Difference between revisions of "Archaea" - New World Encyclopedia
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) (added most recent Wikipedia version of article) |
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| name = Archaea | | name = Archaea | ||
| domain = '''Archaea''' | | domain = '''Archaea''' | ||
| − | | domain_authority = [[Carl Woese|Woese]], [[Otto Kandler|Kandler]] & [[Mark Wheelis|Wheelis]], 1990 | + | | domain_authority = [[Carl Woese|Woese]], [[Otto Kandler|Kandler]]* & [[Mark Wheelis|Wheelis]]*, 1990 |
| subdivision_ranks = Phyla / Classes | | subdivision_ranks = Phyla / Classes | ||
| subdivision = | | subdivision = | ||
| − | Phylum [[Crenarchaeota]]<br /> | + | Phylum [[Crenarchaeota]]*<br /> |
| − | Phylum [[Euryarchaeota]]<br /> | + | Phylum [[Euryarchaeota]]*<br /> |
| − | [[Halobacteria]]<br /> | + | [[Halobacteria]]*<br /> |
| − | [[Methanobacteria]]<br /> | + | [[Methanobacteria]]*<br /> |
| − | [[Methanococci]]<br /> | + | [[Methanococci]]*<br /> |
| − | [[Methanopyri]]<br /> | + | [[Methanopyri]]*<br /> |
| − | [[Archaeoglobi]]<br /> | + | [[Archaeoglobi]]*<br /> |
| − | [[Thermoplasmata]]<br /> | + | [[Thermoplasmata]]*<br /> |
| − | [[Thermococci]]<br /> | + | [[Thermococci]]*<br /> |
| − | Phylum [[Korarchaeota]]<br /> | + | Phylum [[Korarchaeota]]*<br /> |
| − | Phylum [[Nanoarchaeum|Nanoarchaeota]] | + | Phylum [[Nanoarchaeum|Nanoarchaeota]]* |
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Archaea''' ( | + | '''Archaea''' (singular ''Archaeum'', ''Archaean'', or ''Archaeon''), also called '''Archaebacteria''', is a major division of [[life|living]] [[organism]]s. Like [[bacteria]], Archaea are single-celled organisms lacking [[cell nucleus|nuclei]] and are therefore [[prokaryote]]s. However, they differ significantly from bacteria, and therefore in recent classifications are generally separated from Bacteria. In the [[taxonomy#Domain and Kingdom systems|three-domain system]] of biological classification, Archaea joins [[Eukaryote|Eukaryota]] and Bacteria as the three domains, the top-level grouping of organisms. In the six-kingdom classification, the six top-level groupings are Archaea (or Archaebacteria), Monera (the bacteria and cyanobacteria), Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. In the traditional five-kingdom classification, developed in 1969 by Robert Whittaker and still popular today, the Arachaebacteria or Archaea are placed together with other prokaryotes in the kingdom Monera. |
| + | |||
| + | They were originally described in [[extremophile|extreme]] environments, but have since been found in all types of [[Habitat (ecology)|habitat]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | from [[Greek language|Greek]] αρχαία, "ancient ones"; One of the reasons such a classification has been developed is because research has revealed the unique nature of anaerobic bacteria (called Archaeobacteria, or simply Archaea). These "living fossils" are genetically and metabolically very different from oxygen-breathing organisms. Various numbers of Kingdoms are recognized under the domain category. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the three-domain system, which was introduced by Carl Woese in 1990,This scheme emphasizes the separation of prokaryotes into two groups, the Bacteria (originally labelled Eubacteria) and the Archaea (originally labelled Archaebacteria). | ||
A ''single'' organism from this domain has been called an "'''archaean'''." Furthermore, this biologic term is also used as an adjective. | A ''single'' organism from this domain has been called an "'''archaean'''." Furthermore, this biologic term is also used as an adjective. | ||
Revision as of 22:35, 28 February 2007
| Archaea | ||
|---|---|---|
| Scientific classification | ||
| ||
|
Phylum Crenarchaeota |
Archaea (singular Archaeum, Archaean, or Archaeon), also called Archaebacteria, is a major division of living organisms. Like bacteria, Archaea are single-celled organisms lacking nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. However, they differ significantly from bacteria, and therefore in recent classifications are generally separated from Bacteria. In the three-domain system of biological classification, Archaea joins Eukaryota and Bacteria as the three domains, the top-level grouping of organisms. In the six-kingdom classification, the six top-level groupings are Archaea (or Archaebacteria), Monera (the bacteria and cyanobacteria), Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. In the traditional five-kingdom classification, developed in 1969 by Robert Whittaker and still popular today, the Arachaebacteria or Archaea are placed together with other prokaryotes in the kingdom Monera.
