Difference between revisions of "Human body" - New World Encyclopedia
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) (Adding human body article) |
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) (added a few mptes) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
'''Human anatomy''' or '''anthropotomy''' is a special field within [[anatomy]]. It studies organs and organ systems of the '''[[homo sapiens|human]] body''', leaving the study of tissues to [[histology]] and cells to [[cytology]]. | '''Human anatomy''' or '''anthropotomy''' is a special field within [[anatomy]]. It studies organs and organ systems of the '''[[homo sapiens|human]] body''', leaving the study of tissues to [[histology]] and cells to [[cytology]]. | ||
The human body, like the bodies of all animals, is made up of systems, that are made up of [[Organ (anatomy)|organ]]s, that are made up of [[Biological tissue|tissue]]s, that are made up of [[Biological cell|cell]]s. | The human body, like the bodies of all animals, is made up of systems, that are made up of [[Organ (anatomy)|organ]]s, that are made up of [[Biological tissue|tissue]]s, that are made up of [[Biological cell|cell]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | : From Britannica: the physical substance of the human organism, composed of living cells and extracellular materials and organized into tissues, organs, and systems. Human anatomy and physiology are treated in many different articles. For detailed coverage of the body's biochemical constituents, see protein; carbohydrate; lipid; nucleic acid; vitamin; and hormone. For information… | ||
| + | |||
| + | : From New Book of Knowledge: traces from elements, to cells, to systems | ||
| + | |||
See [[History of anatomy]] for a history of anatomy, including human anatomy. | See [[History of anatomy]] for a history of anatomy, including human anatomy. | ||
Revision as of 13:18, 30 October 2005
Note: This is only a very rough draft, with notes. Please do not edit this article until the actual article is complete — i.e., when this notice is removed. You may add comments on what you would like to see included. Rick Swarts 13:12, 30 Oct 2005 (UTC)
Human anatomy or anthropotomy is a special field within anatomy. It studies organs and organ systems of the human body, leaving the study of tissues to histology and cells to cytology. The human body, like the bodies of all animals, is made up of systems, that are made up of organs, that are made up of tissues, that are made up of cells.
- From Britannica: the physical substance of the human organism, composed of living cells and extracellular materials and organized into tissues, organs, and systems. Human anatomy and physiology are treated in many different articles. For detailed coverage of the body's biochemical constituents, see protein; carbohydrate; lipid; nucleic acid; vitamin; and hormone. For information…
- From New Book of Knowledge: traces from elements, to cells, to systems
See History of anatomy for a history of anatomy, including human anatomy.
Major systems of the human body
- Cardiovascular system: blood circulations with heart and blood vessels
- Digestive system: processing food with mouth, stomach and intestines
- Endocrine system: communicating within the body using hormones
- Excretory system: eliminating wastes from the body
- Immune system: defending against disease-causing agents
- Integumentary system: skin, hair and nails
- Muscular system: moving the body
- Nervous system: collecting, transferring and processing information with brain and nerves
- Reproductive system: the sex organs
- Respiratory system: the organs used for breathing, the lungs
- Skeletal system: structural support and protection through bones.
External features
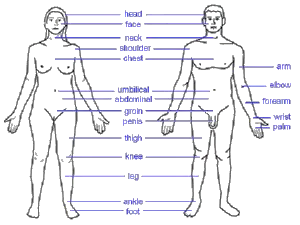
Common names of well known parts of the human body, from top to bottom :
- Skin
- Head — Forehead — Eye — Ear — Nose — Mouth — Tongue — Teeth — Jaw — Face — Cheek — Chin
- Neck — Throat — Adam's apple — Shoulders
- Arm — Elbow — Wrist — Hand — Fingers — Thumb
- Spine — Chest — Breast — Ribcage
- Abdomen — Belly button — Sex organs (Penis/Scrotum or Clitoris/Vagina) — Rectum — Anus
- Hip — Buttocks — Leg — Thigh — Knee — Calf — Heel — Ankle — Foot — Toes
Internal organs
Common names of internal organs (in alphabetical order) :
- Adrenal glands — Appendix — Bladder — Brain — Duodenum — Gall bladder — Heart — Intestines — Kidney —Liver— Lungs — Ovaries — Pancreas — Parathyroid gland — Pituitary gland — Prostate gland — Spleen — Stomach — Thymus gland — Thyroid gland — Testicles — Womb
Anatomy of the brain
- Amygdala — Brainstem — Cerebellum — Cerebral cortex — Hypothalamus — Limbic system — medulla— midbrain — Pituitary gland — pons
- See also: Human brain, List of regions in the human brain
Studying human anatomy
Certain professions, especially medicine and physiotherapy, require the study of human anatomy in depth. Textbooks usually split the body into the following regional groups:
- Head and Neck - includes everything above the thoracic inlet
- Upper limb - includes everything from your hand, forearm, arm, shoulder, axilla, pectoral region and scapular region.
- Thorax - contains the region of the chest from the thoracic inlet to the thoracic diaphragm.
- Abdomen - everything from the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvic brim or to the pelvic inlet.
- The back - about the spine and its components, the intervetebral disks and bodies
- Pelvis and Perineum - the pelvis consists of everything from the pelvic inlet to the pelvic diaphragm. The perineum is everything below the pelvic diaphragm.
- Lower limb - the lower limb is usually everything below the inguinal ligament, including the thigh, the hip joint, the leg, and the foot.
See also
- Anatomy
- Body orifices
- Death - physical consequences of death
- Human
- Human biology
- Terms for anatomical location
- List of human anatomical features
- List of human anatomical parts named after people
- List of regions in the human brain
- List of bones of the human skeleton
- List of muscles of the human body
- List of distinct cell types in the adult human body
an:Anatomía umana zh-min-nan:Sin-khu de:Anatomie des Menschen et:Inimese anatoomia es:Anatomía humana eo:Homa anatomio fa:کالبدشناسی انسان fr:Anatomie humaine it:Anatomia umana he:גוף האדם hu:Emberi test nl:Menselijke anatomie ja:人体解剖学 no:Menneskets anatomi pl:Anatomia człowieka pt:Corpo humano sk:Anatómia človeka sl:Anatomija človeka uk:Анатомія людини zh:人体
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.