Hajj

The Hajj (Arabic: حج, transliterated Ḥaǧǧ; "greater pilgrimage")[1] is the pilgrimage to Mecca in Islam. It is the fifth pillar of Islam, an obligation that must be carried out by every able-bodied Muslim who can afford to do so, at least once in their lifetime.[2] It is the demonstration of the solidarity of the Muslim people, and their submission to God.[3] While pilgrims are permitted to visit Mecca and perform the appropriate rituals at other times of the year (a practice known as the "lesser pilgrimage" or Umrah), this does not release them from their holy obligation to perform the Hajj at some other point in their lifetime.
The hajj is an ancient ritual, which many of the faithful believe dates back to the time of Abraham in 2000 B.C.E. Since time immemorial, those participating would join processions of tens of thousands of people, who would simultaneously converge on Mecca for the week of the Hajj, and perform a series of rituals. Each person would walk counter-clockwise seven times about the Kaaba, kiss the Black Stone of Mecca, run back and forth between the hills of Al-Safa and Al-Marwah, drink from the Zamzam Well, go to the plains of Mount Arafat to stand in vigil, then proceed to Muzdalifah to gather pebbles, which they would throw at a rock in Mina to perform the ritual of the Stoning of the Devil. The pilgrims would then shave their heads, perform an animal sacrifice, and celebrate the three day global festival of Eid ul-Adha.[4] [5] This particular set of ritualized practices was explicitly designed to commemorate certain formative elements in the history of Islam, from the travels of Abraham to the last sermon delivered by Muhammad.[6]
While the hajj includes many diverse ritual elements (from prayers, to throwing stones at pillars, to circumambulating the Kaaba), the overarching unity of these rituals is to create an atmosphere of sacred time. Thus, the ritual can be seen as a definitive example of a rite of passage, designed to transform the attitudes and world-views of those who perform it:
- Few Muslims are unchanged by their experience of the Hajj: on their return to their homes and their normal lives, the religious element of life remains in the foreground, more real than the visible realities of normal life. Forever after, a photograph of the Kabaa reminds the former pilgrim of the intensity of the experience of Hajj, rather as a photograph of a small child warms the heart of its grandparent.[7]
| Part of the series on History of Islam |
| Beliefs and practices |
|
Oneness of God |
| Major figures |
|
Muhammad |
| Texts & law |
|
Qur'an · Hadith · Sharia |
| Branches of Islam |
| Sociopolitical aspects |
|
Art · Architecture |
| See also |
|
Vocabulary of Islam |
History and Context
The Hajj was an ancient ritual, even in the time of Muhammad in the 7th Century. Some elements of the Hajj trace back to the time of Abraham, around 2000 B.C.E. Muhammad was known to regularly perform both the Hajj and Umrah, even before he began receiving revelations.[4] Historically, Muslims would gather at various meeting points in other great cities, and then proceed en masse towards Mecca, in groups that could comprise tens of thousands of pilgrims. Two of the most famous meetings points were in Cairo and Damascus. In Cairo, the Sultan would stand atop a platform of the famous gate Bab Zuwayla, to officially watch the beginning of the annual pilgrimage.[8]
At present, the hajj is a tremendous engine of economic growth, as it annually brings Muslims from the four corners of the globe back to Saudi Arabia. This influx of "pilgrim dollars" (as opposed to "tourist dollars") from other economies has a large impact throughout the Middle East and Northern Africa. For one example, see Tangban's insightful study of the economic impact of the hajj on the Nigerian economy, where he notes:
- Pilgrimage to Mecca had far-reaching economic consequences for the Nigerian economy. The creation of the National Pilgrims Welfare Board with zonal offices has already been noted. Each zonal office of the Board had a staff strength of not less than twenty workers, ranging from cleaner to zonal supervisor. Apart from the personnel, each zonal office was provided with an office building and other operational facilities, such as motor vehicles, equipment and so on. If one takes into account staff emoluments and maintenance of motor vehicles and equipment, a modest estimate of the running cost per month of each zonal office may not have been less than fifteen thousand naira (N15,000.00). On this basis, the running cost of all the zonal offices put together would have stood at eighty thousand naira (N80,000.00) per month.
