Difference between revisions of "William I of England" - New World Encyclopedia
m (Protected "William I of England": copyedited [edit=sysop:move=sysop]) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Paid}}{{Approved}}{{Images OK}}{{Claimed}}{{Contracted}}{{Submitted}}{{ | + | {{Paid}}{{Approved}}{{Images OK}}{{Claimed}}{{Contracted}}{{Submitted}}{{copyedited}} |
{{Infobox British Royalty|majesty | {{Infobox British Royalty|majesty | ||
| − | | name | + | | name =William I the Conqueror |
| − | | title | + | | title =[[List of English monarchs#Normans|King of the English]]; [[Duke of Normandy]] |
| − | | image | + | | image =William1.jpg |
| − | | imgw | + | | imgw =225 |
| − | | caption | + | | caption =The Duke of Normandy in the [[Bayeux Tapestry]] |
| − | | reign | + | | reign =December 25, 1066–September 9, 1087 |
| − | | coronation | + | | coronation =December 25, 1066 |
| − | | predecessor | + | | predecessor =[[Harold Godwinson|Harold II]]<br />''Normandy:'' [[Robert II, Duke of Normandy|Robert II the Magnificent]] |
| − | | successor | + | | successor =[[William II of England|William II Rufus]]<br />''Normandy:'' [[Robert III, Duke of Normandy|Robert III Curthose]] |
| − | | spouse | + | | spouse =[[Matilda of Flanders]] (1031–1083) |
| − | | issue | + | | issue =[[Robert III, Duke of Normandy|Robert III Curthose]]<br />[[William II of England|William II Rufus]]<br />[[Adela of Normandy|Adela, Countess of Blois]]<br />[[Henry I of England|Henry I Beauclerc]]<br />''[[#Children of William and Matilda|among others...]]'' |
| − | | father | + | | father =[[Robert II, Duke of Normandy|Robert II the Magnificent]] |
| − | | mother | + | | mother =[[Herleva|Herlette of Falaise]] |
| − | | date of birth | + | | date of birth =1027–1028 |
| − | | place of birth | + | | place of birth =[[Falaise]], [[France]] |
| − | | date of death | + | | date of death =September 9, 1087 |
| − | | place of death | + | | place of death =Convent of St. Gervais, [[Rouen]] |
| − | | place of burial | + | | place of burial =[[Abbaye-aux-Hommes|Saint-Étienne de Caen]], [[France]] |
|}} | |}} | ||
| − | '''William of Normandy''' (''[[French language|French]]: Guillaume de Normandie''; | + | '''William of Normandy''' (''[[French language|French]]: Guillaume de Normandie''; 1028 – September 9, 1087) ruled as the [[Duke of Normandy]] from 1035 to 1087 and as [[English monarchy|King of England]] from 1066 to 1087. William invaded [[England]], won a victory at the [[Battle of Hastings]] in 1066, and suppressed subsequent English revolts in what has become known as the [[Norman Conquest]]. No authentic portrait of William has been found but he was described as a muscular man, strong in every sense of the word, balding in front, and of regal dignity. |
| − | In the present nomenclature, William was Duke of Normandy as '''William II''' and King of England as '''William I''' | + | In the present nomenclature, William was Duke of Normandy as '''William II''' and King of England as '''William I.''' He is also known as '''William the Conqueror''' ''(Guillaume le Conquérant)'' and '''William the Bastard''' ''(Guillaume le Bâtard).'' In English memory, the Norman Conquest represents a defining moment, regarded by some as bringing to an end one phase of English history and launching another. The Saxon period, during which England had been relatively uninvolved in European affairs, ended and a period of European engagement began in which relations between the English and French rulers and nobility became much more complex. For the next five centuries, England would become embroiled in contests for European territory based on royal blood-line claims derived from William I. Positively, English culture and French culture blended as a result of the conquest, making England more European. William also imported one hundred Norman peasants, whose blood-line would mix with that of Saxon peasants just as the new Normal nobles would inter-marry with the older Saxon aristocracy. Years later, when [[Elizabeth I of England]] gave up her claim to the last piece of French territory, England turned its attention instead to overseas exploration and colonies. |
==Early life== | ==Early life== | ||
