Difference between revisions of "Gamma-ray astronomy" - New World Encyclopedia
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
'''Gamma-ray astronomy''' is the [[astronomy|astronomical]] study of the [[cosmos]] with [[gamma rays]]. | '''Gamma-ray astronomy''' is the [[astronomy|astronomical]] study of the [[cosmos]] with [[gamma rays]]. | ||
| − | Today, [[gamma ray burst|gamma-ray burst]]s are seen to last for fractions of a second to minutes, popping off like cosmic flashbulbs from unexpected directions, flickering, and then fading after briefly dominating the gamma-ray sky. Studied for over 25 years now with instruments on board a variety of satellites and space probes | + | Today, [[gamma ray burst|gamma-ray burst]]s are seen to last for fractions of a second to minutes, popping off like cosmic flashbulbs from unexpected directions, flickering, and then fading after briefly dominating the gamma-ray sky. Studied for over 25 years now with instruments on board a variety of satellites and space probes, the sources of these enigmatic high-energy flashes remain a mystery. Many of them appear to come from far away in the universe, and currently the most likely theory seems to be that at least some of them come from so-called ''[[hypernova]]'' explosions - supernovas creating [[black hole]]s rather than [[neutron star]]s. |
| + | |||
| + | * high-energy universe, sometimes called the 'violent' universe, because gamma-rays are produced by phenomena such as explosions and high-speed collisions. | ||
== Early history == | == Early history == | ||
| − | + | Long before scientists could detect [[gamma ray]]s from cosmic sources, they had suspected that the universe may be producing [[photon]]s in this energy range. Work by [[Eugene Feenberg]] and H. Primakoff in 1948, [[Sachio Hayakawa]] and I.B. Hutchinson in 1952, and Morrison in 1958 led to the prediction that a number of different phenomena in the cosmos would result in the emission of gamma rays. These phenomena included [[supernova]] explosions, interactions of [[cosmic ray]]s (very energetic charged particles in space) with [[interstellar gas]], and interactions of energetic [[electron]]s with [[magnetic field]]s.<ref>[http://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/science/know_l1/history_gamma.html The History of Gamma-ray Astronomy]. NASA. Retrieved February 18, 2009.</ref> | |
| + | |||
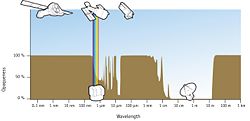
| + | Gamma rays coming from space are mostly absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere. So gamma-ray astronomy could not develop until it became possible to place detectors above most (if not all) of the atmosphere, using [[balloon]]s or spacecraft. The first gamma-ray telescope carried into orbit, on the [[Explorer 11]] satellite in 1961, picked up fewer than 100 cosmic gamma-ray photons. They appeared to come from all directions in the universe, implying some sort of uniform "gamma-ray background." Such a background would be expected from the interaction of cosmic rays with gas found between the stars. | ||
| − | + | The first true astrophysical gamma-ray sources detected were solar flares, which revealed the strong 2.223 MeV line predicted by Morrison. This line results from the formation of deuterium via the union of a neutron and proton; in a solar flare the neutrons appear as secondaries from interactions of high-energy ions accelerated in the flare process. These first gamma-ray line observations were from the spacecrafts [[OSO-3]], [[OSO-7]], and the [[Solar Maximum mission|Solar Maximum Mission]], the last of which was launched in 1980. The solar observations inspired theoretical work by [[Reuven Ramaty]] and others. | |
| − | + | Significant gamma-ray emission from our galaxy was first detected in 1967 by the gamma-ray detector aboard the [[OSO-3]] satellite. It detected 621 events attributable to cosmic gamma rays. | |
| − | + | Some of the most unexpected discoveries in gamma-ray astronomy came in the late 1960s and early 1970s from a constellation of defense satellites that were put into orbit for a completely different reason. Detectors aboard the [[Vela (satellite)|Vela]] satellite series, designed to detect flashes of gamma rays from nuclear bomb blasts, began to record bursts of gamma rays not from the vicinity of the Earth but from deep space. | |
| − | + | The field of gamma-ray astronomy took great leaps forward with the [[Second Small Astronomy Satellite|SAS-2]] (1972) and the [[COS-B]] (1975-1982) satellites. These two satellites provided an exciting view into the high-energy universe. They confirmed the earlier findings of the gamma-ray background, produced the first detailed map of the sky at gamma-ray wavelengths, and detected a number of point sources. However, the poor resolution of the instruments made it impossible to identify most of these point sources with individual stars or stellar systems. | |
| − | == | + | == Recent observations == |
| − | |||
| − | + | During its [[High Energy Astronomy Observatory]] program in 1977, [[NASA]] announced plans to build a "great observatory" for gamma-ray astronomy. The [[Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory]] (CGRO) was designed to take advantage of the major advances in detector technology during the 1980s, and it was launched in 1991. The satellite carried four major instruments which have greatly improved the spatial and temporal resolution of gamma-ray observations. CGRO provided large amounts of data, which are being used to improve our understanding of the high-energy processes in our universe. CGRO was de-orbited in June 2000 as a result of the failure of one of its stabilizing [[gyroscope]]s. | |
