Difference between revisions of "Cayman Islands" - New World Encyclopedia
Mary Anglin (talk | contribs) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (65 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Ebcompleted}}{{2Copyedited}}{{Paid}}{{Approved}}{{Submitted}}{{Images OK}}{{Copyedited}} |
| − | [[ | + | {{Infobox Country |
| − | [[ | + | |conventional_long_name =Cayman Islands |
| + | |demonym = Caymanian | ||
| + | |common_name = the Cayman Islands | ||
| + | |image_skyline = Cayman_montage.jpg | ||
| + | |imagesize = 1000px | ||
| + | |image_caption = ''From top to the bottom and from left to right:'' The lighthouse, West Bay Road, Cayman National Bank, 7 Mile Beach, The Ritz-Carlton Hotel, 7 Mile Beach Road, Water Front, the Port,Owen Roberts International Airport. | ||
| + | |image_flag = Flag of the Cayman Islands.svg | ||
| + | |use = [[Flag| Flag of the Cayman Islands]] | ||
| + | |image_coat = 99px-Cayman Islands coat of arms large svg.png | ||
| + | |image_map = LocationCaymanIslands.png | ||
| + | |national_motto = "He hath founded it upon the seas" | ||
| + | |national_anthem = ''[[God Save the King]]'' (official)<br/>'''''National Song:''''' "[[Beloved Isle Cayman]]" | ||
| + | |official_language = [[English language|English]] | ||
| + | |capital = [[George Town, Cayman Islands|George Town]] | ||
| + | |latd=19 |latm=20 |latNS=N |longd=81 |longm=24 |longEW=W | ||
| + | |largest_city = capital | ||
| + | |ethnic_groups = Mixed 40%, White 20%, African descent 20%, expatriates of various ethnic groups 20% <ref name=CIA>CIA, [https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/cayman-islands/#people-and-society Cayman Islands - People and Society] ''World Factbook''. Retrieved September 15, 2022.</ref> | ||
| + | |largest_district = George Town | ||
| + | |government_type = [[British Overseas Territories|British Overseas Territory]] ([[constitutional monarchy]] and [[parliamentary system|parliamentary]] [[representative democracy|democratic]] [[Dependent territory|dependency]]) | ||
| + | |leader_title1 = [[Monarchy of the United Kingdom|Monarch]] | ||
| + | |leader_name1 = [[Charles III]] | ||
| + | |leader_title2 = [[Governors of the Cayman Islands|Governor]] | ||
| + | |leader_name2 = [[Martyn Roper]] | ||
| + | |leader_title3 = [[Premier of the Cayman Islands|Premier]] | ||
| + | |leader_name3 = [[Wayne Panton]] | ||
| + | |legislature=[[Legislative Assembly of the Cayman Islands|Legislative Assembly]] | ||
| + | |area_km2 = 264 | ||
| + | |area_sq_mi = 102 | ||
| + | |area_rank = 206th | ||
| + | |area_magnitude = 1 E8 | ||
| + | |percent_water = 1.6 | ||
| + | | population_census = 69,656<ref>[https://www.eso.ky/preliminary-2021-census-report-published.html#4 Preliminary 2021 Census Report Published] ''Economics and Statistics Office'', Government of the Cayman Islands. Retrieved September 15, 2022.</ref> | ||
| + | |population_estimate = 64,309<ref name=CIA/> | ||
| + | | population_estimate_year = 2022 | ||
| + | | population_estimate_rank = 206th | ||
| + | | population_census_year = 2021 | ||
| + | | population_density_km2 = 244 | ||
| + | | population_density_rank = 59th | ||
| + | | population_density_sq_mi = 631 <!-- Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]] —> | ||
| + | | GDP_PPP = $2.507 billion<ref name=CIA-E/> | ||
| + | | GDP_PPP_year = 2014<ref name=CIA-E>CIA, [https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/cayman-islands/#economy Cayman Islands - Economy] ''World Factbook''. Retrieved September 15, 2022.</ref> | ||
| + | | GDP_PPP_rank = | ||
| + | | GDP_PPP_per_capita = $73,800 (2004 est.)<ref name=CIA-E/> | ||
| + | | GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | ||
| + | | GDP_nominal = US$5,936,000,000<ref>[https://data.worldbank.org/country/KY Cayman Islands] ''The World Bank''. Retrieved September 15, 2022.</ref> | ||
| + | | GDP_nominal_year = 2019 | ||
| + | | GDP_nominal_rank = 160th | ||
| + | | GDP_nominal_per_capita = US$91,392 | ||
| + | | GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 7th | ||
| + | |sovereignty_type = Establishment | ||
| + | |established_event1 = British Overseas Territory | ||
| + | |established_date1= 1962 | ||
| + | |established_event2 = Current Constitution | ||
| + | |established_date2= November 6, 2009 | ||
| + | |currency = [[Cayman Islands dollar]] | ||
| + | |currency_code = KYD | ||
| + | |time_zone = | ||
| + | |utc_offset = -5 | ||
| + | |time_zone_DST = not observed | ||
| + | |utc_offset_DST = -5 | ||
| + | |drives_on = left | ||
| + | |cctld = [[.ky]] | ||
| + | |calling_code = [[+1-345]] | ||
| + | |footnotes = | ||
| + | }} | ||
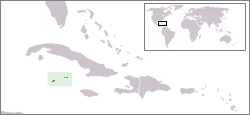
| − | + | The '''Cayman Islands''' are an overseas territory of the [[United Kingdom]] located in the western [[Caribbean Sea]]. It is comprised of three islands, Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac, and Little Cayman. Located south of [[Cuba]] and northwest of [[Jamaica]], the Cayman Islands lie on the outer edge of the [[Caribbean]] and are the closest to [[Central America]]. | |
| − | + | {{toc}} | |
| − | + | The Caymans are one of the most popular tourist attractions in the world due to its pristine beaches and [[Scuba diving|scuba diving]] opportunities. It contains a major global offshore financial services center. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | == Geography == | |
| − | + | [[Image:Cayman Islands-CIA WFB Map.png|thumb|right|350px|Map of the Cayman Islands]] | |
| − | + | The Cayman Islands are a largely self-governing British dependency located in the [[Caribbean Sea]]. Comprised of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, the Cayman Islands are a three-island [[archipelago]] lying between [[Cuba]] and [[Central America]]. They are located 268 km northwest of [[Jamaica]] and 240 km south of Cuba. Its [[geographic coordinate]]s are 19°30 north, 80°30 west. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | With a land area of 101.2 square miles (259 km²), the islands are approximately 1.5 times the size of [[Washington, D.C.]], with a coastline of 99 miles (160 km). These islands make a maritime claim of a 200-nautical mile exclusive fishing zone which includes 12 nautical miles of territorial sea. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The Cayman Islands' lowest [[elevation]] is the Caribbean Sea at [[sea level]]. The highest point is [[The Bluff]], a limestone outcrop 43 m (141 feet) in length on the eastern end of eastern Cayman Brac. The terrain is mostly low-lying [[limestone]] base, surrounded by [[coral reef]]s. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The Cayman Islands have a tropical marine climate, with a wet season of warm but rainy summers lasting from May through October. The winter is dry and relatively cool, lasting from November through April. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | An important environmental issue is the lack of fresh water resources. Drinking water supplies must be met by [[rainwater]] catchment and [[desalination]]. | |
