Difference between revisions of "Space debris" - New World Encyclopedia
(import credit version number) |
(applied ready tag) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Ready}} | ||
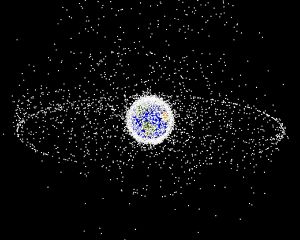
[[Image:Debris-GEO1280.jpg|thumb|Space debris populations seen from outside [[geosynchronous orbit]].]] | [[Image:Debris-GEO1280.jpg|thumb|Space debris populations seen from outside [[geosynchronous orbit]].]] | ||
[[Image:Hypervelocity Impact Demonstration.jpg|thumb|The "energy flash" of a [[hypervelocity]] impact during a simulation of what happens when a piece of orbital debris hits a spacecraft in orbit.]] | [[Image:Hypervelocity Impact Demonstration.jpg|thumb|The "energy flash" of a [[hypervelocity]] impact during a simulation of what happens when a piece of orbital debris hits a spacecraft in orbit.]] | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
In 1958, the United States launched a satellite named [[Vanguard I]]. It became one of the longest surviving pieces of space junk, and remained the oldest piece still in orbit through at least August 2007.<ref name="usaweekend">[http://www.usaweekend.com/07_issues/070826/070826space.html#junk Space junk], USA WEEKEND Magazine, by Julian Smith, August 26, 2007</ref> | In 1958, the United States launched a satellite named [[Vanguard I]]. It became one of the longest surviving pieces of space junk, and remained the oldest piece still in orbit through at least August 2007.<ref name="usaweekend">[http://www.usaweekend.com/07_issues/070826/070826space.html#junk Space junk], USA WEEKEND Magazine, by Julian Smith, August 26, 2007</ref> | ||
| − | According to [[Edward Tufte]]'s book ''[[Envisioning Information]]'', space debris objects have included a glove lost by astronaut [[Edward Higgins White|Ed White]] on the first American [[Extra-vehicular activity|space-walk]], a camera [[Michael Collins (astronaut)|Michael Collins]] lost near the spacecraft [[Gemini 10]], garbage bags jettisoned by the Soviet [[Mir]] [[Cosmonaut]]s throughout that space station's 15-year life,<ref name="usaweekend"/> a [[wrench]] and a [[toothbrush]]. [[Sunita Williams]] of [[STS-116]] also lost a [[camera]] during an | + | According to [[Edward Tufte]]'s book ''[[Envisioning Information]]'', space debris objects have included a glove lost by astronaut [[Edward Higgins White|Ed White]] on the first American [[Extra-vehicular activity|space-walk]], a camera [[Michael Collins (astronaut)|Michael Collins]] lost near the spacecraft [[Gemini 10]], garbage bags jettisoned by the Soviet [[Mir]] [[Cosmonaut]]s throughout that space station's 15-year life,<ref name="usaweekend"/> a [[wrench]] and a [[toothbrush]]. [[Sunita Williams]] of [[STS-116]] also lost a [[camera]] during an EVA. During the EVA to reinforce a torn solar panel during [[STS-120]] a pair of pliers was similarly liberated. Most of those unusual objects have re-entered the atmosphere of the Earth within weeks due to the orbits where they were released and their small sizes. Things like these are not major contributors to the space debris environment. On the other side, explosion events are a major contribution to the space debris problem. About 100 tons of fragments generated during approximately 200 such events are still in orbit. Space debris is most concentrated in [[low Earth orbit]], though some extends out past [[geosynchronous orbit]]. |
| − | The first official Space Shuttle collision avoidance maneuver was during [[STS-48]] in September | + | The first official Space Shuttle collision avoidance maneuver was during [[STS-48]] in September 1991. A 7-second [[reaction control system]] burn was performed to avoid debris from the [[Cosmos (satellite)|Cosmos satellite]] 955. |
==Mitigation measures== | ==Mitigation measures== | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
Proposals have been made for ways to "sweep" space debris back into Earth's atmosphere, including automated tugs, [[laser broom]]s to vaporize or nudge particles into rapidly-decaying orbits, or huge [[aerogel]] blobs to absorb impacting junk and eventually fall out of orbit with them trapped inside. However, currently most effort is being devoted to prevention of collisions by keeping track of larger debris, and prevention of more debris. | Proposals have been made for ways to "sweep" space debris back into Earth's atmosphere, including automated tugs, [[laser broom]]s to vaporize or nudge particles into rapidly-decaying orbits, or huge [[aerogel]] blobs to absorb impacting junk and eventually fall out of orbit with them trapped inside. However, currently most effort is being devoted to prevention of collisions by keeping track of larger debris, and prevention of more debris. | ||
