Difference between revisions of "Ptolemaic dynasty" - New World Encyclopedia
(credit Wiki) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ||
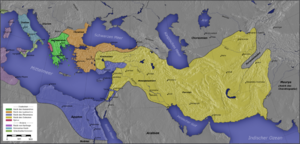
[[Image:Diadochen1.png|thumb|right|float|300px| | [[Image:Diadochen1.png|thumb|right|float|300px| | ||
{{legend|#787CAD|Kingdom of [[Ptolemy I Soter|Ptolemy]]}} | {{legend|#787CAD|Kingdom of [[Ptolemy I Soter|Ptolemy]]}} | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
{{legend|#85AB54|[[Greek colonies]]}} | {{legend|#85AB54|[[Greek colonies]]}} | ||
]] | ]] | ||
| − | The '''Ptolemaic dynasty''' (sometimes also known as the '''Lagids''', from the name of Ptolemy I's father, | + | The '''Ptolemaic dynasty''' (sometimes also known as the '''Lagids''', from the name of Ptolemy I's father, Lagus) was a Hellenistic [[Ancient Greece|Macedonian]] royal family which ruled the Ptolemaic Empire in [[Egypt]] for nearly 300 years, from 305 B.C.E. to 30 B.C.E. |
| − | [[Ptolemy I Soter|Ptolemy]], a | + | [[Ptolemy I Soter|Ptolemy]], a somatophylax, one of the seven bodyguards who served as [[Alexander the Great]]'s generals and deputies, was appointed satrap of [[Egypt]] after Alexander's death in 323 B.C.E. In 305 B.C.E., he declared himself King Ptolemy I, later known as "Soter" (saviour). The [[Egyptians]] soon accepted the Ptolemies as the successors to the [[pharaoh]]s of independent Egypt. Ptolemy's family ruled Egypt until the [[Rome|Roman]] conquest of 30 B.C.E. |
| − | All the male rulers of the dynasty took the name Ptolemy. | + | All the male rulers of the dynasty took the name Ptolemy. Ptolemaic queens, some of whom were the sisters of their husbands, were usually called Cleopatra, Arsinoe or Berenice. The most famous member of the line was the last queen, [[Cleopatra|Cleopatra VII]], known for her role in the Roman political battles between [[Julius Caesar]] and [[Pompey]], and later between [[Augustus Caesar|Octavian]] and [[Mark Antony]]. Her suicide at the conquest by Rome marked the end of Ptolemaic rule in Egypt. |
== Ptolemaic rulers and consorts == | == Ptolemaic rulers and consorts == | ||
| − | The dates in brackets are regnal dates for the kings. They frequently ruled jointly with their wives, who were often also their sisters. Several queens exercised regal authority, but the most famous and successful was [[Cleopatra VII]] ( | + | The dates in brackets are regnal dates for the kings. They frequently ruled jointly with their wives, who were often also their sisters. Several queens exercised regal authority, but the most famous and successful was [[Cleopatra VII]] (51 B.C.E.-30 B.C.E.), with her two brothers and her son as successive nominal co-rulers. Several systems exist for numbering the later rulers; the one used here is the one most widely used by modern scholars. Dates are years of reign. |
| − | * [[Ptolemy I Soter]] ( | + | * [[Ptolemy I Soter]] (305 B.C.E.-282 B.C.E.) married first (probably) Thais, secondly Artakama, thirdly Eurydice]] and finally Berenice I |
| − | * [[Ptolemy II Philadelphus]] ( | + | * [[Ptolemy II Philadelphus]] (284 B.C.E.-246 B.C.E.) married Arsinoe I, then Arsinoe II Philadelphus; ruled jointly with Ptolemy the Son (267 B.C.E.-259 B.C.E.) |
| − | * | + | * Ptolemy III Euergetes (246 B.C.E.-222 B.C.E.) married [[Berenice II of Egypt|Berenice II]] |
| − | * [[Ptolemy IV Philopator]] ( | + | * [[Ptolemy IV Philopator]] (222 B.C.E.-204 B.C.E.) married [[Arsinoe III of Egypt|Arsinoe III]] |
