Difference between revisions of "Saint Lawrence River" - New World Encyclopedia
John Willis (talk | contribs) (created, categorized & credited) |
John Willis (talk | contribs) (preliminary edit) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | The '''Saint Lawrence River''' ( | + | The '''Saint Lawrence River''' (French: '''fleuve Saint-Laurent''') is a large west-to-east flowing river in the middle latitudes of [[North America]], connecting the [[Great Lakes]] with the [[Atlantic Ocean]]. It was called ''Kaniatarowanenneh'' ("big waterway") in the Mohawk language. It traverses the Canadian province of [[Quebec]] and forms part of the border between the state of [[New York]] in the [[United States]] and the province of [[Ontario]] in [[Canada]]. |
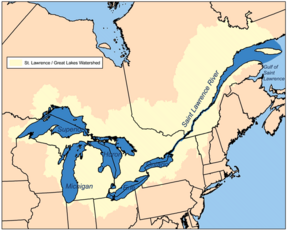
| − | The Saint Lawrence | + | The part of the river named the Saint Lawrence is born at the outflow of [[Lake Ontario]] at Kingston, Ontario. From there, it passes Brockville and Cornwall in Ontario, and Quebec's [[Montreal]], Trois-Rivières, and Quebec City, before draining into the [[Gulf of Saint Lawrence]], the largest estuary in the world. It runs 3,058 kilometers (1,900 miles) from the furthest headwater to the mouth (and 1,197 km or 744 miles from the outflow of Lake Ontario). The furthest headwater is the North River in the [[Mesabi Range]] of [[Minnesota]]. Its drainage area, which includes the Great Lakes and hence the world's largest system of freshwater lakes, has a size of 1.03 million km². The average discharge at the mouth is 10,400 m³/s. |
The river includes [[Lac Saint-Louis]] south of Montreal, [[Lac Saint-François]] at [[Salaberry-de-Valleyfield, Quebec]] and [[Lac Saint-Pierre]] east of Montreal. It surrounds such islands as the [[Thousand Islands]] near Kingston, the [[Island of Montreal]], [[Île Jésus]] ([[Laval, Quebec|Laval]]), [[Île d'Orléans]] near Quebec City, and [[Anticosti Island]] north of the [[Gaspé]]. | The river includes [[Lac Saint-Louis]] south of Montreal, [[Lac Saint-François]] at [[Salaberry-de-Valleyfield, Quebec]] and [[Lac Saint-Pierre]] east of Montreal. It surrounds such islands as the [[Thousand Islands]] near Kingston, the [[Island of Montreal]], [[Île Jésus]] ([[Laval, Quebec|Laval]]), [[Île d'Orléans]] near Quebec City, and [[Anticosti Island]] north of the [[Gaspé]]. | ||
| − | [[Lake Champlain]] and the | + | [[Lake Champlain]] and the Ottawa, Richelieu, and Saguenay rivers drain into the St. Lawrence. |
| − | The first European to navigate the St. Lawrence was [[Jacques Cartier]], who | + | The first European to navigate the St. Lawrence was [[Jacques Cartier]], who in 1534 first sighted the river and also claimed [[New France]] for [[Francis I]]. Until the early 1600s, the French used the name ''Rivière du Canada'' to designate the Saint Lawrence upstream to Montreal and the Ottawa River after Montreal. The Saint Lawrence River served as the main route for exploration of the North American interior from Europe. |
The St. Lawrence was formerly continuously navigable only as far as Montreal due to the [[Lachine Rapids]]. The [[Lachine Canal]] was the first to allow ships to pass the rapids; the [[Saint Lawrence Seaway]], an extensive system of canals and locks, now permits ocean-going vessels to pass all the way to [[Lake Superior]]. | The St. Lawrence was formerly continuously navigable only as far as Montreal due to the [[Lachine Rapids]]. The [[Lachine Canal]] was the first to allow ships to pass the rapids; the [[Saint Lawrence Seaway]], an extensive system of canals and locks, now permits ocean-going vessels to pass all the way to [[Lake Superior]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Image:DSCN4262 rmosesspstlawrence e.jpg|250px|right|thumb|Saint Lawrence River along the New York-Ontario border]] | [[Image:DSCN4262 rmosesspstlawrence e.jpg|250px|right|thumb|Saint Lawrence River along the New York-Ontario border]] | ||
==Names== | ==Names== | ||
| − | A note on translation: Occasionally, the French name ''fleuve Saint-Laurent'' is wrongly translated as Saint Lawrence Seaway, | + | A note on translation: Occasionally, the French name ''fleuve Saint-Laurent'' is wrongly translated as Saint Lawrence Seaway, from the use of the word ''fleuve'', not ''rivière''. However, the word ''fleuve'' simply means a river that runs to the sea, and is appropriately translated by ''river''. The seaway is a system of artificial canals, and is called in French ''voie maritime du Saint-Laurent''. |