| − | Other ideas include the gathering of larger objects into an orbital "junk yard" | + | Other ideas include the gathering of larger objects into an orbital "junk yard," where they could be used as resources should future needs arise, while keeping them out of the way. |
==Space debris measurements== | ==Space debris measurements== | ||
| Line 32: | Line 33: | ||
Other sources of knowledge on the actual space debris environment include measurement campaigns by the [[ESA Space Debris Telescope]], TIRA<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.fas.org/spp/military/program/track/klinkrad.pdf| format=PDF| title=Monitoring Space – Efforts Made by European Countries| first=H.| last=Klinkrad| accessdate=2006-03-08}}</ref>, Goldstone radar, Haystack radar,<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.haystack.mit.edu/| title=MIT Haystack Observatory| accessdate=2006-03-08}}</ref> and the [[Cobra Dane]] phased array radar.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.fas.org/spp/military/program/track/cobra_dane.htm| title=AN/FPS-108 COBRA DANE| accessdate=2006-03-08}}</ref> The data gathered during these campaigns is used to validate models of the debris environment like ESA-MASTER. Such models are the only means of assessing the impact risk caused by space debris as only larger objects can be regularly tracked. | Other sources of knowledge on the actual space debris environment include measurement campaigns by the [[ESA Space Debris Telescope]], TIRA<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.fas.org/spp/military/program/track/klinkrad.pdf| format=PDF| title=Monitoring Space – Efforts Made by European Countries| first=H.| last=Klinkrad| accessdate=2006-03-08}}</ref>, Goldstone radar, Haystack radar,<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.haystack.mit.edu/| title=MIT Haystack Observatory| accessdate=2006-03-08}}</ref> and the [[Cobra Dane]] phased array radar.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.fas.org/spp/military/program/track/cobra_dane.htm| title=AN/FPS-108 COBRA DANE| accessdate=2006-03-08}}</ref> The data gathered during these campaigns is used to validate models of the debris environment like ESA-MASTER. Such models are the only means of assessing the impact risk caused by space debris as only larger objects can be regularly tracked. | ||
| − | Returned space debris hardware is also a valuable source of information on the (sub[[millimetre]]) space debris environment. The [[LDEF]] satellite deployed by [[STS-41-C]] [[Space Shuttle Challenger|''Challenger'']] and retrieved by [[STS-32]] [[Space Shuttle Columbia|''Columbia'']] spent 68 months in orbit. The close examination of its surfaces allowed the analysis of the directional distribution and the composition of debris flux. The EURECA satellite deployed by [[STS-46]] [[Space Shuttle Atlantis|''Atlantis'']] in 1992 and retrieved by [[STS-57]] [[Space Shuttle | + | Returned space debris hardware is also a valuable source of information on the (sub[[millimetre]]) space debris environment. The [[LDEF]] satellite deployed by [[STS-41-C]] [[Space Shuttle Challenger|''Challenger'']] and retrieved by [[STS-32]] [[Space Shuttle Columbia|''Columbia'']] spent 68 months in orbit. The close examination of its surfaces allowed the analysis of the directional distribution and the composition of debris flux. The EURECA satellite deployed by [[STS-46]] [[Space Shuttle Atlantis|''Atlantis'']] in 1992 and retrieved by [[STS-57]] [[Space Shuttle Endeavor|''Endeavor'']] in 1993 could provide additional insight. |
| − | The solar arrays of the [[Hubble Space Telescope]] returned during missions [[STS-61]] [[Space Shuttle | + | The solar arrays of the [[Hubble Space Telescope]] returned during missions [[STS-61]] [[Space Shuttle Endeavor|''Endeavor'']] and [[STS-109]] [[Space Shuttle Columbia|''Columbia'']] are an important source of information on the debris environment. The impact craters found on the surface were counted and classified by [[ESA]] to provide another means for validating debris environment models. |
