Difference between revisions of "Planarian" - New World Encyclopedia
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
| familia = '''Planariidae''' | | familia = '''Planariidae''' | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Planaria''' are | + | '''Planaria''' are [[Platyhelminthes|flatworms]] (phylum [[Platyhelminthes]]) of the suborder (or order) Tricladida of the class [[Turbellaria]]. Primarily free-living, planarians are characterized by a soft, broad, leaf-shaped (when elongated) body with [[cilia]] and a three-branched digestive tract (as reflected in the name Tricladida). |
| + | |||
| + | Planarians or '''triclads''' are widely distributed, common, and diverse. While chiefly found in freshwater [[ecosystem]]s, they also can be found in marine and terrestrial environments. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Carranza et al. (1998) notes that Tricladida is best considered a suborder of the order Seriata, but there are taxonomies where Tricladida is placed as an order. Systematists have traditionally recognized three major groups of triclads: Paludicola (freshwater planarians), Maricola (marine planarians), and Terricola (land planarians), but some propose a fourth planarian infraorder Cavernicola (Carranza et al. 1998). | ||
The term "planaria" is most often used as a common name, but is also the name of a genus within the family Planariidae. There are several families of planarians within Tricladida. | The term "planaria" is most often used as a common name, but is also the name of a genus within the family Planariidae. There are several families of planarians within Tricladida. | ||
| − | Planarians are common organisms for scientific research and classroom teaching. Their ability to regenerate body parts, and in some species reproduce asexually, adds to research interest in them. | + | Planarians are common organisms for scientific research and classroom teaching. Their ability to regenerate body parts, and in some species reproduce [[asexual reproduction|asexually]], adds to research interest in them. Carranza et al. (1998) note that they are probably the best known of the free-living platyhelminthes, largely because of intensive research related to cellular regeneration, pattern formation, and Hox gene expression. |
| + | |||
| + | Some planarians have achieved pest status as a result of being [[invasive species]]. | ||
==Characteristics== | ==Characteristics== | ||
| − | + | Planaria are globally distributed and common to many parts of the world, residing in freshwater ponds and rivers. They are also found residing on [[plant]]s or in marine environments. | |
| − | + | Planarians range in size from about 3 to 12 mm. As with all flatworms, planaria have 3 germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm), but lack a true coelom (they are acoelomate). | |
| − | + | , and the body has two eye-spots (also known as ocelli) that can detect the intensity of light. The eye-spots act as [[photoreceptors]] and are used to move away from light sources. | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | They have a single-opening digestive tract, consisting of one anterior branch and two posterior branches in freshwater planarians. Because of this three-branched organization, freshwater flatworms are often referred to as triclad planarians. They are active carnivious flatworms that feed on daphnia and midges. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Flatworm.Mgiangrasso.jpg|thumb|left|Planarian on the glass of an aquarium.]]The planarian has very simple organ systems. The [[digestive system]] consists of a [[mouth]], [[pharynx]], and an [[intestine]]. The mouth is located in the center of the underside of the body. Digestive enzymes secrete from mouth to begin external digestion. The pharynx connects the mouth to the intestines. The intestines of the Planaria branch throughout the body. They eat living or dead small animals that they suck with their muscular mouth. From there, the food passes through the pharynx into the intestines and digesting of the food takes place in the cells lining the intestine, which then diffuses to the rest of the body. | |
| − | [[Image:Flatworm.Mgiangrasso.jpg|thumb|left|Planarian on the glass of an aquarium.]]The planarian has very simple organ systems. The digestive system consists of a [[mouth]], [[pharynx]], and an [[intestine]]. The mouth is located in the center of the underside of the body. Digestive enzymes secrete from mouth to begin external digestion. The pharynx connects the mouth to the intestines. The intestines of the Planaria branch throughout the body. They eat living or dead small animals that they suck with their muscular mouth. From there, the food passes through the pharynx into the intestines and digesting of the food takes place in the cells lining the intestine, which then diffuses to the rest of the body. | ||
| − | |||
