Difference between revisions of "Salicylic acid" - New World Encyclopedia
({{Contracted}}) |
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
! {{chembox header}}| '''Salicylic acid''' | ! {{chembox header}}| '''Salicylic acid''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | align="center" colspan="2" | [[Image:Salicylic-acid- | + | | align="center" colspan="2" | [[Image:Salicylic-acid-skeletal_svg.png|120px|Chemical structure of salicylic acid]] [[Image:Salicylic-acid-3D-vdW.png|120px|Space-filling model of salicylic acid]] |
|- | |- | ||
| [[IUPAC nomenclature|Chemical name]] | | [[IUPAC nomenclature|Chemical name]] | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
|} | |} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
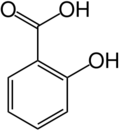
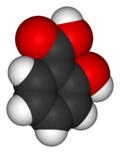
| − | '''Salicylic acid''' is | + | '''Salicylic acid''' is a crystalline, solid (up to 159<sup>o</sup>C) organic acid that is used to make [[aspirin]] and various pharmaceutical products, including for skin conditions. It also functions as a [[plant]] [[hormone]]. The name derives from the Latin word for the willow tree (''[[Salix]]''), from whose bark it can be obtained. |
| + | |||
| + | ==Chemistry== | ||
| + | The chemical formula for salicyclic acid is C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>4</sub>(OH)CO<sub>2</sub>H. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Salicylic acid is both a caroxylic acid and a phenol. A ''carboxylic acid'' is an organic (carbon-containing) acid characterized by the presence of a carboxyl group, which has the formula -C(=O)OH, usually written -COOH or -CO<sub>2</sub>H. A ''phenol'', in the general sense of the term, is any any compound which contains a six-membered [[aromatic]] ring, bonded directly to a [[hydroxyl group]] (-OH). | ||
| + | |||
| + | In salicylic acid the OH group is adjacent to the carboxyl group. | ||
| + | |||
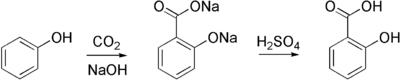
==Production== | ==Production== | ||
| Line 46: | Line 54: | ||
:[[Image:Kolbe-Schmitt.png|left|400px]]{{clear}} | :[[Image:Kolbe-Schmitt.png|left|400px]]{{clear}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | To produce aspirin: Salicylic acid is then acetylated using acetic anhydride, yielding aspirin and acetic acid as a byproduct. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Aspirin''' or '''acetylsalicylic acid''' is a [[drug]] in the family of [[salicylate]]s (carboxylic acid), often used as an ''analgesic'' (against minor pains and aches), ''antipyretic'' (against [[fever]]), and ''anti-inflammatory'' (against localized redness, swelling, heat, and pain). It has also an anticoagulant ("blood-thinning") effect and is used in long-term low-doses to prevent [[heart attack]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Medicinal and cosmetic uses== | ==Medicinal and cosmetic uses== | ||
Revision as of 00:27, 9 April 2007
| Salicylic acid | |
|---|---|
| |
| Chemical name | 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid |
| Chemical formula | C7H6O3 |
| Molecular mass | 138.123 g/mol |
| Melting point | 160 °C |
| Boiling point | 211 °C (2666 Pa) |
| Density | 1.44 g/cm³ (at 20 °C) |
| pKa | 2.97 |
| CAS number | [69-72-7] |
| SMILES | c1(O)ccccc1C(O)=O |
| Disclaimer and references | |
Salicylic acid is a crystalline, solid (up to 159oC) organic acid that is used to make aspirin and various pharmaceutical products, including for skin conditions. It also functions as a plant hormone. The name derives from the Latin word for the willow tree (Salix), from whose bark it can be obtained.
Chemistry
The chemical formula for salicyclic acid is C6H4(OH)CO2H.
Salicylic acid is both a caroxylic acid and a phenol. A carboxylic acid is an organic (carbon-containing) acid characterized by the presence of a carboxyl group, which has the formula -C(=O)OH, usually written -COOH or -CO2H. A phenol, in the general sense of the term, is any any compound which contains a six-membered aromatic ring, bonded directly to a hydroxyl group (-OH).
In salicylic acid the OH group is adjacent to the carboxyl group.