| − | * [[Ptolemy V Epiphanes]] ( | + | * [[Ptolemy V Epiphanes]] (204 B.C.E.-180 B.C.E.) married [[Cleopatra I of Egypt|Cleopatra I]] |
| − | * [[Ptolemy VI Philometor]] ( | + | * [[Ptolemy VI Philometor]] (180 B.C.E.-164 B.C.E., 163 B.C.E.-145 B.C.E.) married [[Cleopatra II of Egypt|Cleopatra II]], briefly ruled jointly with [[Ptolemy Eupator]] in 152 B.C.E. |
* [[Ptolemy VII Neos Philopator]] (never reigned) | * [[Ptolemy VII Neos Philopator]] (never reigned) | ||
| − | * [[Ptolemy VIII Physcon|Ptolemy VIII Euergetes II (Physcon)]] ( | + | * [[Ptolemy VIII Physcon|Ptolemy VIII Euergetes II (Physcon)]] (170 B.C.E.-163 B.C.E., 145 B.C.E.-116 B.C.E.) married [[Cleopatra II of Egypt|Cleopatra II]] then [[Cleopatra III of Egypt|Cleopatra III]]; temporarily expelled from Alexandria by Cleopatra II between 131 B.C.E. and 127 B.C.E., reconciled with her in 124 B.C.E. |
| − | * [[Cleopatra II of Egypt|Cleopatra II Philometora Soteira]] ( | + | * [[Cleopatra II of Egypt|Cleopatra II Philometora Soteira]] (131 B.C.E.-127 B.C.E.), in opposition to [[Ptolemy VIII of Egypt|Ptolemy VIII]] |
| − | * [[Cleopatra III of Egypt|Cleopatra III Philometor Soteira Dikaiosyne Nikephoros (Kokke)]] ( | + | * [[Cleopatra III of Egypt|Cleopatra III Philometor Soteira Dikaiosyne Nikephoros (Kokke)]] (116 B.C.E.-101 B.C.E.) ruled jointly with [[Ptolemy IX of Egypt|Ptolemy IX]] (116 B.C.E.-107 B.C.E.) and [[Ptolemy X of Egypt|Ptolemy X]] (107 B.C.E.-101 B.C.E.) |
| − | * [[Ptolemy IX Lathyros|Ptolemy IX Soter II (Lathyros)]] ( | + | * [[Ptolemy IX Lathyros|Ptolemy IX Soter II (Lathyros)]] (116 B.C.E.-107 B.C.E., 88 B.C.E.-81 B.C.E. as Soter II) married [[Cleopatra IV of Egypt|Cleopatra IV]] then [[Cleopatra Selene I|Cleopatra Selene]]; ruled jointly with [[Cleopatra III of Egypt|Cleopatra III]] in his first reign |
| − | * [[Ptolemy X of Egypt|Ptolemy X]] Alexander I ( | + | * [[Ptolemy X of Egypt|Ptolemy X]] Alexander I (107 B.C.E.-88 B.C.E.) married [[Cleopatra Selene I|Cleopatra Selene]] then [[Berenice III of Egypt|Berenice III]]; ruled jointly with [[Cleopatra III of Egypt|Cleopatra III]] till 101 B.C.E. |
| − | * [[Berenice III of Egypt|Berenice III Philopator]] ( | + | * [[Berenice III of Egypt|Berenice III Philopator]] (81 B.C.E.-80 B.C.E.) |
| − | * [[Ptolemy XI]] Alexander II ( | + | * [[Ptolemy XI]] Alexander II (80 B.C.E.) married and ruled jointly with [[Berenice III of Egypt|Berenice III]] before murdering her; ruled alone for 19 days after that. |
| − | * [[Ptolemy XII Auletes|Ptolemy XII Neos Dionysos (Auletes)]] ( | + | * [[Ptolemy XII Auletes|Ptolemy XII Neos Dionysos (Auletes)]] (80 B.C.E.-58 B.C.E., 55 B.C.E.-51 B.C.E.) married [[Cleopatra V of Egypt|Cleopatra V Tryphaena]] |
| − | * [[Cleopatra V of Egypt|Cleopatra V Tryphaena]] ( | + | * [[Cleopatra V of Egypt|Cleopatra V Tryphaena]] (58 B.C.E.-57 B.C.E.) ruled jointly with [[Berenice IV of Egypt|Berenice IV Epiphaneia]] (58 B.C.E.-55 B.C.E.) |
| − | * [[Cleopatra VII of Egypt|Cleopatra VII Philopator]] ( | + | * [[Cleopatra VII of Egypt|Cleopatra VII Philopator]] (51 B.C.E.-30 B.C.E.) ruled jointly with [[Ptolemy XIII of Egypt|Ptolemy XIII]] (51 B.C.E.-47 B.C.E.), [[Ptolemy XIV of Egypt|Ptolemy XIV]] (47 B.C.E.-44 B.C.E.) and [[Caesarion|Ptolemy XV Caesarion]] (44 B.C.E.-30 B.C.E.). |
| − | * [[Arsinoe IV of Egypt|Arsinoe IV]] ( | + | * [[Arsinoe IV of Egypt|Arsinoe IV]] (48 B.C.E.-47 B.C.E.) in opposition to [[Cleopatra VII of Egypt|Cleopatra VII]] |
==Simplified Ptolemaic family tree== | ==Simplified Ptolemaic family tree== | ||
