Ulfilas
m (→Biography) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (45 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Images OK}}{{submitted}}{{approved}}{{copyedited}} | ||
| + | {{epname|Ulfilas}} | ||
{{Infobox clergy | {{Infobox clergy | ||
| name = Wulfila or Ulfilas | | name = Wulfila or Ulfilas | ||
| − | | image = | + | | image = Codex Argenteus.jpg |
| − | | image_size = | + | | image_size = 175px |
| − | | caption = | + | | caption = Page of the [[Silver Codex]] version of Ulfilas' Gothic Bible |
| birth_date = c. 311 | | birth_date = c. 311 | ||
| − | | birth_place = | + | | birth_place = Europe |
| death_date = 383 | | death_date = 383 | ||
| death_place = Constantinople | | death_place = Constantinople | ||
| church = | | church = | ||
| − | | other_names = | + | | other_names = Urphilas, Uphila |
| education = | | education = | ||
| − | | ordained = | + | | ordained = 330 |
| writings = translated the Bible into [[Gothic Language|Gothic]] | | writings = translated the Bible into [[Gothic Language|Gothic]] | ||
| − | | congregations = | + | | congregations = Goths and other Teutonic tribes |
| offices_held = Bishop of the [[Goths]] | | offices_held = Bishop of the [[Goths]] | ||
| − | | title = | + | | title = Apostle of the Goths |
| spouse = | | spouse = | ||
| − | | children = (adopted) [[Auxentius of | + | | children = (adopted) [[Auxentius of Milan]] |
| parents = | | parents = | ||
| footnotes = | | footnotes = | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | '''Wulfila''' (Gothic: "Little wolf" or Latin: '''Ulfilas/Ulphilas''') (c. 311 - 380 C.E.) was the [[apostle]] of the Goths, [[missionary]], translator of the [[Bible]], and inventor of the first Gothic alphabet. He was probably descended from Christians of [[Anatolia]] who were brought to Europe after being captured by the [[Goths]]. He was sent to [[Constantinople]] as a young man by the Goths as either an ambassador or a hostage, and was ordained a [[bishop]] by [[Eusebius of Nicomedia]] at the height of the [[arianism|Arian controversy]]. He then returned to the Goths in [[Dacia]] to work as a missionary. | |
| − | '''Wulfila''' ( | + | |
| + | In 348, to escape religious [[persecution]] by a Gothic chief, probably [[Athanaric]], Wulfia obtained permission from Emperor [[Constantius II]] to immigrate with part of his flock of converts to [[Moesia]] in what is now northern [[Bulgaria]]. Others among his converts became [[martyr]]s to their faith, a form of [[arianism|Arian Christianity]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In Moesia, Ulfilas translated the [[Bible]] from [[Greek language|Greek]] into the [[Gothic language]] after devising the first [[Gothic alphabet]]. He later participated in the church council at [[Constantinople]] in 360. The council attempted to solve the conflict between Arian and [[council of Nicaea|Nicene Christians]] by banning the previous [[creed]]s of both factions. | ||
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | Wulfia [[Christianization|converted]] many among the [[Goths]] who, when they conquered Rome as "[[barabarians]]," were in fact [[arianism|Arian Christians]]. Though largely unheralded by history due to his "heretical" views, he ranks among the greatest Christian missionaries of all time. Emperor Constantius II reportedly called him "the Moses of his day." | ||
| − | |||
==Biography== | ==Biography== | ||
| − | Born probably in 311 Ulfilas was descended from [[Cappadocia]]ns captured, during raids in Asia Minor by the Goths from the north of the Danube. According to fragments of the Cappadocian church historian Philostorgius, preserved by Saint [[Photius]] | + | [[Image:Young Folks' History of Rome illus368.png|thumb|200px|Gothic warriors on campaign in the fourth century.]] |