Planaria receive oxygen and release carbon dioxide by [[diffusion]]. The excretory system is made of many tubes with many [[flame cell]]s and excretory pores on them. Flame cells remove unwanted liquids from the body by passing them through ducts that lead to excretory pores where the waste is released on the dorsal surface of the planarian. | Planaria receive oxygen and release carbon dioxide by [[diffusion]]. The excretory system is made of many tubes with many [[flame cell]]s and excretory pores on them. Flame cells remove unwanted liquids from the body by passing them through ducts that lead to excretory pores where the waste is released on the dorsal surface of the planarian. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 47: | ||
A planarian can reproduce either [[asexual reproduction|asexually]] or [[sexual reproduction|sexually]]. In asexual reproduction the planarian detaches its tail end and each half regrows the lost parts. In sexual reproduction each Planaria gives and receives sperm. Planaria have both testes and ovaries. Eggs develop inside the body and are shed in capsules. Weeks later the eggs hatch and grow into adults. Planarians can also reproduce by [[Regeneration (biology)|regeneration]]. If a Planaria is cut into two halves, both halves may become two new Planaria (regeneration). In one experiment, [[T.H. Morgan]] found that a piece corresponding to <sup>1</sup>⁄<sub>279</sub><sup>th</sup> of a planarian could successfully regenerate into a new worm. This size (about 10,000 cells) is typically accepted as the smallest fragment that could regrow into a new planarian. | A planarian can reproduce either [[asexual reproduction|asexually]] or [[sexual reproduction|sexually]]. In asexual reproduction the planarian detaches its tail end and each half regrows the lost parts. In sexual reproduction each Planaria gives and receives sperm. Planaria have both testes and ovaries. Eggs develop inside the body and are shed in capsules. Weeks later the eggs hatch and grow into adults. Planarians can also reproduce by [[Regeneration (biology)|regeneration]]. If a Planaria is cut into two halves, both halves may become two new Planaria (regeneration). In one experiment, [[T.H. Morgan]] found that a piece corresponding to <sup>1</sup>⁄<sub>279</sub><sup>th</sup> of a planarian could successfully regenerate into a new worm. This size (about 10,000 cells) is typically accepted as the smallest fragment that could regrow into a new planarian. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Planarians move by beating [[cilia]] on the [[ventral]] [[dermis]], allowing it to glide along on a film of [[mucus]]. Some move by undulations of the whole body by the contractions of muscles built into the body wall. | ||
| + | |||
| + | They exhibit an extraordinary ability to [[Regeneration (biology)|regenerate]] lost body parts. For example, a Planaria split length wise or crosswise will regenerate into 2 separate individuals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The most frequently used in the high school and first-year college laboratories is the brownish ''[[Dugesia tigrina]]''. Other common varieties are the blackish ''[[Planaria maculata]]'' and ''[[Dugesia dorotocephala]]''. Recently, however, the species ''[[Schmidtea mediterranea]]'' has emerged as the species of choice for modern molecular biological and genomic research due to its diploid chromosomes and existence in both asexual and sexual strains. Recent genetic screens utilizing double-stranded RNA technology have uncovered 240 genes that affect regeneration in ''S. mediterranea''. Interestingly, many of these genes are found in the human genome (see link below). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Anatomy and physiology== | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Revision as of 23:54, 11 February 2007
| Planaria | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
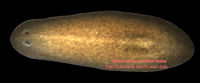 The planarian Schmidtea mediterranea
| ||||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||||
|
Planaria are flatworms (phylum Platyhelminthes) of the suborder (or order) Tricladida of the class Turbellaria. Primarily free-living, planarians are characterized by a soft, broad, leaf-shaped (when elongated) body with cilia and a three-branched digestive tract (as reflected in the name Tricladida).
Planarians or triclads are widely distributed, common, and diverse. While chiefly found in freshwater ecosystems, they also can be found in marine and terrestrial environments.
Carranza et al. (1998) notes that Tricladida is best considered a suborder of the order Seriata, but there are taxonomies where Tricladida is placed as an order. Systematists have traditionally recognized three major groups of triclads: Paludicola (freshwater planarians), Maricola (marine planarians), and Terricola (land planarians), but some propose a fourth planarian infraorder Cavernicola (Carranza et al. 1998).