| − | Many of the relationships shown in this tree are controversial. | + | Many of the relationships shown in this tree are controversial. The issues are fully discussed in the external links. |
[[Image:EgyptianPtolemies.png|center|]] | [[Image:EgyptianPtolemies.png|center|]] | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
==Other members of the Ptolemaic dynasty== | ==Other members of the Ptolemaic dynasty== | ||
| − | *[[Ptolemy Keraunos]] (died 279 | + | *[[Ptolemy Keraunos]] (died 279 B.C.E.) - eldest son of Ptolemy I Soter. Eventually became king of Macedon. |
| − | *[[Ptolemy Apion]] (died 96 | + | *[[Ptolemy Apion]] (died 96 B.C.E.) - son of Ptolemy VIII Physcon. Made king of Cyrenaica. Bequeathed Cyrenaica to Rome. |
| − | *[[Ptolemy Philadelphus (Cleopatra)|Ptolemy Philadelphus]] (born 36 | + | *[[Ptolemy Philadelphus (Cleopatra)|Ptolemy Philadelphus]] (born 36 B.C.E.) - son of [[Mark Antony]] and Cleopatra VII. |
| − | *[[Ptolemy of Mauretania]] (died AD | + | *[[Ptolemy of Mauretania]] (died AD 40) - son of [[Juba II]] of Mauretania and [[Cleopatra Selene II]], daughter of [[Cleopatra VII]] and [[Mark Antony]]. King of [[Mauretania]]. |
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
{{Hellenistic rulers}} | {{Hellenistic rulers}} | ||
| − | [[Category:305 | + | [[Category:305 B.C.E. establishments]] |
[[Category:Ptolemaic dynasty| ]] | [[Category:Ptolemaic dynasty| ]] | ||
[[Category:Royal families]] | [[Category:Royal families]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[cv:Птолемейсем]] | [[cv:Птолемейсем]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[jv:Dinasti Ptolemeus]] | [[jv:Dinasti Ptolemeus]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[sh:Ptolemeidi]] | [[sh:Ptolemeidi]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Credit|232493373}} | {{Credit|232493373}} | ||
Revision as of 19:21, 18 September 2008
The Ptolemaic dynasty (sometimes also known as the Lagids, from the name of Ptolemy I's father, Lagus) was a Hellenistic Macedonian royal family which ruled the Ptolemaic Empire in Egypt for nearly 300 years, from 305 B.C.E. to 30 B.C.E.
Ptolemy, a somatophylax, one of the seven bodyguards who served as Alexander the Great's generals and deputies, was appointed satrap of Egypt after Alexander's death in 323 B.C.E. In 305 B.C.E., he declared himself King Ptolemy I, later known as "Soter" (saviour). The Egyptians soon accepted the Ptolemies as the successors to the pharaohs of independent Egypt. Ptolemy's family ruled Egypt until the Roman conquest of 30 B.C.E.
All the male rulers of the dynasty took the name Ptolemy. Ptolemaic queens, some of whom were the sisters of their husbands, were usually called Cleopatra, Arsinoe or Berenice. The most famous member of the line was the last queen, Cleopatra VII, known for her role in the Roman political battles between Julius Caesar and Pompey, and later between Octavian and Mark Antony. Her suicide at the conquest by Rome marked the end of Ptolemaic rule in Egypt.
Ptolemaic rulers and consorts
The dates in brackets are regnal dates for the kings. They frequently ruled jointly with their wives, who were often also their sisters. Several queens exercised regal authority, but the most famous and successful was Cleopatra VII (51 B.C.E.-30 B.C.E.), with her two brothers and her son as successive nominal co-rulers. Several systems exist for numbering the later rulers; the one used here is the one most widely used by modern scholars. Dates are years of reign.