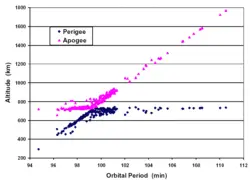
[[Image:Gabbard diagram.png|left|250px|thumb|Gabbard diagram of almost 300 debris from the disintegration of the 5-months old third stage of the Chinese Long March 4 booster on March 11, 2000. The spread of debris to longer orbital periods and higher apogees indicates that those debris were propelled in the [[prograde]] direction.]] | [[Image:Gabbard diagram.png|left|250px|thumb|Gabbard diagram of almost 300 debris from the disintegration of the 5-months old third stage of the Chinese Long March 4 booster on March 11, 2000. The spread of debris to longer orbital periods and higher apogees indicates that those debris were propelled in the [[prograde]] direction.]] | ||
| Line 41: | Line 42: | ||
Space debris groups resulting from satellite breakups are often studied using [[scatterplot]]s known as Gabbard diagrams. In a Gabbard diagram the [[perigee]] and [[apogee]] altitudes of the individual debris fragments resulting from a collision are plotted with respect to the [[orbital period]] of each fragment. The distribution of the resulting diagram can be used to infer information such as direction and point of impact.<ref>{{cite paper | author=Portree, David and Loftus, Joseph | title=Orbital Debris: A Chronology | date=1999 |publisher=NASA| url=http://ston.jsc.nasa.gov/collections/TRS/_techrep/TP-1999-208856.pdf }} See p.13.</ref> <ref>{{cite paper | author=Whitlock, David O. | title=History of On-Orbit Satellite Fragmentations | date=2004 | publisher=NASA JSC | url=http://www.orbitaldebris.jsc.nasa.gov/library/SatelliteFragHistory/13thEditionofBreakupBook.pdf }} "Gabbard | Space debris groups resulting from satellite breakups are often studied using [[scatterplot]]s known as Gabbard diagrams. In a Gabbard diagram the [[perigee]] and [[apogee]] altitudes of the individual debris fragments resulting from a collision are plotted with respect to the [[orbital period]] of each fragment. The distribution of the resulting diagram can be used to infer information such as direction and point of impact.<ref>{{cite paper | author=Portree, David and Loftus, Joseph | title=Orbital Debris: A Chronology | date=1999 |publisher=NASA| url=http://ston.jsc.nasa.gov/collections/TRS/_techrep/TP-1999-208856.pdf }} See p.13.</ref> <ref>{{cite paper | author=Whitlock, David O. | title=History of On-Orbit Satellite Fragmentations | date=2004 | publisher=NASA JSC | url=http://www.orbitaldebris.jsc.nasa.gov/library/SatelliteFragHistory/13thEditionofBreakupBook.pdf }} "Gabbard | ||
diagrams of the early debris cloud prior to the effects of perturbations, if the data were available, are | diagrams of the early debris cloud prior to the effects of perturbations, if the data were available, are | ||
| − | reconstructed. These diagrams often include | + | reconstructed. These diagrams often include uncatalogued as well as cataloged debris data. When |
used correctly, Gabbard diagrams can provide important insights into the features of the | used correctly, Gabbard diagrams can provide important insights into the features of the | ||
fragmentation."</ref> | fragmentation."</ref> | ||
| Line 50: | Line 51: | ||
The largest space debris incident in history was the [[2007 Chinese anti-satellite missile test|Chinese anti-satellite weapon (ASAT) test on January 11, 2007]].<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.centerforspace.com/asat/| title=Chinese ASAT Test| accessdate=2007-07-04}}</ref> The event created more than 2000 pieces (updated 8/5/07) of trackable debris (approximately golf ball size or larger), estimates of over 1 million pieces 1mm or larger and over 35,000 pieces 1cm or larger. The debris event is more significant than previous ASAT tests in that the debris field is in a higher orbital plane resulting in deorbit times of 35 years and greater. In June, 2007, NASA's [[Terra (satellite)|Terra environmental spacecraft]] was the first to be moved in order to prevent impacts from this debris.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.space.com/news/070706_sn_china_terra.html| title=NASA's Terra Satellite Moved to Avoid Chinese ASAT Debris | accessdate=2007-07-06 |last=Burger| first=Brian}}</ref> | The largest space debris incident in history was the [[2007 Chinese anti-satellite missile test|Chinese anti-satellite weapon (ASAT) test on January 11, 2007]].