Difference between revisions of "Siege of Vienna" - New World Encyclopedia
Laura Brooks (talk | contribs) (→Siege) |
Laura Brooks (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
== Aftermath == | == Aftermath == | ||
| − | Some historians speculate that Suleiman's final assault wasn't necessarily intended to take the city but to cause as much damage as possible and weaken it for a later attack, a tactic he had employed at Buda in 1526. He led his next campaign in 1532 but was held up too long reducing the western Hungarian fort of [[Kőszeg]], by which time winter was close and Charles V, now awakened to Vienna's vulnerability, assembling 80,000 troops. | + | Some historians speculate that Suleiman's final assault wasn't necessarily intended to take the city but to cause as much damage as possible and weaken it for a later attack, a tactic he had employed at Buda in 1526. He led his next campaign in 1532 but was held up too long reducing the western Hungarian fort of [[Kőszeg]], by which time winter was close and Charles V, now awakened to Vienna's vulnerability, assembling 80,000 troops. So instead of carrying out the planned siege, the invading troops retreated through and laid waste to Styria. The two campaigns proved that Vienna was situated at the extreme limit of Ottoman logistical capability. The army needed to winter at Istanbul so that its troops could attend to their fiefs and recruit for the next year's campaigning. |
| − | Suleiman's retreat did not mark a complete failure. The campaign underlined Ottoman control of southern Hungary and left behind enough destruction in Hapsburg Hungary and in those Austrian lands it had ravaged to impair Ferdinand's capacity to mount a sustained counterattack. Suleiman's achievement was to consolidate the gains of 1526 and establish the puppet kingdom of John Zápolya as a buffer against the Holy Roman Empire. | + | Suleiman's retreat did not mark a complete failure. The campaign underlined Ottoman control of southern Hungary and left behind enough destruction in Hapsburg Hungary and in those Austrian lands it had ravaged to impair Ferdinand's capacity to mount a sustained counterattack. Suleiman's achievement was to consolidate the gains of 1526 and establish the puppet kingdom of John Zápolya as a buffer against the Holy Roman Empire. |
| − | The invasion and its climactic siege, however, exacted a heavy price from both sides, with tens of thousands of soldiers and civilians dead and thousands more sold into slavery. It marked the end of the Ottomans' expansion towards the centre of Europe and arguably the beginning of their long decline as the dominant power of the [[Renaissance]] world. | + | The invasion and its climactic siege, however, exacted a heavy price from both sides, with tens of thousands of soldiers and civilians dead and thousands more sold into slavery. It marked the end of the Ottomans' expansion towards the centre of Europe and arguably the beginning of their long decline as the dominant power of the [[Renaissance]] world. |
| − | Ferdinand I set up a funeral monument for Niklas, Graf Salm—who had been injured during the last Ottoman assault and died on 4 May 1530—to express his gratitude to the defender of Vienna. | + | Ferdinand I set up a funeral monument for Niklas, Graf Salm—who had been injured during the last Ottoman assault and died on 4 May 1530—to express his gratitude to the defender of Vienna. This Renaissance [[sarcophagus]] is now on display in the baptistry of the [[Votivkirche]] in Vienna. Ferdinand's son, [[Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor|Maximilian II]], later built the summer palace of Neugebaeude on the spot where Suleiman is said to have pitched his tent. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | + | *Chirot, Daniel. ''The Origins of backwardness in Eastern Europe: economics and politics from the Middle Ages until the early twentieth century''. Berkeley: University of California Press. 1989. ISBN 9780520064218 | |
| − | *Chirot, Daniel | + | *Dupuy, Trevor N., Curt Johnson, and David L. Bongard. ''The encyclopedia of military biography''. London: I. B. Tauris. 1992, ISBN 9781850435693 |
| − | |||
| − | *Dupuy, Trevor | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*Kann, Robert Adolf, ''A History of the Habsburg Empire: 1526-1918'', University of California Press, 1980, ISBN 0-52-004206-9 | *Kann, Robert Adolf, ''A History of the Habsburg Empire: 1526-1918'', University of California Press, 1980, ISBN 0-52-004206-9 | ||
*Keegan, John, and Andrew Wheatcroft, ''Who's Who in Military History: From 1453 to the Present Day'', Routledge (UK), 1996, ISBN 0-41-512722-X | *Keegan, John, and Andrew Wheatcroft, ''Who's Who in Military History: From 1453 to the Present Day'', Routledge (UK), 1996, ISBN 0-41-512722-X | ||
| Line 92: | Line 85: | ||
*Walton, Mark.W., George.F.Nafziger, and Laurent.W.Mbanda, ''Islam at War: A History'', Praeger/Greenwood, 2003, ISBN 0-27-598101-0 | *Walton, Mark.W., George.F.Nafziger, and Laurent.W.Mbanda, ''Islam at War: A History'', Praeger/Greenwood, 2003, ISBN 0-27-598101-0 | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:History and biography]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Politics and social sciences]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{credit|99235899}} | {{credit|99235899}} | ||
Revision as of 23:19, 6 July 2007
| Siege of Vienna | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Ottoman wars in Europe | |||||||
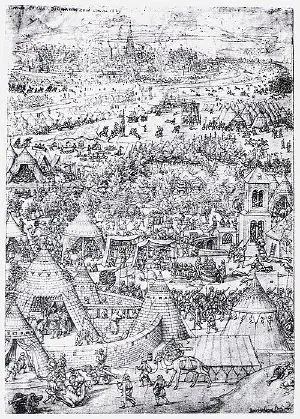 Engraving of clashes between the Austrians and Ottomans outside Vienna, 1529 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Combatants | |||||||
| Austria, with Bohemian, German, and Spanish mercenaries |
Ottoman Empire, with Zápolya's Hungarian force | ||||||
| Commanders | |||||||
| Wilhelm von Roggendorf, Niklas, Graf Salm † | Suleiman I | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| c. 17,000 | c. 120,000 | ||||||
| Casualties | |||||||
| Unknown | Unknown | ||||||
The Siege of Vienna in 1529, as distinct from the Battle of Vienna in 1683, was the first attempt of the Ottoman Empire, led by Sultan Suleiman I, to capture the city of Vienna, Austria. Traditionally the siege held special significance in western history, indicating the Ottoman Empire's highwater mark and signalling the end of Ottoman expansion in central Europe, though 150 years of tension and incursions followed, culminating in the Battle of Vienna in 1683.