| − | The sole son of [[Robert the Magnificent]] and [[Herleva]], most likely the daughter of a local tanner named Fulbert, William was born [[Illegitimacy|illegitimate]] in [[Falaise, Calvados, France|Falaise]], [[Normandy]]. The exact date of birth is uncertain, but is known to have been either in 1027 or 1028, and more likely in the autumn of the latter year.<ref> | + | The sole son of [[Robert the Magnificent]] and [[Herleva]], most likely the daughter of a local tanner named Fulbert, William was born [[Illegitimacy|illegitimate]] in [[Falaise, Calvados, France|Falaise]], [[Normandy]]. The exact date of birth is uncertain, but is known to have been either in 1027 or 1028, and more likely in the autumn of the latter year.<ref>History of the Monarchy. [http://www.royal.gov.uk/output/Page18.asp William I ‘The Conqueror’ (r. 1066-1087)] Retrieved June 5, 2007. </ref> He was the [[Family#Western kinship terminology|grandnephew]] of Queen [[Emma of Normandy|Emma]], wife of King [[Ethelred the Unready]] and later of King [[Canute the Great|Canute]]. |
| − | William succeeded to his father's [[Duchy of Normandy]] at the young age of seven in 1035 and was known as Duke William II of Normandy ([[French language| | + | William succeeded to his father's [[Duchy of Normandy]] at the young age of seven in 1035 and was known as Duke William II of Normandy ([[French language|French]] ''Guillaume II, duc de Normandie''). He lost three guardians to plots to usurp his place. Count [[Dukes of Brittany family tree|Alan of Brittany]] was a later guardian. King [[Henri I of France|Henry I of France]] knighted him at the age of 15. By the time he turned 19 he was successfully dealing with threats of rebellion and invasion. With the assistance of King Henry, William finally secured control of Normandy by defeating the rebel Norman barons at [[Caen]] in the [[Battle of Val-ès-Dunes]] in 1047. |
| − | He married his cousin [[Matilda of Flanders]], against the wishes of Pope Leo IX in 1053 at the Cathedral of Notre Dame at [[Eu, Seine-Maritime|Eu]], Normandy (now in [[Seine-Maritime]]). At the time, William was 26 and Matilda was 22. Their marriage produced four sons and six daughters | + | He married his cousin [[Matilda of Flanders]], against the wishes of Pope Leo IX in 1053 at the Cathedral of Notre Dame at [[Eu, Seine-Maritime|Eu]], Normandy (now in [[Seine-Maritime]]). At the time, William was 26 and Matilda was 22. Their marriage produced four sons and six daughters. |
His half-brothers [[Odo of Bayeux]] and [[Robert, Count of Mortain]] played significant roles in his life. He also had a sister, [[Adelaide of Normandy]]. | His half-brothers [[Odo of Bayeux]] and [[Robert, Count of Mortain]] played significant roles in his life. He also had a sister, [[Adelaide of Normandy]]. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
==Conquest of England== | ==Conquest of England== | ||
| − | Upon the death of William's cousin King [[Edward the Confessor]] of England (January 1066), William claimed the throne of England, asserting that the childless and purportedly celibate Edward had named him his heir during a visit by William (probably in 1052) and that [[Harold Godwinson]], England's foremost [[magnate]] and brother-in-law of the late King Edward | + | Upon the death of William's cousin King [[Edward the Confessor]] of England (January 1066), William claimed the throne of England, asserting that the childless and purportedly celibate Edward had named him his heir during a visit by William (probably in 1052) and that [[Harold Godwinson]], England's foremost [[magnate]] and brother-in-law of the late King Edward, had reportedly pledged his support while shipwrecked in Normandy in 1064. Harold made this pledge while in captivity and was reportedly tricked into swearing on a saint's bones that he would give the throne to William. Even if this story is true, however, Harold made the promise under duress and so may have felt free to break it. More realistically, by the mid 1050s, Harold was effectively ruling England through the weak King Edward and was unlikely to surrender the throne to a foreign noble. |
| − | The assembly of England's leading nobles known as the [[Witenagemot]] approved Harold Godwinson’s coronation which took place on 5 | + | The assembly of England's leading nobles known as the [[Witenagemot]] approved Harold Godwinson’s coronation which took place on January 5, 1066 making him King [[Harold II of England]]. In order to pursue his own claim, William obtained the support of [[Pope Alexander II]] for his cause. He assembled a Norman invasion fleet of around six hundred ships and an army of seven thousand men. He landed at [[Pevensey]] in [[Sussex]] on September 28, 1066 and assembled a prefabricated wooden castle([[Motte-and-bailey]]) near [[Hastings]] as a base. This was a direct provocation to Harold Godwinson as this area of Sussex was Harold's own personal estate, and William began immediately to lay waste to the land. It may have prompted Harold to respond immediately and in haste rather than await reinforcements in [[London]]. |
