Difference between revisions of "National Basketball Association" - New World Encyclopedia
Mihir Shah (talk | contribs) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Copyedited}}{{Images OK}}{{submitted}}{{approved}}{{Paid}} |
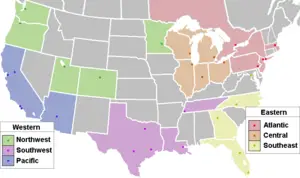
| + | [[Image:NBA Conferences Divisions.PNG|thumb|300px|right|National Basketball Association Conferences and Divisions. Locations of teams marked with square.]] | ||
| − | + | The '''National Basketball Association''' ('''NBA''') is the world's premier men's [[basketball]] league. It has 30 teams; 29 in the [[United States]] and 1 in [[Canada]]. It is an active member<ref>[http://www.usabasketball.com/news/members.html USA Basketball] Retrieved April 22, 2008.</ref> of USA Basketball, which is recognized by the International Basketball Federation as the National Governing Body (NGB) for basketball in the United States. | |
| − | The '''National Basketball Association''' ('''NBA''') is the world's premier men's [[basketball]] league. It has 30 teams; 29 in the [[United States]] and 1 in [[Canada]]. It is an active member<ref>http://www.usabasketball.com/news/members.html</ref> of USA Basketball, which is recognized by the International Basketball Federation as the National Governing Body (NGB) for basketball in the United States | + | The league was founded in [[New York City]], on June 6, 1946 as the '''Basketball Association of America''' (BAA). The league adopted the name National Basketball Association in the Autumn of 1949 after merging with the rival National Basketball League (United States). The league's several international and individual team offices are directed out of its head offices located in the Olympic Tower (New York) at 645 Fifth Avenue in New York City. The NBA represents the highest level of competition in the world of [[basketball]]. It has grown in international popularity as the best players of the world have joined [[United States|America's]] top players. |
| − | + | {{toc}} | |
| − | The league was founded in [[New York City]], on June 6, 1946 as the '''Basketball Association of America''' (BAA). The league adopted the name National Basketball Association in the Autumn of 1949 after merging with the rival National Basketball League (United States). The league's several international and individual team offices are directed out of its head offices located in the Olympic Tower (New York) at 645 Fifth Avenue in New York City. | + | [[Image:Wilt Chamberlain.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Wilt Chamberlain, American basketball player wearing uniform of Harlem Globetrotters.]] |
==History== | ==History== | ||
===1940s: BAA & NBL merge to include 17 teams=== | ===1940s: BAA & NBL merge to include 17 teams=== | ||
| − | + | Madison Square Garden in [[New York City]] played an instrumental role in the formation of the Basketball Association of America (BAA). On November 1, 1946, the Toronto Huskies hosted the New York Knickerbockers, which the NBA now regards as the first game played in the league's history.<ref>[http://www.nba.com/canada/History_of_Basketball_in_Canad-Canada_Generic_Article-18023.html History of Basketball in Canada] NBA Media Ventures, LLC. Retrieved April 13, 2007.</ref> | |
| − | + | ||
| + | ===1946-47=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the first season of the BAA, a new professional star emerged, one who had gained little notoriety in college. Joe Fulks, a 6-5 forward from Kentucky, averaged 23.2 ppg, an astonishing amount considering most games were won by teams scoring in the 70s and 80s and nearly seven points per game more than any other player in the league. Field goal percentages were in the 30 percent range, and Ernest Calverley of the Providence Steamrollers led the league with 3.4 assists per game. Other stars in the fledgling league were Washington's Bob Feerick and Bones McKinney, Detroit's Stan Miasek and Chicago's Max Zaslofsky. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The 60-game regular season title belonged to the Washington Capitols, coached by [[Red Auerbach]] with a 49-11 record, including a 29-1 mark at home. But in the Playoffs, Chicago shocked the Capitols behind the play of Max Zaslofsky and center Chuck Halbert to advance to the Finals. Philadelphia, coached by Eddie Gottlieb, who had the most extensive pro background of anyone in the BAA, defeated St. Louis and New York to advance to the Finals. Fulks, Howie Dallmar and Angelo Musi led Philadelphia past Chicago as the Warriors won the first league title 4-1 (four games to one). The first year of the BAA was no indication of what was to come, as television was still a thing of the future and games on radio were not universal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As the end of the 1940s approached, the 60 game BAA schedule was reduced to 48 games. Of the 11 teams original teams, four of them folded, and the Baltimore Bullets were brought in to make it an even 8 teams and balance the number of teams. To everyone's surprise, the Bullets won the title in 1947 in six games as an expansion team. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Although basketball didn't begin until mid-decade in the ‘40s, it was quickly known for its physical style of play. One of the players, Buddy Jeanette of the Bullets said, "I remember in the last game with Philly, George Senesky hit me in the mouth and split my lip open." "Right after the game I had to go get my mouth sewed up. Then we went out and had a few beers." | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===1948-49: The Year of the Center=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | When [[George Mikan]] stepped foot on the basketball court, he completely changed the way the game was played. For the first time, a dominant center playing with his back to the basket became the cornerstone of a team. He took the league by storm, and led his Minneapolis Lakers to the first of their five titles by beating the 1st seeded Baltimore Bullets in six games. | ||
| + | |||
| + | On August 3, 1949, the BAA agreed to merge with the National Basketball League, creating the '''National Basketball Association,''' with seventeen franchises located in a mix of large and small cities, as well as large arenas and smaller gymnasiums. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===1950s:24-second shot clock introduced=== | ||
| + | This decade began with a three division bracket (Eastern, Western, and Central Division) and a total of 17 teams. Mikan's Lakers won again to win back to back titles, and were clearly head and shoulders above the rest of the teams in the league. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====1950-51==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | This season marked the introduction of the first black player to be given a contract to play in the NBA. Nat "Sweetwater" Clifton, Chuck Cooper, and Early Lloyd opened the doors for [[African-American]] players to enter the NBA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====1952-54==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1952 marked the emergence of young talents Paul Arizin and Bob Cousy, and the extension of the lane from six feet to twelve feet. This period marked a three-peat for the Minneapolis Lakers, making it five championships in the league's first six years. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the 1954-55 season, Danny Biasone came up with the idea of the shot clock to prevent teams from stalling after building a large lead. This increased scoring (from 79 points to 93 points per game) drastically and increased the pace of the game. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Boston Celtics had been waiting in the Lakers shadows, and with the arrival of rookie center Bill Russell, their time had come. The 1956-57 NBA Finals was one for the ages, as the Celtics earned their first NBA title in a dramatic, double OT victory over the St. Louis Hawks. Their big men, Russell and Tom Heinsohn produced monster games: 19 points and 32 rebounds for Russell, and 37 points and 23 rebounds for Heinsohn. They would go on to win 11 titles in 13 years and become the greatest sports dynasty in [[United States]] history. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The 1957-58 seasons marked a break from Celtic brass, and brought glory to explosive scorer Bob Petit, who scored 50 points in the clinching Game 6 of the NBA finals, leading the St. Louis Hawks to victory against the Celtics. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The end of the '50s brought Laker great Elgin Baylor onto the scene. After several losing seasons following Mikan's retirement, Baylor brought the Lakers back to the playoffs, and eventually to the NBA finals, where they would be swept by the Celtics. The Celtics would go on to win eight straight titles and separate themselves from the other great teams in NBA history. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===1960s: Boston Dominance=== | ||