<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.centerforspace.com/asat/| title=Chinese ASAT Test| accessdate=2007-07-04}}</ref> The event created more than 2000 pieces (updated 8/5/07) of trackable debris (approximately golf ball size or larger), estimates of over 1 million pieces 1mm or larger and over 35,000 pieces 1cm or larger. The debris event is more significant than previous ASAT tests in that the debris field is in a higher orbital plane resulting in deorbit times of 35 years and greater. In June, 2007, NASA's [[Terra (satellite)|Terra environmental spacecraft]] was the first to be moved in order to prevent impacts from this debris.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.space.com/news/070706_sn_china_terra.html| title=NASA's Terra Satellite Moved to Avoid Chinese ASAT Debris | accessdate=2007-07-06 |last=Burger| first=Brian}}</ref> | ||
| − | An event of similar magnitude occurred on | + | An event of similar magnitude occurred on February 19, 2007, when a Russian [[Briz-M]] booster stage exploded in orbit over Australia. The booster had been launched on February 28, 2006, carrying an [[Arabsat-4A]] communication satellite but malfunctioned before it could use all of its fuel. The explosion was captured on film by several astronomers, but due to the path of the orbit the debris cloud has been hard to quantify using radar. Although similar in magnitude, the debris field is at a lower altitude than the Chinese ASAT test and much debris re-enters the atmosphere in a relatively short time. As of February 21, 2007, over 1,000 fragments had been identified.<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.spaceweather.com/| title=Rocket Explosion| date=22 Feb 2007 | accessdate=2007-02-21| publisher=Spaceweather.com}}</ref><ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.space.com/news/070221_rocket_explodes.html| publisher=Space.com| title=Rocket Explodes Over Australia, Showers Space with Debris| first= Ker| last= Than| date=21 February 2007| accessdate=2007-02-21}}</ref> A third breakup event also occurred on 14 February 2007 as recorded by Celes Trak.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://celestrak.com/events/debris-events.asp|publisher=celestrak.com|title=Recent Debris Events|accessdate=2007-03-16}}</ref> This makes three observed events in the first two months of 2007. In 2006, the most breakups occurred since 1993 with eight breakups.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://space.newscientist.com/article/dn10979-spate-of-rocket-breakups-creates-new-space-junk.html|publisher=NewScientist.com|title=Spate of rocket breakups creates new space junk|date=2007-01-17|accessdate=2007-03-16}}</ref> |
==Significant debris impact events== | ==Significant debris impact events== | ||
| − | The first verified collision with catalogued space debris occurred in | + | The first verified collision with catalogued space debris occurred in 1996, tearing off a boom from the French satellite [[Cerise (satellite)|Cerise]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/4486049.stm| title=CO2 prolongs life of space junk| publisher=BBC News| accessdate=2006-03-08}}</ref> |
| − | Lottie Williams is on record as the first and only (as of September 2006) person ever to be hit by space debris created by humans. While walking in a park in [[Tulsa, Oklahoma]], on | + | Lottie Williams is on record as the first and only (as of September 2006) person ever to be hit by space debris created by humans. While walking in a park in [[Tulsa, Oklahoma]], on January 22, 1997 at 3:30 am, she noticed a light in the sky that she said looked like a [[meteor]]. Minutes later, Williams was hit in the shoulder by a 10 x 13 cm. piece of blackened, woven metallic material that was later confirmed to be part of the fuel tank of a [[Delta II]] rocket which had launched a [[United States Air Force|U.S. Air Force]] satellite in 1996. Ms. Williams was not injured.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.todayinsci.com/1/1_22.htm| title=Today in Science History| accessdate=2006-03-08}}</ref><ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.eclipsetours.com/sat/debris.html| title=Paul Maley's Sattelite Page| accessdate=2007-10-28}}</ref> |
