of National Intelligence and the CIA director no longer acts as DCI. The agency has been refocused as the primary human-intelligence gathering agency of the government.
CIA headquarters is in the community of Langley in the McLean, Virginia, a few miles northwest from downtown Washington, D.C., along the Potomac River.
History and operations
Creation

William J. Donovan, widely credited as the "father" of the CIA

Original sign with seal from the CIA's first building on E Street in Washington, DC
The Central Intelligence Agency was created by Congress with passage of the National Security Act of 1947, signed into law by President Harry S. Truman. It is the descendant of the Office of Strategic Services (OSS) of World War II, which was dissolved in October 1945, and its functions transferred to the State and War Departments. However, the need for a centralized postwar intelligence-gathering operation was clearly recognized.
Eleven months earlier, in 1944, William J. Donovan (also known as Wild Bill Donovan), the OSS's creator, proposed to President Franklin D. Roosevelt creating a new espionage organization directly supervised by the President. Under Donovan's plan, a powerful, centralized civilian agency would coordinate all the intelligence services. He also proposed that this agency have authority to conduct "subversive operations abroad," but no police or law enforcement functions, either at home or abroad.
President Harry S. Truman, established the Central Intelligence Group in January 1946, over objections from the State Department and the FBI, who saw the creation of the agency as a rival to their own functions. Later, under the National Security Act of 1947, the National Security Council and the Central Intelligence Agency were established. Rear Admiral Roscoe H. Hillenkoetter was appointed as the first Director of Central Intelligence.
The now declassified National Security Council Directive on the Office of Special Projects, June 18, 1948 (NSC 10/2), provided the operating instructions for the CIA's covert operations:
Plan and conduct covert operations which are conducted or sponsored by this government against hostile foreign states or groups or in support of friendly foreign states or groups but which are so planned and conducted that any U.S. Government responsibility for them is not evident to unauthorized persons and that if uncovered the U.S. Government can plausibly disclaim any responsibility for them. Covert action shall include any covert activities related to: Propaganda; economic warfare; preventive direct action, including sabotage, anti-sabotage, demolition, and evacuation measures; subversion against hostile states, including assistance to underground resistance movements, guerrillas and refugee liberation groups, and support of indigenous anti-Communist elements in threatened countries of the free world.
Fighting communism
The CIA was successful in limiting native Communist influence in France and Italy, notably in the 1948 Italian election. It also cooperated in a clandestine NATO "stay-behind" operation in Italy called Operation Gladio, which was set up in Western Europe, intended to counter a Warsaw Pact invasion of Western Europe. In addition, the CIA managed to acquire the Rosenholz files, containing the list of foreign spies of the Stasi, in the former German Democratic Republic (East Germany).
The CIA also helped recruit many scientists who had worked in Nazi Germany to aid the United States. Several former Nazi operational agents were also reportedly recruited as United States' secret agents.
In 1949, the Central Intelligence Agency Act (Public Law 81-110) was passed, permitting the agency to use confidential fiscal and administrative procedures, and exempting it from most of the usual limitations on the use of federal funds. The act also exempted the CIA from having to disclose its "organization, functions, officials, titles, salaries, or numbers of personnel employed." The act also created the program "PL-110," to handle defectors and other "essential aliens" who fall outside normal immigration procedures, as well as giving those persons cover stories and economic support.
In the 1950s, with Europe stabilizing along the Iron Curtain, the CIA worked to limit the spread of Soviet influence elsewhere around the world, especially in the poor countries of the Third World. Encouraged by DCI Allen Dulles, clandestine operations quickly dominated the organization's actions.

This U-2 photo revealed Soviet missile installation in Cuba
In 1950, the CIA organized the Pacific Corporation, the first of many CIA private enterprises used effectively by the CIA both for intelligence gathering and covert operations. In 1951, the Columbia Broadcasting System began cooperating with the CIA, as did several other news-gathering groups in later years. It also pioneered the use of new technologies in intelligence work, including the famous U-2 high altitude spy plane.
One of the CIA's major successes came during the Cuban Missile Crisis, which began on October 16, 1962. On that day, President John F. Kennedy was informed that a U-2 mission flown over western Cuba two days before had taken photographs of Soviet-nuclear missile sites. The event was a watershed for the intelligence community and the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), in particular. It demonstrated that the technological collection capabilities so painstakingly constructed to monitor the Soviet Union had matured to give the U.S. intelligence community an unmatched ability to provide policymakers with sophisticated warning and situational awareness. The CIA took the lead in developing aerial and space photographic systems.