| − | During its [[High Energy Astronomy Observatory]] program in 1977, [[NASA]] announced plans to build a "great observatory" for gamma-ray astronomy. The [[Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory]] (CGRO) was designed to take advantage of the major advances in detector technology during the 1980s, and was launched in 1991. The satellite carried four major instruments which have greatly improved the spatial and temporal resolution of gamma-ray observations. | ||
| − | [[BeppoSAX]] was launched in 1996 and deorbited in 2003. It predominantly studied X-rays, but also observed gamma-ray bursts. By identifying the first non-gamma ray counterparts to gamma-ray bursts, it opened the way for | + | [[BeppoSAX]] was launched in 1996 and deorbited in 2003. It predominantly studied X-rays, but also observed gamma-ray bursts. By identifying the first non-gamma ray counterparts to gamma-ray bursts, it opened the way for precise determination of their positions and optical observation of their fading remnants in distant galaxies. |
| − | The [[High Energy Transient Explorer]] 2 (HETE-2) was launched in October 2000 (on a nominally 2 | + | The [[High Energy Transient Explorer]] 2 (HETE-2) was launched in October 2000 (on a nominally 2-year mission) and was still operational in March 2007. [[Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission|Swift]], a NASA spacecraft, was launched in 2004 and carries the BAT instrument for gamma-ray burst observations. Following BeppoSAX and HETE-2, it has observed numerous X-ray and optical counterparts to bursts, leading to distance determinations and detailed optical follow-up. These have established that most bursts originate in the explosions of massive stars ([[supernova]]s and [[hypernova]]s) in distant galaxies. |
| − | Following BeppoSAX and HETE-2, it has observed numerous X-ray and optical counterparts to bursts, leading to distance determinations and detailed optical follow-up. These have established that most bursts originate in the explosions of massive stars ([[supernova]]s and [[hypernova]]s) in distant galaxies. | ||
Currently, the main space-based gamma-ray observatories are the INTErnational Gamma-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory, ([[INTEGRAL]]), and the [[Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope]] (GLAST). | Currently, the main space-based gamma-ray observatories are the INTErnational Gamma-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory, ([[INTEGRAL]]), and the [[Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope]] (GLAST). | ||
INTEGRAL is an ESA mission with additional contributions from [[Czech republic|Czech]], Poland, USA, and Russia. It was launched on 17 October 2002. NASA launched [[Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope|GLAST]] on 11 June 2008. It includes LAT, the Large Area Telescope, and GBM, the GLAST Burst Monitor, for studying gamma-ray bursts. | INTEGRAL is an ESA mission with additional contributions from [[Czech republic|Czech]], Poland, USA, and Russia. It was launched on 17 October 2002. NASA launched [[Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope|GLAST]] on 11 June 2008. It includes LAT, the Large Area Telescope, and GBM, the GLAST Burst Monitor, for studying gamma-ray bursts. | ||
| − | Very energetic gamma rays, with photon energies | + | Very energetic gamma rays, with photon energies higher than about 30 GeV, can also be detected by ground-based experiments. The extremely low photon fluxes at such high energies require detector effective areas that are too large for current space-based instruments. Fortunately, such high-energy photons produce extensive showers of secondary particles in the atmosphere that can be observed on the ground, both directly by radiation counters and optically via the [[Cherenkov radiation|Cherenkov light]] the ultra-relativistic shower particles emit. The Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescope technique currently achieves the highest sensitivity. |
The [[Crab Nebula]], a steady source of so-called TeV gamma-rays, was first detected in 1989 by the Whipple Observatory at Mt. Hopkins, in [[Arizona]] in the USA. Modern Cherenkov telescope experiments like [[High Energy Stereoscopic System|H.E.S.S.]], [[VERITAS]], [[MAGIC (telescope)|MAGIC]], and CANGAROO III can detect the Crab Nebula in a few minutes. | The [[Crab Nebula]], a steady source of so-called TeV gamma-rays, was first detected in 1989 by the Whipple Observatory at Mt. Hopkins, in [[Arizona]] in the USA. Modern Cherenkov telescope experiments like [[High Energy Stereoscopic System|H.E.S.S.]], [[VERITAS]], [[MAGIC (telescope)|MAGIC]], and CANGAROO III can detect the Crab Nebula in a few minutes. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 39: | ||
The most energetic photons (up to 16 [[TeV]]) observed from an extragalactic object originate from the [[blazar]] [[Markarian 501]] (Mrk 501). These measurements were done by the High-Energy-Gamma-Ray Astronomy ([[HEGRA]]) air [[Cherenkov effect|Cherenkov]] telescopes. | The most energetic photons (up to 16 [[TeV]]) observed from an extragalactic object originate from the [[blazar]] [[Markarian 501]] (Mrk 501). These measurements were done by the High-Energy-Gamma-Ray Astronomy ([[HEGRA]]) air [[Cherenkov effect|Cherenkov]] telescopes. | ||
| − | Gamma-ray astronomy observations are still limited by non-gamma ray backgrounds at lower energies, and, at higher energy, by the number of photons that can be detected. Larger area detectors and better background suppression are essential for progress in the field. | + | Gamma-ray astronomy observations are still limited by non-gamma-ray backgrounds at lower energies, and, at higher energy, by the number of photons that can be detected. Larger area detectors and better background suppression are essential for progress in the field. |
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Revision as of 00:32, 19 February 2009
Gamma-ray astronomy is the astronomical study of the cosmos with gamma rays.