| − | == | + | [[Natural resource]]s include [[fish]] and a climate and beaches that foster [[tourism]], which is the islands' major industry. A major [[natural hazard]] are the [[tropical cyclone]]s that form during the [[Atlantic hurricane|Atlantic hurricane season]] from July to November. |
| + | |||
| + | ==Fauna== | ||
| + | [[File:Blue iguana (Cyclura lewisi) male.JPG|thumb|400px|Blue iguana]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[mammal]]ian species in the Cayman Islands include the introduced [[Dasyprocta punctata|Central American agouti]] and eight species of [[bat]]. At least three now extinct native [[rodent]] species were present until the discovery of the islands by Europeans. Marine life around the island of the Grand Cayman includes [[tarpon]], silversides (''[[Atheriniformes]]''), [[French angelfish]] (''Pomacanthus paru''), and [[giant barrel sponge]]s. A number of [[List of cetacean species|cetaceans]] are found in offshore waters. These species include the [[Ziphius cavirostris|goose-beaked whale]] (''Ziphius cavirostris''), [[Blainville's beaked whale]] (''Mesoplodon densirostris'') and [[sperm whale]] (''Physeter macrocephalus''). | ||
| − | + | Cayman [[birds|avian fauna]] includes two [[endemic]] subspecies of ''[[Amazona]]'' parrots: ''Amazona leucocephala hesterna'' or [[Cuban amazon]], presently restricted to the island of [[Cayman Brac]], but formerly also on [[Little Cayman]], and ''Amazona leucocephala caymanensis'' or [[Grand Cayman parrot]], which is native to the Cayman Islands, forested areas of [[Cuba]], and the [[Isla de la Juventud]]. Little Cayman and Cayman Brac are also home to [[Red-footed booby|red-footed]] and [[brown booby|brown]] boobies.<ref>[https://doe.ky/terrestrial/animals/birds/bird-guide/boobies-tropicbirds-frigatebirds-and-pelicans/redfootedbooby/ Red-footed Booby] ''Department of Environment'', Cayman Islands Government. Retrieved September 15, 2022.</ref> Although the barn owl (''[[Tyto alba]]'') occurs in all three of the islands they are not commonplace. The Cayman Islands also possess five endemic subspecies of butterflies.<ref> R. R. Askew and P. A. van B. Stafford, ''Butterflies of the Cayman Islands'' (Apollo Books, 2008, ISBN 978-8788757859).</ref> These butterfly breeds can be viewed at the [[Queen Elizabeth II Botanic Park]] on the Grand Cayman. | |
| − | + | Among other notable fauna at the Queen Elizabeth II Botanic Park is the critically threatened [[blue iguana]] which is also known as the Grand Cayman iguana (''Cyclura lewisi''). The blue iguana is endemic to the Grand Cayman particularly because of rocky, sunlit, open areas near the island's shores that are advantageous for the laying of eggs. Nevertheless, habitat destruction and invasive mammalian predators remain the primary reasons that blue iguana hatchlings do not survive naturally.<ref>Wildlife Conservation Society, [https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2011/07/110718141038.htm Grand Cayman blue iguana: Back from the brink of extinction] ''Science News'', July 18, 2011. Retrieved September 15, 2022.</ref> | |
| − | The | + | The [[Cuban crocodile]] (''Crocodylus rhombifer'') once inhabited the islands. The name "Cayman" is derived from a [[Cariban languages|Carib]] word for various crocodilians.<ref>[https://www.gov.ky/about-us/our-islands/history The Cayman Islands – History] ''Cayman Islands Government''. Retrieved September 15, 2022.</ref> |
== History == | == History == | ||
| + | On May 10, 1503 [[Christopher Columbus]] discovered the Cayman Islands and named them ''Las Tortugas'' which literally translates into "the turtles" in Spanish, after the numerous sea turtles found there. He had found Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, the two smaller islands. | ||
| − | [[ | + | A map from 1523 shows the islands being referred to as ''"Lagartos",'' meaning [[alligator]]s or large [[lizard]]s, but by 1530 they were known as the Caymanas, the Carib Indian word for the marine [[crocodile]] that also lived in the area. |
| − | + | The first recorded English visitor was [[Francis Drake|Sir Francis Drake]] in 1586. He allegedly reported that the caymanas, marine crocodiles, were edible. However, it was the abundant turtles that ships were attracted to, in search of fresh meat for their crews. Overfishing the turtles nearly extinguished them from the local waters. | |
| − | + | Around 1700, the first recorded permanent inhabitant of the Cayman Islands was born, Isaac Bodden. He was the grandson of one of the original settlers, who was likely one of [[Oliver Cromwell]]'s soldiers at the taking of [[Jamaica]] in 1655. | |
| − | + | Over time and throughout history a variety of people have settled on the Cayman Islands and have called it home: pirates, refugees from the [[Spanish Inquisition]], [[Slavery|slave]]s and shipwrecked sailors. The majority of Caymanians are from [[Africa]]n and [[Great Britain|British]] descent, with considerable interracial mixing. | |
| − | + | === British rule === | |
| + | [[Great Britain|Britain]] took formal control of the Caymans, along with [[Jamaica]], under the [[Treaty of Madrid (1670)|Treaty of Madrid]] in 1670 after the first settlers came from Jamaica in 1661-1671 to Little Cayman and Cayman Brac. | ||
| − | + | These first settlements were abandoned after attacks by Spanish [[privateer]]s, but British privateers often used the Islands as a base, and in the eighteenth century they became an increasingly popular hideout for [[pirate]]s, even after the end of legitimate privateering in 1713. Following several unsuccessful attempts, permanent settlement of the islands began in the 1730s. | |
| − | |||
=== Dependency of Jamaica === | === Dependency of Jamaica === | ||
| − | + | Beginning in 1670, the Cayman Islands became dependencies of [[Jamaica]], although there was considerable self-government. On December 5, 1831, a Legislative Assembly was established through consent, during a meeting held by principal inhabitants. Elections were held on December 10 of the same year; later on December 31 the legislature passed the first local legislation. Because of this the Governor of Jamaica authorized a legislature consisting of eight magistrates appointed by the Governor himself and ten, later increased to 27, elected representatives. | |