- Apart from the National Pilgrims Board there were also State Pilgrims Welfare Boards, particularly in the northern states. Each State Pilgrim Board had a Board of Governors, a Secretary, a Principal Pilgrim Welfare Officer, a Senior Accountant and a number of intermediate and junior employees, resulting in a staff strength of between thirty and forty workers, Board members not included. A fleet of official vehicles were also maintained, both at home and in Saudi Arabia, by each State Pilgrim Board. To meet expenses in all these areas, each State Pilgrim Board may have required not less than fifty thousand naira (N50,000.00) per month.[9]
As of 2007, an estimated two million pilgrims participate in this annual pilgrimage.[10] Crowd-control techniques have become critical, and because of the large numbers of people, many of the rituals have become more stylized. It is not necessary to kiss the Black Stone, but merely to point at it on each circuit around the Kaaba. Throwing pebbles was done at large pillars, which for safety reasons were in 2004 changed to long walls with catchbasins below to catch the stones. The slaughter of an animal can be done either personally, or by appointing someone else to do it, and so forth.[11] But even with the crowd control techniques, there are still many accidental incidents during the hajj, as pilgrims are trampled in the crush, or ramps collapse under the weight of the many visitors, causing hundreds of deaths. The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia's Ministry of Hajj has a website, with the message, "Be peaceful, orderly and kind. No crushing."[12]
The Hajj occurs from the 8th to the 12th day of Dhul Hijjah, the 12th month of the Islamic calendar. This date cannot be aligned directly with Western calendars, but in the early 21st century, it occurs roughly in the November-January timeframe. In 2007, the next month of Dhul Hijjah begins on December 11, with the week of the Hajj beginning on December 18, 2007.
Preparations
Pilgrims generally travel to Hajj in groups, as an expression of unity. Some airlines have special package holidays for Muslims going to Mecca. And now ships have also taken the job of taking the pilgrims to Mecca so they can perform Hajj.
During the Hajj, male pilgrims are required to dress only in a garment consisting of two sheets of white unhemmed cloth, with the top draped over the torso and the bottom secured by a white sash; plus a pair of sandals. Women are simply required to maintain their hijab - normal modest dress, which does not cover the hands or face.[11]
The Ihram clothing is intended to show the equality of all pilgrims in the eyes of Allah, symbolizing the idea that there is no difference between a prince and a pauper when everyone is dressed equally. The Ihram also symbolizes purity and absolution of sins. A place designated for changing into Ihram is called a miqat.
While the pilgrim is wearing the Ihram, they cannot shave, cut their nails, wear deodorant or perfume. They may not swear or quarrel, kill any living thing (even an insect) or engage in sexual intercourse.
An invocation, known as the talbiyah, is to be chanted after the pilgrim makes his or her intention for the Hajj.
Rites
Upon arrival in Mecca, the pilgrim (now known as a Hajji), performs a series of ritual acts symbolic of the lives of Abraham (Ibrahim) and Hagar, his concubine. The acts also symbolize the solidarity with Muslims worldwide.
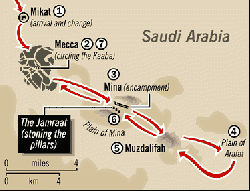
The greater Hajj (al-hajj al-akbar) begins on the eighth day of the lunar month of Dhu al-Hijjah. If they are not already wearing it upon their arrival, pilgrims put on ihram clothing, and then leave Mecca for the nearby town of Mina, where they spend the rest of the day. The Saudi government has put up thousands of large white tents at Mina, to provide accommodations for all the pilgrims.[5]
Tawaf
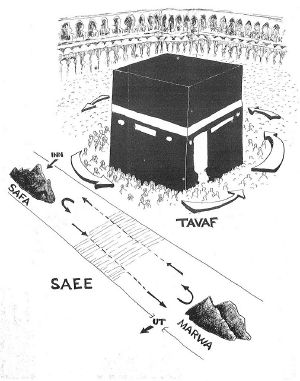
On the first day of the Hajj, the 8th day of Dhul Hijjah {the 12th month}, the pilgrims perform their first Tawaf. This consists of walking anti-clockwise around the Kaaba seven times. Men are encouraged to perform the first three circuits at a hurried pace, followed by four times, more closely, at a leisurely pace.[11] On each circuit the pilgrim is supposed to kiss the Black Stone, but this is not possible because of the large crowds, and so it is acceptable to simply point at the Stone on each circuit.
Sa'i
After Tawaf, the pilgrims perform sa`i, running or walking seven times back and forth between the hills of Safa and Marwah. This is a re-enactment of Hajar's frantic search for water, before the Zamzam Well was revealed to her by an angel sent by God. The circuit used to be in the open air, but is now entirely enclosed by the Masjid al-Haram mosque, and can be accessed via air-conditioned tunnels. Pilgrims are advised to walk the circuit, though two green pillars mark a short section of the path where they are allowed to run, along with an 'express lane' for the disabled. The safety procedures are in place because previous incidents in this ritual have resulted in stampedes which resulted in the deaths of hundreds of people.