| − | King Harold Godwinson was in the north of England and had just defeated another rival, [[Harald III of Norway]], supported by his own brother Tostig. He marched an army of similar size to William's 250 miles in | + | King Harold Godwinson was in the north of England and had just defeated another rival, [[Harald III of Norway]], supported by his own brother Tostig. He marched an army of similar size to William's 250 miles in nine days to challenge him at the crucial battle of Senlac, which later became known as the [[Battle of Hastings]]. This took place on October 14, 1066. According to some accounts, perhaps based on an interpretation of the [[Bayeux Tapestry]] commemorating the Norman victory, Harold was allegedly killed by an arrow through the eye, and the English forces fled giving William victory. |
| − | This was the defining moment of what is now known as the [[Norman Conquest]]. Unable to enter London, William | + | This was the defining moment of what is now known as the [[Norman Conquest]]. Unable to enter London, William traveled to [[Wallingford]], was welcomed in by [[Wigod]] who supported his cause. This is where the first submissions took place, including that of the Archbishop of Canterbury.<ref>Ford, David Nash. [http://www.berkshirehistory.com/villages/wallingford.html Wallingford: Saxon Planning Lives On] Retrieved June 5, 2007.</ref> The remaining Anglo-Saxon noblemen surrendered to William at [[Berkhamsted]], [[Hertfordshire]] and he was acclaimed King of England there. William was then crowned on December 25, 1066 in [[Westminster Abbey]]. |
| − | Although the south of England submitted quickly to Norman rule, resistance continued, especially in the North for six more years until 1072. Harold's illegitimate sons attempted an invasion of the | + | Although the south of England submitted quickly to Norman rule, resistance continued, especially in the North, for six more years until 1072. Harold's illegitimate sons attempted an invasion of the southwest peninsula. Uprisings occurred in the [[Welsh Marches]] and at [[Stafford]]. Separate attempts at invasion by the [[Denmark|Danes]] and the [[Scotland|Scots]] also occurred. William's defeat of these led to what became known as the [[harrying of the North]], in which William laid [[Northumbria]] to waste in revenge as well as to deny his enemies its resources. The last serious resistance came with the [[Revolt of the Earls]] in 1075. It is estimated that one-fifth of the population of England was killed during these years by war, massacre, and starvation. |
==William's reign== | ==William's reign== | ||
| − | [[Image:acrdwnch.JPG|right|thumb|300px|The signatures of William I and Matilda are the first two large crosses on the [[Accord of Winchester]] from 1072.]]William initiated many major changes. In 1085, in order to ascertain the extent of his new dominions and maximize taxation, William commissioned the compilation of the [[Domesday Book]], a survey of England's productive capacity similar to a modern [[census]]. He also ordered many [[castle]]s, [[keep]]s, and [[motte-and-bailey|mottes]], among them the [[Tower of London]], to be built across England to ensure that the rebellions by the English people or his own followers would not succeed. His conquest also led to [[Norman language|Norman]] replacing [[History of the English Language#Period of French Domination|English]] as the language of the ruling classes for nearly | + | [[Image:acrdwnch.JPG|right|thumb|300px|The signatures of William I and Matilda are the first two large crosses on the [[Accord of Winchester]] from 1072.]]William initiated many major changes. In 1085, in order to ascertain the extent of his new dominions and maximize taxation, William commissioned the compilation of the [[Domesday Book]], a survey of England's productive capacity similar to a modern [[census]]. He also ordered many [[castle]]s, [[keep]]s, and [[motte-and-bailey|mottes]], among them the [[Tower of London]], to be built across England to ensure that the rebellions by the English people or his own followers would not succeed. His conquest also led to [[Norman language|Norman]] replacing [[History of the English Language#Period of French Domination|English]] as the language of the ruling classes for nearly three hundred years. This is why Anglo-Saxon words such as cow and sheep were used by the peasants who farmed the livestock but when the meat reached the noblemen's tables the food became beef and mutton. |