| − | In 1835, Governor Sligo arrived in Cayman | + | In 1835, Governor Sligo of Jamaica arrived in Grand Cayman to announce that all [[slave]]s were free, in accordance with the Emancipation Act of 1833. |
| − | + | In 1863 the Cayman Islands were officially declared and administered as a dependency of Jamaica, but were rather like a parish of Jamaica with the nominated justices of the peace and elected vestrymen in their Legislature. From 1750 to 1898 the Chief Magistrate was the official administer of the dependency, who was appointed by the Jamaican governor. In 1898 the Governor of Jamaica began appointing a Commissioner for the Islands. The first Commissioner was Frederick Sanguinetti. | |
| − | In 1953 the first airfield in the Cayman Islands was opened as well as the George Town Public | + | In 1959, upon the formation of the [[Federation of the West Indies]], the dependency status with regards to Jamaica ceased officially although the Governor of Jamaica remained the Governor of the Cayman Islands and had reserve powers over the Islands. Starting in 1959 the chief official overseeing the day to day affairs of the islands (for the Governor) was the Administrator. Upon Jamaica's independence in 1962, the Cayman Islands broke its administrative links with Jamaica and opted to become a direct dependency of the British Crown, with the chief official of the islands being the Administrator. |
| + | |||
| + | In 1953 the first airfield in the Cayman Islands was opened as well as the George Town Public Hospital. The British firm Barclays ushered in the age of formalized commerce by opening the first commercial bank. | ||
=== Independence === | === Independence === | ||
| − | + | In 1959, following a two year campaign lead by women to improve their circumstances, the Cayman Islands received its first constitution that finally allowed women to vote. At the same time, Cayman ceased to be a dependency of Jamaica. | |
During 1966, legislation was passed to enable and encourage the banking industry in Cayman. | During 1966, legislation was passed to enable and encourage the banking industry in Cayman. | ||
| − | In 1971 the governmental structure of the Islands was again changed with a Governor now running the Cayman Islands. Athel Long CMG, CBE was the last Administrator and the first Governor of the Cayman Islands. | + | In 1971 the governmental structure of the Islands was again changed with a Governor now running the Cayman Islands. Mr. Athel Long CMG, CBE was the last Administrator and the first Governor of the Cayman Islands. |
| + | |||
| + | In 1991 a review of the 1972 constitution recommended several constitutional changes to be debated by the Legislative Assembly. The post of [[Chief Secretary]] was reinstated in 1992 after having been abolished in 1986. The establishment of the post of [[Chief Minister]] was also proposed. However, in November 1992, elections were held for an enlarged Legislative Assembly and the Government was soundly defeated, casting doubt on constitutional reform. The "National Team" of government critics won 12 (later reduced to 11) of the 15 seats, and independents won the other three, after a campaign opposing the appointment of the Chief Minister and advocating spending cuts. The unofficial leader of the team, Thomas Jefferson, had been the appointed Financial Secretary until March 1992, when he resigned over public spending disputes to fight the election. After the elections, Mr. Jefferson was appointed Minister and leader of government business; he also held the portfolios of Tourism, Aviation and Commerce in the Executive Council. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Three teams with a total of 44 candidates contested the general election held on November 20, 1996: the governing National Team, Team Cayman and the Democratic Alliance Group. The National Team were returned to office but with a reduced majority, winning nine seats. The Democratic Alliance won two seats in George Town, Team Cayman won one in Bodden Town and independents won seats in George Town, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman. | ||
| − | + | Although all administrative links with Jamaica were broken in 1962, the Cayman Islands and Jamaica continue to share many links and experiences, including membership in the [[Commonwealth of Nations]], Commonwealth citizenship and a common united church, The United Church in Jamaica and the Cayman Islands. Until 1972 they shared a common [[currency]], the Jamaican dollar. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Also, by 1999, 38-40 percent of the population of the Cayman Islands was of Jamaican origin and in 2004/2005, a little over 50 percent of the expatriates working in the Cayman Islands (8,000) were Jamaicans with other significant numbers of aliens moving in from communities from the [[United States]], [[United Kingdom]] and [[Canada]]. | |
=== Hurricane Ivan 2004 === | === Hurricane Ivan 2004 === | ||
| − | In September 2004, | + | [[File:Hurricane signs rum point.jpg|thumb|350px|Signs at Rum Point commemorating landed and near-miss hurricanes]] |
| + | In September 2004, [[Hurricane Ivan]] hit the Cayman Islands. The results were devastating, with loss of human life, animal life both domestic (livestock) and wild. Flooding was major throughout the island of Grand Cayman with some accounts reporting that 25 percent or more of the island was underwater. Lower floors of many buildings were completely flooded. This disaster also led to bankruptcy of the heavily invested insurance company known as Doyle. The company released estimates covering 20 percent of damages to be reinsured at minimal fees when in actuality the damage was over 65 percent and every claim was in the millions. The company was unable to continue to keep paying out and the adjusters could not help lower the payments any further due to the strict building codes that the islands are required to follow. | ||
| − | + | The islands were bustling again by the following year, though they still showed some signs of damage. Vegetation had not totally returned, and construction had not yet begun in some places. | |
| − | == Government and | + | == Government and Politics== |
