Difference between revisions of "Ptah" - New World Encyclopedia
Scott Dunbar (talk | contribs) (Approved) |
Chris Jensen (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
In Memphis, Ptah was worshipped in his own right, and was seen as Atum's father, or rather, the father of [[Nefertum]], the younger form of Atum. When the beliefs about the Ennead and [[Ogdoad]] were later merged, and Atum was identified as [[Ra]] (''Atum-Ra''), himself seen as [[Horus]] (''Ra-Herakhty''), this led to Ptah being said to be married to [[Sekhmet]], at the time considered the earlier form of [[Hathor]], Horus', thus Atum's, [[mother]]. | In Memphis, Ptah was worshipped in his own right, and was seen as Atum's father, or rather, the father of [[Nefertum]], the younger form of Atum. When the beliefs about the Ennead and [[Ogdoad]] were later merged, and Atum was identified as [[Ra]] (''Atum-Ra''), himself seen as [[Horus]] (''Ra-Herakhty''), this led to Ptah being said to be married to [[Sekhmet]], at the time considered the earlier form of [[Hathor]], Horus', thus Atum's, [[mother]]. | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Ptah in an Egyptian Context== | ==Ptah in an Egyptian Context== | ||
| + | {{Hiero|Ptah|<hiero>p:t-H</hiero>|align=right|era=egypt}} | ||
{{main|Egyptian Religion}} | {{main|Egyptian Religion}} | ||
| + | {{seealso|Egyptian mythology}} | ||
As an Egyptian deity, Ptah belonged to a complex religious, mythological and cosmological belief system developed in the [[Nile]] river basin from earliest prehistory to 525 B.C.E.<ref>This particular "cut-off" date has been chosen because it corresponds to the Persian conquest of the kingdom, which marks the end of its existence as a discrete and (relatively) circumscribed cultural sphere. Indeed, as this period also saw an influx of immigrants from Greece, it was also at this point that the Hellenization of Egyptian religion began. While some scholars suggest that even when "these beliefs became remodeled by contact with Greece, in essentials they remained what they had always been" (Erman, 203), it still seems reasonable to address these traditions, as far as is possible, within their own cultural milieu.</ref> Indeed, it was during this relatively late period in Egyptian cultural development, a time when they first felt their beliefs threatened by foreigners, that many of their myths, legends and religious beliefs were first recorded.<ref>The numerous inscriptions, stelae and papyri that resulted from this sudden stress on historical posterity provide much of the evidence used by modern archeologists and Egyptologists to approach the ancient Egyptian tradition (Pinch, 31-32).</ref> The cults within this framework, whose beliefs comprise the myths we have before us, were generally fairly localized phenomena, with different deities having the place of honor in different communities.<ref>These local groupings often contained a particular number of deities and were often constructed around the incontestably primary character of a creator god (Meeks and Meeks-Favard, 34-37).</ref> Despite this apparently unlimited diversity, however, the gods (unlike those in many other pantheons) were relatively ill-defined. As Frankfort notes, “the Egyptian gods are imperfect as individuals. If we compare two of them … we find, not two personages, but two sets of functions and emblems. … The hymns and prayers addressed to these gods differ only in the epithets and attributes used. There is no hint that the hymns were addressed to individuals differing in character.”<ref>Frankfort, 25-26.</ref> One reason for this was the undeniable fact that the Egyptian gods were seen as utterly [[immanent|immanental]]—they represented (and were continuous with) particular, discrete elements of the natural world.<ref>Zivie-Coche, 40-41; Frankfort, 23, 28-29.</ref> Thus, those who did develop characters and mythologies were generally quite portable, as they could retain their discrete forms without interfering with the various cults already in practice elsewhere. Also, this flexibility was what permitted the development of multipartite cults (i.e. the cult of [[Amun-Re]], which unified the domains of [[Amun]] and [[Re]]), as the spheres of influence of these various deities were often complimentary.<ref>Frankfort, 20-21.</ref> | As an Egyptian deity, Ptah belonged to a complex religious, mythological and cosmological belief system developed in the [[Nile]] river basin from earliest prehistory to 525 B.C.E.<ref>This particular "cut-off" date has been chosen because it corresponds to the Persian conquest of the kingdom, which marks the end of its existence as a discrete and (relatively) circumscribed cultural sphere. Indeed, as this period also saw an influx of immigrants from Greece, it was also at this point that the Hellenization of Egyptian religion began. While some scholars suggest that even when "these beliefs became remodeled by contact with Greece, in essentials they remained what they had always been" (Erman, 203), it still seems reasonable to address these traditions, as far as is possible, within their own cultural milieu.</ref> Indeed, it was during this relatively late period in Egyptian cultural development, a time when they first felt their beliefs threatened by foreigners, that many of their myths, legends and religious beliefs were first recorded.<ref>The numerous inscriptions, stelae and papyri that resulted from this sudden stress on historical posterity provide much of the evidence used by modern archeologists and Egyptologists to approach the ancient Egyptian tradition (Pinch, 31-32).</ref> The cults within this framework, whose beliefs comprise the myths we have before us, were generally fairly localized phenomena, with different deities having the place of honor in different communities.<ref>These local groupings often contained a particular number of deities and were often constructed around the incontestably primary character of a creator god (Meeks and Meeks-Favard, 34-37).