Difference between revisions of "Radio astronomy" - New World Encyclopedia
(ready) |
(imported latest version of article from Wikipedia) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
[[Image:USA.NM.VeryLargeArray.02.jpg|thumb|200px|The [[Very Large Array]], a radio [[interferometry|interferometer]] in [[New Mexico]], [[United States|USA]]]] | [[Image:USA.NM.VeryLargeArray.02.jpg|thumb|200px|The [[Very Large Array]], a radio [[interferometry|interferometer]] in [[New Mexico]], [[United States|USA]]]] | ||
| − | '''Radio astronomy''' is a subfield of [[astronomy]] that studies [[Astronomical object|celestial objects]] | + | '''Radio astronomy''' is a subfield of [[astronomy]] that studies [[Astronomical object|celestial objects]] at [[radio frequency|radio frequencies]]. The physical processes which produce radio waves are very different to those that produce light in other parts of the [[electromagnetic spectrum]] and the great advances in radio astronomy that took place after the Second World War yielded a number of important discoveries including [[Radio galaxy|Radio Galaxies]], [[Pulsars]], [[Astrophysical maser|Masers]] and the [[Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation]]. The development of [[Astronomical interferometer|radio interferometry]] and [[aperture synthesis]] has allowed radio sources to be imaged with unprecedented angular resolution. |
== History == | == History == | ||
| − | The idea that celestial bodies may be emitting radio waves had been suspected some time before its discovery. In the 1860's [[James Clerk Maxwell]]'s [[Maxwell's equations|equations]] had shown that electromagnetic radiation from stellar sources could exist with any wavelength, not just optical. Several notable scientists and experimenters such as [[ | + | The idea that celestial bodies may be emitting radio waves had been suspected some time before its discovery. In the 1860's [[James Clerk Maxwell]]'s [[Maxwell's equations|equations]] had shown that electromagnetic radiation from stellar sources could exist with any wavelength, not just optical. Several notable scientists and experimenters such as [[Nikola Tesla]], [[Oliver Lodge]], and [[Max Planck]] predicted that the sun should be emitting radio waves. Lodge tried to observe solar signals but was unable to detect them due to technical limitations of his apparatus<ref>http://www.nrao.edu/whatisra/hist_prehist.shtml NRAO.org, ''"Pre-History of Radio Astronomy"'' Compiled by F. Ghigo</ref>. |
| − | The first identified astronomical radio source was one discovered [[Serendipity|serendipitously]] in the early 1930s when [[Karl Guthe Jansky]], an engineer with [[Bell Labs|Bell Telephone Laboratories]], was investigating static that interfered with [[short wave]] transatlantic voice transmissions. Using a large [[directional antenna]], Jansky noticed that his [[analog signal|analog]] pen-and-paper recording system kept recording a repeating signal of unknown origin. Since the signal peaked once a day, Jansky originally suspected the source of the interference was the sun. Continued analysis showed that the source was not following the rising and setting of the sun | + | The first identified astronomical radio source was one discovered [[Serendipity|serendipitously]] in the early 1930s when [[Karl Guthe Jansky]], an engineer with [[Bell Labs|Bell Telephone Laboratories]], was investigating static that interfered with [[short wave]] transatlantic voice transmissions. Using a large [[directional antenna]], Jansky noticed that his [[analog signal|analog]] pen-and-paper recording system kept recording a repeating signal of unknown origin. Since the signal peaked once a day, Jansky originally suspected the source of the interference was the sun. Continued analysis showed that the source was not following the 24 hour cycle for the rising and setting of the sun but instead repeating on a cycle of 23 hours and 56 minutes, typical of an astronomical source "fixed" on the [[celestial sphere]] rotating in sync with [[sidereal day|sidereal time]]. By comparing his observations with optical astronomical maps, Jansky concluded that the radiation was coming from the [[Milky Way]] and was strongest in the direction of the center of the galaxy, in the [[constellation]] of [[Sagittarius (constellation)|Sagittarius]] <ref>Karl G. Jansky, "Radio waves from outside the solar system", Nature, 132, p.66. 1933</ref>. He announced his discovery in [[1933]]. Jansky wanted to investigate the radio waves from the Milky Way in further detail but Bell Labs re-assigned Jansky to another project, so he did no further work in the field of astronomy. |