| − | On | + | On October 10, 2006, a brief Reuters report suggested a cottage in Germany was burned down by a fire that was speculated to have been started by a small [[bolide]] (no more than 10mm). The fire "badly burned the man's hands and face".<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.theregister.co.uk/2006/10/20/meteor_destroys_cottage|title=The Register, Meteor totals German cottage|accessdate=2007-08-08}}</ref><ref>{{cite web| url=http://news.yahoo.com/s/nm/20061020/sc_nm/germany_meteor_dc;_ylt=AoceK7r0x3flAEWo4e8TLXjMWM0F;_ylu=X3oDMTA3ODdxdHBhBHNlYwM5NjQ-| title=German cottage destroyed by meteor|accessdate=2006-10-21}}</ref>. A comment made on the web pointed out that the word used in German news reports did not refer to a house, "but only a 'Gartenlaube', i.e. a small (and not exactly solidly-built) 'garden cottage.'"<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.toytowngermany.com/lofi/index.php/t51874.html|title=Meteor stike in Siegburg near Bonn - Germany|accessdate=2007-08-08}}</ref> Other skeptical web comments cast doubt that a meteorite of that size could be responsible for the fire.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.badastronomy.com/bablog/2006/10/28/meteorite-burns-a-german-cottage/| title=Bad Astronomy Blog, Meteorite burns a German cottage?| accessdate=2007-08-08}}</ref>. The news item made no report of any tangible evidence being retrieved to substantiate the assumption. |
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 65: | Line 66: | ||
*[[6Q0B44E]] | *[[6Q0B44E]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Notes== |
<div class="references-small"><references/></div> | <div class="references-small"><references/></div> | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| + | All links retrieved November 22, 2007 | ||
{{Commons|Space debris}} | {{Commons|Space debris}} | ||
*[http://www.orbitaldebris.jsc.nasa.gov/ NASA Orbital Debris Program Office] | *[http://www.orbitaldebris.jsc.nasa.gov/ NASA Orbital Debris Program Office] | ||
| Line 74: | Line 76: | ||
*[http://www.aero.org/capabilities/cords/debris-basics.html "What is Orbital Debris?" from the Center for Orbital and Reentry Debris Studies at The Aerospace Corporation] | *[http://www.aero.org/capabilities/cords/debris-basics.html "What is Orbital Debris?" from the Center for Orbital and Reentry Debris Studies at The Aerospace Corporation] | ||
*[http://lasp.colorado.edu/~lix/class/asen5335/hw6.html Intro to mathematical modeling of space debris flux] | *[http://lasp.colorado.edu/~lix/class/asen5335/hw6.html Intro to mathematical modeling of space debris flux] | ||
| − | + | <nowiki>Insert non-formatted text here</nowiki>*[http://celestrak.com/SOCRATES SOCRATES: A free daily service predicting close encounters on orbit between satellites and the thousands of rocket bodies and other pieces of debris orbiting Earth.] | |
| − | *[http://celestrak.com/SOCRATES SOCRATES: A free daily service predicting close encounters on orbit between satellites and the thousands of rocket bodies and other pieces of debris orbiting Earth.] | ||
*[http://www.theglobaleducationproject.org/earth/global-ecology.php#8 A summary of current space debris by type and orbit.] | *[http://www.theglobaleducationproject.org/earth/global-ecology.php#8 A summary of current space debris by type and orbit.] | ||
*[http://www.eclipsetours.com/sat/debris.html Paul Maley's Satellite Page - Space debris (with photos) which has reentered the atmosphere intact.] | *[http://www.eclipsetours.com/sat/debris.html Paul Maley's Satellite Page - Space debris (with photos) which has reentered the atmosphere intact.] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Physical sciences]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Space exploration]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{credit|172279419}} | {{credit|172279419}} | ||
Revision as of 02:37, 23 November 2007
Space debris or orbital debris, also called space junk and space waste, are the objects in orbit around Earth created by humans, that no longer serve any useful purpose. They consist of everything from entire spent rocket stages and defunct satellites to explosion fragments, paint flakes, dust, and slag from solid rocket motors, coolant released by RORSAT nuclear powered satellites, deliberate insertion of small needles, and other small particles.[1] Clouds of very small particles may cause erosive damage, like sandblasting.