| + | Born probably in 311, Ulfilas was descended from [[Cappadocia]]ns captured, during raids in [[Asia Minor]] by the [[Goths]] from the north of the [[Danube]]. According to fragments of the Cappadocian church historian [[Philostorgius]], preserved by Saint [[Photius]], the Goths during the time of Emperor [[Valerian]] took many Christian prisoners, probably including Ulfilas' ancestors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As a young man he was sent by the Goths to [[Constantinople]], reportedly as an ambassador, though possibly as a hostage. There, he held the position of [[lector]] in the church of Constantinople and was consecrated as a [[bishop]] at the age of 30 by [[Eusebius of Nicomedia]], himself the [[archbishop]] of Constantinople and a celebrated [[arianism|Arian]] leader with high connections in the imperial court of [[Constantius II]]. | ||
| − | + | Shortly after his consecration, Ulfilas returned to [[Dacia]] as a [[missionary]]. During the remaining 40 years of his life he labored among his fellow countrymen, teaching them the Christian faith, though not adhering to the [[Nicene Creed]]. | |
| − | + | The first eight or ten years of his missionary life were spent in [[Dacia]]. The church historian [[Socrates Scholasticus]] attributes to Ulfilas the conversion of many of the Goths under the leadership of both [[Fritigernes]] and [[Athanaric]]. The latter, says Socrates, regarded this as "a violation of the privileges of the religion of his ancestors." Thus, "many of Arian Goths of that period became [[martyr]]s." (''Hist. eccl.'' IV) As a result of this persecution, Ulfilas was compelled to seek refuge in [[Moesia]], along with many of his Christian converts. | |
| − | + | In Moesia, he conceived the idea of translating the [[Bible]] into the language of the Goths. The task demanded as a preliminary that he should invent a special [[alphabet]]. His familiarity with [[Greek]] made the task comparatively simple, with only a few letters being borrowed from other sources, either [[Runic]] or [[Latin]]. | |
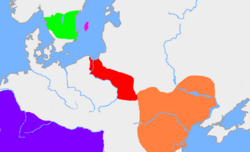
| − | + | [[Image:Chernyakhov.PNG|right|250px|thumb|Gothic territories through the early fourth century: The green area is [[Götaland]], the original land of the Goths in today's [[Sweden]]. The red area represents their area of influence in the early third century, and the orange area is the [[Chernyakhov culture]] of the early fourth century, the time of Ulfilas' birth. The purple area is the [[Roman Empire]].]] | |
| − | Ulfilas | + | Despite his many other activities, Ulfilas succeeded in translating "all the books of [[Scripture]] with the exception of the [[Books of Kings]], which he omitted because they are a mere narrative of military exploits, and the Gothic tribes were especially fond of war, and were in more need of restraints to check their military passions than of spurs to urge them on to deeds of war" (Philostorgius, ''Hist. eccl.,'' II, 5). He translated the books of the [[Old Testament]] from the [[Septuagint]] Greek version, and those of the [[New Testament]] from their original Greek. |
| − | + | Ulfilas was one of the bishops in attendance at the important church council called by [[Constantius II]] at Constantinople in 360, where Bishop [[Acacius of Caesarea]] triumphed and the council issued its compromise creed as a substitute for the formulas of both the Nicene and the Arian parties. In an effort to end the bitter acrimony between the conflicting sects, the council decreed that neither the word "substance" ''(ousia)'' nor ''hypostasis'' (translated as "persona" in Latin) should be used in theological creeds and declarations henceforth. Although affirming the [[Trinity]] of Father, Son, and Holy Spirit, it adopted what came to be known by its opponents as the "Semi-Arian" position: "We affirm that the Son is like the Father, in such a manner as the scared Scriptures declare and teach." The policy failed to win over the extreme partisans of either camp and was especially offensive to the Nicene party, since it abrogated the decision of a previous [[ecumenical council]], which had accepted the term ''homoousios'' ("same substance") in speaking of the Son and the Father. | |
| − | + | Ulfilas is thus be considered by "orthodox" Christianity to be an Arian [[heretic]]. The more sympathetic Philostorgius, however, reported that no less a personage that the Roman emperor himself "held Ulfilas in such high honor that he would often speak of him in conversation as 'the Moses of his day.'" | |