| − | [[Grote Reber]] helped pioneer radio astronomy when he built a large parabolic "dish" radio telescope (9m in diameter) in 1937. He was instrumental in repeating Karl Guthe Jansky's pioneering but somewhat simple work, and went on to conduct the first sky survey in the radio frequencies <ref>[http://www.nrao.edu/whatisra/hist_reber.shtml Grote Reber] | + | [[Grote Reber]] helped pioneer radio astronomy when he built a large parabolic "dish" radio telescope (9m in diameter) in 1937. He was instrumental in repeating Karl Guthe Jansky's pioneering but somewhat simple work, and went on to conduct the first sky survey in the radio frequencies <ref>[http://www.nrao.edu/whatisra/hist_reber.shtml Grote Reber<!-- Bot generated title —>]</ref>. On [[February 27]] [[1942]], [[J.S. Hey]], a [[British Army]] research officer, helped progress radio astronomy further, when he discovered that the sun emitted radio waves <ref> J. S. Hey. The Radio Universe, 2nd Ed., Pergamon Press, Oxford-New York (1975), </ref>. By the early 1950s [[Martin Ryle]] and [[Antony Hewish]] at [[University of Cambridge|Cambridge University]] had used the [[Cambridge Interferometer]] to map the radio sky, producing the famous [[Second Cambridge Catalogue of Radio Sources|2C]] and [[Third Cambridge Catalogue of Radio Sources|3C]] surveys of radio sources. |
==Techniques== | ==Techniques== | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
===Radio telescopes=== | ===Radio telescopes=== | ||
{{main|Radio telescope}} | {{main|Radio telescope}} | ||
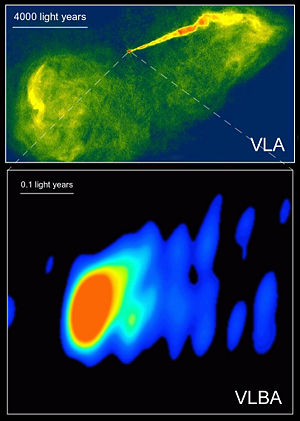
| − | [[Image: M87_optical_image.jpg |thumb|300px]][[Image: M87_VLA_VLBA_radio_astronomy.jpg|thumb|300px| An '''optical''' image of the galaxy M87 ([[Hubble Space Telescope|HST]]), a radio image of same galaxy using '''Interferometry''' ([[Very Large Array]]-'''VLA'''), and an image of the center section | + | [[Image: M87_optical_image.jpg |thumb|300px]][[Image: M87_VLA_VLBA_radio_astronomy.jpg|thumb|300px| An '''optical''' image of the galaxy M87 ([[Hubble Space Telescope|HST]]), a radio image of same galaxy using '''Interferometry''' ([[Very Large Array]]-'''VLA'''), and an image of the center section ('''VLBA''') using a ''Very Long Baseline Array'' (Global VLBI) consisting of antennas in the US, Germany, Italy, Finland, Sweden and Spain. The jet of particles is suspected to be powered by a [[black hole]] in the center of the galaxy.]] |
Radio telescopes may need to be extremely large in order to receive signals with low [[signal-to-noise ratio]]. Also since [[angular resolution]] is a function of the diameter of the "[[Objective (optics)|objective]]" in proportion to the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation being observed, ''[[radio telescope]]s'' have to be much larger in comparison to their [[Optical telescope|optical]] counterparts. For example a 1 meter diameter optical telescope is two million times bigger than the wavelength of light observed giving it a resolution of a few [[arc second]]s, whereas a radio telescope "dish" many times that size may, depending on the wavelength observed, may only be able to resolve an object the size of the full moon (30 minutes of arc). | Radio telescopes may need to be extremely large in order to receive signals with low [[signal-to-noise ratio]]. Also since [[angular resolution]] is a function of the diameter of the "[[Objective (optics)|objective]]" in proportion to the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation being observed, ''[[radio telescope]]s'' have to be much larger in comparison to their [[Optical telescope|optical]] counterparts. For example a 1 meter diameter optical telescope is two million times bigger than the wavelength of light observed giving it a resolution of a few [[arc second]]s, whereas a radio telescope "dish" many times that size may, depending on the wavelength observed, may only be able to resolve an object the size of the full moon (30 minutes of arc). | ||
