Difference between revisions of "Epithelium" - New World Encyclopedia
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[Image:Illu epithelium.jpg|thumb|350px|Types of epithelium]] | [[Image:Illu epithelium.jpg|thumb|350px|Types of epithelium]] | ||
| − | + | '''Epithelium''' is a [[biological tissue|tissue]] (collection of interconnected [[cell (biology)|cells that perform a similar function within an organism) that covers organ systems of the bodies of [[animal]]s, including both the outside [[skin]] and the inside cavities and [[lumen (anatomy)|lumen]] (interior of a vessel within the body, such as the small central space in an artery or vein, or any of their relating vessels through which blood flows). | |
| + | |||
| + | Epithelium is one of four primary body tissues of animals, including the human body and lower multicellular organisms, such as insects. The other three basic tissues are ''connective tissue'' (holds everything together), ''[[muscle]] tissue'' (contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell), and ''nervous tissue'' (forming the [[brain]], spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The outermost layer of our [[skin]] is composed of dead stratified [[squamous]] epithelial cells, as are the [[mucous membranes]] lining the inside of mouths and body cavities. Other epithelial cells line the insides of the [[lung]]s, the [[gastrointestinal tract]], the reproductive and urinary tracts, and make up the [[exocrine]] and [[endocrine]] glands. | ||
Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, absorption, protection, transcellular transport, sensation detection, and selective permeability. | Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, absorption, protection, transcellular transport, sensation detection, and selective permeability. | ||
[[Endothelium]] (the inner lining of [[blood vessel]]s) is a specialized form of epithelium. | [[Endothelium]] (the inner lining of [[blood vessel]]s) is a specialized form of epithelium. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 20:14, 1 March 2007
Epithelium is a tissue (collection of interconnected [[cell (biology)|cells that perform a similar function within an organism) that covers organ systems of the bodies of animals, including both the outside skin and the inside cavities and lumen (interior of a vessel within the body, such as the small central space in an artery or vein, or any of their relating vessels through which blood flows).
Epithelium is one of four primary body tissues of animals, including the human body and lower multicellular organisms, such as insects. The other three basic tissues are connective tissue (holds everything together), muscle tissue (contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell), and nervous tissue (forming the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system).
The outermost layer of our skin is composed of dead stratified squamous epithelial cells, as are the mucous membranes lining the inside of mouths and body cavities. Other epithelial cells line the insides of the lungs, the gastrointestinal tract, the reproductive and urinary tracts, and make up the exocrine and endocrine glands.
Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, absorption, protection, transcellular transport, sensation detection, and selective permeability. Endothelium (the inner lining of blood vessels) is a specialized form of epithelium.
Classification
Epithelial cells are classified by the following three factors:
- shape
- Stratification
- Specializations
Shape
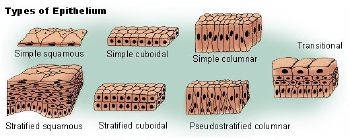
- Squamous: Squamous cells are flat cells with an irregular flattened shape
. The one-cell layer of simple squamous epithelium that forms the alveoli of the respiratory membrane, and the endothelium of capillaries, and is a minimal barrier to diffusion. Places where squamous cells can be found include the alveoli of the lungs, the filtration tubules of the kidneys, and the major cavities of the body. These cells are relatively inactive metabolically, and are associated with the diffusion of water, electrolytes, and other substances.
- Cuboidal: As the name suggests, these cells have a shape similar to a cube, meaning its width is the same size as its height. The nuclei of these cells are usually located in the center.
- Columnar: These cells are taller than they are wide. Simple columnar epithelium is made up of a single layer of cells that are longer than they are wide. The nucleus is also closer to the base of the cell. The small intestine is a tubular organ lined with this type of tissue. Unicellular glands called goblet cells are scattered throughout the simple columnar epithelial cells and secrete mucus. The free surface of the columnar cell has tiny hairlike projections called microvilli. They increase the surface area for absorption.
- Transitional: This is a specialized type of epithelium found lining organs that can stretch, such as the urothelium that lines the bladder and ureter of mammals. Since the cells can slide over each other, the appearance of this epithelium depends on whether the organ is distended or contracted: if distended, it appears as if there are only a few layers; when contracted, it appears as if there are several layers.
Stratification
- Simple: There is a single layer of cells.
- Stratified: More than one layer of cells. The superficial layer is used to classify the layer. Only one layer touches the basal lamina. Stratified cells can usually withstand large amounts of stress.
- Pseudostratified with cilia: This is used mainly in one type of classification (pseudostratified columnar epithelium). There is only a single layer of cells, but the position of the nuclei gives the impression that it is stratified. If a specimen looks stratified, but you can identify cilia, the specimen is pseudostratified ciliated epithelium since stratified epithelium cannot have cilia.
Specializations
- Keratinized cells contain keratin (a cytoskeletal protein). While keratinized epithelium occurs mainly in the skin, it is also found in the mouth and nose, providing a tough, impermeable barrier.