===The testimony of Auxentius=== | ===The testimony of Auxentius=== | ||
| − | The most detailed description of Ulfilas' life comes from a letter of [[Auxentius of Milan]], | + | The most detailed description of Ulfilas' life comes from a letter of his foster son and disciple, Bishop [[Auxentius of Milan]], (also called Auxentius Durostorum). Following the trinitarian formula that had been endorsed at Constantinople, Auxentius portrays Ulfilas not as an Arian ''per se,'' but as a semi-Arian who supported the view that neither ''homoousios'' (same substance: The Nicene term) nor ''homoiousos'' (like substance: The Arian term) should be used to describe the relationship between [[God the Father]] and [[God the Son]]. |
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Oratio Dominica.jpg|thumb|Part of [[The Lord's Prayer]] in Ulfilas' Gothic aplphabet]] | ||
| − | Auxentius declared Ulfilas to be "verily a confessor of Christ, a teacher of piety and a preacher of truth," who never hesitated to preach the Gospel to people of all ranks. Auxentius credits Ulfilas with "scatter(ing) the sect of the | + | Auxentius declared Ulfilas to be "verily a [[confessor]] of [[Christ]], a teacher of piety and a preacher of truth," who never hesitated to preach the Gospel to people of all ranks, even in dangerous circumstances among the pagan Goths. Auxentius also credits Ulfilas with "scatter(ing) the sect of the Homoousians (Nicene Christians), because he believed not in confused and concrete persons, but in discrete and distinct ones." On the other hand, Ulfilas also put the "Homoiousians" (Arians) to flight, "since they defended the assumption that (the Son and the Father) were not of comparable but different substance." |
Other heretics which Auxentius credits Ulfilas with opposing include: [[Manichaeans]], [[Marcion]]ists, [[Montanists]], [[Novatian]]ists, and [[Donatists]], among others. | Other heretics which Auxentius credits Ulfilas with opposing include: [[Manichaeans]], [[Marcion]]ists, [[Montanists]], [[Novatian]]ists, and [[Donatists]], among others. | ||
| − | Auxentius further testifies that "by the kindness of God and the grace of Christ he reared me bodily and spiritually as a son in the faith." He concludes his account | + | Auxentius further testifies that "by the kindness of God and the grace of Christ he reared me bodily and spiritually as a son in the faith." He concludes his account by appending Ulfilas' personal creed, which reads as follows: |
| − | <blockquote>I, Ulfila, bishop and confessor, have always so believed, and in this, the one true faith, I make the journey to my Lord | + | <blockquote>I, Ulfila, [[bishop]] and confessor, have always so believed, and in this, the one true faith, (as) I make the journey to my Lord: I believe in one God the Father, the only unbegotten and invisible, and in his only-begotten Son, our Lord and God, the designer and maker of all creation, having none other like him (so that one alone among all beings is God the Father, who is also the God of our God); and in one Holy Spirit, the illuminating and sanctifying power, as Christ said after his resurrection to his apostles: "And behold, I send the promise of my Father upon you; but tarry ye in the city of Jerusalem, until ye be clothed with power from on high" (Luke 24:49) and again: "But ye shall receive power, when the Holy Ghost is come upon you" (Acts 1:8); being neither God (the Father) nor our God (Christ), but the minister of Christ… subject and obedient in all things to the Son; and the Son, subject and obedient in all things to God who is his Father… (whom) he ordained in the Holy Spirit through his Christ.</blockquote> |
==Legacy== | ==Legacy== | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Alaric.jpg|thumb|300px|[[Alaric I]], who conquered Rome in 410 C.E., was an Arian Christian, and thus one of the fruits of Ulfilas' labors.]] | |
