Difference between revisions of "Nitrous acid" - New World Encyclopedia
({{Contracted}}) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Claimed}}{{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Approved}} | + | {{Claimed}}{{Contracted}}{{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Approved}} |
<!-- Here is a table of data; skip past it to edit the text. —> | <!-- Here is a table of data; skip past it to edit the text. —> | ||
{| class="toccolours" border="1" style="float: right; clear: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; border-collapse: collapse;" | {| class="toccolours" border="1" style="float: right; clear: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; border-collapse: collapse;" | ||
Revision as of 20:47, 25 May 2007
| Nitrous acid | |
|---|---|
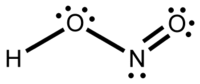
| |
| General | |
| Systematic name | Dioxonitric(III) acid |
| Other names | Nitrous acid |
| Molecular formula | HNO2 |
| Molar mass | 47.0134 g/mol |
| CAS number | 7782-77-6 |
| Properties | |
| Density | ? g/cm3 |
| Solubility (water) | |
| Melting point | ? °C |
| Boiling point | ? °C |
| Acid dissociation constant pKa |
3.34 |
| Disclaimer and references | |
Nitrous acid (molecular formula HNO2) is a weak monobasic acid known only in solution and in the form of nitrite salts.
Nitrous acid is used to make diazides from amines; this occurs by nucleophilic attack of the amine onto the nitrite, reprotonation by the surrounding solvent, and double elimination of water. The diazide can then be liberated as a carbene.
Preparation
It can be prepared by adding any mineral acid to sodium nitrite.
Decomposition
It rapidly decomposes into nitrogen dioxide, nitric oxide and water when in solution.
2HNO2------>NO2 + NO + H2O
It also decomposes into nitric acid and nitrous oxide and water
4HNO2 -> 2HNO3 + N2O + H2O
Chemistry
Nitrous acid can be used to prepare diazonium salts which couple with anilines and phenols to form brightly colored azo compounds in a qualitative test for aromatic amines. This reaction is also used to produce azo-dyes. Nitrous acid is used to destroy toxic and potentially explosive sodium azide solutions. Nitrous acid is usually formed in situ by the action of mineral acid on sodium nitrite.
Atmospheric relevance
Nitrous acid is an important atmospheric intermediate. It is produced by the heterogeneous reaction of NO2 and water on various surfaces such as atmospheric aerosols. It is readily photolysed to produce hydroxyl radicals which are intricately involved in the ozone budget of the troposphere (lower atmosphere).
See also
- Demjanov rearrangement
- Nitric acid (HNO3)
- Tiffeneau-Demjanov rearrangement
External links
Template:ChemicalSources
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.