Difference between revisions of "Same color illusion" - New World Encyclopedia
(Claimed) |
(Copied from wikipedia) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Claimed}} | {{Claimed}} | ||
| + | [[Category:Politics and social sciences]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Psychology]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
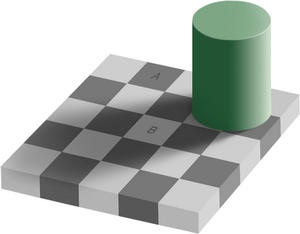
| + | The '''same color illusion''' — also known as '''Adelson’s checker shadow illusion''', '''checker shadow illusion''' and '''checker shadow''' — is an [[optical illusion]] published by [[Edward H. Adelson]] in [[1995]].<ref name="JudgeMaterial">{{cite web|url=http://web.mit.edu/persci/people/adelson/checkershadow_illusion.html|title=Checkershadow Illusion|first=Edward H.|last=Adelson|year=2005|accessdate=2007-04-21}}</ref> The squares A and B on the illusion are of the same color (or shade), although they seem to be different. | ||
| + | |||
| + | "When interpreted as a 3-dimensional scene, our visual system immediately estimates a lighting vector and uses this to judge the property of the material."<ref name="MichaelBach">{{cite web|url=http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/lum_adelson_check_shadow/|title=michaelbach.de|accessdate=2006-06-10}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Same color illusion.png|thumb|none|300px|Squares A and B have the same color.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The image below proves that the squares A and B have the same color. | ||
| + | [[Image:Same color illusion proof.png|thumb|none|300px|The part between the red lines is copied to show that the squares A and B really have the same color.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | As a further example, the two "A"s are both the same color and do not change. The shadow is removed in two frames, and the colors of the chess board are reversed. | ||
| + | [[Image:Aniopticalillusion.gif|thumb|none|300px|The two squares marked A have the same color.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | * [[Chubb illusion]] | ||
| + | * [[Lilac chaser]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <div class="references-small"> | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==External links== | ||
| + | * [http://web.mit.edu/persci/people/adelson/checkershadow_description.html Explanation of the effect] | ||
| + | * [http://www.archimedes-lab.org/color_optical_illusions.html Illusion of colours] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Credits|Same_color_illusion|124977470|}} | ||
Revision as of 02:03, 24 April 2007
The same color illusion — also known as Adelson’s checker shadow illusion, checker shadow illusion and checker shadow — is an optical illusion published by Edward H. Adelson in 1995.[1] The squares A and B on the illusion are of the same color (or shade), although they seem to be different.
"When interpreted as a 3-dimensional scene, our visual system immediately estimates a lighting vector and uses this to judge the property of the material."[2]
The image below proves that the squares A and B have the same color.
As a further example, the two "A"s are both the same color and do not change. The shadow is removed in two frames, and the colors of the chess board are reversed.
See also
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ Adelson, Edward H. (2005). Checkershadow Illusion. Retrieved 2007-04-21.
- ↑ michaelbach.de. Retrieved 2006-06-10.
External links
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.