- Ciliated cells have apical plasma membrane extensions composed of microtubules capable of beating rhythmically to move mucus or other substances through a duct. Cilia are common in the respiratory system and the lining of the oviduct.
Examples
| System | Tissue | Epithelium | Subtype |
| circulatory | blood vessels | Simple squamous | endothelium |
| digestive | ducts of submandibular glands | Stratified columnar | - |
| digestive | attached gingiva | Stratified squamous, keratinized | - |
| digestive | dorsum of tongue | Stratified squamous, keratinized | - |
| digestive | hard palate | Stratified squamous, keratinized | - |
| digestive | esophagus | Stratified squamous, non-keratinised | - |
| digestive | stomach | Simple columnar, non-ciliated | - |
| digestive | small intestine | Simple columnar, non-ciliated | - |
| digestive | large intestine | Simple columnar, non-ciliated | - |
| digestive | rectum | Stratified squamous, non-keratinised | - |
| digestive | anus | Stratified squamous, keratinised | - |
| digestive | gallbladder | Simple columnar, non-ciliated | - |
| endocrine | thyroid follicles | Simple cuboidal | - |
| nervous | ependyma | Simple cuboidal | - |
| lymphatic | lymph vessel | Simple squamous | endothelium |
| integumentary | skin - dead superficial layer | Stratified squamous, keratinized | - |
| integumentary | sweat gland ducts | Stratified cuboidal | - |
| integumentary | mesothelium of body cavities | Simple squamous | - |
| reproductive - female | ovaries | Simple cuboidal | germinal epithelium (female) |
| reproductive - female | Fallopian tubes | Simple columnar, ciliated | - |
| reproductive - female | uterus | Simple columnar, ciliated | - |
| reproductive - female | endometrium | Simple columnar | - |
| reproductive - female | cervix (endocervix) | Simple columnar | - |
| reproductive - female | cervix (ectocervix) | Stratified squamous, non-keratinised | - |
| reproductive - female | vagina | Stratified squamous, non-keratinised | - |
| reproductive - female | labia majora | Stratified squamous, keratinised | - |
| reproductive - male | tubuli recti | Simple cuboidal | germinal epithelium (male) |
| reproductive - male | rete testis | Simple cuboidal | - |
| reproductive - male | ductuli efferentes | Pseudostratified columnar | - |
| reproductive - male | epididymis | Pseudostratified columnar, with stereocilia | - |
| reproductive - male | vas deferens | Pseudostratified columnar | - |
| reproductive - male | ejaculatory duct | Simple columnar | - |
| reproductive - male (gland) | bulbourethral glands | Simple columnar | - |
| reproductive - male (gland) | seminal vesicle | Pseudostratified columnar | - |
| respiratory | oropharynx | Stratified squamous, non-keratinised | - |
| respiratory | larynx | Pseudostratified columnar, ciliated | respiratory epithelium |
| respiratory | trachea | Pseudostratified columnar, ciliated | respiratory epithelium |
| respiratory | respiratory bronchioles | Simple cuboidal | - |
| sensory | cornea | Stratified squamous, non-keratinised | corneal epithelium |
| sensory | nose | Pseudostratified columnar | olfactory epithelium |
| urinary | kidney - proximal convoluted tubule | Simple columnar, ciliated | - |
| urinary | kidney - ascending thin limb | Simple squamous | - |
| urinary | kidney - distal convoluted tubule | Simple columnar, non-ciliated | - |
| urinary | kidney - collecting duct | Simple cuboidal | - |
| urinary | renal pelvis | Transitional | urothelium |
| urinary | ureter | Transitional | urothelium |
| urinary | urinary bladder | Transitional | urothelium |
| urinary | prostatic urethra | Transitional | urothelium |
| urinary | membranous urethra | Pseudostratified columnar, non-ciliated | - |
| urinary | penile urethra | Pseudostratified columnar, non-ciliated | - |
| urinary | external urethral orifice | Stratified squamous | - |
Cell junctions
A cell junction is a structure within a tissue of a multicellular organism. Cell junctions are especially abundant in epithelial tissues. They consist of protein complexes and provide contact between neighbouring cells, between a cell and the extracellular matrix, or they built up the paracellular barrier of epithelia and control the paracellular transport.
Secretory epithelia
As stated above, secretion is one major function of epithelial cells. Glands are formed from the invagination / infolding of epithelial cells and subsequent growth in the underlying connective tissue. There are two major classification of glands: endocrine glands and exocrine glands.
Embryology
There are epithelial tissues deriving from all of the embryological germ layers:
- from ectoderm (e.g., the epidermis);
- from endoderm (e.g., the lining of the gastrointestinal tract);
- from mesoderm (e.g., the inner linings of body cavities).
Additional images
- Tkanka nablonkowa.png
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th edition, Alberts et al., 2002
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.