</ref> Despite this apparently unlimited diversity, however, the gods (unlike those in many other pantheons) were relatively ill-defined. As Frankfort notes, “the Egyptian gods are imperfect as individuals. If we compare two of them … we find, not two personages, but two sets of functions and emblems. … The hymns and prayers addressed to these gods differ only in the epithets and attributes used. There is no hint that the hymns were addressed to individuals differing in character.”<ref>Frankfort, 25-26.</ref> One reason for this was the undeniable fact that the Egyptian gods were seen as utterly [[immanent|immanental]]—they represented (and were continuous with) particular, discrete elements of the natural world.<ref>Zivie-Coche, 40-41; Frankfort, 23, 28-29.</ref> Thus, those who did develop characters and mythologies were generally quite portable, as they could retain their discrete forms without interfering with the various cults already in practice elsewhere. Also, this flexibility was what permitted the development of multipartite cults (i.e. the cult of [[Amun-Re]], which unified the domains of [[Amun]] and [[Re]]), as the spheres of influence of these various deities were often complimentary.<ref>Frankfort, 20-21.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 15:46, 25 June 2007
In Egyptian mythology, Ptah (also spelled Peteh) was the deification of the primordial mound in the Ennead cosmogony, which was more literally referred to as Ta-tenen (also spelt Tathenen), meaning risen land, or as Tanen, meaning submerged land. The importance Ptah was given in history can readily be understood since the name Egypt derives from Classical Greek Aigyptos which in turn derives from the native name of a temple at Memphis (transcribed as Ḥwt-k3-Ptḥ or Hut-ka-Ptah "temple of the soul of Ptah"). Mythologically-speaking, Ptah was most renowned for his association with the creation of the cosmos.
In Memphis, Ptah was worshipped in his own right, and was seen as Atum's father, or rather, the father of Nefertum, the younger form of Atum. When the beliefs about the Ennead and Ogdoad were later merged, and Atum was identified as Ra (Atum-Ra), himself seen as Horus (Ra-Herakhty), this led to Ptah being said to be married to Sekhmet, at the time considered the earlier form of Hathor, Horus', thus Atum's, mother.
Ptah in an Egyptian Context
| Ptah in hieroglyphs | |||
|
As an Egyptian deity, Ptah belonged to a complex religious, mythological and cosmological belief system developed in the Nile river basin from earliest prehistory to 525 B.C.E.[1] Indeed, it was during this relatively late period in Egyptian cultural development, a time when they first felt their beliefs threatened by foreigners, that many of their myths, legends and religious beliefs were first recorded.[2] The cults within this framework, whose beliefs comprise the myths we have before us, were generally fairly localized phenomena, with different deities having the place of honor in different communities.[3] Despite this apparently unlimited diversity, however, the gods (unlike those in many other pantheons) were relatively ill-defined. As Frankfort notes, “the Egyptian gods are imperfect as individuals. If we compare two of them … we find, not two personages, but two sets of functions and emblems. … The hymns and prayers addressed to these gods differ only in the epithets and attributes used. There is no hint that the hymns were addressed to individuals differing in character.”[4] One reason for this was the undeniable fact that the Egyptian gods were seen as utterly immanental—they represented (and were continuous with) particular, discrete elements of the natural world.[5] Thus, those who did develop characters and mythologies were generally quite portable, as they could retain their discrete forms without interfering with the various cults already in practice elsewhere. Also, this flexibility was what permitted the development of multipartite cults (i.e. the cult of Amun-Re, which unified the domains of Amun and Re), as the spheres of influence of these various deities were often complimentary.[6]
The worldview engendered by ancient Egyptian religion was uniquely appropriate to (and defined by) the geographical and calendrical realities of its believer’s lives. Unlike the beliefs of the Hebrews, Mesopotamians and others within their cultural sphere, the Egyptians viewed both history and cosmology as being well ordered, cyclical and dependable. As a result, all changes were interpreted as either inconsequential deviations from the cosmic plan or cyclical transformations required by it.[7] The major result of this perspective, in terms of the religious imagination, was to reduce the relevance of the present, as the entirety of history (when conceived of cyclically) was ultimately defined during the creation of the cosmos. The only other aporia in such an understanding is death, which seems to present a radical break with continuity. To maintain the integrity of this worldview, an intricate system of practices and beliefs (including the extensive mythic geographies of the afterlife, texts providing moral guidance (for this life and the next) and rituals designed to facilitate the transportation into the afterlife) was developed, whose primary purpose was to emphasize the unending continuation of existence.[8] Given these two cultural foci, it is understandable that the tales recorded within this mythological corpus tend to be either creation accounts or depictions of the world of the dead and of the gods place within it.
Mythological Accounts
It was said (in the Shabaka Stone) that it was Ptah who called the world into being, having dreamt creation in his heart, and speaking it, his name meaning opener, in the sense of opener of the mouth. Indeed the opening of the mouth ceremony, performed by priests at funerals to release souls from their corpses, was said to have been created by Ptah. Atum was said to have been created by Ptah to rule over the creation, sitting upon the primordial mound.