| + | Had he not sided with the losing party in the crucial theological controversy of his day, Ulfilas would certainly have been known as one of the greatest [[saint]]s in history. He courageously brought the [[Gospel]] to the [[Goths]], instilling in them a faith that led many to accept [[martyrdom]]. Although condemned in most histories as "barbarians," the Gothic tribes who overtook Europe and eventually captured even [[Rome]] itself were in reality not [[pagans]], but [[arianism|Arian Christians]], due largely to Ulfilas' influence. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Goths tended not to interfere in the theological affairs of the Christians of the [[Roman Empire]]. Even though they were technically heretics, their ascendancy in the West actually aided the [[Catholic Church]] immensely. It allowed the Roman church to develop relatively free from state influence, providing a much-needed counterbalance to the meddling of the eastern Roman emperors at [[Constantinople]], who sought to use the Christian religion as an instrument of the state. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Theologically, Ulfilas' legacy was ultimately wiped out by the resurgence of Nicene [[orthodoxy]] and the demise of both Arian and Semi-Arian Christianity. A more lasting contribution is his invention of the [[Gothic alphabet]] and his translation of the [[Bible]] into the previously unwritten Gothic language. A few chapters of Ulfilas' translation of the [[Old Testament]] are still in existence. Of the [[New Testament]], the greater portion of the Gospels have been maintained in the beautiful [[Silver Codex]] (a purple parchment with silver and gold letters) now at [[Upsala]], dating from the fifth century. Nearly all of his translations of [[Saint Paul]]'s epistles can still be found in a Milanese codex as well. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Goths]] |
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Arianism]] |
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Semiarianism]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| + | * Marchand, James Woodrow.'' The Sounds and Phonemes of Wulfila's Gothic''. Janua linguarum. Series practica, v. 25. The Hague: Mouton, 1973. OCLC 730566. | ||
| + | * Sumruld, William A. ''Augustine and the Arians: the Bishop of Hippo's encounters with Ulfilan Arianism''. Selinsgrove: Susquehanna Univ. Press u.a, 1994. ISBN 9780945636465. | ||
| + | * Thompson, E. A. ''The Visigoths in the Time of Ulfila''. London: Duckworth, 2008. ISBN 9780715637005. | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| − | + | All links retrieved May 20, 2023. | |
| − | *[http://www.wulfila.be Project Wulfila] | + | |
| + | *[http://www.wulfila.be Project Wulfila internet resource]. ''wulfila.be'' | ||
[[Category:religion]] | [[Category:religion]] | ||
[[Category:Christianity]] | [[Category:Christianity]] | ||
| + | [[Category:biography]] | ||
| + | [[Category:religious figures]] | ||
| + | [[Category:literature]] | ||
| + | [[Category:theology]] | ||
{{credit|246120978}} | {{credit|246120978}} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:10, 20 May 2023
Wulfila (Gothic: "Little wolf" or Latin: Ulfilas/Ulphilas) (c. 311 - 380 C.E.) was the apostle of the Goths, missionary, translator of the Bible, and inventor of the first Gothic alphabet. He was probably descended from Christians of Anatolia who were brought to Europe after being captured by the Goths. He was sent to Constantinople as a young man by the Goths as either an ambassador or a hostage, and was ordained a bishop by Eusebius of Nicomedia at the height of the Arian controversy. He then returned to the Goths in Dacia to work as a missionary.
In 348, to escape religious persecution by a Gothic chief, probably Athanaric, Wulfia obtained permission from Emperor Constantius II to immigrate with part of his flock of converts to Moesia in what is now northern Bulgaria. Others among his converts became martyrs to their faith, a form of Arian Christianity.
In Moesia, Ulfilas translated the Bible from Greek into the Gothic language after devising the first Gothic alphabet. He later participated in the church council at Constantinople in 360. The council attempted to solve the conflict between Arian and Nicene Christians by banning the previous creeds of both factions.