| − | Although it is a British dependency, the Cayman Islands are largely self-governing concerning local affairs. A 15-seat legislative assembly is elected by the people every | + | [[Image:7 Mile Beach Grand Cayman.jpg|400px|thumb|White sands of Seven Mile Beach, Grand Cayman.]] |
| + | Although it is a British dependency, the Cayman Islands are largely self-governing concerning local affairs. A 15-seat legislative assembly is elected by the people every four years to handle domestic affairs. Of the elected Members of the Legislative Assembly, or MLA's, five are chosen to serve as government ministers. The head of government is the Leader of Government Business. | ||
| − | + | The British government appoints a governor to represent the monarch. In recent years, the powers of the governor have been limited to handling defense, the police force and foreign affairs. However, most of these affairs are handled by the chief secretary, who acts as governor when the governor is unable to discharge his usual duties. On a day-to-day basis the governor usually oversees the civil service including the portfolio of Internal & External Affairs. | |
| − | + | Since becoming part of the British Crown Colony in 1962, the islands have been governed by a written constitution. The Governor has called for the constitution to be modernized, an issue which is being debated with the Legislative Assembly. Great Britain has made it well known that such an action should originate within the people of the Cayman Islands and follow the referendum route. | |
=== Foreign relations === | === Foreign relations === | ||
| − | The foreign relations of the [[Cayman Islands]] are largely managed from the [[United Kingdom]], as the islands remain an overseas territory of the UK. However, the government | + | The foreign relations of the [[Cayman Islands]] are largely managed from the [[United Kingdom]], as the islands remain an overseas territory of the UK. However, the islands' government often handles important issues with foreign governments solitarily, without any intervention from the Britain. |
| − | Though the Cayman Islands are involved in no major international disputes, they have come under some criticism due to the use of their territory for narcotics trafficking and money laundering. In an attempt to address this, the Government entered into the Narcotics Agreement of 1984 and the Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty of 1986 with the United States, in order to reduce the use of their facilities associated with these activities. In more recent years, they have stepped up the fight against money laundering, by limiting banking secrecy, introducing requirements for customer identification and record keeping, and requiring banks to cooperate with foreign investigators. | + | Although in the country's beginning years, the Cayman Islands' most important relationships were with Britain and [[Jamaica]], this has shifted, and they now rely more on the [[United States]]. |
| + | |||
| + | Though the Cayman Islands are involved in no major international disputes, they have come under some criticism due to the use of their territory for [[narcotics trafficking]] and [[money laundering]]. In an attempt to address this, the Government entered into the Narcotics Agreement of 1984 and the [[Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty]] of 1986 with the United States, in order to reduce the use of their facilities associated with these activities. In more recent years, they have stepped up the fight against [[money laundering]], by limiting banking secrecy, introducing requirements for customer identification and record keeping, and requiring banks to cooperate with foreign investigators. | ||
=== Military === | === Military === | ||
| − | The [[United Kingdom]] is in charge of the Cayman Islands' military | + | The [[United Kingdom]] is in charge of the Cayman Islands' military defense. Because of this the islands have no permanently established military. However, they do have their own police force, the Royal Cayman Islands Police Service. In 2001 the small [[Cayman Islands Cadet Corps]] was formed in the place of a traditional army. |
=== Taxation === | === Taxation === | ||
| − | As a tax haven | + | As a [[tax haven]] neither Caymanians nor Caymanian companies are subject to any form of direct taxation. However, an import tax of between 5-20 percent is levied on almost all imported goods. |
== Demographics == | == Demographics == | ||
| − | + | The vast majority of the population resides on Grand Cayman. Cayman Brac is the second most populated with about 2,000 residents, followed by Little Cayman with around 200 permanent residents. Approximately one quarter of the Islands' population left following Hurricane Ivan, due to the myriad of problems, financial and otherwise, caused by the hurricane. | |
| + | |||
| + | The capital and major city of the Cayman Islands is George Town, which is located on the west coast of Grand Cayman. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The islanders are almost exclusively [[Christian]], with large number of [[Presbyterian]]s and [[Anglican Church|Anglicans]]. | ||
| − | + | Caymanians enjoy one of the highest standards of living in the [[West Indies]]. | |
=== Education === | === Education === | ||
| − | The | + | The Cayman Islands Education Council operates state funded schools on the island, with a Caribbean-oriented education curriculum. Caymanian children are entitled to free primary and secondary education. Various churches and private foundations operate several private schools offering curricula derived from [[U.S.|American]] and [[Great Britain|British]] education systems from kindergarten to twelfth grade. Grand Cayman is also home to Saint Matthew's University, which includes a medical school and a school of veterinary medicine. |
| − | + | The Cayman Islands Law School (CILS), a branch of the University of Liverpool in the UK, is also based on Grand Cayman. Situated in George Town, the law school has been in operation since 1982. As taken from the student handbook, "The Law School provides tuition for both full and part-time programmes leading to the Bachelor of Law (Honours) Degree of the University of Liverpool and the qualification of Attorney-at-Law of the Cayman Islands, following successful completion of the postgraduate Professional Practicum Course." | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Grand Cayman is home to University College of the Cayman Islands, the only government-run University on the island. The International College of the Cayman Islands is located in Newlands, about seven miles east of George Town. The college, established in 1970, is accredited by the Accrediting Council for Independent Colleges and Schools; it offers degree programs at the Associate, Bachelor and Post-Graduate levels. | |