Some historians believe that Suleiman's main objective in 1529 was to re-establish Ottoman control over Hungary, and that the decision to attack Vienna so late in the season was opportunistic.
Background
In August 1526, Sultan Suleiman I, also known as Suleiman the Lawgiver and Suleiman the Magnificent, had defeated the forces of King Louis II of Hungary at the Battle of Mohács. As a result, the Ottomans gained control of southern Hungary, while the Archduke of Austria, Ferdinand I of Habsburg, brother of the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, claimed the vacant Hungarian throne in right of his wife, Anna Jagellonica, sister of the childless Louis II. Ferdinand, however, won recognition only in western Hungary; a noble called John Zápolya, from a power-base in Transylvania, north-eastern Hungary, challenged him for the crown and was recognised as king by Suleiman in return for accepting vassal status within the Ottoman Empire.
Ottoman army
In spring 1529, Suleiman mustered a great army in Ottoman Bulgaria, with the aim of securing control of Hungary and reducing the threat posed at his new borders by Ferdinand and the Holy Roman Empire. Various historians have estimated Suleiman's troop strength at anything from 120,000 to more than 300,000 men. As well as units of sipahi, or light cavalry, and elite janissary infantry, the Ottoman army incorporated a contingent of Christian Hungarians fighting for their new Turkish ruler. Suleiman acted as the commander-in-chief, and in April he appointed his grand vizier, a former Greek slave called Ibrahim Pasha, as serasker, a commander with powers to give orders in the sultan's name.
Suleiman launched his campaign on 10 May 1529 and faced obstacles from the outset. The spring rains characteristic of south-eastern Europe were particularly heavy that year, causing flooding in Bulgaria and rendering parts of the route barely passable. Many large-calibre guns became hoplessly mired and had to be left behind, and camels were lost in large numbers.
Suleiman arrived in Osijek on 6 August. On 18 August, on the Mohács plain, he met up with a substantial cavalry force led by John Zápolya, who paid him homage and helped him recapture several fortresses lost since the Battle of Mohács to the Austrians, including Buda, which fell on 8 September. The only resistance came at Bratislava, where the Turkish fleet was bombarded as it sailed up the Danube.
Defensive measures
As the Ottomans advanced, those inside Vienna prepared to resist, their determination stiffened by news of the massacre of the Buda garrison in early September. Ferdinand I had withdrawn to the safety of Habsburg Bohemia following pleas for assistance to his brother, Emperor Charles V, who was too stretched by his war with France to spare more than a few Spanish infantry to the cause.
The able Marshall of Austria, Wilhelm von Roggendorf, assumed charge of the garrison, with operational command entrusted to a seventy-year-old German mercenary named Niklas, Graf Salm, who had distinguished himself at the Battle of Pavia in 1525. Salm arrived in Vienna at the head of a relief force which included German Landsknechte mercenary pikemen and Spanish musketmen and set about shoring up the three-hundred-year-old walls surrounding St. Stephen's Cathedral, near which he established his headquarters. To make sure the city could withstand a lengthy siege, he blocked the four city gates and reinforced the walls, which in some places were no more than six feet thick, and erected earthen bastions and an inner earthen rampart, levelling buildings where necessary.
Siege
The Ottoman army which arrived in late September had been depleted during the long advance into Austrian territory, leaving Suleiman short of camels and heavy equipment. Many of his troops arrived at Vienna in a poor state of health after the privations of the long march, and of those fit to fight, a third were light cavalry, or sipahis, ill-suited for siege warfare. The sultan despatched emissaries to negotiate the city's surrender; Salm sent them back without a reply. Suleiman's artillery then began pounding the city's walls, but it failed to significantly damage the Austrian defensive earthworks; his archers fared little better, achieving nuisance value at best.