===Radio interferometry=== | ===Radio interferometry=== | ||
| − | The difficulty in achieving high resolutions with single radio telescopes led to radio [[interferometry]], developed by British radio astronomer [[Martin Ryle]] and Australian-born engineer, | + | The difficulty in achieving high resolutions with single radio telescopes led to radio [[interferometry]], developed by British radio astronomer [[Martin Ryle]] and Australian-born engineer, radiophysicist, and radio astronomer [[Joseph Lade Pawsey]] in [[1946]]. [[Radio telescope#Radio interferometry|Radio interferometers]] consist of widely separated radio telescopes observing the same object that are connected together using [[coaxial cable]], [[waveguide]], [[optical fiber]], or other type of [[transmission line]]. This not only increases the total signal collected, it can also be used in a process called [[Aperture synthesis]] to vastly increase resolution. This technique works by superposing ('''[[Interference|interfering]]''') the signal [[wave]]s from the different telescopes on the principle that [[wave]]s that coincide with the same [[phase (waves)|phase]] will add to each other while two waves that have opposite phases will cancel each other out. This creates a combined telescope that is the size of the antennas furthest apart in the array. In order to produce a high quality image, a large number of different separations between different telescopes are required (the projected separation between any two telescopes as seen from the radio source is called a '''baseline''') - as many different baselines as possible are required in order to get a good quality image. For example the [[Very Large Array]] has 27 telescopes giving 351 independent baselines at once. |
==== Very Long Baseline Interferometry==== | ==== Very Long Baseline Interferometry==== | ||
| − | Since the 1970s telescopes from all over the world (and even in Earth orbit) have been combined to perform [[Very Long Baseline Interferometry]]. Data received at each antenna is paired with timing information, usually from a local [[atomic clock]], and then stored for later analysis on magnetic tape or hard disk. At that later time, the data is correlated with data from other antennas similarly recorded, to produce the resulting image. Using this method it is possible to | + | Since the 1970s telescopes from all over the world (and even in Earth orbit) have been combined to perform [[Very Long Baseline Interferometry]]. Data received at each antenna is paired with timing information, usually from a local [[atomic clock]], and then stored for later analysis on magnetic tape or hard disk. At that later time, the data is correlated with data from other antennas similarly recorded, to produce the resulting image. Using this method it is possible to synthesise an antenna that is effectively the size of the Earth. The large distances between the telescopes enable very high angular resolutions to be achieved, much greater in fact than in any other field of astronomy. At the highest frequencies, synthesised beams less than 1 [[milliarcsecond]] are possible. |
| − | + | The pre-eminent VLBI arrays operating today are the [[Very Long Baseline Array]] (with telescopes located across the North America) and the [[European VLBI Network]] (telescopes in Europe, China, South Africa and Puerto Rico). Each array usually operates separately, but occasional projects are observed together producing increased sensitivity. This is referred to as Global VLBI. There is also a VLBI network, the Long Baseline Array, operating in Australia. | |
| + | |||