| − | With | + | == Economy == |
| + | With an average annual income of around $42,000, Caymanians enjoy the highest standard of living in the [[Caribbean]]. According to the ''CIA World Factbook,'' the Cayman Islands GDP per capita is the eighth highest in the world. The islands print their own currency, the [[Cayman Islands Dollar]] (KYD), which is pegged to the [[U.S. dollar]] at a fixed rate of 1 KYD = 1.227 USD. Thus, the C.I. Dollar's rate of exchange with all other world countries is directly tied to the U.S. dollar's rate of exchange with those same countries. | ||
| − | + | The government's primary source of income is [[indirect tax]]ation. An import duty of 20 percent is levied against goods imported into the islands. Few goods are exempt; notable examples include books, cameras and [[baby formula]]. Duty on automobiles is charged on a sliding scale with the duty reaching 40 percent for expensive models. The government charges a flat licensing fee to financial institutions that operate in the islands. A small fee is also charged to each tourist who arrives on the islands. | |
===Tourism=== | ===Tourism=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Cayman Islands' beautiful beaches and warm climate foster [[tourism]], the major industry, which accounts for 30-40 percent of the annual gross domestic product. Of the millions of tourists that visit the islands each year, 99 percent of the them stay on Grand Cayman; possibly because George Town serves as a major [[cruise-ship]] port, which brings in 2,000 - 3,000 tourists every day of the week. | |
| − | The Cayman Islands are also | + | Grand Cayman's major tourist attraction is the world-famous Seven Mile Beach on which most of the island's hotels and resorts are located. It is regarded by many as one of the best [[beach]]es in the world. |
| + | |||
| + | The Cayman Islands are also world famous as a scuba diving destination because of their proximity to the [[Cayman Wall]] and the [[Cayman Trench]], which extend deep into the [[coral reef]]s of the Caribbean. Cayman Brac and Little Cayman are also considered to be elite [[deep sea diving|dive]] destinations. | ||
===Financial services industry=== | ===Financial services industry=== | ||
| − | + | Because the Cayman Islands are not subject to direct taxation by the British government, nor is there a local income tax, they serve as an international offshore-banking hub and tax haven for millions of people and corporations. As of 2000, almost 40,000 companies were incorporated on the Cayman Islands including 600 banking and trust companies with assets in excess of $500 billion. Approximately 6,000 of the world's 8,000 hedge funds are also domiciled in the Cayman Islands. This industry provides approximately 40 percent of the Cayman's GDP. | |
| + | |||
| + | ==Notes== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | * Askew, R. R., and P. A. van B. Stafford. ''Butterflies of the Cayman Islands''. Apollo Books, 2008. ISBN 978-8788757859 | ||
| + | * Brunt, M.A., and J.E. Davies (eds.). ''The Cayman Islands: Natural History and Biogeography''. Springer, 1994. ISBN 0792324625 | ||
| + | * Craton, Michael, and the New History Committee. ''Founded upon the Seas: A History of the Cayman Islands and Their People.'' Kingston, Jamaica: Ian Randle Publishers, 2003. ISBN 0972935835 | ||
| + | * Smith, Roger C. ''The Maritime Heritage of the Cayman Islands''. University Press of Florida, 2019. ISBN 978-0813068091 | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| + | All links retrieved December 3, 2023. | ||
| + | * [https://www.gov.ky/ Cayman Islands Government] | ||
| + | * [https://www.investcayman.gov.ky/ Invest Cayman] | ||
| + | * [https://www.visitcaymanislands.com/en-us/region-selector Visit Cayman Islands] | ||
| + | * [https://www.caribbeanislands.com/cayman-islands/ Cayman Islands] ''Caribbean Islands'' | ||
| + | * [https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/cayman-islands/ Cayman Islands] CIA ''World Factbook'' | ||
| − | + | {{credit|Cayman_Islands|31951098|Geography_of_the_Cayman_Islands|114363293|History_of_the_Cayman_Islands|127714902}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Category:Geography]] | |
| + | [[Category:Islands]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Territories]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:23, 3 December 2023
Cayman Islands |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: "He hath founded it upon the seas" | ||||||
| Anthem: God Save the King (official) National Song: "Beloved Isle Cayman" |
||||||
| Capital (and largest city) | George Town 19°20′N 81°24′W | |||||
| Ethnic groups | Mixed 40%, White 20%, African descent 20%, expatriates of various ethnic groups 20% [1] | |||||
| Demonym | Caymanian | |||||
| Government | British Overseas Territory (constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democratic dependency) | |||||
| - | Monarch | Charles III | ||||
| - | Governor | Martyn Roper | ||||
| - | Premier | Wayne Panton | ||||
| Legislature | Legislative Assembly | |||||
| Establishment | ||||||
| - | British Overseas Territory | 1962 | ||||
| - | Current Constitution | November 6, 2009 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 264 km² (206th) 102 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | 1.6 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2022 estimate | 64,309[1] (206th) | ||||
| - | 2021 census | 69,656[2] | ||||
| - | Density | 244/km² (59th) 631/sq mi |
||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2014[3] estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $2.507 billion[3] | ||||
| - | Per capita | $73,800 (2004 est.)[3] | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | US$5,936,000,000[4] (160th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | US$91,392 (7th) | ||||
| Currency | Cayman Islands dollar (KYD) |
|||||
| Time zone | (UTC-5) | |||||
| - | Summer (DST) | not observed (UTC-5) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .ky | |||||
| Calling code | [[++1-345]] | |||||
The Cayman Islands are an overseas territory of the United Kingdom located in the western Caribbean Sea. It is comprised of three islands, Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac, and Little Cayman. Located south of Cuba and northwest of Jamaica, the Cayman Islands lie on the outer edge of the Caribbean and are the closest to Central America.
