Difference between revisions of "Info: Popular articles" - New World Encyclopedia
Svemir Brkic (talk | contribs) (Add August) |
(changed to weekly number) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<div class="infobox" style="padding:4px"> | <div class="infobox" style="padding:4px"> | ||
==August 2007== | ==August 2007== | ||
| − | {{Popular article 2007 | + | {{Popular article 2007 31}} |
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
<div class="infobox" style="padding:4px"> | <div class="infobox" style="padding:4px"> | ||
==June 2007== | ==June 2007== | ||
| − | {{Popular article 2007 | + | {{Popular article 2007 26}} |
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | {{Popular article 2007 | + | {{Popular article 2007 25}} |
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | {{Popular article 2007 | + | {{Popular article 2007 24}} |
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | {{Popular article 2007 | + | {{Popular article 2007 23}} |
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
<div class="infobox" style="padding:4px"> | <div class="infobox" style="padding:4px"> | ||
==July 2007== | ==July 2007== | ||
| − | {{Popular article 2007 | + | {{Popular article 2007 30}} |
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | {{Popular article 2007 | + | {{Popular article 2007 29}} |
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | {{Popular article 2007 | + | {{Popular article 2007 28}} |
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | {{Popular article 2007 | + | {{Popular article 2007 27}} |
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
<div class="infobox" style="padding:4px"> | <div class="infobox" style="padding:4px"> | ||
==May 2007== | ==May 2007== | ||
| − | {{Popular article 2007 | + | {{Popular article 2007 22}} |
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 15:14, 3 August 2007
August 2007
Ecology or ecological science, is the scientific study of the distribution and abundance of living organisms and how these properties are affected by interactions between the organisms and their environment.
June 2007
Isabella of Castile (April 22, 1451 – November 26, 1504) was queen of Castile and Aragon and her husband, Ferdinand II of Aragon, were responsible for establishing the foundation for the political unification of Spain that occurred during the reign of their grandson, Carlos I of Spain.
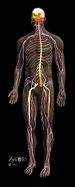
The human body is the physical manifestation of a human being, including the chemical elements, cells, and extracellular materials and the organization of these materials into tissues, organs, and systems.
The Aztecs were a Mesoamerican people of central Mexico in the fourteenth, fifteenth, and sixteenth centuries.
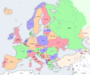
In general discussion, a nation-state is variously called a "country," a "nation," or a "state."
July 2007
Broadly defined, evolution is any heritable change in a population of organisms over time.
Trees are the largest plants. They are not a single taxon (unit of biological classification) but include members of many plant taxa.
The Inca Civilization (called Tawantinsuyu in modern spelling, and Quechua, or Tahuantinsuyu in old spelling), was an empire located in South America from 1438 c.e. to 1533 c.e.
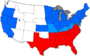
The watershed event of United States history was the American Civil War (1861–1865), fought in North America between 24 mostly northern states of the Union and the Confederate States of America, a coalition of eleven southern states.
May 2007
Birds (class Aves) are bipedal, warm-blooded, oviparous (egg-laying) vertebrates characterized primarily by feathers, forelimbs modified as wings, and a bony beak without teeth.