Space debris has become a growing concern in recent years, since collisions at orbital velocities can be highly damaging to functioning satellites and can also produce even more space debris in the process, called Kessler Syndrome. Some spacecraft, like the International Space Station, are now armored to mitigate damage with this hazard. [citation needed] Astronauts on EVAs are also vulnerable.
History
In 1958, the United States launched a satellite named Vanguard I. It became one of the longest surviving pieces of space junk, and remained the oldest piece still in orbit through at least August 2007.[2]
According to Edward Tufte's book Envisioning Information, space debris objects have included a glove lost by astronaut Ed White on the first American space-walk, a camera Michael Collins lost near the spacecraft Gemini 10, garbage bags jettisoned by the Soviet Mir Cosmonauts throughout that space station's 15-year life,[2] a wrench and a toothbrush. Sunita Williams of STS-116 also lost a camera during an EVA. During the EVA to reinforce a torn solar panel during STS-120 a pair of pliers was similarly liberated. Most of those unusual objects have re-entered the atmosphere of the Earth within weeks due to the orbits where they were released and their small sizes. Things like these are not major contributors to the space debris environment. On the other side, explosion events are a major contribution to the space debris problem. About 100 tons of fragments generated during approximately 200 such events are still in orbit. Space debris is most concentrated in low Earth orbit, though some extends out past geosynchronous orbit.
The first official Space Shuttle collision avoidance maneuver was during STS-48 in September 1991. A 7-second reaction control system burn was performed to avoid debris from the Cosmos satellite 955.
Mitigation measures
In order to mitigate the generation of additional space debris, a number of measures have been proposed: The passivation of spent upper stages by the release of residual fuels is aimed at decreasing the risk of on-orbit explosions that could generate thousands of additional debris objects.
Taking satellites out of orbit at the end of their operational life would also be an effective mitigation measure. This could be facilitated with a "terminator tether," an electrodynamic tether that is rolled out, and slows down the spacecraft.[3] In cases when a direct (and controlled) de-orbit would require too much fuel the satellite can also be brought to an orbit where atmospheric drag would cause it to de-orbit after some years. Such a maneuver was successfully performed with the French Spot-1 satellite at the end of 2003. It will re-enter in approximately 15 years.
In orbital altitudes where it would not be economically feasible to de-orbit a satellite, like in the geostationary ring they are brought to a graveyard orbit where no operational satellites are present.
Proposals have been made for ways to "sweep" space debris back into Earth's atmosphere, including automated tugs, laser brooms to vaporize or nudge particles into rapidly-decaying orbits, or huge aerogel blobs to absorb impacting junk and eventually fall out of orbit with them trapped inside. However, currently most effort is being devoted to prevention of collisions by keeping track of larger debris, and prevention of more debris.
Other ideas include the gathering of larger objects into an orbital "junk yard," where they could be used as resources should future needs arise, while keeping them out of the way.