As part of this ritual, the pilgrims also drink water from the Zamzam Well, which is made available in coolers throughout the Mosque. The pilgrims then return to their tents
Arafat
The next morning, on the ninth of Dhu al-Hijjah, the pilgrims leave Mina for Mount Arafat. This is considered the highlight of the Hajj, as they stand in contemplative vigil, near a hill from which Muhammad gave his last sermon. Pilgrims must spend the afternoon within a defined area on the plain of Arafat until after sunset. No specific rituals or prayers are required during the stay at Arafat, although many pilgrims spend time praying, talking to God, and thinking about the course of their lives.[5]
Muzdalifah
As soon as the sun sets, the pilgrims leave Arafat for Muzdalifah, an area between Arafat and Mina, where 49 pebbles are gathered for the next day's ritual of the stoning of the Devil (Shaitan). Many pilgrims spend the night sleeping on the ground at Muzdalifah, before returning to Mina. It is now the 10th of the month, the day of Eid ul-Adha.
Ramy al-Jamarat
At Mina, the pilgrims perform Ramy al-Jamarat, throwing stones to signify their defiance of the Devil. This symbolizes the trials experienced by Abraham, as he wrestled with whether or not to sacrifice his son per God's demand. The Devil challenged him three times, and three times Abraham refused. Each pillar marks the location of one of these refusals. Because of the crowds, in 2004 the pillars were changed to long walls. Pilgrims climb ramps to the multi-leveled Jamarat Bridge, from which they can throw pebbles at the three jamarat. Each pilgrim must hit each pillar at least seven times.[5]
Eid ul-Adha
After the Stoning of the Devil, an animal is sacrificed. This symbolizes God having mercy on Abraham, and replacing his son with a ram, which Abraham then sacrificed.
Traditionally the pilgrim slaughtered the animal himself or oversaw the slaughtering. Today many pilgrims buy a sacrifice voucher in Mecca before the greater Hajj begins; this allows an animal to be slaughtered in their name on the 10th without the pilgrim being physically present. Centralized butcher houses will sacrifice a single sheep for each pilgrim, or a cow can represent the sacrifice of seven people. The meat is then packaged and given to charity, shipped to poor people around the world.[5] At the same time as the sacrifices occur at Mecca, Muslims worldwide perform similar sacrifices, in a three day global festival called Eid ul-Adha.
Tawaf az-Ziyarah
On this or the following day the pilgrims re-visit the Masjid al-Haram in Mecca for a tawaf called the Tawaf az-Ziyarah (or Tawaf al-Ifadah) which is an obligatory part of the Hajj. The night of the 10th is spent back at Mina.
On the afternoon of the 11th, pilgrims must again stone all three jamarat in Mina (seven pebbles per jamarat). The same ritual must be performed on the following day.
Pilgrims must leave Mina for Mecca before sunset on the 12th. If they are unable to leave Mina before sunset, they must perform the stoning ritual again on the 13th before returning to Mecca.
Tawaf al-Wada
Finally, before leaving Mecca, pilgrims perform a farewell tawaf called the Tawaf al-Wada.[5]
Journey to Medina
Though it is not required as part of the Hajj, many pilgrims also travel to visit the city of Medina and the Mosque of the Prophet. Muhammad's tomb is enclosed by the mosque. Pilgrims may also visit the tomb of Muhammad's daughter, Fatimah.
Incidents during the Hajj
There have been many incidents during the Hajj that have led to the loss of hundreds of lives. The worst of these incidents have usually occurred during the Stoning of the Devil ritual. During the 2006 Hajj on January 12, 362 pilgrims died. Tramplings have also occurred at the stage known as the sa'y, when pilgrims try to run but can walk between two hills known as As-Safa and Al-Marwa. In 2006 there were some 600 casualties among pilgrims performing the Hajj.
The Saudi Government is often criticized for not being proactive in providing facilities and infrastructure for the annual pilgrimage, and many measures are put in place in response to annual catastrophes.
Non-Muslims
The second caliph, Umar, is believed by many Sunni Muslims to have expelled non-Muslims from the Hejaz (Western part of Arabia). Non-Muslims were not to visit nor to live in the holy land. There is much evidence against this claim, at least so far as it relates to the early centuries of the Islamic empire, but it is well documented that by the 18th and 19th centuries, there were small colonies of merchants in various port and trading cities such as Jeddah as well as communities of Yemeni Jews. The prohibition was not so much imposed by the authorities as enforced by rioting crowds and was most strictly enforced with regard to the Hejaz, and the Islamic holy cities of Mecca and Medina.