Today, gamma-ray bursts are seen to last for fractions of a second to minutes, popping off like cosmic flashbulbs from unexpected directions, flickering, and then fading after briefly dominating the gamma-ray sky. Studied for over 25 years now with instruments on board a variety of satellites and space probes, the sources of these enigmatic high-energy flashes remain a mystery. Many of them appear to come from far away in the universe, and currently the most likely theory seems to be that at least some of them come from so-called hypernova explosions - supernovas creating black holes rather than neutron stars.
- high-energy universe, sometimes called the 'violent' universe, because gamma-rays are produced by phenomena such as explosions and high-speed collisions.
Early history
Long before scientists could detect gamma rays from cosmic sources, they had suspected that the universe may be producing photons in this energy range. Work by Eugene Feenberg and H. Primakoff in 1948, Sachio Hayakawa and I.B. Hutchinson in 1952, and Morrison in 1958 led to the prediction that a number of different phenomena in the cosmos would result in the emission of gamma rays. These phenomena included supernova explosions, interactions of cosmic rays (very energetic charged particles in space) with interstellar gas, and interactions of energetic electrons with magnetic fields.[1]
Gamma rays coming from space are mostly absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere. So gamma-ray astronomy could not develop until it became possible to place detectors above most (if not all) of the atmosphere, using balloons or spacecraft. The first gamma-ray telescope carried into orbit, on the Explorer 11 satellite in 1961, picked up fewer than 100 cosmic gamma-ray photons. They appeared to come from all directions in the universe, implying some sort of uniform "gamma-ray background." Such a background would be expected from the interaction of cosmic rays with gas found between the stars.
The first true astrophysical gamma-ray sources detected were solar flares, which revealed the strong 2.223 MeV line predicted by Morrison. This line results from the formation of deuterium via the union of a neutron and proton; in a solar flare the neutrons appear as secondaries from interactions of high-energy ions accelerated in the flare process. These first gamma-ray line observations were from the spacecrafts OSO-3, OSO-7, and the Solar Maximum Mission, the last of which was launched in 1980. The solar observations inspired theoretical work by Reuven Ramaty and others.
Significant gamma-ray emission from our galaxy was first detected in 1967 by the gamma-ray detector aboard the OSO-3 satellite. It detected 621 events attributable to cosmic gamma rays.
Some of the most unexpected discoveries in gamma-ray astronomy came in the late 1960s and early 1970s from a constellation of defense satellites that were put into orbit for a completely different reason. Detectors aboard the Vela satellite series, designed to detect flashes of gamma rays from nuclear bomb blasts, began to record bursts of gamma rays not from the vicinity of the Earth but from deep space.
The field of gamma-ray astronomy took great leaps forward with the SAS-2 (1972) and the COS-B (1975-1982) satellites. These two satellites provided an exciting view into the high-energy universe. They confirmed the earlier findings of the gamma-ray background, produced the first detailed map of the sky at gamma-ray wavelengths, and detected a number of point sources. However, the poor resolution of the instruments made it impossible to identify most of these point sources with individual stars or stellar systems.