The term "planaria" is most often used as a common name, but is also the name of a genus within the family Planariidae. There are several families of planarians within Tricladida.
Planarians are common organisms for scientific research and classroom teaching. Their ability to regenerate body parts, and in some species reproduce asexually, adds to research interest in them. Carranza et al. (1998) note that they are probably the best known of the free-living platyhelminthes, largely because of intensive research related to cellular regeneration, pattern formation, and Hox gene expression.
Some planarians have achieved pest status as a result of being invasive species.
Characteristics
Planaria are globally distributed and common to many parts of the world, residing in freshwater ponds and rivers. They are also found residing on plants or in marine environments.
Planarians range in size from about 3 to 12 mm. As with all flatworms, planaria have 3 germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm), but lack a true coelom (they are acoelomate).
, and the body has two eye-spots (also known as ocelli) that can detect the intensity of light. The eye-spots act as photoreceptors and are used to move away from light sources.
They have a single-opening digestive tract, consisting of one anterior branch and two posterior branches in freshwater planarians. Because of this three-branched organization, freshwater flatworms are often referred to as triclad planarians. They are active carnivious flatworms that feed on daphnia and midges.
The planarian has very simple organ systems. The digestive system consists of a mouth, pharynx, and an intestine. The mouth is located in the center of the underside of the body. Digestive enzymes secrete from mouth to begin external digestion. The pharynx connects the mouth to the intestines. The intestines of the Planaria branch throughout the body. They eat living or dead small animals that they suck with their muscular mouth. From there, the food passes through the pharynx into the intestines and digesting of the food takes place in the cells lining the intestine, which then diffuses to the rest of the body.
Planaria receive oxygen and release carbon dioxide by diffusion. The excretory system is made of many tubes with many flame cells and excretory pores on them. Flame cells remove unwanted liquids from the body by passing them through ducts that lead to excretory pores where the waste is released on the dorsal surface of the planarian.
At the head of the planarian there is a brain under the eyespots. From the brain there are two nerve cords which connect at the tail. There are many transverse nerves connected to the nerve cords which make it look like a ladder. With a ladder-like nerve system it is able to respond in a coordinated manner.
A planarian can reproduce either asexually or sexually. In asexual reproduction the planarian detaches its tail end and each half regrows the lost parts. In sexual reproduction each Planaria gives and receives sperm. Planaria have both testes and ovaries. Eggs develop inside the body and are shed in capsules. Weeks later the eggs hatch and grow into adults. Planarians can also reproduce by regeneration. If a Planaria is cut into two halves, both halves may become two new Planaria (regeneration). In one experiment, T.H. Morgan found that a piece corresponding to 1⁄279th of a planarian could successfully regenerate into a new worm. This size (about 10,000 cells) is typically accepted as the smallest fragment that could regrow into a new planarian.
Planarians move by beating cilia on the ventral dermis, allowing it to glide along on a film of mucus. Some move by undulations of the whole body by the contractions of muscles built into the body wall.
They exhibit an extraordinary ability to regenerate lost body parts. For example, a Planaria split length wise or crosswise will regenerate into 2 separate individuals.
The most frequently used in the high school and first-year college laboratories is the brownish Dugesia tigrina. Other common varieties are the blackish Planaria maculata and Dugesia dorotocephala. Recently, however, the species Schmidtea mediterranea has emerged as the species of choice for modern molecular biological and genomic research due to its diploid chromosomes and existence in both asexual and sexual strains. Recent genetic screens utilizing double-stranded RNA technology have uncovered 240 genes that affect regeneration in S. mediterranea. Interestingly, many of these genes are found in the human genome (see link below).
Anatomy and physiology
See also
- Memory RNA
- Mario Benazzi
- Behzad Ghorbani
External links
- More information on freshwater planarians and their biology
- More information on the genetic screen to identify regeneration genes
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Alvarado, Alejandro Sánchez, "Quick Guide - Planarians" Current Biology Vol. 14, No. 18 (Retrieved online)
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