| + | [[Wilt Chamberlain]] entered the NBA with a bang. He captured the Rookie of the Year and the Most Valuable Player in the same year with astounding numbers: 37.6 ppg and 27 rebounds per game. This, however, was not enough to stop the Russell lead Celtics, as they easily disposed of Chamberlain and the Warriors. Once again, the Celtics captured the title. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The NBA was not short on excitement, but with the arrival of young stars [[Oscar Robertson]] and [[Jerry West]], the NBA was throbbing with excitement and highlight-reel plays. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====1961-62==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | This season was the stuff of legends and folklore that would be passed down from generation to generation. As if what [[Wilt Chamberlain|Wilt]] did in his first few seasons was mere child's play, what he did in his third season will likely never be duplicated. Chamberlain, who played all but eight possible minutes of the entire season and averaged 48.5 minutes per game, averaged 50.4 points per game, a full 12 points more than his NBA record set the year before. On March 2, 1962, Chamberlain scored 100 points against the New York Knicks in Hershey, PA in a 169-147 triumph. Although 4,124 were in attendance, many thousands more would claim to have been there for decades afterward. The end result was still the same; Wilt lead the league in scoring, and the Celtics added one more title to their dynasty. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====1964-65==== | ||
| + | In an effort to lessen the dominance of big men and keep the game open and moving, the NBA widened the foul lane from 12 to 16 feet. A major trade that took place at the NBA All-Star break would have far-reaching implications for years to come. Wilt Chamberlain, in the midst of his greatness at 28 years old, was dealt by the San Francisco Warriors to the Philadelphia 76ers for Paul Neumann, Connie Dierking, Lee Shaffer and cash. The immediate results: San Francisco went from 48-32 the season before to 17-63, while Philadelphia improved slightly, from 34-46 to 40-40. More importantly, Chamberlain was back in the same division as the Celtics, and would have to be dealt with even before the NBA Finals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | After trailing the Lakers for the majority of the series in Red Auerbach's last season as coach, the Celtics sent him off a winner with their eighth consecutive title. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====1966-67==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | In this magical season, the [[Wilt Chamberlain]]-led Sixers posted the (then) best record in league history with 68 wins and 13 losses. Bill Russell was chosen as Red Auerbach's successor, becoming the first ever African-American coach in the NBA. The Sixers demolished the Celtics and Russell in five games (4-1), and went on to win the NBA title in an almost flawless season. Celtics player, K.C. Jones, put it best: "They're playing the same game we've played for the last nine years. In other words, team ball." | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 1967, the league faced a new external threat with the formation of the American Basketball Association. The leagues engaged in a bidding war for talent. The NBA landed the most important college star of the era, [[Kareem Abdul-Jabbar]] (then known as Lew Alcindor), who together with Oscar Robertson led the [[Milwaukee Bucks]] to a title in his second season, and who later played on five Los Angeles Lakers' championship teams. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 1968, the Celtics were predicted to crumble due to age. They fell behind 3-1 in the Eastern Conference finals to Wilt's Sixers, but overcame the deficit and won the NBA title with a seventh game victory over the Lakers on the Lakers' home court. After a one-year hiatus, they were back at the top. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Wilt Chamberlain was again traded. In 1969, the Lakers acquired Wilt's rights for Jerry Chambers, Archie Clark and Darrall Imhoff prior to the beginning of the season. Wilt or no Wilt, it made no difference to the Celtics. They escaped again with a two point game seven win in Los Angeles when Don Nelson's shot careened high off the rim and through the hoop, marking the 11th title in 13 seasons as the sun set on the 1960's. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Through this period, the NBA continued to expand its scope with the shift of the Minneapolis Lakers to Los Angeles, the Philadelphia Warriors to [[San Francisco]], and the Syracuse Nationals to [[Philadelphia, Pennsylvania|Philadelphia]], as well as the addition of its first expansion franchises. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===1970s- NBA-A New Era=== | ||
| + | The 1969-70 year presented many new opportunities, largely because Bill Russell, the Celtic coach and defensive juggernaut, retired from his position as a player/coach. A rejuvenated New York Knicks team, led by Walt Frazier, Willis Reed, and Bill Bradley defeated the Lakers in game seven of the NBA Finals, to capture their first title. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====1970-71: From the Sky==== | ||