| + | Since its inception, recording data onto hard media has been the only way to bring the data recorded at each telescope together for later correlation. However, the availability today of worldwide, high-bandwidth optical fibre networks makes it possible to do VLBI in real time. This technique (referred to as e-VLBI) has been pioneered by the EVN who now perform an increasing number of scientific e-VLBI projects per year.<ref>[http://www.innovations-report.com/html/reports/physics_astronomy/report-25117.html A technological breakthrough for radio astronomy - Astronomical observations via high-speed data link<!-- Bot generated title —>]</ref> | ||
==Astronomical sources == | ==Astronomical sources == | ||
| Line 30: | Line 31: | ||
Radio astronomy has led to substantial increases in astronomical knowledge, particularly with the discovery of several classes of new objects, including [[pulsar]]s, [[quasar]]s and [[radio galaxy|radio galaxies]]. This is because radio astronomy allows us to see things that are not detectable in optical astronomy. Such objects represent some of the most extreme and energetic physical processes in the universe. | Radio astronomy has led to substantial increases in astronomical knowledge, particularly with the discovery of several classes of new objects, including [[pulsar]]s, [[quasar]]s and [[radio galaxy|radio galaxies]]. This is because radio astronomy allows us to see things that are not detectable in optical astronomy. Such objects represent some of the most extreme and energetic physical processes in the universe. | ||
| − | Radio astronomy is also partly responsible for the idea that [[dark matter]] is an important component of our universe; radio measurements of the rotation of [[galaxy|galaxies]] suggest that there is much more mass in galaxies than has been directly observed | + | Radio astronomy is also partly responsible for the idea that [[dark matter]] is an important component of our universe; radio measurements of the rotation of [[galaxy|galaxies]] suggest that there is much more mass in galaxies than has been directly observed. The [[cosmic microwave background radiation]] was also first detected using radio telescopes. However, radio telescopes have also been used to investigate objects much closer to home, including observations of the [[Sun]] and solar activity, and radar mapping of the [[solar system|planets]]. |
Other sources include: | Other sources include: | ||
| + | * [[Sun]] | ||
* [[Sagittarius A]], the [[galactic center]] of the [[Milky Way]] | * [[Sagittarius A]], the [[galactic center]] of the [[Milky Way]] | ||
* [[Active Galactic Nucleus|Active galactic nuclei]] and [[pulsar]]s have jets of charged particles which emit [[synchrotron radiation]] | * [[Active Galactic Nucleus|Active galactic nuclei]] and [[pulsar]]s have jets of charged particles which emit [[synchrotron radiation]] | ||
| Line 39: | Line 41: | ||
* The [[Cosmic microwave background]] is [[blackbody]] radio emission | * The [[Cosmic microwave background]] is [[blackbody]] radio emission | ||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | {{Portal|Radio|Radio icon.png}} | ||
| + | *[[History of astronomical interferometry]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Notes == | ||
| + | <div style="font-size:87.5%; -moz-column-count:2; column-count:2;"> | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | * [http://www.nrao.edu/ nrao.edu], [http://www.nrao.edu/whatisra/radiotel.shtml How Radio Telescopes Work] | ||
| + | * [http://www.mpa-garching.mpg.de/~lxl/personal/images/science/m87.html The Jet of Galaxy M87] | ||
| + | * [http://www.nrao.edu/whatisra/radiotel.shtml NRAO—What is Radio Astronomy] | ||
==Further reading== | ==Further reading== | ||
====Journals==== | ====Journals==== | ||
| Line 49: | Line 64: | ||
====Books==== | ====Books==== | ||
<div style="font-size:87.5%; -moz-column-count:2; column-count:2;"> | <div style="font-size:87.5%; -moz-column-count:2; column-count:2;"> | ||
| − | * Sullivan, | + | * Woodruff T. Sullivan, III, ''The early years of radio astronomy''. 1984. |
| − | * Sullivan, | + | * Woodruff T. Sullivan, III, ''Classics in Radio Astronomy''. Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht, 1982. |