Wulfia converted many among the Goths who, when they conquered Rome as "barabarians," were in fact Arian Christians. Though largely unheralded by history due to his "heretical" views, he ranks among the greatest Christian missionaries of all time. Emperor Constantius II reportedly called him "the Moses of his day."
Biography
Born probably in 311, Ulfilas was descended from Cappadocians captured, during raids in Asia Minor by the Goths from the north of the Danube. According to fragments of the Cappadocian church historian Philostorgius, preserved by Saint Photius, the Goths during the time of Emperor Valerian took many Christian prisoners, probably including Ulfilas' ancestors.
As a young man he was sent by the Goths to Constantinople, reportedly as an ambassador, though possibly as a hostage. There, he held the position of lector in the church of Constantinople and was consecrated as a bishop at the age of 30 by Eusebius of Nicomedia, himself the archbishop of Constantinople and a celebrated Arian leader with high connections in the imperial court of Constantius II.
Shortly after his consecration, Ulfilas returned to Dacia as a missionary. During the remaining 40 years of his life he labored among his fellow countrymen, teaching them the Christian faith, though not adhering to the Nicene Creed.
The first eight or ten years of his missionary life were spent in Dacia. The church historian Socrates Scholasticus attributes to Ulfilas the conversion of many of the Goths under the leadership of both Fritigernes and Athanaric. The latter, says Socrates, regarded this as "a violation of the privileges of the religion of his ancestors." Thus, "many of Arian Goths of that period became martyrs." (Hist. eccl. IV) As a result of this persecution, Ulfilas was compelled to seek refuge in Moesia, along with many of his Christian converts.
In Moesia, he conceived the idea of translating the Bible into the language of the Goths. The task demanded as a preliminary that he should invent a special alphabet. His familiarity with Greek made the task comparatively simple, with only a few letters being borrowed from other sources, either Runic or Latin.
Despite his many other activities, Ulfilas succeeded in translating "all the books of Scripture with the exception of the Books of Kings, which he omitted because they are a mere narrative of military exploits, and the Gothic tribes were especially fond of war, and were in more need of restraints to check their military passions than of spurs to urge them on to deeds of war" (Philostorgius, Hist. eccl., II, 5). He translated the books of the Old Testament from the Septuagint Greek version, and those of the New Testament from their original Greek.
Ulfilas was one of the bishops in attendance at the important church council called by Constantius II at Constantinople in 360, where Bishop Acacius of Caesarea triumphed and the council issued its compromise creed as a substitute for the formulas of both the Nicene and the Arian parties. In an effort to end the bitter acrimony between the conflicting sects, the council decreed that neither the word "substance" (ousia) nor hypostasis (translated as "persona" in Latin) should be used in theological creeds and declarations henceforth. Although affirming the Trinity of Father, Son, and Holy Spirit, it adopted what came to be known by its opponents as the "Semi-Arian" position: "We affirm that the Son is like the Father, in such a manner as the scared Scriptures declare and teach." The policy failed to win over the extreme partisans of either camp and was especially offensive to the Nicene party, since it abrogated the decision of a previous ecumenical council, which had accepted the term homoousios ("same substance") in speaking of the Son and the Father.
Ulfilas is thus be considered by "orthodox" Christianity to be an Arian heretic. The more sympathetic Philostorgius, however, reported that no less a personage that the Roman emperor himself "held Ulfilas in such high honor that he would often speak of him in conversation as 'the Moses of his day.'"
The testimony of Auxentius
The most detailed description of Ulfilas' life comes from a letter of his foster son and disciple, Bishop Auxentius of Milan, (also called Auxentius Durostorum). Following the trinitarian formula that had been endorsed at Constantinople, Auxentius portrays Ulfilas not as an Arian per se, but as a semi-Arian who supported the view that neither homoousios (same substance: The Nicene term) nor homoiousos (like substance: The Arian term) should be used to describe the relationship between God the Father and God the Son.