| − | William is said to have deported some of the Anglo-Saxon land owning classes into [[slavery]] | + | William is said to have deported some of the Anglo-Saxon land owning classes into [[slavery]] throughout Bristol. Many ended up in [[Umayyads|Umayyad]] Spain and [[Moorish]] lands. Ownership of nearly all land in England and titles to religious and public offices were given to Normans. Many surviving Anglo-Saxon nobles emigrated to other European kingdoms. |
==Death, burial, and succession== | ==Death, burial, and succession== | ||
| − | William died at the age of 59, at the Convent of St Gervais, near [[Rouen]], France, on 9 | + | |
| + | William died at the age of 59, at the Convent of St Gervais, near [[Rouen]], France, on September 9, 1087, from abdominal injuries received from his saddle pommel when he fell off a horse at the Siege of [[Mantes]]. William was [[burial|buried]] in the church of St. Stephen in [[Caen]], [[Normandy]]. In a most undignified postmortem, his [[obesity|corpulent]] body would not fit into the stone [[sarcophagus]], and burst after some unsuccessful prodding by the assembled [[bishop]]s, filling the chapel with a foul smell and dispersing the mourners.<ref>History House. [http://historyhouse.com/in_history/william/ William the Conqueror] Retrieved June 5, 2007. </ref> | ||
William was succeeded in 1087 as King of England by his younger son [[William II of England|William Rufus]] and as Duke of Normandy by his elder son [[Robert Curthose]]. This led to the [[Rebellion of 1088]]. His youngest son [[Henry I of England|Henry]] also became King of England later, after William II died without a child to succeed him. | William was succeeded in 1087 as King of England by his younger son [[William II of England|William Rufus]] and as Duke of Normandy by his elder son [[Robert Curthose]]. This led to the [[Rebellion of 1088]]. His youngest son [[Henry I of England|Henry]] also became King of England later, after William II died without a child to succeed him. | ||
==Genealogy== | ==Genealogy== | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:Cronological tree william I.svg|thumb|600px|center|Diagram based on the information found on Wikipedia]] | [[Image:Cronological tree william I.svg|thumb|600px|center|Diagram based on the information found on Wikipedia]] | ||
| Line 64: | Line 66: | ||
==Children of William and Matilda == | ==Children of William and Matilda == | ||
| − | |||
| − | #[[Robert Curthose]] ( | + | There is some discussion over how many daughters William actually had. This list includes some entries which are obscure. |
| − | #Adeliza (or Alice) ( | + | |
| − | #Cecilia (or Cecily) ( | + | #[[Robert Curthose]] (1054–1134), Duke of Normandy, married [[Sybil of Conversano]], daughter of Geoffrey of Conversano |
| − | #[[William II of England|William Rufus]] ( | + | #Adeliza (or Alice) (1055–?), reportedly betrothed to [[Harold II of England]] (Her existence is in some doubt.) |
| − | #Richard ( | + | #Cecilia (or Cecily) (1056–1126), Abbess of Holy Trinity, Caen |
| − | #[[Adela of Blois|Adela]] ( | + | #[[William II of England|William Rufus]] (1056–1100), King of England |
| − | #[[Gundred]] ( | + | #Richard (1057–1081), killed by a stag in [[New Forest]] |
| − | #Agatha ( | + | #[[Adela of Blois|Adela]] (1062–1138), married [[Stephen, Count of Blois]] |
| − | #Constance ( | + | #[[Gundred]] (1063–1085), married [[William de Warenne, First Earl of Surrey|William de Warenne]] (1055–1088) Some scholars question whether Gundred was an illegitimate child of William I or merely a step-daughter, foundling, or adopted daughter. |
| + | #Agatha (1064–1080), betrothed to (1) Harold of [[Wessex]], (2) [[Alfonso VI of Castile]] | ||
| + | #Constance (1066–1090), married [[Alan IV, Duke of Brittany|Alan IV Fergent]], [[Duke of Brittany]]; poisoned, possibly by her own servants | ||
#Matilda (very obscure, her existence is in some doubt) | #Matilda (very obscure, her existence is in some doubt) | ||
| − | #[[Henry I of England|Henry Beauclerc]] ( | + | #[[Henry I of England|Henry Beauclerc]] (1068–1135), King of England, married (1) [[Edith of Scotland]], daughter of [[Malcolm III of Scotland|Malcolm III, King of Scotland]], (2) [[Adeliza]] of [[Louvain]] |
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <references/> | ||