| + | Kareem Abdul Jabbar's sky hook was the most dangerous weapon in the NBA. His talent, along with Oscar Robertson, allowed the Milwaukee Bucks to surge to only the second NBA Finals sweep in history. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====1971-72: Resurrection==== | ||
| + | After years and years of getting to the Finals and being turned back by the Celtics, the Lakers put together a streak that still stands: 33 straight victories, en route to a 69-13 record (then the best record in NBA history). | ||
| + | |||
| + | While the Knicks regained their championship form in 1972-73, it was 6 foot guard, Nate Archibald, that stole the show, and the passion of the fans. The Cincinnati Royals failed to make the playoffs but Archibald led the league in both scoring and assists, with 34 ppg and an astounding 11.4 assists, a feat that has yet to be repeated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 1973-74, the old stars were about to set. Wilt Chamberlain, Jerry West, Oscar Robertson, and Willis Reed were all playing in their final season. The Celtics teams benefited the most from this, as they once again rose to the top to win championship number 12. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The 1974-75 season was a return to dominance for the Baltimore Bullets, and surprising success for the Golden State Warriors. Led by star Rick Barry, they shocked the Bullets 4-0, only the third sweep in NBA finals history. After the series, Barry said, "It has to be the greatest upset in the history of the NBA Finals. It was like a fairy-tale season. Everything just fell into place. It's something I'll treasure for the rest of my life." | ||
| + | |||
| + | After six straight losing seasons, a healthy [[Bill Walton]] and the Blazers shocked the world as they defeated the 76ers to win their first championship. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The transfer of Dr.J from the ABA to the NBA, and thereafter the trade that sent him to Philadelphia had great ramifications. [[Julius Erving]] electrified the NBA with hair-raising dunks, particularly the "tomahawk," en route to leading his team to the NBA finals against Portland. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The National Basketball Association adapted the ABA's innovative three-point field goal beginning in 1979 to create spacing of all ten players on the court. That same year, rookies Larry Bird and Magic Johnson joined the Boston Celtics and Los Angeles Lakers respectively, continuing a rivalry that began when the two played in the 1979 NCAA Basketball Finals, sparking a period of significant growth in fan interest in the NBA throughout the country and the world. Bird went on to lead the Celtics to three NBA titles, while Johnson led the Lakers to five. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===1980s: Lakers Dynasty=== | ||
| + | [[Earvin "Magic" Johnson]] was absolutely magical in the 1979-80 season. Lakers' stars Magic and Kareem shouldered the load and dominated in the NBA Finals against Dr. J's 76ers. Game 6 was a classic. The rookie point guard Magic Johnson started at center for the injured Kareem Abdul-Jabaar and turned in the game of his life: 42 points, 15 rebounds, and 7 assists, while playing at every position during the game. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Not surprisingly, the very next season, the Celtics countered with a title of their own, the first of the Larry Bird, Robert Parish and Kevin McHale era. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the 1981-82 season, the Lakers and the 76ers faced off again, as the Lakers prevailed for the second straight time against the 76ers, to win the second title of the 1980s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===="Fo-Fi-Fo"==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The famous prediction Moses Malone made when signing with the 76ers almost came true. "Fo-Fo-Fo" indicated a sweep of every team, but they ended up going 12-1 in the playoffs, hence, "Fo-Fi-Fo." While the 1960s were dominated by Celtics-Lakers NBA Finals, three of the first four years of the 1980s saw Lakers-Sixers NBA Finals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Larry Bird and the Celtics won their second title of the decade in 1983-84 against Magic's Lakers. It took them seven games to do it, and after the series, Larry Bird said, "To be honest, they should have swept." | ||
| − | + | ====1984-85 Lakers Finally Put Garden Leprechaun to Sleep==== | |