As the Ottoman army settled into position, the garrison launched sorties to disrupt the digging of sap trenches and mines, in one case almost capturing Ibrahim Pasha. The Austrians detected and blew up several mineheads, and on 6 October they sent out 8,000 troops to attack the Ottoman mining operations, destroying many of the mines but sustaining serious losses when congestion hindered their retreat into the city.
More rain fell on October 11, and with the failure of the mining strategy, the chances of a quick Ottoman victory were receding by the hour. In addition, the Turks were running out of fodder for their horses, and casualties, sickness, and desertions began taking a toll on their ranks. Even the janissaries now voiced discontent at the state of affairs. In view of these factors, Suleiman had no alternative but to contemplate retreat. He held a council of war on 12 October which decided on one last attack, with extra rewards offered to the troops. However, this assault, too, was repulsed, as once again the harquebuses and long pikes of the defenders prevailed in keeping out the Turks. On the night of 14 October, screams were heard from the opposing camp, the sound of the Ottomans killing their prisoners prior to moving out.
Unseasonably heavy snow helped turn the Turkish retreat into a disaster, in which they lost much baggage and artillery. Their fleet was again attacked at Bratislava, and more Turks than attackers are thought to have died in the skirmishes along the route.
Aftermath
Some historians speculate that Suleiman's final assault wasn't necessarily intended to take the city but to cause as much damage as possible and weaken it for a later attack, a tactic he had employed at Buda in 1526. He led his next campaign in 1532 but was held up too long reducing the western Hungarian fort of Kőszeg, by which time winter was close and Charles V, now awakened to Vienna's vulnerability, assembling 80,000 troops. So instead of carrying out the planned siege, the invading troops retreated through and laid waste to Styria. The two campaigns proved that Vienna was situated at the extreme limit of Ottoman logistical capability. The army needed to winter at Istanbul so that its troops could attend to their fiefs and recruit for the next year's campaigning.
Suleiman's retreat did not mark a complete failure. The campaign underlined Ottoman control of southern Hungary and left behind enough destruction in Hapsburg Hungary and in those Austrian lands it had ravaged to impair Ferdinand's capacity to mount a sustained counterattack. Suleiman's achievement was to consolidate the gains of 1526 and establish the puppet kingdom of John Zápolya as a buffer against the Holy Roman Empire.
The invasion and its climactic siege, however, exacted a heavy price from both sides, with tens of thousands of soldiers and civilians dead and thousands more sold into slavery. It marked the end of the Ottomans' expansion towards the centre of Europe and arguably the beginning of their long decline as the dominant power of the Renaissance world.
Ferdinand I set up a funeral monument for Niklas, Graf Salm—who had been injured during the last Ottoman assault and died on 4 May 1530—to express his gratitude to the defender of Vienna. This Renaissance sarcophagus is now on display in the baptistry of the Votivkirche in Vienna. Ferdinand's son, Maximilian II, later built the summer palace of Neugebaeude on the spot where Suleiman is said to have pitched his tent.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Chirot, Daniel. The Origins of backwardness in Eastern Europe: economics and politics from the Middle Ages until the early twentieth century. Berkeley: University of California Press. 1989. ISBN 9780520064218
- Dupuy, Trevor N., Curt Johnson, and David L. Bongard. The encyclopedia of military biography. London: I. B. Tauris. 1992, ISBN 9781850435693
- Kann, Robert Adolf, A History of the Habsburg Empire: 1526-1918, University of California Press, 1980, ISBN 0-52-004206-9
- Keegan, John, and Andrew Wheatcroft, Who's Who in Military History: From 1453 to the Present Day, Routledge (UK), 1996, ISBN 0-41-512722-X
- Louthan, Howard, The Quest for Compromise: Peacemakers in Counter-Reformation Vienna, 1997, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-52-158082-X
- Murphey, Rhoads, Ottoman Warfare 1500-1700, Rutgers University Press, 1999, ISBN 0-81-352685-X
- Riley-Smith, Jonathan, The Oxford History of the Crusades, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-280312-3
- Shaw, Stanford Jay, and Ezel Kural Shaw, History of the Ottoman Empire and Modern Turkey, Cambridge University Press, 1977, ISBN 0-52-129163-1
- Sicker, Martin, The Islamic World in Decline: from the Treaty of Karlowitz to the Disintegration of the Ottoman Empire, Praeger/Greenwood, 2000, ISBN 0-27-596891-X
- Spielman, John Philip, The City and the Crown: Vienna and the Imperial Court, Purdue University Press, 1993, ISBN 1-55-753021-1
- Toynbee, Arnold, A Study of History, Oxford University Press, 1987 edition, ISBN 0-19-505080-0
- Turnbull, Stephen, The Ottoman Empire: 1326-1699, Osprey Publishing, 2003, ISBN 1-84-176569-4
- Tracy, James. D., Europe's Reformations: 1450-1650, Rowman and Littlefield, 2006, ISBN 0-74-253789-7
- Walton, Mark.W., George.F.Nafziger, and Laurent.W.Mbanda, Islam at War: A History, Praeger/Greenwood, 2003, ISBN 0-27-598101-0
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.


