Difference between revisions of "Arctic Circle" - New World Encyclopedia
John Willis (talk | contribs) (added, categorized & credited article) |
John Willis (talk | contribs) (s'more editing) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Geography and demographics]] | [[Category:Geography and demographics]] | ||
[[Category:Global lines and points]] | [[Category:Global lines and points]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
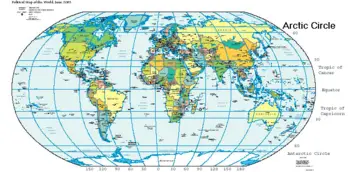
[[Image:WorldMapLongLat-special-lats-emph-ArcticCircle-non.png|thumb|350px|World map showing the five major [[circle of latitude|circles of latitude]]]] | [[Image:WorldMapLongLat-special-lats-emph-ArcticCircle-non.png|thumb|350px|World map showing the five major [[circle of latitude|circles of latitude]]]] | ||
| Line 8: | Line 6: | ||
[[Image:Arctic Circle sign.jpg|thumb|right|200px|A sign along the [[Dalton Highway]] marking the location of the Arctic Circle]] | [[Image:Arctic Circle sign.jpg|thumb|right|200px|A sign along the [[Dalton Highway]] marking the location of the Arctic Circle]] | ||
| − | The '''Arctic Circle''' is one of the five major | + | The '''Arctic Circle''' is one of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of the [[Earth]]. This is the parallel of [[latitude]] that (in 2000) runs 66° 33' 39" north of the [[Equator]]. Everything north of this circle is known as the [[Arctic]], and the zone just to the south of this circle is the [[Northern Temperate Zone]]. |
| − | The Arctic Circle marks the southern extremity of the | + | The Arctic Circle marks the southern extremity of the polar day of the summer solstice in June and the polar night of the winter solstice in December. Within the Arctic Circle, the Sun is above the horizon for at least 24 continuous hours once per year, in conjunction with the Arctic's summer solstice - this is often referred to as [[midnight sun]]. Likewise, in conjunction with the Arctic's Winter Solstice, the Arctic sun will be below the horizon for at least 24 continuous hours. |
| − | |||
| − | + | (In fact, because of [[refraction]] and because the sun appears as a disk and not a point, part of the midnight sun may be seen at the night of the summer solstice up to about 50' (90 km) south of the geometric arctic circle; similarly, at the day of the winter solstice part of the sun may be seen up to about 50' north of the geometric arctic circle. This is true at sea level; these limits increase with elevation above sea level, but in mountainous regions there is often no direct view of the horizon.) | |
| − | Countries | + | The position of the Arctic Circle is determined by the [[axial tilt]] (angle) of the polar axis of rotation of the Earth on the [[ecliptic]]. This angle is not constant, but has a complex motion determined by many cycles of short to very long periods. Due to [[nutation]] the tilt oscillates over 9" (about 280 m on the surface) over a period of 18.6 years. The main long-term cycle has a period of 41,000 years and an amplitude of about 0.68°, or 76 km on the surface. Currently the tilt is decreasing by about 0.47" per year, so the Arctic Circle is moving north by about 14 meters per year. Also see [[precession]]. |
| + | |||
| + | Countries that have significant territory within the Arctic Circle are: | ||
* Russia | * Russia | ||
| Line 28: | Line 27: | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | + | ||
*[http://www.bugbog.com/images/maps/arctic_circle_map.jpg Topographical map of Arctic Circle, centered about North Pole] | *[http://www.bugbog.com/images/maps/arctic_circle_map.jpg Topographical map of Arctic Circle, centered about North Pole] | ||
*[http://www.world-maps.co.uk/maps/600-arctic.jpg Map of Arctic Circle (dotted line), showing major population areas] | *[http://www.world-maps.co.uk/maps/600-arctic.jpg Map of Arctic Circle (dotted line), showing major population areas] | ||
| − | |||
{{credit|33819864}} | {{credit|33819864}} | ||
Revision as of 08:51, 9 January 2006
The Arctic Circle is one of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of the Earth. This is the parallel of latitude that (in 2000) runs 66° 33' 39" north of the Equator. Everything north of this circle is known as the Arctic, and the zone just to the south of this circle is the Northern Temperate Zone.
The Arctic Circle marks the southern extremity of the polar day of the summer solstice in June and the polar night of the winter solstice in December. Within the Arctic Circle, the Sun is above the horizon for at least 24 continuous hours once per year, in conjunction with the Arctic's summer solstice - this is often referred to as midnight sun. Likewise, in conjunction with the Arctic's Winter Solstice, the Arctic sun will be below the horizon for at least 24 continuous hours.
(In fact, because of refraction and because the sun appears as a disk and not a point, part of the midnight sun may be seen at the night of the summer solstice up to about 50' (90 km) south of the geometric arctic circle; similarly, at the day of the winter solstice part of the sun may be seen up to about 50' north of the geometric arctic circle. This is true at sea level; these limits increase with elevation above sea level, but in mountainous regions there is often no direct view of the horizon.)
The position of the Arctic Circle is determined by the axial tilt (angle) of the polar axis of rotation of the Earth on the ecliptic. This angle is not constant, but has a complex motion determined by many cycles of short to very long periods. Due to nutation the tilt oscillates over 9" (about 280 m on the surface) over a period of 18.6 years. The main long-term cycle has a period of 41,000 years and an amplitude of about 0.68°, or 76 km on the surface. Currently the tilt is decreasing by about 0.47" per year, so the Arctic Circle is moving north by about 14 meters per year. Also see precession.
Countries that have significant territory within the Arctic Circle are:
- Russia
- Canada
- Greenland
- United States (Alaska)
- Norway
- Sweden
- Finland
The country of Iceland also has territory within the Arctic Circle, but less than 1 sq km. This area is on a few small islets, of which only Grímsey (which lies directly on the Arctic Circle) is inhabited.
External links
- Topographical map of Arctic Circle, centered about North Pole
- Map of Arctic Circle (dotted line), showing major population areas
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.