| + | Magic and Kareem finally accomplished what no other Laker great could before. In fact, they did what only Bob Petit's St. Louis Hawks had done in 1958 by beating the Celtics at the Garden. | ||
| − | + | ====A Draft Like No Other==== | |
| + | The 1984 draft is arguably the deepest draft in NBA history. It has produced future Hall of Famers Hakeem Olajuwon, Michael Jordan, Charles Barkley, and John Stockton. | ||
| − | + | The 1985-1986 season continued the trend of Lakers/Celtics domination. After the Lakers earned their third title of the decade, Larry Bird was intent on doing the same for his Celtics, winning back to back MVP awards and leading the Celtics to the best record in franchise history, 67-15, and a stellar 40-1 home record. Title number 16 was brought to Boston after Bird and company dispatched the Rockets in six games. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ====Showtime==== | |
| + | In 1986-87, the Lakers had entered the phase in their franchise's history that would always be remembered as "Showtime." The Lakers coasted to their fourth title of the decade. During the championship celebration, coach Pat Riley made a daring statement guaranteeing a repeat. It took them seven games against the Detroit Pistons, but that is just what they did, making them only the second team in NBA history (Boston Celtics) to accomplish the feat. Somewhat overshadowed in their loss, Isaiah Thomas's third quarter in the deciding game will never be forgotten. On a sprained ankle, Thomas scored 25 points in the third quarter to give the Pistons a chance to win. The Pistons finally beat the Lakers, sweeping them in 1988-89 to close out the decade. | ||
| − | + | ===1990s: The Years of the Bull=== | |
| + | The 1990s opened up with the Detroit Pistons posting the second straight repeat (Lakers 1986-87,1987-88). | ||
| − | + | The 1991 NBA Finals was billed as a matchup between two larger-than-life superstars, Michael Jordan and Magic Johnson. But as the series played out, it became obvious that it took a team, not one superlative individual, to win an NBA Championship. Jordan was superb, as his series averages of 31.2 points, 11.4 assists and 6.6 rebounds demonstrated, but the Bulls were no one-man team. Their defense held the Lakers to a record-low 458 points for a five-game series. Jordan, who had won his fifth straight scoring title in April, had finally silenced those who said he couldn't lead the Bulls all the way. | |
| − | + | The next season proved to be Larry Bird's last. Coupled with Magic's shocking revelation that he had contracted the HIV virus, Jordan's way had been opened up. The Jordan-led Bulls put their stamp on the 1990s decade by winning six titles, and more astoundingly, two three-peats. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ====1993-94==== | |
| − | + | [[Michael Jordan]] shocked the NBA world by announcing his retirement at the peak of his career. More shocking news was yet to come, however, as the 63-win Seattle Supersonics were toppled by the number eight seeded Denver Nuggets, in the first round of the playoffs. The Houston Rockets would go on to beat the New York Knicks in seven to win the first of their back-to-back titles. | |
| − | === | + | ====1995-96 72-10: The Bulls Dominate==== |
| − | |||
| − | The | + | The Chicago Bulls returned to dominance with the return of their star, Michael Jordan. In fact, they posted the best record in NBA history, and coasted to their 4th championship of the decade. |
| + | John Stockton captured his ninth straight assist title, and became the all-time steals leader in NBA history. | ||
| + | A bit more surprising was Magic Johnson's announcement that he was coming out of retirement, although concerns from other players would scuttle the attempt. | ||
| + | The National Basketball Association went international with the birth of the Vancouver Grizzlies and the Toronto Raptors. | ||
| − | + | The Bulls went on to complete their three-peat in 1996-97 and 1997-98. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | The end of the decade saw a lockout by the owners to institute a salary cap, one that lasted 191 days. As a result, only 50 games were played in the 1998-99 season. The Spurs went 37-13 and beat the Knicks in five games in the finals in what many claim was an "asterisk" championship season. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===2000s: Lakers and Spurs Dominate=== | |
| − | + | The end of the 1990s and this decade thus far have been a stage for utter domination by two teams: the Los Angeles Lakers and the San Antonio Spurs. The Lakers sandwiched their three-peat in between Spurs' titles in 1999 and 2003. The Spurs have since won in 2005 and again in 2007. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The Lakers 2001 championship was marked by a historic 15-1 route in the NBA playoffs of the Spurs, Blazers, Kings, and Sixers. In fact, the Lakers were the only team in Playoff history to go unbeaten on the road. | |