They were originally described in extreme environments, but have since been found in all types of habitat.
from Greek αρχαία, "ancient ones"; One of the reasons such a classification has been developed is because research has revealed the unique nature of anaerobic bacteria (called Archaeobacteria, or simply Archaea). These "living fossils" are genetically and metabolically very different from oxygen-breathing organisms. Various numbers of Kingdoms are recognized under the domain category.
In the three-domain system, which was introduced by Carl Woese in 1990,This scheme emphasizes the separation of prokaryotes into two groups, the Bacteria (originally labelled Eubacteria) and the Archaea (originally labelled Archaebacteria).
A single organism from this domain has been called an "archaean." Furthermore, this biologic term is also used as an adjective.
History
Archaea were identified in 1977 by Carl Woese and George E. Fox as being a separate branch based on their separation from other prokaryotes on 16S rRNA phylogenetic trees.[1] These two groups were originally named the Archaebacteria and Eubacteria, treated as kingdoms or subkingdoms, which Woese and Fox termed Urkingdoms. Woese argued that they represented fundamentally different branches of living things. He later renamed the groups Archaea and Bacteria to emphasize this, and argued that together with Eukarya they compose three Domains of living organisms.[2]
The biological term, Archaea, should not be confused with the geologic phrase Archean eon, also known as the Archeozoic era. This latter term refers to the primordial period of earth history when Archaea and Bacteria were the only cellular organisms living on the planet. Probable fossils of these microbes have been dated to almost 3.8 billion years ago. Their remains have been found in sediment from western Greenland, the oldest sediment to be discovered. (3800 mya).[3][4]
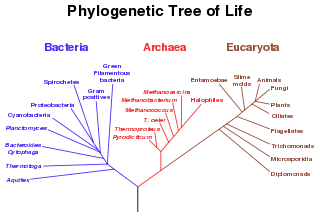
Archaea, Bacteria and Eukaryotes
Archaea are similar to other prokaryotes in most aspects of cell structure and metabolism. However, their genetic transcription and translation — the two central processes in molecular biology — do not show many typical bacterial features, and are in many aspects similar to those of eukaryotes. For instance, archaean translation uses eukaryotic-like initiation and elongation factors, and their transcription involves TATA-binding proteins and TFIIB as in eukaryotes. Many archaeal tRNA and rRNA genes harbor unique archaeal introns which are neither like eukaryotic introns, nor like bacterial (type I and type II etc which can "home") introns.
Several other characteristics also set the Archaea apart. Like bacteria and eukaryotes, archaea possess glycerol-based phospholipids. However, three features of the archaeal lipids are unusual:
- The archaeal lipids are unique because the stereochemistry of the glycerol is the reverse of that found in bacteria and eukaryotes. This is strong evidence for a different biosynthetic pathway.
- Most bacteria and eukaryotes have membranes composed mainly of glycerol-ester lipids, whereas archaea have membranes composed of glycerol-ether lipids. Even when bacteria have ether-linked lipids, the stereochemistry of the glycerol is the bacterial form. These differences may be an adaptation on the part of Archaea to hyperthermophily. However, it is worth noting that even mesophilic archaea have ether-linked lipids.
- Archaeal lipids are based upon the isoprenoid sidechain. This is a five-carbon unit that is also common in rubber and as a component of some vitamins common in bacteria and eukaryotes. However, only the archaea incorporate these compounds into their cellular lipids, frequently as C-20 (four monomers) or C-40 (eight monomers) side-chains. In some archaea, the C-40 isoprenoid side-chain is actually long enough to span the membrane, forming a monolayer for a cell membrane with glycerol phosphate moieties on both ends. Although dramatic, this adaptation is most common in the extremely thermophilic archaea.
Although not unique, the archaeal cell walls are also unusual. For instance, the cell walls of most archaea are formed by surface-layer proteins or an S-layer. S-layers are common in bacteria, where they serve as the sole cell-wall component in some organisms (like the Planctomyces) or an outer layer in many organisms with peptidoglycan. With the exception of one group of methanogens, archaea lack a peptidoglycan wall (and in the case of the exception, the peptidoglycan is very different from the type found in bacteria). Archaeans also have flagella that are notably different in composition and development from the superficially similar flagella of bacteria. Bacterial flagella is a modified type III secretion system, while archeal flagella resemble type IV pilli which use a sec dependent secretion system somewhat similar to but different from type II secretion system. Archea are single celled. They are prokaryotic, have no nucleus, and have one circular chromosome.