The Caymans are one of the most popular tourist attractions in the world due to its pristine beaches and scuba diving opportunities. It contains a major global offshore financial services center.
Geography
The Cayman Islands are a largely self-governing British dependency located in the Caribbean Sea. Comprised of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, the Cayman Islands are a three-island archipelago lying between Cuba and Central America. They are located 268 km northwest of Jamaica and 240 km south of Cuba. Its geographic coordinates are 19°30 north, 80°30 west.
With a land area of 101.2 square miles (259 km²), the islands are approximately 1.5 times the size of Washington, D.C., with a coastline of 99 miles (160 km). These islands make a maritime claim of a 200-nautical mile exclusive fishing zone which includes 12 nautical miles of territorial sea.
The Cayman Islands' lowest elevation is the Caribbean Sea at sea level. The highest point is The Bluff, a limestone outcrop 43 m (141 feet) in length on the eastern end of eastern Cayman Brac. The terrain is mostly low-lying limestone base, surrounded by coral reefs.
The Cayman Islands have a tropical marine climate, with a wet season of warm but rainy summers lasting from May through October. The winter is dry and relatively cool, lasting from November through April.
An important environmental issue is the lack of fresh water resources. Drinking water supplies must be met by rainwater catchment and desalination.
Natural resources include fish and a climate and beaches that foster tourism, which is the islands' major industry. A major natural hazard are the tropical cyclones that form during the Atlantic hurricane season from July to November.
Fauna
The mammalian species in the Cayman Islands include the introduced Central American agouti and eight species of bat. At least three now extinct native rodent species were present until the discovery of the islands by Europeans. Marine life around the island of the Grand Cayman includes tarpon, silversides (Atheriniformes), French angelfish (Pomacanthus paru), and giant barrel sponges. A number of cetaceans are found in offshore waters. These species include the goose-beaked whale (Ziphius cavirostris), Blainville's beaked whale (Mesoplodon densirostris) and sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus).
Cayman avian fauna includes two endemic subspecies of Amazona parrots: Amazona leucocephala hesterna or Cuban amazon, presently restricted to the island of Cayman Brac, but formerly also on Little Cayman, and Amazona leucocephala caymanensis or Grand Cayman parrot, which is native to the Cayman Islands, forested areas of Cuba, and the Isla de la Juventud. Little Cayman and Cayman Brac are also home to red-footed and brown boobies.[5] Although the barn owl (Tyto alba) occurs in all three of the islands they are not commonplace. The Cayman Islands also possess five endemic subspecies of butterflies.[6] These butterfly breeds can be viewed at the Queen Elizabeth II Botanic Park on the Grand Cayman.
Among other notable fauna at the Queen Elizabeth II Botanic Park is the critically threatened blue iguana which is also known as the Grand Cayman iguana (Cyclura lewisi). The blue iguana is endemic to the Grand Cayman particularly because of rocky, sunlit, open areas near the island's shores that are advantageous for the laying of eggs. Nevertheless, habitat destruction and invasive mammalian predators remain the primary reasons that blue iguana hatchlings do not survive naturally.[7]
The Cuban crocodile (Crocodylus rhombifer) once inhabited the islands. The name "Cayman" is derived from a Carib word for various crocodilians.[8]
History
On May 10, 1503 Christopher Columbus discovered the Cayman Islands and named them Las Tortugas which literally translates into "the turtles" in Spanish, after the numerous sea turtles found there. He had found Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, the two smaller islands.
A map from 1523 shows the islands being referred to as "Lagartos", meaning alligators or large lizards, but by 1530 they were known as the Caymanas, the Carib Indian word for the marine crocodile that also lived in the area.
The first recorded English visitor was Sir Francis Drake in 1586. He allegedly reported that the caymanas, marine crocodiles, were edible. However, it was the abundant turtles that ships were attracted to, in search of fresh meat for their crews. Overfishing the turtles nearly extinguished them from the local waters.
Around 1700, the first recorded permanent inhabitant of the Cayman Islands was born, Isaac Bodden. He was the grandson of one of the original settlers, who was likely one of Oliver Cromwell's soldiers at the taking of Jamaica in 1655.
Over time and throughout history a variety of people have settled on the Cayman Islands and have called it home: pirates, refugees from the Spanish Inquisition, slaves and shipwrecked sailors. The majority of Caymanians are from African and British descent, with considerable interracial mixing.
British rule
Britain took formal control of the Caymans, along with Jamaica, under the Treaty of Madrid in 1670 after the first settlers came from Jamaica in 1661-1671 to Little Cayman and Cayman Brac.
These first settlements were abandoned after attacks by Spanish privateers, but British privateers often used the Islands as a base, and in the eighteenth century they became an increasingly popular hideout for pirates, even after the end of legitimate privateering in 1713. Following several unsuccessful attempts, permanent settlement of the islands began in the 1730s.
Dependency of Jamaica
Beginning in 1670, the Cayman Islands became dependencies of Jamaica, although there was considerable self-government. On December 5, 1831, a Legislative Assembly was established through consent, during a meeting held by principal inhabitants. Elections were held on December 10 of the same year; later on December 31 the legislature passed the first local legislation. Because of this the Governor of Jamaica authorized a legislature consisting of eight magistrates appointed by the Governor himself and ten, later increased to 27, elected representatives.
In 1835, Governor Sligo of Jamaica arrived in Grand Cayman to announce that all slaves were free, in accordance with the Emancipation Act of 1833.