| − | * Rohlfs, | + | * Kristen Rohlfs, Thomas L Wilson, ''Tools of Radio Astronomy''. Springer 2003. 461 pages. ISBN 3540403876 |
| − | * Haynes, | + | * Raymond Haynes, Roslynn Haynes, and Richard McGee, ''Explorers of the Southern Sky: A History of Australian Astronomy''. Cambridge University Press 1996. 541 pages. ISBN 0521365759 |
| − | * Nakayama, | + | * Shigeru Nakayama, ''A Social History of Science and Technology in Contemporary Japan: Transformation Period 1970-1979''. Trans Pacific Press 2006. 580 pages. ISBN 1876843462 |
| − | * | + | * David L. Jauncey, ''Radio Astronomy and Cosmology''. Springer 1977. 420 pages. ISBN 9027708398 |
| − | * | + | * Allan A. Needell, ''Science, Cold War and American State: Lloyd V. Berkner and the Balance of Professional Ideals''. Routledge 2000. ISBN 905702621X (ed., see Chapter 10, Expanding Federal Support of Private Research: The Case of Radio Astronomy (Pages 259 - 596)) |
| − | * Bertotti, | + | * Bruno Bertotti, ''Modern Cosmology in Retrospect''. Cambridge University Press 1990. 446 pages. ISBN 0521372135 (ed., see essays by Robert Wilson, ''Discovery of the cosmic microwave background'' and Woodruff T. Sullivan, III, ''The entry of radio astronomy into cosmology: radio stars and 309 Martin Ryle's 2C survey''.)) |
| − | * | + | * J. S. Hey, ''The Evolution of Radio Astronomy''. Neale Watson Academic, 1973. |
| − | * | + | * D. T. Wilkinson and P. J. E. Peebles, ''Serendipitous Discoveries in Radio Astronomy''. National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Green Bank, WV, 1983. |
| − | * Pawsey | + | *Joseph Lade Pawsey and Ronald Newbold Bracewell, ''Radio Astronomy''. Clarendon Press, 1955. 361 pages. |
| − | * | + | *J. C.Kapteyn, P. C. v. d. Kruit, & K. v. Berkel,'' The legacy of J.C. Kapteyn: studies on Kapteyn and the development of modern astronomy''. Astrophysics and space science library, v. 246. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers 2000. |
| − | * Jennison, | + | * Roger Clifton Jennison, ''Introduction to Radio Astronomy''. 1967. 160 pages. |
| − | * Green, | + | * Robin Michael Green, ''Spherical Astronomy''. Cambridge University Press 1985. 546 pages. ISBN 0521317797 |
| − | * Krüger, | + | * Albrecht Krüger, ''Introduction to Solar Radio Astronomy and Radio Physics''. Springer 1979. 356 pages. ISBN 9027709572 |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| Line 84: | Line 87: | ||
;History (America, Post 1930s) | ;History (America, Post 1930s) | ||
* [http://www.nrao.edu/whatisra/history.shtml History of Radio Astronomy], National Radio Astronomy Observatory | * [http://www.nrao.edu/whatisra/history.shtml History of Radio Astronomy], National Radio Astronomy Observatory | ||
| − | * [http://www.haystack.edu/ Haystack Observatory], [[MIT]] | + | * [http://web.haystack.mit.edu/education/radiohist.html The History of Radio Astronomy] - [http://www.haystack.edu/ Haystack Observatory], [[MIT]] |
| + | * Hanes, Dave, "''Physics 014: The Course Notes, [http://www.astro.queensu.ca/~hanes/p014/Notes/Topic_048.html Radio Astronomy]''". Astronomy Group and Department of Physics, Queen's University. 2000-2001. | ||
* [http://www.cr.nps.gov/history/online_books/butowsky5/astro4o.htm Reber Radio Telescope] - National Park Services | * [http://www.cr.nps.gov/history/online_books/butowsky5/astro4o.htm Reber Radio Telescope] - National Park Services | ||
* [http://edmall.gsfc.nasa.gov/aacps/news/Radio_Telescope.html Radio Telescope Developed] - a brief history from [[NASA]] [[Goddard Space Flight Center]] | * [http://edmall.gsfc.nasa.gov/aacps/news/Radio_Telescope.html Radio Telescope Developed] - a brief history from [[NASA]] [[Goddard Space Flight Center]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Observational astronomy]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Astronomical imaging]] |
| + | [[Category:Radio astronomy| ]] | ||
| − | + | [[bn:রেডিও জ্যোতির্বিজ্ঞান]] | |
| + | [[bg:Радиоастрономия]] | ||
| + | [[cs:Radioastronomie]] | ||
| + | [[da:Radioastronomi]] | ||
| + | [[de:Radioastronomie]] | ||
| + | [[es:Radioastronomía]] | ||
| + | [[eo:Radioastronomio]] | ||
| + | [[fa:اخترشناسی رادیویی]] | ||