Habitats
Many archaeans are extremophiles. They can survive and thrive at even relatively high temperatures, often above 100°C, as found in geysers,black smokers,and oil wells. Others are found in very cold habitats or in highly-saline, acidic, or alkaline water. However, other archaeans are mesophiles, and have been found in environments like marshland, sewage, sea water and soil. Many methanogenic archaea are found in the digestive tracts of animals such as ruminants, termites, and humans. As of 2007, no clear examples of archaean pathogens are known,[5][6] although a relationship has been proposed between the presence of some methanogens and human periodontal disease.[7]
Archaea are usually placed into three groups based on preferred habitat. These are the halophiles, methanogens, and thermophiles. Halophiles, sometimes known as Halobacterium live in extremely saline environments. Methanogens live in anaerobic environments and produce methane. These can be found in sediments or in the intestines of animals. Thermophiles live in places that have high temperatures, such as hot springs. These groups do not necessarily agree with molecular phylogenies, are not necessarily complete, nor are they mutually exclusive. Nonetheless, they are a useful starting point for more detailed studies.
Recently, several studies have shown that archaea exist not only in mesophilic and thermophilic environments but are also present, sometimes in high numbers, at low temperatures as well. It is increasingly becoming recognised that methanogens are commonly present in low-temperature environments such as cold sediments. Some studies have even suggested that at these temperatures the pathway by which methanogenesis occurs may change due to the thermodynamic constraints imposed by low temperatures. Perhaps even more significant are the large numbers of archaea found throughout most of the world's oceans, a predominantly cold environment (Giovannoni and Stingl, 2005). These archaea, which belong to several deeply branching lineages unrelated to those previously known, can be present in extremely high numbers (up to 40% of the microbial biomass) although almost none have been isolated in pure culture.[8] Currently we have almost no information regarding the physiology of these organisms meaning that their effects on global biogeochemical cycles remain unknown. One recent study has shown, however, that one group of marine crenarchaeota are capable of nitrification, a trait previously unknown among the archaea.[9]
Form
Individual archaeans range from 0.1 μm to over 15 μm in diameter, and some form aggregates or filaments up to 200 μm in length. They occur in various shapes, such as spherical, rod-shape, spiral, lobed, or rectangular. Archaea have no murein in their cell walls. Recently, a species of flat, square archaean that lives in hypersaline pools has been discovered.[10] They also exhibit a variety of different types of metabolism. Of note, the halobacteria can use light to produce ATP, although no Archaea conduct photosynthesis with an electron transport chain, as occurs in other groups. Rather light-activated ion pumps like bacteriorhodopsin and halorhodopsin play a role in generating ion gradients, whose energy then leads to production of ATP. Archaea can reproduce using binary and multiple fission, fragmentation, and budding.
Evolution and classification
Archaea are divided into two main groups based on rRNA trees, the Euryarchaeota and Crenarchaeota. Two other groups have been tentatively created for certain environmental samples and the peculiar species Nanoarchaeum equitans, discovered in 2002 by Karl Stetter, but their affinities are uncertain.[11]
Woese argued that the bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes each represent a primary line of descent that diverged early on from an ancestral progenote with poorly-developed genetic machinery. This hypothesis is reflected in the name Archaea, from the Greek archae or ancient. Later he treated these groups formally as domains, each comprising several kingdoms. This division has become very popular, although the idea of the progenote itself is not generally supported. Some biologists, however, have argued that the archaebacteria and eukaryotes arose from specialized eubacteria.
The relationship between Archaea and Eukarya remains an important problem. Aside from the similarities noted above, many genetic trees group the two together. Some place eukaryotes closer to Eurarchaeota than Crenarchaeota are, although the membrane chemistry suggests otherwise. However, the discovery of archaean-like genes in certain bacteria, such as Thermotoga, makes their relationship difficult to determine, as horizontal gene transfer may have occurred[12]. Some have suggested that eukaryotes arose through fusion of an archaean and eubacterium, which became the nucleus and cytoplasm, which accounts for various genetic similarities but runs into difficulties explaining cell structure.[13]
Single gene sequencing for systematics has led to whole genome sequencing; by January, 2007, 31 archaeal genomes have been completed with 29 partially completed [14].