==Further reading== | ==Further reading== | ||
| − | * Bates, David. ''William the Conqueror'' | + | * Bates, David. ''William the Conqueror.'' London: G. Philip. 1989. ISBN 0540011754 Retrieved June 5, 2007. |
| − | * Douglas, David C. ''William the Conqueror : the Norman Impact Upon England'' | + | * Douglas, David C. ''William the Conqueror: the Norman Impact Upon England.'' New Haven, CT: Yale University. 1999. ISBN 0300078846 Retrieved June 5, 2007. |
| − | * Howarth, David. ''1066 The Year of the Conquest'' | + | * Howarth, David. ''1066 The Year of the Conquest.'' New York: Penguin. 1981. ISBN 0140058508 Retrieved June 5, 2007. |
| − | * Prescott, Hilda Frances Margaret. ''Son of Dust'' | + | * Prescott, Hilda Frances Margaret. ''Son of Dust.'' Chicago: Loyola Press. 2007. ISBN 9780829423525 Retrieved June 5, 2007; ISBN 0829423524 Retrieved June 5, 2007. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * Savage, Anne. ''The Anglo-Saxon Chronicles.'' New York: St. Martin’s/Marek. 1983. ISBN 0312037406 Retrieved June 5, 2007. | |
| − | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | * [http://www.royal.gov.uk/output/Page18.asp | + | * History of the Monarchy [http://www.royal.gov.uk/output/Page18.asp William I 'The Conqueror' (r. 1066-1087)] Retrieved June 5, 2007. |
| − | * E. A. | + | * Freeman, E. A. [http://www.gutenberg.net/etext/1066 William the Conqueror] Retrieved June 5, 2007. |
| − | * [http://www.englishmonarchs.co.uk/normans.htm | + | * English Monarchs. [http://www.englishmonarchs.co.uk/normans.htm William 'the Conqueror'] Retrieved June 5, 2007. |
| − | *[http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GRid=1948 | + | * Find a Grave. [http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GRid=1948 King ‘William the Conqueror’ William, I] Retrieved June 5, 2007. |
| − | *[http://www.historyhouse.com/in_history/william/ | + | * History House. [http://www.historyhouse.com/in_history/william/ William the Conqueror] Retrieved June 5, 2007. |
Revision as of 17:30, 5 June 2007
| William I the Conqueror | |
|---|---|
| King of the English; Duke of Normandy | |
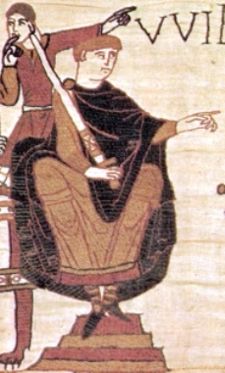
| |
| The Duke of Normandy in the Bayeux Tapestry | |
| Reign | December 25, 1066–September 9, 1087 |
| Coronation | December 25, 1066 |
| Predecessor | Harold II Normandy: Robert II the Magnificent |
| Successor | William II Rufus Normandy: Robert III Curthose |
| Consort | Matilda of Flanders (1031–1083) |
| Issue | |
| Robert III Curthose William II Rufus Adela, Countess of Blois Henry I Beauclerc among others... | |
| Father | Robert II the Magnificent |
| Mother | Herlette of Falaise |
| Born | 1027–1028 Falaise, France |
| Died | September 9, 1087 Convent of St. Gervais, Rouen |
| Buried | Saint-Étienne de Caen, France |
William of Normandy (French: Guillaume de Normandie; 1028 – September 9, 1087) ruled as the Duke of Normandy from 1035 to 1087 and as King of England from 1066 to 1087. William invaded England, won a victory at the Battle of Hastings in 1066, and suppressed subsequent English revolts in what has become known as the Norman Conquest. No authentic portrait of William has been found but he was described as a muscular man, strong in every sense of the word, balding in front, and of regal dignity.
In the present nomenclature, William was Duke of Normandy as William II and King of England as William I. He is also known as William the Conqueror (Guillaume le Conquérant) and William the Bastard (Guillaume le Bâtard). In English memory, the Norman Conquest represents a defining moment, regarded by some as bringing to an end one phase of English history and launching another. The Saxon period, during which England had been relatively uninvolved in European affairs, ended and a period of European engagement began in which relations between the English and French rulers and nobility became much more complex. For the next five centuries, England would become embroiled in contests for European territory based on royal blood-line claims derived from William I. Positively, English culture and French culture blended as a result of the conquest, making England more European. William also imported one hundred Norman peasants, whose blood-line would mix with that of Saxon peasants just as the new Normal nobles would inter-marry with the older Saxon aristocracy. Years later, when Elizabeth I of England gave up her claim to the last piece of French territory, England turned its attention instead to overseas exploration and colonies.