Production
Sodium salicylate is commercially prepared from sodium phenoxide and carbon dioxide at high pressure and temperature in the Kolbe-Schmitt reaction. It is acidified to give the desired salicylic acid:
To produce aspirin: Salicylic acid is then acetylated using acetic anhydride, yielding aspirin and acetic acid as a byproduct.
Aspirin or acetylsalicylic acid is a drug in the family of salicylates (carboxylic acid), often used as an analgesic (against minor pains and aches), antipyretic (against fever), and anti-inflammatory (against localized redness, swelling, heat, and pain). It has also an anticoagulant ("blood-thinning") effect and is used in long-term low-doses to prevent heart attacks.
Medicinal and cosmetic uses
Also known as 2-hydroxybenzoic acid (one of several beta hydroxy acids (compare to AHA), salicylic acid is the key additive in many skin-care products for the treatment of acne, psoriasis, calluses, corns, keratosis pilaris and warts. It treats acne by causing skin cells to slough off more readily, preventing pores from clogging up. This effect on skin cells also makes salicylic acid an active ingredient in several shampoos meant to treat dandruff. Use of straight salicylic solution may cause hyperpigmentation on unpretreated skin for those with darker skin types (Fitzpatrick phototypes IV, V, VI), as well as with the lack of use of a broad spectrum sunblock.[1][2]
Salicylic acid is also used as an active ingredient in gels which remove verrucas (plantar warts).
The medicinal properties of salicylate (mainly for fever relief) have been known since ancient times. The substance occurs in the bark of willow trees; the name salicylic acid is derived from salix, the Latin name for the willow tree. [3]

Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid or ASA) can be prepared by the esterification of the phenolic hydroxyl group of salicylic acid, retaining some of its potency as an analgesic as well as reducing its acidity.
Subsalicylate in combination with bismuth form the popular stomach relief aid known commonly as Pepto-Bismol. When combined, the two key ingredients help control diarrhea, nausea, heartburn, and gas. It is also a very mild antibiotic.
Toxicological effects of 100% salicylic acid, however, are mostly harmful. It is harmful by ingestion, inhalation, and through skin absorption. It acts as an irritant, and chronic effects have shown 100% salicylic acid to cause DNA damage, and also cause allergic reactions after repeated exposure. This is why most acne treatment medications use a percent range of 2-5 in solution.
Other uses
- Salicylic acid is toxic if ingested in large quantities, but in small quantities is used as a food preservative and antiseptic in toothpaste. For some people with salicylate sensitivity even these small doses can be harmful.
- Sodium Salicylate is a useful phosphor in the vacuum ultraviolet with nearly flat quantum efficiency for wavelengths between 100 to 1000 Angstroms [4]. It fluoresces in the blue at 4200 Angstroms. It is easily prepared on a clean surface by creating a supersaturated solution of the Salicylate in methanol, spraying the solution on the surface, and waiting for the methanol to evaporate.
See also
- Benzoic acid
- Benzene ring
- Phenol
- Aspirin
- Alpha hydroxy acid
- 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid
- Magnesium salicylate
- Bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto Bismol)
- Sulfosalicylic acid
Footnotes
- ↑ Grimes P.E. (1999). The Safety and Efficacy of Salicylic Acid Chemical Peels in Darker Racial-ethnic Groups. Dermatologic Surgery 25: 18-22.
- ↑ Roberts W. E. (2004). Chemical peeling in ethnic/dark skin. Dermatologic Therapy 17 (2): 196.
- ↑ Philip A. Mackowiak (2000). Brief History of Antipyretic Therapy. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 31: 154–156.
- ↑ JAR Samson Techniques of Vacuum Ultraviolet Spectroscoply
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- http://www.chemexper.com/. Retrieved July 18, 2005.
- http://www.inchem.org/. Retrieved July 18, 2005.
- http://www.jtbaker.com/. Retrieved July 18, 2005.
- Salicylic acid. Retrieved July 18, 2005.
External links
Template:ChemicalSources
Template:Acne Agents Template:Antifungals
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Plant hormones | edit |
|
Abscisic acid - Auxins - Cytokinins - Ethylene (Ethene) - Gibberellins Brassinosteroids - Jasmonates - Salicylic acid |
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.