| + | [[fr:Radioastronomie]] | ||
| + | [[hr:Radio astronomija]] | ||
| + | [[id:Astronomi radio]] | ||
| + | [[it:Radioastronomia]] | ||
| + | [[lt:Radioastronomija]] | ||
| + | [[nl:Radioastronomie]] | ||
| + | [[ja:電波天文学]] | ||
| + | [[no:Radioastronomi]] | ||
| + | [[pl:Radioastronomia]] | ||
| + | [[pt:Radioastronomia]] | ||
| + | [[ru:Радиоастрономия]] | ||
| + | [[sk:Rádioastronómia]] | ||
| + | [[sr:Radioastronomija]] | ||
| + | [[fi:Radioastronomia]] | ||
| + | [[sv:Radioastronomi]] | ||
| + | [[vi:Thiên văn vô tuyến]] | ||
| + | [[tr:Radyo astronomi]] | ||
| + | [[zh:射电天文学]] | ||
Revision as of 13:27, 25 August 2008
Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies celestial objects at radio frequencies. The physical processes which produce radio waves are very different to those that produce light in other parts of the electromagnetic spectrum and the great advances in radio astronomy that took place after the Second World War yielded a number of important discoveries including Radio Galaxies, Pulsars, Masers and the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation. The development of radio interferometry and aperture synthesis has allowed radio sources to be imaged with unprecedented angular resolution.
History
The idea that celestial bodies may be emitting radio waves had been suspected some time before its discovery. In the 1860's James Clerk Maxwell's equations had shown that electromagnetic radiation from stellar sources could exist with any wavelength, not just optical. Several notable scientists and experimenters such as Nikola Tesla, Oliver Lodge, and Max Planck predicted that the sun should be emitting radio waves. Lodge tried to observe solar signals but was unable to detect them due to technical limitations of his apparatus[1].
The first identified astronomical radio source was one discovered serendipitously in the early 1930s when Karl Guthe Jansky, an engineer with Bell Telephone Laboratories, was investigating static that interfered with short wave transatlantic voice transmissions. Using a large directional antenna, Jansky noticed that his analog pen-and-paper recording system kept recording a repeating signal of unknown origin. Since the signal peaked once a day, Jansky originally suspected the source of the interference was the sun. Continued analysis showed that the source was not following the 24 hour cycle for the rising and setting of the sun but instead repeating on a cycle of 23 hours and 56 minutes, typical of an astronomical source "fixed" on the celestial sphere rotating in sync with sidereal time. By comparing his observations with optical astronomical maps, Jansky concluded that the radiation was coming from the Milky Way and was strongest in the direction of the center of the galaxy, in the constellation of Sagittarius [2]. He announced his discovery in 1933. Jansky wanted to investigate the radio waves from the Milky Way in further detail but Bell Labs re-assigned Jansky to another project, so he did no further work in the field of astronomy.
Grote Reber helped pioneer radio astronomy when he built a large parabolic "dish" radio telescope (9m in diameter) in 1937. He was instrumental in repeating Karl Guthe Jansky's pioneering but somewhat simple work, and went on to conduct the first sky survey in the radio frequencies [3]. On February 27 1942, J.S. Hey, a British Army research officer, helped progress radio astronomy further, when he discovered that the sun emitted radio waves [4]. By the early 1950s Martin Ryle and Antony Hewish at Cambridge University had used the Cambridge Interferometer to map the radio sky, producing the famous 2C and 3C surveys of radio sources.
Techniques
Radio astronomers use different types of techniques to observe objects in the radio spectrum. Instruments may simply be pointed at an energetic radio source to analyze what type of emissions it makes. To “image” a region of the sky in more detail, multiple overlapping scans can be recorded and piece together in an image ('mosaicing'). The types of instruments being used depends on the weakness of the signal and the amount of detail needed.