Auxentius declared Ulfilas to be "verily a confessor of Christ, a teacher of piety and a preacher of truth," who never hesitated to preach the Gospel to people of all ranks, even in dangerous circumstances among the pagan Goths. Auxentius also credits Ulfilas with "scatter(ing) the sect of the Homoousians (Nicene Christians), because he believed not in confused and concrete persons, but in discrete and distinct ones." On the other hand, Ulfilas also put the "Homoiousians" (Arians) to flight, "since they defended the assumption that (the Son and the Father) were not of comparable but different substance."
Other heretics which Auxentius credits Ulfilas with opposing include: Manichaeans, Marcionists, Montanists, Novatianists, and Donatists, among others.
Auxentius further testifies that "by the kindness of God and the grace of Christ he reared me bodily and spiritually as a son in the faith." He concludes his account by appending Ulfilas' personal creed, which reads as follows:
I, Ulfila, bishop and confessor, have always so believed, and in this, the one true faith, (as) I make the journey to my Lord: I believe in one God the Father, the only unbegotten and invisible, and in his only-begotten Son, our Lord and God, the designer and maker of all creation, having none other like him (so that one alone among all beings is God the Father, who is also the God of our God); and in one Holy Spirit, the illuminating and sanctifying power, as Christ said after his resurrection to his apostles: "And behold, I send the promise of my Father upon you; but tarry ye in the city of Jerusalem, until ye be clothed with power from on high" (Luke 24:49) and again: "But ye shall receive power, when the Holy Ghost is come upon you" (Acts 1:8); being neither God (the Father) nor our God (Christ), but the minister of Christ… subject and obedient in all things to the Son; and the Son, subject and obedient in all things to God who is his Father… (whom) he ordained in the Holy Spirit through his Christ.
Legacy
Had he not sided with the losing party in the crucial theological controversy of his day, Ulfilas would certainly have been known as one of the greatest saints in history. He courageously brought the Gospel to the Goths, instilling in them a faith that led many to accept martyrdom. Although condemned in most histories as "barbarians," the Gothic tribes who overtook Europe and eventually captured even Rome itself were in reality not pagans, but Arian Christians, due largely to Ulfilas' influence.
The Goths tended not to interfere in the theological affairs of the Christians of the Roman Empire. Even though they were technically heretics, their ascendancy in the West actually aided the Catholic Church immensely. It allowed the Roman church to develop relatively free from state influence, providing a much-needed counterbalance to the meddling of the eastern Roman emperors at Constantinople, who sought to use the Christian religion as an instrument of the state.
Theologically, Ulfilas' legacy was ultimately wiped out by the resurgence of Nicene orthodoxy and the demise of both Arian and Semi-Arian Christianity. A more lasting contribution is his invention of the Gothic alphabet and his translation of the Bible into the previously unwritten Gothic language. A few chapters of Ulfilas' translation of the Old Testament are still in existence. Of the New Testament, the greater portion of the Gospels have been maintained in the beautiful Silver Codex (a purple parchment with silver and gold letters) now at Upsala, dating from the fifth century. Nearly all of his translations of Saint Paul's epistles can still be found in a Milanese codex as well.
See also
- Goths
- Arianism
- Semiarianism
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Marchand, James Woodrow. The Sounds and Phonemes of Wulfila's Gothic. Janua linguarum. Series practica, v. 25. The Hague: Mouton, 1973. OCLC 730566.
- Sumruld, William A. Augustine and the Arians: the Bishop of Hippo's encounters with Ulfilan Arianism. Selinsgrove: Susquehanna Univ. Press u.a, 1994. ISBN 9780945636465.
- Thompson, E. A. The Visigoths in the Time of Ulfila. London: Duckworth, 2008. ISBN 9780715637005.
External links
All links retrieved May 20, 2023.
- Project Wulfila internet resource. wulfila.be
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.