Particularly during the Cold War, the CIA supported numerous governments opposed to Communist insurgencies and Marxist political movements. Some of these were led by military dictators friendly to perceived United States' geopolitical interests. In some cases, the CIA reportedly supported coups against elected governments.
The CIA also supported the Congress of Cultural Freedom, which published literary and political journals such as Encounter (as well as Der Monat in Germany and Preuves in France), and hosted dozens of conferences bringing together some of the most eminent Western thinkers; it also gave assistance to intellectuals behind the Iron Curtain.
Controversy mounts
In the early 1970s, revelations about past CIA activities, such as assassinations of foreign leaders and illegal domestic spying on U.S. citizens, provided opportunities to execute Congressional oversight of U.S. intelligence operations. In 1973, then-DCI James R. Schlesinger had commissioned reports—known as the "Family Jewels"—on illegal activities by the Agency. In December 1974, Investigative journalist Seymour Hersh broke the news of the "Family Jewels" in a front-page article in the New York Times, revealing that the CIA had assassinated foreign leaders, and had conducted surveillance on some 7,000 American citizens involved in the antiwar movement (Operation CHAOS). The CIA also suffered a major public relations setback when it was revealed that the infamous burglary of the Watergate headquarters of the Democratic Party was conducted by ex-CIA agents.
Congress responded in 1975, investigating the CIA in the Senate via the Church Committee, chaired by Senator Frank Church (D-Idaho), and in the House of Representatives via the Pike Committee, chaired by Congressman Otis Pike (D-NY). In addition, President Gerald Ford created the Rockefeller Commission to investigate CIA activities within the U.S. and issued a directive prohibiting the assassination of foreign leaders.
Under the Carter Administration, CIA Director Adm. Stansfield Turner carried out what became known as the “Halloween Massacre,” firing large numbers of the agency’s most experienced operations officers with a terse note. The action was part of a shift in emphasis away from human-based spying operations to electronic spying. Today, the CIA is working to recover from the loss of its human spying capabilities, shortcomings that were highlighted by the failures related to the September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks.
A high point for the CIA was its running, along with British intelligence, of a Soviet military spy inside the GRU military intelligence service, Colonel Oleg Penkovsky. Penkovsky provided documents on Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile capabilities that allowed the United States to understand the threat it was facing from Moscow’s nuclear missiles. It is an example today of the kind of intelligence that can only be provided by human spies.
Under CIA Counterintelligence Chief James Jesus Angleton, the CIA imprisoned Soviet defector Yuri Nosenko, whom Angleton believed to be an agent sent to provide disinformation to the CIA. Angleton had become close to another defector, Anatoli Golitsyn, who reported that a secret unit within the Kremlin was engaged in strategic disinformation against the West. The dueling defectors set off an internal struggle within the CIA and led to Angleton’s "mole hunt," a search for Soviet penetration agents working within the CIA.
Angleton had sought to reorient the CIA into a strategic counterintelligence agency, whose main goal would be targeting the Soviet KGB and its sister services with the initiative of bringing down the Soviet empire. Angleton, however, lost out in the power struggle to CIA Director William Colby, who favored a more traditional intelligence and covert action approach.
The Farewell Dossier—a collection of documents containing intelligence gathered and handed over to NATO by the KGB defector Colonel Vladimir Vetrov (code-named "Farewell")—in 1981-82, revealed massive Soviet espionage on Western technology. The CIA created a successful counter-espionage program which involved giving defective technologies to Soviet agents.
In 1983, the CIA had more spies working inside the Soviet Union than at any time in its history. Infamous CIA operative Aldrich Ames would betray 25 active agents, some working at senior levels within the Soviet establishment. Many of these were taken to prison and then shot in the back of the head, so that the exit wound would render the face unrecognizable. In return, Ames received over $1.3 million in payments from the KGB from 1985-91. The total would eventually rise to $4 million. Ames was finally caught after a CIA mole-hunting team—with the assistance of the FBI—uncovered Ames's access to compromised cases and his suspect personal finances.
Repercussions from the Iran-Contra arms smuggling scandal included the creation of the Intelligence Authorization Act in 1991. It required an authorizing chain of command, including an official presidential report and the informing of the House and Senate Intelligence Committees.
In 1996, the U.S. House Permanent Select Committee on Intelligence issued a congressional report estimating that the clandestine service part of the intelligence community "easily" breaks "extremely serious laws" in countries around the world 100,000 times every year.