| − | + | ==Ethnic Diversity== | |
| + | Worldwide, basketball tournaments are held for boys and girls of all age levels. The global popularity of the sport is reflected in the nationalities represented in the NBA. Players from all over the globe can be found in NBA teams. Steve Nash, who won the 2005 and 2006 NBA Most Valuable Player Award, is [[Canada|Canadian]]; Kobe Bryant is an [[United States|American]] who spent much of his childhood in [[Italy]]; Dallas Mavericks superstar and 2007 NBA MVP Dirk Nowitzki is [[Germany|German]]; All-Star Pau Gasol of the Memphis Grizzlies is from [[Spain]]; 2005 NBA Draft's top overall pick Andrew Bogut of the Milwaukee Bucks is Australian; 2006 NBA Draft's top overall pick Andrea Bargnani of the Toronto Raptors is from Italy; Houston Rockets Center Yao Ming is from [[China]]; Cleveland Cavaliers big man Zydrunas Ilgauskas is [[Lithuania]]n; and the San Antonio Spurs feature Tim Duncan of the [[United States Virgin Islands|U.S. Virgin Islands]], Manu Ginobili of [[Argentina]] (like Chicago Bulls player Andrés Nocioni) and Tony Parker of [[France]]. | ||
| + | The all-tournament teams at the two most recent FIBA World Championships, held in 2002 FIBA World Championship in [[Indianapolis, Indiana|Indianapolis]] and 2006 FIBA World Championship in [[Japan]], demonstrate the globalization of the game equally dramatically. Only one member of either team was American, namely Carmelo Anthony in 2006. The 2002 team featured Nowitzki, Ginobili, Predrag Stojaković of Yugoslavia, Yao Ming of [[China national basketball team|China]], and Pero Cameron of New Zealand. Ginobili also made the 2006 team; the other members were Anthony, Gasol, his [[Spain national basketball team|Spanish]] teammate Jorge Garbajosa and Theodoros Papaloukas of [[Greece national basketball team|Greece]]. The only players on either team to never have joined the NBA are Cameron and Papaloukas. The only Japanese NBA player is Kenny Nakazawa. | ||
| − | ==Teams== | + | ==30 Teams== |
| − | The National Basketball Association originated in 1946 with 11 teams | + | The National Basketball Association originated in 1946 with 11 teams. Through a sequence of team expansions, reductions, and relocations, the NBA currently consists of 30 teams. The United States is home to 29 teams and one is located in Canada (Toronto Raptors). The Boston Celtics have won the most championships, with 16 NBA Finals wins. The next most successful franchise is the Los Angeles Lakers, who have 14 championships. Following the Lakers are the Chicago Bulls with six championships, all of them won over an eight-year span during the 1990s. The San Antonio Spurs, who have won four championships since 1999, are the defending champions. |
| − | The current league organization divides the teams into two conferences. Each conference has three divisions, and each division has five teams. The current divisional alignment was introduced in the | + | The current league organization divides the teams into two conferences. Each conference has three divisions, and each division has five teams. The current divisional alignment was introduced in the 2004-05 NBA season. |
===Eastern Conference=== | ===Eastern Conference=== | ||
| Line 68: | Line 163: | ||
! width=10%|Founded | ! width=10%|Founded | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! rowspan="5" | | + | ! rowspan="5" | Atlantic Division |
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Boston Celtics''' |
| − | | | + | | Boston, Massachusetts |
| − | | Green and White | + | | Green and White |
| − | | | + | | TD Banknorth Garden |
| 1946 | | 1946 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''New Jersey Nets''' |
| − | | | + | | East Rutherford, New Jersey |
| Midnight Blue, Red, Silver | | Midnight Blue, Red, Silver | ||
| − | | | + | | Continental Airlines Arena |
| 1967* | | 1967* | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''New York Knicks''' |
| [[New York City|New York]], [[New York]] | | [[New York City|New York]], [[New York]] | ||
| Blue, Black, Orange | | Blue, Black, Orange | ||
| − | | | + | | Madison Square Garden |
| 1946 | | 1946 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Philadelphia 76ers''' |
| − | | | + | | Philadelphia, Pennsylvania |
| Black, Red, Gold, Blue | | Black, Red, Gold, Blue | ||
| − | | | + | | Wachovia Center |
| 1939* | | 1939* | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Toronto Raptors''' |
| − | | | + | | Toronto, Ontario |
| Purple,Red,Black,Silver,White | | Purple,Red,Black,Silver,White | ||