In 1863 the Cayman Islands were officially declared and administered as a dependency of Jamaica, but were rather like a parish of Jamaica with the nominated justices of the peace and elected vestrymen in their Legislature. From 1750 to 1898 the Chief Magistrate was the official administer of the dependency, who was appointed by the Jamaican governor. In 1898 the Governor of Jamaica began appointing a Commissioner for the Islands. The first Commissioner was Frederick Sanguinetti.
In 1959, upon the formation of the Federation of the West Indies, the dependency status with regards to Jamaica ceased officially although the Governor of Jamaica remained the Governor of the Cayman Islands and had reserve powers over the Islands. Starting in 1959 the chief official overseeing the day to day affairs of the islands (for the Governor) was the Administrator. Upon Jamaica's independence in 1962, the Cayman Islands broke its administrative links with Jamaica and opted to become a direct dependency of the British Crown, with the chief official of the islands being the Administrator.
In 1953 the first airfield in the Cayman Islands was opened as well as the George Town Public Hospital. The British firm Barclays ushered in the age of formalized commerce by opening the first commercial bank.
Independence
In 1959, following a two year campaign lead by women to improve their circumstances, the Cayman Islands received its first constitution that finally allowed women to vote. At the same time, Cayman ceased to be a dependency of Jamaica.
During 1966, legislation was passed to enable and encourage the banking industry in Cayman.
In 1971 the governmental structure of the Islands was again changed with a Governor now running the Cayman Islands. Mr. Athel Long CMG, CBE was the last Administrator and the first Governor of the Cayman Islands.
In 1991 a review of the 1972 constitution recommended several constitutional changes to be debated by the Legislative Assembly. The post of Chief Secretary was reinstated in 1992 after having been abolished in 1986. The establishment of the post of Chief Minister was also proposed. However, in November 1992, elections were held for an enlarged Legislative Assembly and the Government was soundly defeated, casting doubt on constitutional reform. The "National Team" of government critics won 12 (later reduced to 11) of the 15 seats, and independents won the other three, after a campaign opposing the appointment of the Chief Minister and advocating spending cuts. The unofficial leader of the team, Thomas Jefferson, had been the appointed Financial Secretary until March 1992, when he resigned over public spending disputes to fight the election. After the elections, Mr. Jefferson was appointed Minister and leader of government business; he also held the portfolios of Tourism, Aviation and Commerce in the Executive Council.
Three teams with a total of 44 candidates contested the general election held on November 20, 1996: the governing National Team, Team Cayman and the Democratic Alliance Group. The National Team were returned to office but with a reduced majority, winning nine seats. The Democratic Alliance won two seats in George Town, Team Cayman won one in Bodden Town and independents won seats in George Town, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman.
Although all administrative links with Jamaica were broken in 1962, the Cayman Islands and Jamaica continue to share many links and experiences, including membership in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth citizenship and a common united church, The United Church in Jamaica and the Cayman Islands. Until 1972 they shared a common currency, the Jamaican dollar.
Also, by 1999, 38-40 percent of the population of the Cayman Islands was of Jamaican origin and in 2004/2005, a little over 50 percent of the expatriates working in the Cayman Islands (8,000) were Jamaicans with other significant numbers of aliens moving in from communities from the United States, United Kingdom and Canada.
Hurricane Ivan 2004
In September 2004, Hurricane Ivan hit the Cayman Islands. The results were devastating, with loss of human life, animal life both domestic (livestock) and wild. Flooding was major throughout the island of Grand Cayman with some accounts reporting that 25 percent or more of the island was underwater. Lower floors of many buildings were completely flooded. This disaster also led to bankruptcy of the heavily invested insurance company known as Doyle. The company released estimates covering 20 percent of damages to be reinsured at minimal fees when in actuality the damage was over 65 percent and every claim was in the millions. The company was unable to continue to keep paying out and the adjusters could not help lower the payments any further due to the strict building codes that the islands are required to follow.
The islands were bustling again by the following year, though they still showed some signs of damage. Vegetation had not totally returned, and construction had not yet begun in some places.
Government and Politics
Although it is a British dependency, the Cayman Islands are largely self-governing concerning local affairs. A 15-seat legislative assembly is elected by the people every four years to handle domestic affairs. Of the elected Members of the Legislative Assembly, or MLA's, five are chosen to serve as government ministers. The head of government is the Leader of Government Business.
The British government appoints a governor to represent the monarch. In recent years, the powers of the governor have been limited to handling defense, the police force and foreign affairs. However, most of these affairs are handled by the chief secretary, who acts as governor when the governor is unable to discharge his usual duties. On a day-to-day basis the governor usually oversees the civil service including the portfolio of Internal & External Affairs.
Since becoming part of the British Crown Colony in 1962, the islands have been governed by a written constitution. The Governor has called for the constitution to be modernized, an issue which is being debated with the Legislative Assembly. Great Britain has made it well known that such an action should originate within the people of the Cayman Islands and follow the referendum route.
Foreign relations
The foreign relations of the Cayman Islands are largely managed from the United Kingdom, as the islands remain an overseas territory of the UK. However, the islands' government often handles important issues with foreign governments solitarily, without any intervention from the Britain.
Although in the country's beginning years, the Cayman Islands' most important relationships were with Britain and Jamaica, this has shifted, and they now rely more on the United States.
Though the Cayman Islands are involved in no major international disputes, they have come under some criticism due to the use of their territory for narcotics trafficking and money laundering. In an attempt to address this, the Government entered into the Narcotics Agreement of 1984 and the Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty of 1986 with the United States, in order to reduce the use of their facilities associated with these activities. In more recent years, they have stepped up the fight against money laundering, by limiting banking secrecy, introducing requirements for customer identification and record keeping, and requiring banks to cooperate with foreign investigators.
Military
The United Kingdom is in charge of the Cayman Islands' military defense. Because of this the islands have no permanently established military. However, they do have their own police force, the Royal Cayman Islands Police Service. In 2001 the small Cayman Islands Cadet Corps was formed in the place of a traditional army.