The lives of 83 fallen CIA officers are represented by 83 stars on the CIA memorial wall in the Old Headquarters building.
Some of the post-Watergate restrictions upon the Central Intelligence Agency were lifted after the September 11, 2001 attacks on the World Trade Center in New York City and The Pentagon. Critics charge this violates the requirement in the U.S. Constitution that the federal budget be openly published.
In the findings of the independent National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States released on July 22, 2004, detailed several failures of the CIA in taking proper measures related to the September 11, 2001 attacks were called into account:
- "The CIA was limited in its effort to try to capture al Qaeda founder Osama bin Laden and his lieutenants in Afghanistan by the agency's use of proxies."
- "The failure of the CIA and FBI to communicate with each other… led to missed 'operational opportunities' to hinder or break the terror plot."
- "The CIA did not put 9/11 hijacker Khalid Almihdhar on a 'watch list' or notify the FBI when he had a U.S. visa in January 2000, or when he met with a key figure in the USS ''Cole'' bombing. And the CIA failed to develop plans to track Almihdhar, or hijacker Nawaf Alhazmi when he obtained a U.S. visa and flew to Los Angeles."
On November 5, 2002, newspapers reported that Al-Qaeda operatives in a car traveling through Yemen had been killed by a missile launched from a CIA-controlled Predator drone. On May 15, 2005, it was reported that another of these drones had been used to assassinate Al-Qaeda figure Haitham al-Yemeni inside Pakistan.
Reorganization
In the same year President George W. Bush appointed the CIA to be in charge of all human intelligence and manned spying operations. This was the culmination of a years-old turf war regarding influence, philosophy, and budget between the Defense Intelligence Agency of The Pentagon and the CIA. The Pentagon, through the DIA, wished to take control of the CIA's paramilitary operations and many of its human assets. The CIA, which has for years held that human intelligence is the core of the agency, successfully argued that the CIA's decades-long experience with human resources and civilian oversight made it, rather than the DIA, the ideal choice. Thus, the CIA was given charge of all United States' human intelligence, but as a compromise, The Pentagon was authorized to include increased paramilitary capabilities in future budget requests. Despite reforms which led it back to what the CIA considers its traditional principal capacities, the CIA Director's position has lost influence in the White House. For years, the Director of the CIA met regularly with the President to issue daily reports on ongoing operations. After the creation of the post of Director of National Intelligence, the report is now given by the DNI, who oversees all United States' Intelligence activities.
On July 9, 2004, the Senate Report of Pre-war Intelligence on Iraq of the Senate Intelligence Committee reported that the CIA exaggerated the danger presented by weapons of mass destruction in Iraq, largely unsupported by the available intelligence.
Earlier, in Novemeber 2002, the CIA successfully ended the life of Qaed Salim Sinan al-Harethi, a prominent member of Osama bin Laden’s al Qaeda terrorist network, through a Predator drone attack in Yemen. It has also been involved in identifying, capturing, and interrogating numerous terrorists, as well as in operations assisting troops fighting al Qaeda in Afghanistan and Iraq. In 2003, the CIA reportedly assisted in the capture of al Qaeda operations director Khalid Shaikh Mohammed, who was later reported to have cooperated with CIA interrogators, providing valuable information on al Qaeda methods, plans, and personnel. On January 13, 2006, the CIA launched an airstrike on Damadola, a Pakistani village near the Afghan border, where they believed Ayman al-Zawahiri was located. The airstrike killed a number of civilians, but al-Zawahiri escaped. Because al-Zawahiri is named as a terrorist enemy combatant by the United States, this and similar attacks are not covered under Executive Order 12333, which banned assassinations. Many of the CIA's activities in the war on terror remain undisclosed for security reasons.
Current organization
Agency seal

The 16-foot diameter granite CIA seal in the lobby of the Original Headquarters Building

The entrance of the CIA Headquarters
The heraldic symbol of the CIA consists of three representative parts: The left-facing bald eagle head atop, the compass star (or compass rose), and the shield. The eagle is the national bird, standing for strength and alertness. The 16-point compass star represents the CIA's world-wide search for intelligence outside the United States, which is then reported to the headquarters for analysis, reporting, and re-distribution to policymakers. The compass rests upon a shield, symbolic of defense and intelligence.