Early life
The sole son of Robert the Magnificent and Herleva, most likely the daughter of a local tanner named Fulbert, William was born illegitimate in Falaise, Normandy. The exact date of birth is uncertain, but is known to have been either in 1027 or 1028, and more likely in the autumn of the latter year.[1] He was the grandnephew of Queen Emma, wife of King Ethelred the Unready and later of King Canute.
William succeeded to his father's Duchy of Normandy at the young age of seven in 1035 and was known as Duke William II of Normandy (French Guillaume II, duc de Normandie). He lost three guardians to plots to usurp his place. Count Alan of Brittany was a later guardian. King Henry I of France knighted him at the age of 15. By the time he turned 19 he was successfully dealing with threats of rebellion and invasion. With the assistance of King Henry, William finally secured control of Normandy by defeating the rebel Norman barons at Caen in the Battle of Val-ès-Dunes in 1047.
He married his cousin Matilda of Flanders, against the wishes of Pope Leo IX in 1053 at the Cathedral of Notre Dame at Eu, Normandy (now in Seine-Maritime). At the time, William was 26 and Matilda was 22. Their marriage produced four sons and six daughters.
His half-brothers Odo of Bayeux and Robert, Count of Mortain played significant roles in his life. He also had a sister, Adelaide of Normandy.
Conquest of England
Upon the death of William's cousin King Edward the Confessor of England (January 1066), William claimed the throne of England, asserting that the childless and purportedly celibate Edward had named him his heir during a visit by William (probably in 1052) and that Harold Godwinson, England's foremost magnate and brother-in-law of the late King Edward, had reportedly pledged his support while shipwrecked in Normandy in 1064. Harold made this pledge while in captivity and was reportedly tricked into swearing on a saint's bones that he would give the throne to William. Even if this story is true, however, Harold made the promise under duress and so may have felt free to break it. More realistically, by the mid 1050s, Harold was effectively ruling England through the weak King Edward and was unlikely to surrender the throne to a foreign noble.
The assembly of England's leading nobles known as the Witenagemot approved Harold Godwinson’s coronation which took place on January 5, 1066 making him King Harold II of England. In order to pursue his own claim, William obtained the support of Pope Alexander II for his cause. He assembled a Norman invasion fleet of around six hundred ships and an army of seven thousand men. He landed at Pevensey in Sussex on September 28, 1066 and assembled a prefabricated wooden castle(Motte-and-bailey) near Hastings as a base. This was a direct provocation to Harold Godwinson as this area of Sussex was Harold's own personal estate, and William began immediately to lay waste to the land. It may have prompted Harold to respond immediately and in haste rather than await reinforcements in London.
King Harold Godwinson was in the north of England and had just defeated another rival, Harald III of Norway, supported by his own brother Tostig. He marched an army of similar size to William's 250 miles in nine days to challenge him at the crucial battle of Senlac, which later became known as the Battle of Hastings. This took place on October 14, 1066. According to some accounts, perhaps based on an interpretation of the Bayeux Tapestry commemorating the Norman victory, Harold was allegedly killed by an arrow through the eye, and the English forces fled giving William victory.
This was the defining moment of what is now known as the Norman Conquest. Unable to enter London, William traveled to Wallingford, was welcomed in by Wigod who supported his cause. This is where the first submissions took place, including that of the Archbishop of Canterbury.[2] The remaining Anglo-Saxon noblemen surrendered to William at Berkhamsted, Hertfordshire and he was acclaimed King of England there. William was then crowned on December 25, 1066 in Westminster Abbey.
Although the south of England submitted quickly to Norman rule, resistance continued, especially in the North, for six more years until 1072. Harold's illegitimate sons attempted an invasion of the southwest peninsula. Uprisings occurred in the Welsh Marches and at Stafford. Separate attempts at invasion by the Danes and the Scots also occurred. William's defeat of these led to what became known as the harrying of the North, in which William laid Northumbria to waste in revenge as well as to deny his enemies its resources. The last serious resistance came with the Revolt of the Earls in 1075. It is estimated that one-fifth of the population of England was killed during these years by war, massacre, and starvation.