Taxation
As a tax haven neither Caymanians nor Caymanian companies are subject to any form of direct taxation. However, an import tax of between 5-20 percent is levied on almost all imported goods.
Demographics
The vast majority of the population resides on Grand Cayman. Cayman Brac is the second most populated with about 2,000 residents, followed by Little Cayman with around 200 permanent residents. Approximately one quarter of the Islands' population left following Hurricane Ivan, due to the myriad of problems, financial and otherwise, caused by the hurricane.
The capital and major city of the Cayman Islands is George Town, which is located on the west coast of Grand Cayman.
The islanders are almost exclusively Christian, with large number of Presbyterians and Anglicans.
Caymanians enjoy one of the highest standards of living in the West Indies.
Education
The Cayman Islands Education Council operates state funded schools on the island, with a Caribbean-oriented education curriculum. Caymanian children are entitled to free primary and secondary education. Various churches and private foundations operate several private schools offering curricula derived from American and British education systems from kindergarten to twelfth grade. Grand Cayman is also home to Saint Matthew's University, which includes a medical school and a school of veterinary medicine.
The Cayman Islands Law School (CILS), a branch of the University of Liverpool in the UK, is also based on Grand Cayman. Situated in George Town, the law school has been in operation since 1982. As taken from the student handbook, "The Law School provides tuition for both full and part-time programmes leading to the Bachelor of Law (Honours) Degree of the University of Liverpool and the qualification of Attorney-at-Law of the Cayman Islands, following successful completion of the postgraduate Professional Practicum Course."
Grand Cayman is home to University College of the Cayman Islands, the only government-run University on the island. The International College of the Cayman Islands is located in Newlands, about seven miles east of George Town. The college, established in 1970, is accredited by the Accrediting Council for Independent Colleges and Schools; it offers degree programs at the Associate, Bachelor and Post-Graduate levels.
Economy
With an average annual income of around $42,000, Caymanians enjoy the highest standard of living in the Caribbean. According to the CIA World Factbook, the Cayman Islands GDP per capita is the eighth highest in the world. The islands print their own currency, the Cayman Islands Dollar (KYD), which is pegged to the U.S. dollar at a fixed rate of 1 KYD = 1.227 USD. Thus, the C.I. Dollar's rate of exchange with all other world countries is directly tied to the U.S. dollar's rate of exchange with those same countries.
The government's primary source of income is indirect taxation. An import duty of 20 percent is levied against goods imported into the islands. Few goods are exempt; notable examples include books, cameras and baby formula. Duty on automobiles is charged on a sliding scale with the duty reaching 40 percent for expensive models. The government charges a flat licensing fee to financial institutions that operate in the islands. A small fee is also charged to each tourist who arrives on the islands.
Tourism
Cayman Islands' beautiful beaches and warm climate foster tourism, the major industry, which accounts for 30-40 percent of the annual gross domestic product. Of the millions of tourists that visit the islands each year, 99 percent of the them stay on Grand Cayman; possibly because George Town serves as a major cruise-ship port, which brings in 2,000 - 3,000 tourists every day of the week.
Grand Cayman's major tourist attraction is the world-famous Seven Mile Beach on which most of the island's hotels and resorts are located. It is regarded by many as one of the best beaches in the world.
The Cayman Islands are also world famous as a scuba diving destination because of their proximity to the Cayman Wall and the Cayman Trench, which extend deep into the coral reefs of the Caribbean. Cayman Brac and Little Cayman are also considered to be elite dive destinations.
Financial services industry
Because the Cayman Islands are not subject to direct taxation by the British government, nor is there a local income tax, they serve as an international offshore-banking hub and tax haven for millions of people and corporations. As of 2000, almost 40,000 companies were incorporated on the Cayman Islands including 600 banking and trust companies with assets in excess of $500 billion. Approximately 6,000 of the world's 8,000 hedge funds are also domiciled in the Cayman Islands. This industry provides approximately 40 percent of the Cayman's GDP.
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 CIA, Cayman Islands - People and Society World Factbook. Retrieved September 15, 2022.
- ↑ Preliminary 2021 Census Report Published Economics and Statistics Office, Government of the Cayman Islands. Retrieved September 15, 2022.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 CIA, Cayman Islands - Economy World Factbook. Retrieved September 15, 2022.
- ↑ Cayman Islands The World Bank. Retrieved September 15, 2022.
- ↑ Red-footed Booby Department of Environment, Cayman Islands Government. Retrieved September 15, 2022.
- ↑ R. R. Askew and P. A. van B. Stafford, Butterflies of the Cayman Islands (Apollo Books, 2008, ISBN 978-8788757859).
- ↑ Wildlife Conservation Society, Grand Cayman blue iguana: Back from the brink of extinction Science News, July 18, 2011. Retrieved September 15, 2022.
- ↑ The Cayman Islands – History Cayman Islands Government. Retrieved September 15, 2022.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Askew, R. R., and P. A. van B. Stafford. Butterflies of the Cayman Islands. Apollo Books, 2008. ISBN 978-8788757859
- Brunt, M.A., and J.E. Davies (eds.). The Cayman Islands: Natural History and Biogeography. Springer, 1994. ISBN 0792324625
- Craton, Michael, and the New History Committee. Founded upon the Seas: A History of the Cayman Islands and Their People. Kingston, Jamaica: Ian Randle Publishers, 2003. ISBN 0972935835
- Smith, Roger C. The Maritime Heritage of the Cayman Islands. University Press of Florida, 2019. ISBN 978-0813068091
External links
All links retrieved December 3, 2023.
- Cayman Islands Government
- Invest Cayman
- Visit Cayman Islands
- Cayman Islands Caribbean Islands
- Cayman Islands CIA World Factbook
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
- Cayman_Islands history
- Geography_of_the_Cayman_Islands history
- History_of_the_Cayman_Islands history
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.