Structure
- Director of the Central Intelligence Agency (DCIA)—The head of the CIA is given the title of the DCIA. The act that created the CIA in 1947, also created a Director of Central Intelligence (DCI) to serve as head of the United States intelligence community, act as the principal adviser to the President for intelligence matters related to the national security, and serve as head of the Central Intelligence Agency. The Intelligence Reform and Terrorism Prevention Act of 2004, amended the National Security Act to provide for a Director of National Intelligence who would assume some of the roles formerly fulfilled by the DCI, with a separate Director of the Central Intelligence Agency.
- Deputy Director of the Central Intelligence Agency (DDCIA)—Assists the Director in his duties as head of the CIA and exercises the powers of the Director when the Director’s position is vacant or in the Director’s absence or disability.
- Associate Deputy Director of the Central Intelligence Agency (ADD)—Created July 5, 2006, the ADD was delegated all authorities and responsibilities vested previously in the post of Executive Director. The post of Executive Director, which was responsible for managing the CIA on a day-to-day basis, was simultaneously abolished.
- Associate Director for Military Support (AD/MS)—The DCIA's principal adviser and representative on military issues. The AD/MS coordinates Intelligence Community efforts to provide Joint Force commanders with timely, accurate intelligence. The AD/MS also supports Department of Defense officials who oversee military intelligence training and the acquisition of intelligence systems and technology. A senior general officer, the AD/MS ensures coordination of Intelligence Community policies, plans, and requirements relating to support to military forces in the intelligence budget.
Relationship with other agencies
The National Intelligence Council, which oversees production of National Intelligence Estimates, was transferred under reform legislation to the Office of the Director of National Intelligence. It is believed to make use of the product derived from surveillance satellites of the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) and the signal interception capabilities of the National Security Agency (NSA), including the ECHELON system, the surveillance aircraft of the various branches of the U.S. armed forces and the analysts of the State Department, and Department of Energy. At one point, the CIA even operated its own fleet of U-2 and A-12 OXCART surveillance aircraft.
The agency has also operated alongside regular military forces, and also employs a group of clandestine officers with paramilitary skills in its Special Activities Division. The CIA also has strong links with other foreign intelligence agencies such as the UK's Secret Intelligence Service, the Canadian Security Intelligence Service, Israel's Mossad, and the Australian Secret Intelligence Service.
Further, the CIA is currently believed to be financing several Counter-terrorist Intelligence Centers.
Publications
One of the CIA's best-known publications, The World Factbook, is in the public domain and is made freely available without copyright restrictions because it is a work of the United States federal government.
Since 1955, the CIA has published an in-house professional journal known as Studies in Intelligence that addresses historical, operational, doctrinal, and theoretical aspects of the intelligence profession. Unclassified and declassified Studies articles, as well as other books and monographs, are made available by the CIA's Center for the Study of Intelligence on a limited basis through Internet and other publishing mechanisms.
In 2002, the CIA's Sherman Kent School for Intelligence Analysis began publishing the unclassified Kent Center Occasional Papers, aiming to offer "an opportunity for intelligence professionals and interested colleagues-—in an unofficial and unfettered vehicle-—to debate and advance the theory and practice of intelligence analysis."
Notes
- ↑ Error on call to template:cite web: Parameters url and title must be specified. cia.gov (2006-07-28).
- ↑ Public affairs FAQ. cia.gov (July 28, 2006). Retrieved April 28, 2013. However, it was made public for several years in the late 1990s. In 1997 it was of $26.6 billion and in 1998 it was $26.7 billion
- ↑ Cloak Over the CIA Budget (1999-11-29). Retrieved April 28, 2013.
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Andrew, Christopher. For the President's Eyes Only. HarperCollins, 1996. ISBN 0-00-638071-9
- Baer, Robert. See No Evil: The True Story of a Ground Soldier in the CIA's War on Terrorism. Three Rivers Press, 2003. ISBN 1-4000-4684-X
- Bearden, Milton, & Risen, James. The Main Enemy: The Inside Story of the CIA's Final Showdown With the KGB. Random House, 2003. ISBN 0-679-46309-7
- Blum, William. Killing Hope: U.S. Military and CIA Interventions Since World War II. Common Courage Press, 2003. ISBN 1-56751-252-6
- Ranelagh, John. The Agency, the Rise and Decline of the CIA. Touchstone Books, 1987. ISBN 978-0671639945
- Westerfield, H. Bradford. Inside CIA's Private World: Declassified Articles from the Agency's Internal Journal, 1955-1992. Yale University Press, 1997. ISBN 0-300-07264-3
External links
All links retrieved December 3, 2023.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article
in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.