Difference between revisions of "Maple" - New World Encyclopedia
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
==Pests and diseases== | ==Pests and diseases== | ||
| − | + | Maple leaves are consumed by the [[larva]]e of a number of [[Lepidoptera]] species, and [[aphid]]s are very common sap-feeders on maples. | |
| − | Maples are affected by a number of [[fungus|fungal]] diseases. Several are susceptible to Verticillium wilt caused by '' | + | Maples are affected by a number of [[fungus|fungal]] diseases. Several are susceptible to Verticillium wilt caused by ''Verticillium'' species, which can cause significant local mortality. Sooty bark disease, caused by ''Cryptostroma'' species, can kill trees which are under stress due to drought. Death of maples can also be caused more rarely by ''Phytophthora'' root rot and ''Ganoderma'' root decay. Maple leaves in late summer and autumn are commonly disfigured by "tar spot" caused by ''Rhystima'' species and mildew caused by ''Uncinula'' species, though these diseases do not usually have an adverse effect on the trees' long-term health (Phillips and Burdekin 1992). |
==Uses== | ==Uses== | ||
| Line 105: | Line 105: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | .<ref name="phillips">Phillips, D. H. & Burdekin, D. A. (1992). ''Diseases of Forest and Ornamental Trees''. Macmillan. ISBN 0-333-49493-8.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
<ref name="gelderen">van Gelderen, C.J. & van Gelderen, D.M. (1999). ''Maples for Gardens: A Color Encyclopedia''</ref> | <ref name="gelderen">van Gelderen, C.J. & van Gelderen, D.M. (1999). ''Maples for Gardens: A Color Encyclopedia''</ref> | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
Revision as of 00:58, 4 May 2007
| Maple | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Silver Maple (Acer saccharinum) leaves
| ||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
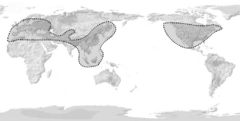 Distribution
| ||||||||||||
Maple is the common name for any member of the flowering plant genus Acer, a group of about 125 species of mostly deciduous trees and shrubs in the Northern Hemisphere. Most maples are native to Asia, but several species also occur in North America, northern Africa, and Europe. They are characterized by opposite, generally palmate (divided into many lobes) leaves, and fruit that is borne in pairs with two long wings for wind dispersal.
The word Acer is derived from a Latin word meaning "sharp" (referring to the characteristic points on the leaves) and was first applied to the genus by the French botanist Joseph Pitton de Tournefort in 1700 (van Geleren and van Gelderen 1999).
Description
While maples are now planted widely as ornamental plants, they are generally found in temperate regions or mountain slopes in more tropical regions. Most species are trees that grow to 10 to 40 meters (30-130 feet) in height. However, there are also shrubs that are less than 10 meters tall and with a number of small trunks originating at ground level. Most species are deciduous, but a few in southern Asia and the Mediterranean region are evergreen.
Maples are distinguished by opposite leaf arrangement. The leaves in most species are palmately veined and lobed, with 3-9 veins each leading to a lobe, one of which is in the middle. A small number of species differ in having palmate compound, pinnate (two rows of leaflets) compound, pinnate veined. or unlobed leaves.
Several species, including the paperbark maple (Acer griseum), Manchurian maple (Acer mandshuricum), nikko maple (Acer maximowiczianum), and three-flowered maple (Acer triflorum), have trifoliate leaves. One species, Manitoba maple (Acer negundo), has pinnately compound leaves that may be simply trifoliate or may have five, seven, or rarely nine leaflets. One maple, the hornbeam maple (Acer carpinifolium), has pinnately-veined simple leaves that resemble those of hornbeam (a genus of relatively small hardwood trees).
Maple flowers are regular, pentamerous, and borne in racemes, corymbs, or umbels. Pentamerous means that they are arranged in roughly equal parts around a central axis at orientations of 72° apart. Maple flowers have five sepals, five petals about 1 to 6 mm long, 12 stamens about 6-10 mm long in two rings of six, and two pistils or a pistil with two styles. The ovary is superior and has two carpels, whose wings elongate the flowers, making it easy to tell which flowers are female. Maples flower in late winter or early spring, in most species with or just after the leaves appear, but in some before them.
Maple flowers are green, yellow, orange or red. Though individually small, the effect of an entire tree in flower can be striking in several species. Some maples are an early spring source of pollen and nectar for bees.
The distinctive fruit are called samaras or "maple keys." These seeds occur in distinctive pairs each containing one seed enclosed in a "nutlet" attached to a flattened wing of fibrous, papery tissue. They are shaped to spin as they fall and to carry the seeds a considerable distance on the wind. Seed maturation is usually in a few weeks to six months of flowering, with seed dispersal shortly after maturity. Most species require stratification in order to germinate, and some seeds can remain dormant in the soil for several years before germinating (van Geleren and van Gelderen 1999).
Maples are variously classified in a family of their own, the Aceraceae, or (together with the Hippocastanaceae) included in the family Sapindaceae. Modern classifications, including the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification, favor inclusion in Sapindaceae.
Pests and diseases
Maple leaves are consumed by the larvae of a number of Lepidoptera species, and aphids are very common sap-feeders on maples.