Recent observations
During its High Energy Astronomy Observatory program in 1977, NASA announced plans to build a "great observatory" for gamma-ray astronomy. The Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory (CGRO) was designed to take advantage of the major advances in detector technology during the 1980s, and it was launched in 1991. The satellite carried four major instruments which have greatly improved the spatial and temporal resolution of gamma-ray observations. CGRO provided large amounts of data, which are being used to improve our understanding of the high-energy processes in our universe. CGRO was de-orbited in June 2000 as a result of the failure of one of its stabilizing gyroscopes.
BeppoSAX was launched in 1996 and deorbited in 2003. It predominantly studied X-rays, but also observed gamma-ray bursts. By identifying the first non-gamma ray counterparts to gamma-ray bursts, it opened the way for precise determination of their positions and optical observation of their fading remnants in distant galaxies.
The High Energy Transient Explorer 2 (HETE-2) was launched in October 2000 (on a nominally 2-year mission) and was still operational in March 2007. Swift, a NASA spacecraft, was launched in 2004 and carries the BAT instrument for gamma-ray burst observations. Following BeppoSAX and HETE-2, it has observed numerous X-ray and optical counterparts to bursts, leading to distance determinations and detailed optical follow-up. These have established that most bursts originate in the explosions of massive stars (supernovas and hypernovas) in distant galaxies.
Currently, the main space-based gamma-ray observatories are the INTErnational Gamma-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory, (INTEGRAL), and the Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope (GLAST). INTEGRAL is an ESA mission with additional contributions from Czech, Poland, USA, and Russia. It was launched on 17 October 2002. NASA launched GLAST on 11 June 2008. It includes LAT, the Large Area Telescope, and GBM, the GLAST Burst Monitor, for studying gamma-ray bursts.
Very energetic gamma rays, with photon energies higher than about 30 GeV, can also be detected by ground-based experiments. The extremely low photon fluxes at such high energies require detector effective areas that are too large for current space-based instruments. Fortunately, such high-energy photons produce extensive showers of secondary particles in the atmosphere that can be observed on the ground, both directly by radiation counters and optically via the Cherenkov light the ultra-relativistic shower particles emit. The Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescope technique currently achieves the highest sensitivity.
The Crab Nebula, a steady source of so-called TeV gamma-rays, was first detected in 1989 by the Whipple Observatory at Mt. Hopkins, in Arizona in the USA. Modern Cherenkov telescope experiments like H.E.S.S., VERITAS, MAGIC, and CANGAROO III can detect the Crab Nebula in a few minutes.
The most energetic photons (up to 16 TeV) observed from an extragalactic object originate from the blazar Markarian 501 (Mrk 501). These measurements were done by the High-Energy-Gamma-Ray Astronomy (HEGRA) air Cherenkov telescopes.
Gamma-ray astronomy observations are still limited by non-gamma-ray backgrounds at lower energies, and, at higher energy, by the number of photons that can be detected. Larger area detectors and better background suppression are essential for progress in the field.
See also
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Aharonian, Felix A. 2004. Very High Energy Cosmic Gamma Radiation: A Crucial Window on the Extreme Universe. Singapore: World Scientific. ISBN 9810245734
- O'Dell, Stephen L., and Giovanni Pareschi, eds. 2007. Optics for EUV, X-Ray, and Gamma-Ray Astronomy III. Proceedings of SPIE, 29-30 August, 2007, San Diego, California, USA. Bellingham, WA: SPIE. Online version. Retrieved February 12, 2009.
- Ramana Murthy, P. V., and A. W. Wolfendale. 1993. Gamma-Ray Astronomy. Cambridge Astrophysics Series, 22. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521420814
- Weekes, Trevor C. 2003. Very High Energy Gamma-Ray Astronomy. Series in Astronomy and Astrophysics. Bristol: Institute of Physics Pub. ISBN 0750306580
External links
- The Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission. NASA. Retrieved February 12, 2009.
- The HETE-2 Satellite. NASA. Retrieved February 12, 2009.
- Exploring the non-thermal Universe . The HEGRA Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescope System, Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik. Retrieved February 12, 2009.
- High Energy Stereoscopic System (H.E.S.S.). (Ground-based observatory studying very high energy (VHE) gamma-ray astrophysics.) Retrieved February 12, 2009.
- Gamma-ray astronomy at low energies with high sensitivity. The MAGIC Telescope. Retrieved February 12, 2009.
- INTEGRAL Latest News. (The space-borne INTEGRAL observatory.) Retrieved February 12, 2009.
- C.A.C.T.U.S.. (CACTUS is a ground-based Air Cherenkov Telescope.) University of California, Davis. Retrieved February 12, 2009.
- MACE, TACTIC. The AstroPhysical Sciences Division. Retrieved February 12, 2009.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
- ↑ The History of Gamma-ray Astronomy. NASA. Retrieved February 18, 2009.