Space debris measurements
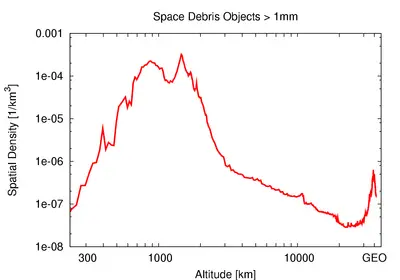
The U.S. Strategic Command is maintaining a catalogue currently containing about 10,000 objects, also to prevent misinterpretation as hostile missiles. Observation data gathered by a number of ground based radar facilities and telescopes as well as by a space based telescope[4] is used to maintain this catalogue. Nevertheless, the majority of debris objects remain unobserved. There are more than 600,000 objects larger than 1 cm in orbit (according to the ESA Meteoroid and Space Debris Terrestrial Environment Reference, the MASTER-2005 model).
Other sources of knowledge on the actual space debris environment include measurement campaigns by the ESA Space Debris Telescope, TIRA[5], Goldstone radar, Haystack radar,[6] and the Cobra Dane phased array radar.[7] The data gathered during these campaigns is used to validate models of the debris environment like ESA-MASTER. Such models are the only means of assessing the impact risk caused by space debris as only larger objects can be regularly tracked.
Returned space debris hardware is also a valuable source of information on the (submillimetre) space debris environment. The LDEF satellite deployed by STS-41-C Challenger and retrieved by STS-32 Columbia spent 68 months in orbit. The close examination of its surfaces allowed the analysis of the directional distribution and the composition of debris flux. The EURECA satellite deployed by STS-46 Atlantis in 1992 and retrieved by STS-57 Endeavor in 1993 could provide additional insight.
The solar arrays of the Hubble Space Telescope returned during missions STS-61 Endeavor and STS-109 Columbia are an important source of information on the debris environment. The impact craters found on the surface were counted and classified by ESA to provide another means for validating debris environment models.
Gabbard diagrams
Space debris groups resulting from satellite breakups are often studied using scatterplots known as Gabbard diagrams. In a Gabbard diagram the perigee and apogee altitudes of the individual debris fragments resulting from a collision are plotted with respect to the orbital period of each fragment. The distribution of the resulting diagram can be used to infer information such as direction and point of impact.[8] [9]
Significant debris-creation events
The largest space debris incident in history was the Chinese anti-satellite weapon (ASAT) test on January 11, 2007.[10] The event created more than 2000 pieces (updated 8/5/07) of trackable debris (approximately golf ball size or larger), estimates of over 1 million pieces 1mm or larger and over 35,000 pieces 1cm or larger. The debris event is more significant than previous ASAT tests in that the debris field is in a higher orbital plane resulting in deorbit times of 35 years and greater. In June, 2007, NASA's Terra environmental spacecraft was the first to be moved in order to prevent impacts from this debris.[11]
An event of similar magnitude occurred on February 19, 2007, when a Russian Briz-M booster stage exploded in orbit over Australia. The booster had been launched on February 28, 2006, carrying an Arabsat-4A communication satellite but malfunctioned before it could use all of its fuel. The explosion was captured on film by several astronomers, but due to the path of the orbit the debris cloud has been hard to quantify using radar. Although similar in magnitude, the debris field is at a lower altitude than the Chinese ASAT test and much debris re-enters the atmosphere in a relatively short time. As of February 21, 2007, over 1,000 fragments had been identified.[12][13] A third breakup event also occurred on 14 February 2007 as recorded by Celes Trak.[14] This makes three observed events in the first two months of 2007. In 2006, the most breakups occurred since 1993 with eight breakups.[15]
Significant debris impact events
The first verified collision with catalogued space debris occurred in 1996, tearing off a boom from the French satellite Cerise.[16]
Lottie Williams is on record as the first and only (as of September 2006) person ever to be hit by space debris created by humans. While walking in a park in Tulsa, Oklahoma, on January 22, 1997 at 3:30 am, she noticed a light in the sky that she said looked like a meteor. Minutes later, Williams was hit in the shoulder by a 10 x 13 cm. piece of blackened, woven metallic material that was later confirmed to be part of the fuel tank of a Delta II rocket which had launched a U.S. Air Force satellite in 1996. Ms. Williams was not injured.[17][18]
On October 10, 2006, a brief Reuters report suggested a cottage in Germany was burned down by a fire that was speculated to have been started by a small bolide (no more than 10mm). The fire "badly burned the man's hands and face".[19][20]. A comment made on the web pointed out that the word used in German news reports did not refer to a house, "but only a 'Gartenlaube', i.e. a small (and not exactly solidly-built) 'garden cottage.'"[21] Other skeptical web comments cast doubt that a meteorite of that size could be responsible for the fire.[22]. The news item made no report of any tangible evidence being retrieved to substantiate the assumption.