As one might expect, the existence of "forbidden cities" and the mystery of the Hajj aroused curiosity in European travelers. A number of them pretended to be Muslims and entered the city of Mecca and then the Kaaba to experience the Hajj for themselves. The most famous account of a foreigner's journey to Mecca is A Personal Narrative of a Pilgrimage to Makkah and Al-Madina, written by Sir Richard Francis Burton. Burton traveled as a Qadiri Sufi from Afghanistan; his name, as he signed it in Arabic below his frontispiece portrait for "The Jew, The Gypsy and al-Islam," was al-Hajj 'Abdullah'.
Umrah
The Umrah comprises the same rituals as the Hajj, and can be taken at any time throughout the year. Although completing it is highly commendable, Muslims are still required to perform the greater Hajj at some point during their lifetime. Pilgrims accomplishing the Umrah usually only perform the Tawaf (walking around the Kaaba) and the Sa'i (running back and forth from the Zamzam well to the hills of Al-Safa and Al-Marwah). They may also drink water from the Zamzam Well when the Umrah is completed, and trim off approximately one inch of their hair, as opposed to shaving their heads. They can then change from the ihram to regular clothes, in a release from ihram known as the mut'ah of Hajj.
Notes
- ↑ Glassé, 358.
- ↑ Farah, 145-147.
- ↑ Dalia Salah-El-Deen, Significance of Pilgrimage (Hajj)
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Armstrong, Karen. Islam: a short history. New York: Modern Library. 2002. ISBN 0-8129-6618-x
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Inside Mecca video documentary National Geographic - Retrieved October 1, 2007.
- ↑ Glassé, 359. John L. Esposito (ed.), "Hajj," Oxford Dictionary of Islam (Oxford University Press, 2003, Oxford Reference Online).
- ↑ Sedgwick, 80.
- ↑ (2001, 2007) Eyewitness Travel: Egypt. Dorlin Kindersley Limited, London, 103. ISBN 978-0-75662-875-8.
- ↑ O. E. Tangban, "The Hajj and the Nigerian Economy 1960-1981," Journal of Religion in Africa 21: Fascicle 3 (August 1991), pp. 241-255. 247.
- ↑ As Hajj begins, more changes and challenges in store - Retrieved October 1, 2007.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Mohamed, Mamdouh N. (1996). Hajj to Umrah: From A to Z. Amana Publications. ISBN 0-915957-54-x.
- ↑ Ministry of Hajj information site - Retrieved October 1, 2007.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Armstrong, Karen. Islam: A Short History. New York: Modern Library, 2002. ISBN 0-8129-6618-x.
- Bianchi, Robert R. Guests of God: Pilgrimage and Politics in the Islamic World. Oxford; New York: Oxford University Press, 2004. ISBN 978-0195171075.
- Eyewitness Travel: Egypt. London: Dorlin Kindersley Limited, 2001/2007. ISBN 978-0-75662-875-8.
- Farah, Caesar. Islam: Beliefs and Observances, 5th ed. Barron's Educational Series, 1994. ISBN 978-0812018530
- Glassé, Cyril. The New Encyclopedia of Islam. Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, 2001. ISBN 0759101892
- Mohamed, Mamdouh N. Hajj to Umrah: From A to Z. Amana Publications, 1996. ISBN 0-915957-54-x.
- Sedgwick, Mark J. Islam & Muslims: A Guide to Diverse Experience in a Modern World. Boston, MA: Intercultural Press, 2006. ISBN 1931930163
- Shariati, Ali. Hajj: Reflection on Its Rituals. Islamic Publications International, 2005. ISBN 1889999385.
- Trojanow,Ilija. From Mumbai to Mecca. London: Haus Publishing, 2007. ISBN 978-1-904950295.
External links
- Hajj Portal - Personal Hajj Experiences, Picture Gallery, Supplications, Hajj Step by Step guides plus more - Retrieved October 1, 2007.
- Ministry of Hajj Official Website - Retrieved October 1, 2007.
- Crowd control during the Hajj - Retrieved October 1, 2007.
- Hajj: The Pilgrimage - Retrieved October 1, 2007.
- 15th-century Hajj certificate: information, zoomable image British Library website - Retrieved October 1, 2007.
- Inside Mecca DVD National Geographic documentary about Mecca - Retrieved October 1, 2007.
- U.S. Army information sheet about the Hajj - Retrieved October 1, 2007.
- Watch the National Geographic Documentary on Hajj - Retrieved October 1, 2007.
Arabic pronunciation
- Hajj & ummrah supplications - Retrieved October 1, 2007.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.