Since Ptah was the primordial mound, and had called creation into being, he was considered the god of craftsmen, and in particular stone-based crafts. Eventually, due to the connection of these things to tombs, and that at Thebes, the craftsmen regarded him so highly as to say that he controlled their destiny. Consequently, first amongst the craftsmen, then the population as a whole, Ptah also became a god of reincarnation. Since Seker was also god of craftsmen, and of re-incarnation, Seker was later assimilated with Ptah becoming Ptah-Seker.
Ptah-Seker gradually became seen as the personification of the sun during the night, since the sun appears to be re-incarnated at this time, and Ptah was the primordial mound, which lay beneath the earth. Consequently, Ptah-Seker became considered an underworld deity, and eventually, by the Middle Kingdom, become assimilated by Osiris, the lord of the underworld, occasionally being known as Ptah-Seker-Osiris.
Representations
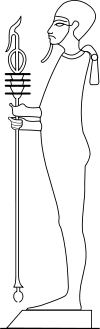
In art, he is portrayed as a bearded mummified man, often wearing a skull cap, with his hands holding an ankh, was, and djed, the symbols of life, power and stability, respectively. It was also considered that Ptah manifested himself in the Apis bull.
Notes
- ↑ This particular "cut-off" date has been chosen because it corresponds to the Persian conquest of the kingdom, which marks the end of its existence as a discrete and (relatively) circumscribed cultural sphere. Indeed, as this period also saw an influx of immigrants from Greece, it was also at this point that the Hellenization of Egyptian religion began. While some scholars suggest that even when "these beliefs became remodeled by contact with Greece, in essentials they remained what they had always been" (Erman, 203), it still seems reasonable to address these traditions, as far as is possible, within their own cultural milieu.
- ↑ The numerous inscriptions, stelae and papyri that resulted from this sudden stress on historical posterity provide much of the evidence used by modern archeologists and Egyptologists to approach the ancient Egyptian tradition (Pinch, 31-32).
- ↑ These local groupings often contained a particular number of deities and were often constructed around the incontestably primary character of a creator god (Meeks and Meeks-Favard, 34-37).
- ↑ Frankfort, 25-26.
- ↑ Zivie-Coche, 40-41; Frankfort, 23, 28-29.
- ↑ Frankfort, 20-21.
- ↑ Assmann, 73-80; Zivie-Coche, 65-67; Breasted argues that one source of this cyclical timeline was the dependable yearly fluctuations of the Nile (8, 22-24).
- ↑ Frankfort, 117-124; Zivie-Coche, 154-166.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Assmann, Jan. In search for God in ancient Egypt. Translated by David Lorton. Ithica: Cornell University Press, 2001. ISBN 0801487293.
- Breasted, James Henry. Development of religion and thought in ancient Egypt. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 1986. ISBN 0812210454.
- Budge, E. A. Wallis (translator). The Egyptian Book of the Dead. 1895. Accessed at sacred-texts.com.
- Budge, E. A. Wallis (translator). The Egyptian Heaven and Hell. 1905. Accessed at [www.sacred-texts.com/egy/ehh.htm sacred-texts.com].
- Budge, E. A. Wallis. The gods of the Egyptians; or, Studies in Egyptian mythology. A Study in Two Volumes. New York: Dover Publications, 1969.
- Budge, E. A. Wallis (translator). Legends of the Gods: The Egyptian texts. 1912. Accessed at sacred-texts.com.
- Budge, E. A. Wallis (translator). The Rosetta Stone. 1893, 1905. Accessed at sacred-texts.com.
- Dennis, James Teackle (translator). The Burden of Isis. 1910. Accessed at sacred-texts.com.
- Dunand, Françoise and Zivie-Coche, Christiane. Gods and men in Egypt: 3000 B.C.E. to 395 C.E.. Translated from the French by David Lorton. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 2004. ISBN 080144165X.
- Erman, Adolf. A handbook of Egyptian religion. Translated by A. S. Griffith. London: Archibald Constable, 1907.
- Frankfort, Henri. Ancient Egyptian Religion. New York: Harper Torchbooks, 1961. ISBN 0061300772.
- Griffith, F. Ll. and Thompson, Herbert (translators). The Leyden Papyrus. 1904. Accessed at sacred-texts.com.
- Meeks, Dimitri. Daily life of the Egyptian gods. Translated from the French by G.M. Goshgarian. Ithaca, NY : Cornell University Press, 1996. ISBN 0801431158.
- Mercer, Samuel A. B. (translator). The Pyramid Texts. 1952. Accessed online at [www.sacred-texts.com/egy/pyt/index.htm sacred-texts.com].
- Pinch, Geraldine. Handbook of Egyptian mythology. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO, 2002. ISBN 1576072428.
- Wilkinson, Richard H. The Complete Gods and Goddesses of Ancient Egypt. London: Thames and Hudson, 2003. ISBN 0500051208.
- Shafer, Byron E. (editor). Temples of ancient Egypt. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 1997. ISBN 0801433991.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.