- Ptolemy I Soter (305 B.C.E.-282 B.C.E.) married first (probably) Thais, secondly Artakama, thirdly Eurydice]] and finally Berenice I
- Ptolemy II Philadelphus (284 B.C.E.-246 B.C.E.) married Arsinoe I, then Arsinoe II Philadelphus; ruled jointly with Ptolemy the Son (267 B.C.E.-259 B.C.E.)
- Ptolemy III Euergetes (246 B.C.E.-222 B.C.E.) married Berenice II
- Ptolemy IV Philopator (222 B.C.E.-204 B.C.E.) married Arsinoe III
- Ptolemy V Epiphanes (204 B.C.E.-180 B.C.E.) married Cleopatra I
- Ptolemy VI Philometor (180 B.C.E.-164 B.C.E., 163 B.C.E.-145 B.C.E.) married Cleopatra II, briefly ruled jointly with Ptolemy Eupator in 152 B.C.E.
- Ptolemy VII Neos Philopator (never reigned)
- Ptolemy VIII Euergetes II (Physcon) (170 B.C.E.-163 B.C.E., 145 B.C.E.-116 B.C.E.) married Cleopatra II then Cleopatra III; temporarily expelled from Alexandria by Cleopatra II between 131 B.C.E. and 127 B.C.E., reconciled with her in 124 B.C.E.
- Cleopatra II Philometora Soteira (131 B.C.E.-127 B.C.E.), in opposition to Ptolemy VIII
- Cleopatra III Philometor Soteira Dikaiosyne Nikephoros (Kokke) (116 B.C.E.-101 B.C.E.) ruled jointly with Ptolemy IX (116 B.C.E.-107 B.C.E.) and Ptolemy X (107 B.C.E.-101 B.C.E.)
- Ptolemy IX Soter II (Lathyros) (116 B.C.E.-107 B.C.E., 88 B.C.E.-81 B.C.E. as Soter II) married Cleopatra IV then Cleopatra Selene; ruled jointly with Cleopatra III in his first reign
- Ptolemy X Alexander I (107 B.C.E.-88 B.C.E.) married Cleopatra Selene then Berenice III; ruled jointly with Cleopatra III till 101 B.C.E.
- Berenice III Philopator (81 B.C.E.-80 B.C.E.)
- Ptolemy XI Alexander II (80 B.C.E.) married and ruled jointly with Berenice III before murdering her; ruled alone for 19 days after that.
- Ptolemy XII Neos Dionysos (Auletes) (80 B.C.E.-58 B.C.E., 55 B.C.E.-51 B.C.E.) married Cleopatra V Tryphaena
- Cleopatra V Tryphaena (58 B.C.E.-57 B.C.E.) ruled jointly with Berenice IV Epiphaneia (58 B.C.E.-55 B.C.E.)
- Cleopatra VII Philopator (51 B.C.E.-30 B.C.E.) ruled jointly with Ptolemy XIII (51 B.C.E.-47 B.C.E.), Ptolemy XIV (47 B.C.E.-44 B.C.E.) and Ptolemy XV Caesarion (44 B.C.E.-30 B.C.E.).
- Arsinoe IV (48 B.C.E.-47 B.C.E.) in opposition to Cleopatra VII
Simplified Ptolemaic family tree
Many of the relationships shown in this tree are controversial. The issues are fully discussed in the external links.
Other members of the Ptolemaic dynasty
- Ptolemy Keraunos (died 279 B.C.E.) - eldest son of Ptolemy I Soter. Eventually became king of Macedon.
- Ptolemy Apion (died 96 B.C.E.) - son of Ptolemy VIII Physcon. Made king of Cyrenaica. Bequeathed Cyrenaica to Rome.
- Ptolemy Philadelphus (born 36 B.C.E.) - son of Mark Antony and Cleopatra VII.
- Ptolemy of Mauretania (died AD 40) - son of Juba II of Mauretania and Cleopatra Selene II, daughter of Cleopatra VII and Mark Antony. King of Mauretania.
See also
- Hellenistic period
- History of ancient Egypt
- Ptolemaic kingdom
- Ptolemy I Soter
- Ptolemaic Decrees
External links
- Ptolemaic Dynasty
- Livius, Ptolemies by Jona Lendering
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
cv:Птолемейсем jv:Dinasti Ptolemeus sh:Ptolemeidi
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.