Radio telescopes
Radio telescopes may need to be extremely large in order to receive signals with low signal-to-noise ratio. Also since angular resolution is a function of the diameter of the "objective" in proportion to the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation being observed, radio telescopes have to be much larger in comparison to their optical counterparts. For example a 1 meter diameter optical telescope is two million times bigger than the wavelength of light observed giving it a resolution of a few arc seconds, whereas a radio telescope "dish" many times that size may, depending on the wavelength observed, may only be able to resolve an object the size of the full moon (30 minutes of arc).
Radio interferometry
The difficulty in achieving high resolutions with single radio telescopes led to radio interferometry, developed by British radio astronomer Martin Ryle and Australian-born engineer, radiophysicist, and radio astronomer Joseph Lade Pawsey in 1946. Radio interferometers consist of widely separated radio telescopes observing the same object that are connected together using coaxial cable, waveguide, optical fiber, or other type of transmission line. This not only increases the total signal collected, it can also be used in a process called Aperture synthesis to vastly increase resolution. This technique works by superposing (interfering) the signal waves from the different telescopes on the principle that waves that coincide with the same phase will add to each other while two waves that have opposite phases will cancel each other out. This creates a combined telescope that is the size of the antennas furthest apart in the array. In order to produce a high quality image, a large number of different separations between different telescopes are required (the projected separation between any two telescopes as seen from the radio source is called a baseline) - as many different baselines as possible are required in order to get a good quality image. For example the Very Large Array has 27 telescopes giving 351 independent baselines at once.
Very Long Baseline Interferometry
Since the 1970s telescopes from all over the world (and even in Earth orbit) have been combined to perform Very Long Baseline Interferometry. Data received at each antenna is paired with timing information, usually from a local atomic clock, and then stored for later analysis on magnetic tape or hard disk. At that later time, the data is correlated with data from other antennas similarly recorded, to produce the resulting image. Using this method it is possible to synthesise an antenna that is effectively the size of the Earth. The large distances between the telescopes enable very high angular resolutions to be achieved, much greater in fact than in any other field of astronomy. At the highest frequencies, synthesised beams less than 1 milliarcsecond are possible.
The pre-eminent VLBI arrays operating today are the Very Long Baseline Array (with telescopes located across the North America) and the European VLBI Network (telescopes in Europe, China, South Africa and Puerto Rico). Each array usually operates separately, but occasional projects are observed together producing increased sensitivity. This is referred to as Global VLBI. There is also a VLBI network, the Long Baseline Array, operating in Australia.
Since its inception, recording data onto hard media has been the only way to bring the data recorded at each telescope together for later correlation. However, the availability today of worldwide, high-bandwidth optical fibre networks makes it possible to do VLBI in real time. This technique (referred to as e-VLBI) has been pioneered by the EVN who now perform an increasing number of scientific e-VLBI projects per year.[5]
Astronomical sources
Radio astronomy has led to substantial increases in astronomical knowledge, particularly with the discovery of several classes of new objects, including pulsars, quasars and radio galaxies. This is because radio astronomy allows us to see things that are not detectable in optical astronomy. Such objects represent some of the most extreme and energetic physical processes in the universe.
Radio astronomy is also partly responsible for the idea that dark matter is an important component of our universe; radio measurements of the rotation of galaxies suggest that there is much more mass in galaxies than has been directly observed. The cosmic microwave background radiation was also first detected using radio telescopes. However, radio telescopes have also been used to investigate objects much closer to home, including observations of the Sun and solar activity, and radar mapping of the planets.
Other sources include:
- Sun
- Sagittarius A, the galactic center of the Milky Way
- Active galactic nuclei and pulsars have jets of charged particles which emit synchrotron radiation
- Merging galaxy clusters often show diffuse radio emission[1]
- Supernova remnants can also show diffuse radio emission
- The Cosmic microwave background is blackbody radio emission
See also
- History of astronomical interferometry
Notes
- ↑ http://www.nrao.edu/whatisra/hist_prehist.shtml NRAO.org, "Pre-History of Radio Astronomy" Compiled by F. Ghigo
- ↑ Karl G. Jansky, "Radio waves from outside the solar system", Nature, 132, p.66. 1933
- ↑ Grote Reber
- ↑ J. S. Hey. The Radio Universe, 2nd Ed., Pergamon Press, Oxford-New York (1975),
- ↑ A technological breakthrough for radio astronomy - Astronomical observations via high-speed data link
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
Further reading
Journals
- Gart Westerhout, The early history of radio astronomy. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 189 Education in and History of Modern Astronomy (August 1972) 211-218 doi 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb12724.x
- Hendrik Christoffel van de Hulst, The Origin of Radio Waves From Space.
