Nitrogen dioxide
| Nitrogen dioxide | |
|---|---|
| |
| |

| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | [] |
| Properties | |
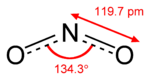
| Molecular formula | NO2 |
| Molar mass | 46.0055 |
| Appearance | brown gas |
| Density | 1443 kg/m³, liquid 3.4 kg/m³, gas at 294.25 K |
| Melting point |
-11.2°C (261.95 K) |
| Boiling point |
21.1°C (293.25 K) |
| Hazards | |
| EU classification | Highly toxic (T+) |
| NFPA 704 |
|
| R-phrases | R26, R34 |
| S-phrases | S1/2, S9, S26, S28,S36/37/39, S45 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
Nitrogen dioxide is the chemical compound NO2. It is one of the several nitrogen oxides. This reddish-brown gas has a characteristic sharp, biting odor. NO2 is one of the most prominent air pollutants and a poison by inhalation.
Safety and pollution considerations
Nitrogen dioxide is toxic by inhalation. Symptoms of poisoning (lung edema) tend to appear several hours after one has inhaled a low but potentially fatal dose. Also, low concentrations (4 ppm) will anesthetize the nose, thus creating a potential for overexposure.
Long-term exposure to NO2 at concentrations above 40–100 µg/m³ causes adverse health effects [1]. The most important source of NO2 is internal combustion engines, which emit nitrogen oxides near people. A major industrial source is pulp mills.
The map shown to the left, depicting results of satellite measurements, illustrates nitrogen dioxide as large scale pollutant, with rural background ground level concentrations in some areas around 30 µg/m³, not far below unhealthful levels. Nitrogen dioxide plays a role in atmospheric chemistry, including the formation of tropospheric ozone. A recent study by researchers at the University of California, San Diego, suggests a link between NO2 levels and Sudden Infant Death Syndrome.
See also
- Nitryl
- Nitrous oxide or N2O, "laughing gas", a linear molecule, isoelectronic with CO2 but with a nonsymmetric arrangement of atoms (NNO)
- Nitric oxide or NO, a problematic pollutant, related to CO but with one additional electron.
- NOx = all of the above in unspecified proportions but tending toward NO2.
More esoteric nitrogen oxides include N2O5 and the blue species N2O3.
Oxidized (cationic) and reduced (anionic) derivatives of many of these oxides exist: nitrite (NO2−), nitrate (NO3−), nitronium or NO2+, and nitrosonium or NO+. NO2 is intermediate between nitrite and nitronium:
- NO2+ + e− → NO2
- NO2 + e− → NO2−
- Birkeland-Eyde process
Notes
- ↑ Health Aspects of Air Pollution with Particulate Matter, Ozone and Nitrogen Dioxide - Report on a WHO Working Group. Retrieved October 24, 2007.
External links
All links retrieved October 24, 2007.
- International Chemical Safety Card 0930 - International Labor Organization.
- Oxides of nitrogen fact sheet- National Pollutant Inventory
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards - CDC.
- WHO-Europe reports: Health Aspects of Air Pollution with Particulate Matter, Ozone and Nitrogen Dioxide - Report on a WHO Working Group, and Answer to follow-up questions from CAFE - World Health Organization.
- Nitrogen Dioxide Air Pollution - Green Facts.
- Nitrogen dioxide pollution in the world (image) - esamultimedia.esa.int
- Computational Chemistry Wiki - compchemwiki.org
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.