See also
- Near-Earth object
- Kessler Syndrome
- J002E3
- 6Q0B44E
Notes
- ↑ Technical report on space debris (PDF). United Nations (1999). Retrieved 2006-04-05.ISBN 92-1-100813-1
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Space junk, USA WEEKEND Magazine, by Julian Smith, August 26, 2007
- ↑ Christensen, Bill. The Terminator Tether Aims to Clean Up Low Earth Orbit. Retrieved 2006-03-08.
- ↑ The Space-Based Visible Program. MIT Lincoln Laboratory. Retrieved 2006-03-08.
- ↑ Klinkrad, H.. Monitoring Space – Efforts Made by European Countries (PDF). Retrieved 2006-03-08.
- ↑ MIT Haystack Observatory. Retrieved 2006-03-08.
- ↑ AN/FPS-108 COBRA DANE. Retrieved 2006-03-08.
- ↑ Portree, David and Loftus, Joseph (1999). "Orbital Debris: A Chronology". NASA. See p.13.
- ↑ Whitlock, David O. (2004). "History of On-Orbit Satellite Fragmentations". NASA JSC. "Gabbard diagrams of the early debris cloud prior to the effects of perturbations, if the data were available, are reconstructed. These diagrams often include uncatalogued as well as cataloged debris data. When used correctly, Gabbard diagrams can provide important insights into the features of the fragmentation."
- ↑ Chinese ASAT Test. Retrieved 2007-07-04.
- ↑ Burger, Brian. NASA's Terra Satellite Moved to Avoid Chinese ASAT Debris. Retrieved 2007-07-06.
- ↑ "Rocket Explosion", Spaceweather.com, 22 Feb 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-21.
- ↑ Than, Ker, "Rocket Explodes Over Australia, Showers Space with Debris", Space.com, 21 February 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-21.
- ↑ "Recent Debris Events", celestrak.com. Retrieved 2007-03-16.
- ↑ "Spate of rocket breakups creates new space junk", NewScientist.com, 2007-01-17. Retrieved 2007-03-16.
- ↑ CO2 prolongs life of space junk. BBC News. Retrieved 2006-03-08.
- ↑ Today in Science History. Retrieved 2006-03-08.
- ↑ Paul Maley's Sattelite Page. Retrieved 2007-10-28.
- ↑ The Register, Meteor totals German cottage. Retrieved 2007-08-08.
- ↑ German cottage destroyed by meteor. Retrieved 2006-10-21.
- ↑ Meteor stike in Siegburg near Bonn - Germany. Retrieved 2007-08-08.
- ↑ Bad Astronomy Blog, Meteorite burns a German cottage?. Retrieved 2007-08-08.
External links
All links retrieved November 22, 2007
- NASA Orbital Debris Program Office
- Space-Track - The Source for Space Surveillance Data
- "What is Orbital Debris?" from the Center for Orbital and Reentry Debris Studies at The Aerospace Corporation
- Intro to mathematical modeling of space debris flux
Insert non-formatted text here*SOCRATES: A free daily service predicting close encounters on orbit between satellites and the thousands of rocket bodies and other pieces of debris orbiting Earth.
- A summary of current space debris by type and orbit.
- Paul Maley's Satellite Page - Space debris (with photos) which has reentered the atmosphere intact.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.