- History of High-Resolution Radio Astronomy. Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, September 2001
Books
- Woodruff T. Sullivan, III, The early years of radio astronomy. 1984.
- Woodruff T. Sullivan, III, Classics in Radio Astronomy. Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht, 1982.
- Kristen Rohlfs, Thomas L Wilson, Tools of Radio Astronomy. Springer 2003. 461 pages. ISBN 3540403876
- Raymond Haynes, Roslynn Haynes, and Richard McGee, Explorers of the Southern Sky: A History of Australian Astronomy. Cambridge University Press 1996. 541 pages. ISBN 0521365759
- Shigeru Nakayama, A Social History of Science and Technology in Contemporary Japan: Transformation Period 1970-1979. Trans Pacific Press 2006. 580 pages. ISBN 1876843462
- David L. Jauncey, Radio Astronomy and Cosmology. Springer 1977. 420 pages. ISBN 9027708398
- Allan A. Needell, Science, Cold War and American State: Lloyd V. Berkner and the Balance of Professional Ideals. Routledge 2000. ISBN 905702621X (ed., see Chapter 10, Expanding Federal Support of Private Research: The Case of Radio Astronomy (Pages 259 - 596))
- Bruno Bertotti, Modern Cosmology in Retrospect. Cambridge University Press 1990. 446 pages. ISBN 0521372135 (ed., see essays by Robert Wilson, Discovery of the cosmic microwave background and Woodruff T. Sullivan, III, The entry of radio astronomy into cosmology: radio stars and 309 Martin Ryle's 2C survey.))
- J. S. Hey, The Evolution of Radio Astronomy. Neale Watson Academic, 1973.
- D. T. Wilkinson and P. J. E. Peebles, Serendipitous Discoveries in Radio Astronomy. National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Green Bank, WV, 1983.
- Joseph Lade Pawsey and Ronald Newbold Bracewell, Radio Astronomy. Clarendon Press, 1955. 361 pages.
- J. C.Kapteyn, P. C. v. d. Kruit, & K. v. Berkel, The legacy of J.C. Kapteyn: studies on Kapteyn and the development of modern astronomy. Astrophysics and space science library, v. 246. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers 2000.
- Roger Clifton Jennison, Introduction to Radio Astronomy. 1967. 160 pages.
- Robin Michael Green, Spherical Astronomy. Cambridge University Press 1985. 546 pages. ISBN 0521317797
- Albrecht Krüger, Introduction to Solar Radio Astronomy and Radio Physics. Springer 1979. 356 pages. ISBN 9027709572
External links
- French History
- The History of the Nancay Radio Observatory - a history of French radio astronomy
- History (America, Post 1930s)
- History of Radio Astronomy, National Radio Astronomy Observatory
- The History of Radio Astronomy - Haystack Observatory, MIT
- Hanes, Dave, "Physics 014: The Course Notes, Radio Astronomy". Astronomy Group and Department of Physics, Queen's University. 2000-2001.
- Reber Radio Telescope - National Park Services
- Radio Telescope Developed - a brief history from NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
bn:রেডিও জ্যোতির্বিজ্ঞান bg:Радиоастрономия cs:Radioastronomie da:Radioastronomi de:Radioastronomie es:Radioastronomía eo:Radioastronomio fa:اخترشناسی رادیویی fr:Radioastronomie hr:Radio astronomija id:Astronomi radio it:Radioastronomia lt:Radioastronomija nl:Radioastronomie ja:電波天文学 no:Radioastronomi pl:Radioastronomia pt:Radioastronomia ru:Радиоастрономия sk:Rádioastronómia sr:Radioastronomija fi:Radioastronomia sv:Radioastronomi vi:Thiên văn vô tuyến tr:Radyo astronomi zh:射电天文学