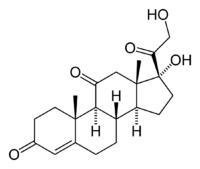
Cortisone
| Cortisone | |
|---|---|
| |
| Systematic name | 17,21-dihydroxypregn-4-ene-3,11,20-trione |
| Chemical formula | C21H28O5 |
| Molecular mass | 360.46 g/mol |
| Density | ? g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 220-224 °C |
| CAS number | [53-06-5] |
| SMILES | C[C@@](C3)4[C@](CC[C@@](O)4 [C@@](CO)=O)([H])[C@]2([H])CCC1=CC (CC[C@@](C)1[C@]([H])2C3=O)=O |
| Disclaimer and references | |
Cortisone (IPA:ˈkôrtəˌsōn) (17-hydroxy-11-dehydrocorticosterone) is a steroid hormone. Chemically, it is a corticosteroid with formula C21H28O5 and IUPAC name 17,21-dihydroxypregn-4-ene-3,11,20-trione. It is closely related to corticosterone.
Cortisone and adrenaline are the main hormones released by the body as a reaction to stress. They elevate blood pressure and prepare the body for a fight or flight response.
Cortisone is the inactive precursor molecule of the active hormone cortisol. It is activated through hydroxylation of the 11-keto-group by an enzyme called 11-beta-steroid dehydrogenase. The active form cortisol is thus sometimes referred to as hydrocortisone.
Cortisone is sometimes used as a drug to treat a variety of ailments. It can be administered intravenously or cutaneously.
One of cortisone's effects on the body, and a potentially harmful side effect when administered clinically, is the suppression of the immune system. This is an explanation for the apparent correlation between high stress and sickness.
Cortisone is less important than a similar steroid cortisol. Cortisol is responsible for 95% of the effects of the glucocorticosteroids while cortisone is about 4 or 5%. Corticosterone is even less important.
Cortisone was first discovered by the American chemist Edward Calvin Kendall. He won the 1950 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine along with Philip S. Hench and Tadeus Reichstein for the discovery of adrenal cortex hormones, their structures, and functions.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 2533
- Woodward R. B., Sondheimer F., Taub D. (1951). The Total Synthesis of Cortisone. Journal of the American Chemical Society 73: 4057 - 4057.
- Ingle D. J. (1950). The biologic properties of cortisone: a review. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology 10: 1312-1354.
See also
- Central serous retinopathy
- Corticosterol
External links
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.