| − | The source of the | + | The source of the North River in the [[Mesabi Range]] in [[Minnesota]] is considered to be the source of the Saint Lawrence River. Because it crosses so many lakes, the Saint Lawrence River frequently changes its name. From source to mouth, the names are: |
* [[North River (Saint Louis)|North River]] | * [[North River (Saint Louis)|North River]] | ||
| Line 50: | Line 45: | ||
* [[Lake Ontario]] | * [[Lake Ontario]] | ||
* Saint Lawrence River | * Saint Lawrence River | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
Revision as of 08:40, 14 January 2006
| Saint Lawrence River | |
|---|---|
| | |
| Origin | Lake Ontario |
| Mouth | Gulf of St. Lawrence/Atlantic Ocean |
| Basin countries | Canada (Ontario, Quebec) United States (Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Vermont, Wisconsin) |
| Length | 1,197 km |
| Source elevation | 250 m (820 ft) |
| Avg. discharge | 10,400 m³/s (367,328 ft³/s) |
| Basin area | 1,030,000 km² (397,683 mi²) |
The Saint Lawrence River (French: fleuve Saint-Laurent) is a large west-to-east flowing river in the middle latitudes of North America, connecting the Great Lakes with the Atlantic Ocean. It was called Kaniatarowanenneh ("big waterway") in the Mohawk language. It traverses the Canadian province of Quebec and forms part of the border between the state of New York in the United States and the province of Ontario in Canada.
The part of the river named the Saint Lawrence is born at the outflow of Lake Ontario at Kingston, Ontario. From there, it passes Brockville and Cornwall in Ontario, and Quebec's Montreal, Trois-Rivières, and Quebec City, before draining into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, the largest estuary in the world. It runs 3,058 kilometers (1,900 miles) from the furthest headwater to the mouth (and 1,197 km or 744 miles from the outflow of Lake Ontario). The furthest headwater is the North River in the Mesabi Range of Minnesota. Its drainage area, which includes the Great Lakes and hence the world's largest system of freshwater lakes, has a size of 1.03 million km². The average discharge at the mouth is 10,400 m³/s.
The river includes Lac Saint-Louis south of Montreal, Lac Saint-François at Salaberry-de-Valleyfield, Quebec and Lac Saint-Pierre east of Montreal. It surrounds such islands as the Thousand Islands near Kingston, the Island of Montreal, Île Jésus (Laval), Île d'Orléans near Quebec City, and Anticosti Island north of the Gaspé.
Lake Champlain and the Ottawa, Richelieu, and Saguenay rivers drain into the St. Lawrence.
The first European to navigate the St. Lawrence was Jacques Cartier, who in 1534 first sighted the river and also claimed New France for Francis I. Until the early 1600s, the French used the name Rivière du Canada to designate the Saint Lawrence upstream to Montreal and the Ottawa River after Montreal. The Saint Lawrence River served as the main route for exploration of the North American interior from Europe.
The St. Lawrence was formerly continuously navigable only as far as Montreal due to the Lachine Rapids. The Lachine Canal was the first to allow ships to pass the rapids; the Saint Lawrence Seaway, an extensive system of canals and locks, now permits ocean-going vessels to pass all the way to Lake Superior.
Names
A note on translation: Occasionally, the French name fleuve Saint-Laurent is wrongly translated as Saint Lawrence Seaway, from the use of the word fleuve, not rivière. However, the word fleuve simply means a river that runs to the sea, and is appropriately translated by river. The seaway is a system of artificial canals, and is called in French voie maritime du Saint-Laurent.
The source of the North River in the Mesabi Range in Minnesota is considered to be the source of the Saint Lawrence River. Because it crosses so many lakes, the Saint Lawrence River frequently changes its name. From source to mouth, the names are:
- North River
- Saint Louis River
- Lake Superior
- Saint Marys River
- Lake Huron
- Saint Clair River
- Lake Saint Clair
- Detroit River
- Lake Erie
- Niagara River
- Lake Ontario
- Saint Lawrence River
External links
- Regional Geography of the St. Lawrence River
- St. Lawrence Parks Commission (Ontario)
- Great Lakes St. Lawrence Seaway System
- Safe Passage: Aids to Navigation on the St. Lawrence — Historical essay, illustrated with drawings and photographs
- Annotated Bibliography on St. Lawrence County and Northern New York region.
- "Save the River"
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.