| − | | | + | | Air Canada Centre |
| 1995 | | 1995 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! rowspan="5" | | + | ! rowspan="5" | Central Division |
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Chicago Bulls''' |
| − | | | + | | Chicago, Illinois |
| Red, Black, White | | Red, Black, White | ||
| − | | | + | | United Center |
| 1966 | | 1966 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Cleveland Cavaliers''' |
| − | | | + | | Cleveland, Ohio |
| Wine, Gold, Navy Blue, White | | Wine, Gold, Navy Blue, White | ||
| − | | | + | | Quicken Loans Arena |
| 1970 | | 1970 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |''' | + | |'''Detroit Pistons''' |
| − | | | + | |Auburn Hills, Michigan |
| Blue, Red, White | | Blue, Red, White | ||
| − | | | + | | The Palace of Auburn Hills |
| 1941* | | 1941* | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Indiana Pacers''' |
| − | | | + | | Indianapolis, Indiana |
| Navy Blue, Gold, Gray | | Navy Blue, Gold, Gray | ||
| − | | | + | | Conseco Fieldhouse |
| 1967 | | 1967 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Milwaukee Bucks''' |
| − | | | + | | Milwaukee, Wisconsin |
| Green, Red, Silver | | Green, Red, Silver | ||
| − | | | + | | Bradley Center |
| 1968 | | 1968 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! rowspan="5" | | + | ! rowspan="5" | Southeast Division |
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Atlanta Hawks''' |
| − | | | + | | Atlanta, Georgia |
| Navy Blue, Red, Silver | | Navy Blue, Red, Silver | ||
| − | | | + | | Philips Arena |
| 1946* | | 1946* | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Charlotte Bobcats''' |
| − | | | + | | Charlotte, North Carolina |
| Orange, Blue, Black, Silver | | Orange, Blue, Black, Silver | ||
| − | | | + | | Charlotte Bobcats Arena |
| 2004 | | 2004 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Miami Heat''' |
| − | | | + | | Miami, Florida |
| Black, Red, White, Yellow | | Black, Red, White, Yellow | ||
| − | | | + | | AmericanAirlines Arena |
| 1988 | | 1988 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Orlando Magic''' |
| − | | | + | | Orlando, Florida |
| White, Blue, Black | | White, Blue, Black | ||
| − | | | + | | Amway Arena |
| 1989 | | 1989 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Washington Wizards''' |
| − | | | + | | Washington, D.C. |
| Blue, Black, Bronze | | Blue, Black, Bronze | ||
| − | | | + | | Verizon Center |
| 1961* | | 1961* | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 172: | Line 267: | ||
! width=10%|Founded | ! width=10%|Founded | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! rowspan="5" | | + | ! rowspan="5" | Southwest Division |
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Dallas Mavericks''' |
| − | | | + | | Dallas, Texas |
| Navy Blue, Royal Blue, Silver, Green | | Navy Blue, Royal Blue, Silver, Green | ||
| − | | | + | | American Airlines Center |
| 1980 | | 1980 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Houston Rockets''' |
| − | | | + | | Houston, Texas |
| Red, White, Silver, Black | | Red, White, Silver, Black | ||
| − | | | + | | Toyota Center |
| 1967* | | 1967* | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Memphis Grizzlies''' |
| − | | | + | | Memphis, Tennessee |
| Navy Blue, Light Blue, Smoke Blue, Gold | | Navy Blue, Light Blue, Smoke Blue, Gold | ||
| − | | | + | | FedExForum |
| 1995* | | 1995* | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''New Orleans Hornets''' |
| − | | | + | | New Orleans, Louisiana |
| Teal, Purple, Gold | | Teal, Purple, Gold | ||
| − | | | + | | New Orleans Arena |
| 1988* | | 1988* | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''San Antonio Spurs''' |
| − | | | + | | San Antonio, Texas |
| Black, Silver | | Black, Silver | ||
| − | | | + | | AT&T Center |
| 1967* | | 1967* | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! rowspan="5" | | + | ! rowspan="5" | Northwest Division |
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Denver Nuggets''' |
| − | | | + | | Denver, Colorado |
| Light Blue, Gold, Cobalt Blue | | Light Blue, Gold, Cobalt Blue | ||
| − | | | + | | Pepsi Center |
| 1967 | | 1967 | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Minnesota Timberwolves''' |
| − | | | + | | Minneapolis, Minnesota |
| Forest Green, Black, Tan, Green | | Forest Green, Black, Tan, Green | ||
| − | | | + | | Target Center |
| 1989 | | 1989 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Portland Trail Blazers''' |
| − | | | + | | Portland, Oregon |
| Black, Red, Silver | | Black, Red, Silver | ||
| − | | | + | | Rose Garden Arena |
| 1970 | | 1970 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Seattle SuperSonics''' |