William's reign
William initiated many major changes. In 1085, in order to ascertain the extent of his new dominions and maximize taxation, William commissioned the compilation of the Domesday Book, a survey of England's productive capacity similar to a modern census. He also ordered many castles, keeps, and mottes, among them the Tower of London, to be built across England to ensure that the rebellions by the English people or his own followers would not succeed. His conquest also led to Norman replacing English as the language of the ruling classes for nearly three hundred years. This is why Anglo-Saxon words such as cow and sheep were used by the peasants who farmed the livestock but when the meat reached the noblemen's tables the food became beef and mutton.
William is said to have deported some of the Anglo-Saxon land owning classes into slavery throughout Bristol. Many ended up in Umayyad Spain and Moorish lands. Ownership of nearly all land in England and titles to religious and public offices were given to Normans. Many surviving Anglo-Saxon nobles emigrated to other European kingdoms.
Death, burial, and succession
William died at the age of 59, at the Convent of St Gervais, near Rouen, France, on September 9, 1087, from abdominal injuries received from his saddle pommel when he fell off a horse at the Siege of Mantes. William was buried in the church of St. Stephen in Caen, Normandy. In a most undignified postmortem, his corpulent body would not fit into the stone sarcophagus, and burst after some unsuccessful prodding by the assembled bishops, filling the chapel with a foul smell and dispersing the mourners.[3]
William was succeeded in 1087 as King of England by his younger son William Rufus and as Duke of Normandy by his elder son Robert Curthose. This led to the Rebellion of 1088. His youngest son Henry also became King of England later, after William II died without a child to succeed him.
Genealogy
Every English monarch down to Queen Elizabeth II is a direct descendant of William the Conqueror as well as Alfred the Great.
Children of William and Matilda
There is some discussion over how many daughters William actually had. This list includes some entries which are obscure.
- Robert Curthose (1054–1134), Duke of Normandy, married Sybil of Conversano, daughter of Geoffrey of Conversano
- Adeliza (or Alice) (1055–?), reportedly betrothed to Harold II of England (Her existence is in some doubt.)
- Cecilia (or Cecily) (1056–1126), Abbess of Holy Trinity, Caen
- William Rufus (1056–1100), King of England
- Richard (1057–1081), killed by a stag in New Forest
- Adela (1062–1138), married Stephen, Count of Blois
- Gundred (1063–1085), married William de Warenne (1055–1088) Some scholars question whether Gundred was an illegitimate child of William I or merely a step-daughter, foundling, or adopted daughter.
- Agatha (1064–1080), betrothed to (1) Harold of Wessex, (2) Alfonso VI of Castile
- Constance (1066–1090), married Alan IV Fergent, Duke of Brittany; poisoned, possibly by her own servants
- Matilda (very obscure, her existence is in some doubt)
- Henry Beauclerc (1068–1135), King of England, married (1) Edith of Scotland, daughter of Malcolm III, King of Scotland, (2) Adeliza of Louvain
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ History of the Monarchy. William I ‘The Conqueror’ (r. 1066-1087) Retrieved June 5, 2007.
- ↑ Ford, David Nash. Wallingford: Saxon Planning Lives On Retrieved June 5, 2007.
- ↑ History House. William the Conqueror Retrieved June 5, 2007.
Further reading
- Bates, David. William the Conqueror. London: G. Philip. 1989. ISBN 0540011754 Retrieved June 5, 2007.
- Douglas, David C. William the Conqueror: the Norman Impact Upon England. New Haven, CT: Yale University. 1999. ISBN 0300078846 Retrieved June 5, 2007.
- Howarth, David. 1066 The Year of the Conquest. New York: Penguin. 1981. ISBN 0140058508 Retrieved June 5, 2007.
- Prescott, Hilda Frances Margaret. Son of Dust. Chicago: Loyola Press. 2007. ISBN 9780829423525 Retrieved June 5, 2007; ISBN 0829423524 Retrieved June 5, 2007.
- Savage, Anne. The Anglo-Saxon Chronicles. New York: St. Martin’s/Marek. 1983. ISBN 0312037406 Retrieved June 5, 2007.
External links
- History of the Monarchy William I 'The Conqueror' (r. 1066-1087) Retrieved June 5, 2007.
- Freeman, E. A. William the Conqueror Retrieved June 5, 2007.
- English Monarchs. William 'the Conqueror' Retrieved June 5, 2007.
- Find a Grave. King ‘William the Conqueror’ William, I Retrieved June 5, 2007.
- History House. William the Conqueror Retrieved June 5, 2007.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.