Maples are affected by a number of fungal diseases. Several are susceptible to Verticillium wilt caused by Verticillium species, which can cause significant local mortality. Sooty bark disease, caused by Cryptostroma species, can kill trees which are under stress due to drought. Death of maples can also be caused more rarely by Phytophthora root rot and Ganoderma root decay. Maple leaves in late summer and autumn are commonly disfigured by "tar spot" caused by Rhystima species and mildew caused by Uncinula species, though these diseases do not usually have an adverse effect on the trees' long-term health (Phillips and Burdekin 1992).
Uses
Horticulture

Maples are planted as ornamental trees by homeowners, businesses and municipalities. Norway Maple (A. platanoides) is especially popular as it is fast-growing and extremely cold-resistant, though is also an invasive species in some regions. Other maples, especially smaller or more unusual species, are popular as specimen trees.[1]
Cultivars
Numerous maple cultivars have been selected for particular characteristics and can be propagated only by grafting. Japanese Maple (A. palmatum) alone has over 1,000 cultivars, most selected in Japan, and many of them no longer propagated or not in cultivation in the western world.[1] Some delicate cultivars are usually grown in pots and rarely reach heights of more than 50-100 cm.
Bonsai
Maples are a popular choice for the art of bonsai. Japanese Maple, Trident Maple (A. buergerianum), Amur Maple (A. ginnala), Field Maple (A. campestre) and Montpellier Maple (A. monspessulanum) are popular choices and respond well to techniques that encourage leaf reduction and ramification, but most species can be used.[1]
Collections
Maple collections, sometimes called aceretums, occupy space in many gardens and arboreta around the world including the "five great W's" in England: Wakehurst Place Garden, Westonbirt Arboretum, Windsor Great Park, Winkworth Arboretum and Wisley Garden. In the United States, the aceretum at the Harvard-owned Arnold Arboretum in Boston is especially notable. In the number of species and cultivars, the Esveld Aceretum in Boskoop, Netherlands is the largest in the world.[1]
Tourism

Many Acer species have bright autumn foliage, and many countries have leaf-watching traditions. In Japan, the custom of viewing the changing color of maples in the autumn is called "momijigari". Nikko and Kyoto are particularly favored destinations for this activity.
The particularly spectacular fall colors of the Red Maple (A. rubrum) are a major contributor to the seasonal landscape in southeastern Canada and in New England. Fall tourism is a boon to the economy of this region, especially in Vermont, New Hampshire and Western Massachusetts.
In the American Pacific Northwest, it is the spectacular fall colors of the Vine Maple (A. circinatum) that draw tourists and photographers.
Commercial uses
Maples are important as source of syrup and wood. They are also cultivated as ornamental plants and have benefits for tourism and agriculture.
Maple syrup
The Sugar Maple (Acer saccharum) is tapped for sap, which is then boiled to produce maple syrup or made into maple sugar or maple candy. Syrup can be made from closely-related species as well, but their output is inferior.
Timber
Some of the larger maple species have valuable timber, particularly Sugar Maple in North America, and Sycamore Maple in Europe. Sugar Maple wood, often known as "hard maple", is the wood of choice for bowling pins, bowling alley lanes, drums and butcher's blocks. Maple wood is also used for the production of wooden baseball bats, though less often than ash or hickory.
Some maple wood has a highly decorative wood grain, known as flame maple and quilt maple. This condition occurs randomly in individual trees of several species, and often cannot be detected until the wood has been sawn, though it is sometimes visible in the standing tree as a rippled pattern in the bark. Maple is considered a tonewood, or a wood that carries sound waves well, and is used in numerous instruments such as guitars and drums.
Agriculture
As they are a major source of pollen in early spring before many other plants have flowered, maples are important to the survival of honeybees that play a commercially-important role later in the spring and summer.
Toys
Maple is also popular among toy manufacturers, most notably wooden toy trains.
Symbolism
The flag of Canada depicts a stylized maple leaf and is a prominent national symbol. In the United States, the maple has been adopted by five states as their official state tree. The sugar maple was adopted by New York,[2] Vermont,[3] Wisconsin[4] and West Virginia.[5] The red maple was adopted as the state tree of Rhode Island.[6] The maple leaf is also the symbol of the online game MapleStory from Wizet and Nexon.
- TenryujiMomiji.jpg
Japanese Maple trees and bamboo in Japan
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedgelderen - ↑ State of New York Dept. of State New York State Symbols. Retrieved Dec. 16 2006.
- ↑ State of Vermont Department of Libraries State Tree. Retrieved Dec. 16 2006.
- ↑ State of Wisconsin State Symbols. Retrieved Dec. 16 2006.
- ↑ Legislature of West Virginia State Symbols. Retrieved Dec. 16 2006.
- ↑ State of Rhode Island, Office of the Secretary of State. History And Facts About The Ocean State. Retrieved Dec. 16 2006.
.[1]
External links
- Flora of China draft synopsis of the family Aceraceae
- Classification of maples
- UVSC Herbarium - Maples
- Compare eastern North American maple species at bioimages.vanderbilt.edu
- Creating Bonsai with Maples
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
- ↑ Phillips, D. H. & Burdekin, D. A. (1992). Diseases of Forest and Ornamental Trees. Macmillan. ISBN 0-333-49493-8.
- ↑ van Gelderen, C.J. & van Gelderen, D.M. (1999). Maples for Gardens: A Color Encyclopedia