Biologists who have studied Archaea
- Aled Edwards, Ph.D., University of Toronto
- Carl Woese, Ph.D., University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
- Karl Stetter, Ph.D.,University of Regensburg, Germany
- John N. Reeve, Ph.D., Ohio State University
- Rolf Bernander, Ph.D., Uppsala University, Sweden
- Michael W. Adams, Ph.D., University of Georgia
See also
- List of sequenced archeal genomes
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ Woese C, Fox G (1977). Phylogenetic structure of the prokaryotic domain: the primary kingdoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 74 (11): 5088–90.
- ↑ Woese, Carl R., Kandler, Otto, Wheelis, Mark L (1990). Towards a natural system of organisms: Proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 87 (12): 4576–4579.
- ↑ Hahn J, Haug P (1986). Traces of Archaebacteria in ancient sediments. System Appl Microbiol 7: 178-183..
- ↑ Chappe, B. and Albrecht, P. and Michaelis, W. ({1982). Polar Lipids of Archaebacteria in Sediments and Petroleums. Science 217: 65-66.
- ↑ Eckburg P, Lepp P, Relman D (2003). Archaea and their potential role in human disease. Infect Immun 71 (2): 591-6. PMID 12540534.
- ↑ Cavicchioli R, Curmi P, Saunders N, Thomas T (2003). Pathogenic archaea: do they exist?. Bioessays 25 (11): 1119-28. PMID 14579252.
- ↑ Lepp P, Brinig M, Ouverney C, Palm K, Armitage G, Relman D (2004). Methanogenic Archaea and human periodontal disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101 (16): 6176-81. PMID 15067114.
- ↑ Giovannoni SJ, Stingl U. (2005). Molecular diversity and ecology of microbial plankton. Nature 427 (7057): 343-8.
- ↑ Konneke M, Bernhard AE, de la Torre JR, Walker CB, Waterbury JB, Stahl DA. (2005). Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 437 (7057): 543-6.
- ↑ Burns DG, Camakaris HM, Janssen PH, Dyall-Smith ML. (2004). Cultivation of Walsby's square haloarchaeon.. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 238 (2): 469-73.
- ↑ Huber H, Hohn MJ, Rachel R, Fuchs T, Wimmer VC, Stetter KO. (2002). A new phylum of Archaea represented by a nanosized hyperthermophilic symbiont.. Nature 417 (6884): 27–8.
- ↑ Nelson KE. et al. (1999). Evidence for lateral gene transfer between Archaea and bacteria from genome sequence of Thermotoga maritima. Nature 399 (6734): 323-9.
- ↑ Lake JA. (1988). Origin of the eukaryotic nucleus determined by rate-invariant analysis of rRNA sequences. Nature 331 (6152): 184-6.
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/lproks.cgi
Further reading and external links
- Howland, John L. (2000). The Surprising Archaea: Discovering Another Domain of Life. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-511183-4.
- Archaea
- ArchaeaWeb - by UNSW - Information about Archaea
- Introduction to the Archaea, ecology, systematics and morphology
- Archaea at The Encyclopedia of Astrobiology, Astronomy, & Spaceflight
- Extremophiles Bioprospecting for antimicrobials, Dr Sarah Maloney Citat: "...Ground breaking research on extremophiles continues to this day, with the recently-discovered 22nd genetically-encoded amino acid – pyrrolysine – from the archaeon, Methanosarcina barkeri, (Hao et al., 2002; Srinivasan et al., 2002)...."
- BBC News July 21, 1999: Toughest bug reveals genetic secrets Citat: "...It [Pyrococcus abyssi] likes conditions that the vast majority of other organisms would find impossible to live in. It thrives best at temperatures of about 103 degrees [Celsius] and under pressures of about 200 atmospheres...."
- Pyrococcus abyssi Home page at Genoscope
- Browse any completed archaeal genome at UCSC
- 3D structures of proteins from archaebacterial membranes
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Categories |
Acidophile •
Alkaliphile •
Barophile •
Capnophile •
Endolith •
Halophile •
Hyperthermophile •
Hypolith •
Lithoautotroph •
Lithophile •
Oligotroph •
Osmophile •
Piezophile •
Polyextremophile •
Psychrophile •
Thermophile •
Xerophile •
| |||
|
Notable extromophiles |
| |||
|
Related articles |
Archaea •
Abiogenic petroleum origin •
Acidithiobacillales •
Acidobacteria •
Archaeoglobaceae •
Berkeley Pit •
Crenarchaeota •
Grylloblattidae •
Halobacteria •
Halobacterium •
Hydrothermal vent •
Methanopyrus •
Radioresistance •
Thermostability •
Thermotogae •
| |||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.