| − | | | + | | Seattle, Washington |
| Green, Gold | | Green, Gold | ||
| − | | | + | | KeyArena |
| 1967 | | 1967 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Utah Jazz''' |
| − | | | + | | Salt Lake City, Utah |
| Navy Blue, Ice Blue, Silver | | Navy Blue, Ice Blue, Silver | ||
| − | | | + | | EnergySolutions Arena |
| 1974* | | 1974* | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! rowspan="5" | | + | ! rowspan="5" | Pacific Division |
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Golden State Warriors''' |
| − | | | + | | Oakland, California |
| Navy Blue, Orange, Gold | | Navy Blue, Orange, Gold | ||
| − | | | + | | Oracle Arena |
| 1946* | | 1946* | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Los Angeles Clippers''' |
| − | | | + | | Los Angeles, California |
| Red, Blue, White | | Red, Blue, White | ||
| − | | | + | | Staples Center |
| 1970* | | 1970* | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Los Angeles Lakers''' |
| − | | | + | | Los Angeles, California |
| Purple, Gold, White | | Purple, Gold, White | ||
| − | | | + | | Staples Center |
| 1946* | | 1946* | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Phoenix Suns''' |
| − | | | + | | Phoenix, Arizona |
| Purple, Orange, Gray | | Purple, Orange, Gray | ||
| − | | | + | | US Airways Center |
| 1968 | | 1968 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ''' | + | | '''Sacramento Kings''' |
| − | | | + | | Sacramento, California |
| Purple, Black, Silver, White, Gold | | Purple, Black, Silver, White, Gold | ||
| − | | | + | | ARCO Arena |
| 1945* | | 1945* | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 272: | Line 367: | ||
*''The [[Philadelphia 76ers|Syracuse Nationals]] and [[Atlanta Hawks|Tri-Cities Blackhawks]] joined the NBA in 1949 as part of the BAA-NBL merger.'' | *''The [[Philadelphia 76ers|Syracuse Nationals]] and [[Atlanta Hawks|Tri-Cities Blackhawks]] joined the NBA in 1949 as part of the BAA-NBL merger.'' | ||
*''The Indiana Pacers, [[New Jersey Nets|New York Nets]], San Antonio Spurs, and Denver Nuggets all joined the NBA in 1976 as part of the NBA-[[American Basketball Association|ABA]] merger.'' | *''The Indiana Pacers, [[New Jersey Nets|New York Nets]], San Antonio Spurs, and Denver Nuggets all joined the NBA in 1976 as part of the NBA-[[American Basketball Association|ABA]] merger.'' | ||
| − | *''Due to arena damages caused by [[Hurricane Katrina]], the New Orleans Hornets played most of their 2005-06 home schedule in Oklahoma City. They did the same for the 2006-07 season. | + | *''Due to arena damages caused by [[Hurricane Katrina]], the New Orleans Hornets played most of their 2005-06 home schedule in Oklahoma City. They did the same for the 2006-07 season. The NBA and the Hornets organization have announced that the team will be returning to New Orleans on a full-time basis for the upcoming 2007-08 season. The 2008 All Star game will be held in New Orleans as well.'' |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Regular season== | ==Regular season== | ||
| − | + | Training camp (begins in October) is a type of guess and check for the coaching staff to evaluate which players fit, which don't, and scout the team's strengths and weaknesses. After training camp, a series of preseason exhibition games are held. The NBA regular season begins in the first week of November. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | In the regular season, each team plays 82 games, which are divided evenly between home and away games. A team faces opponents in its own division four times a year, teams from the other two divisions in its conference either three or four times, and teams in the other conference twice apiece. A team can therefore have a relatively easy or difficult schedule, depending on the division and conference it is located in. [[Image:Bucks vs Bobcats - February 11th, 2006.jpg|thumb|left|Milwaukee Bucks playing the Charlotte Bobcats.]] | |
| − | + | ==All-Star Weekend== | |
| + | In February, the regular season is at its halfway point, the time to celebrate the annual National Basketball Association All-Star Game. Then, Eastern conference players face the Western conference players in the All-Star game. The player with the best performance during the game is rewarded with a Game MVP award. Other attractions of the All-Star break include the Rookie Challenge game, which pits the best rookies and the best second-year players against each other; the Skills Challenge, a competition between players to see who could complete an obstacle course comprising shooting, passing and dribbling in the fastest time; the Three Point Contest, a competition between players to see who is the best three-point shooter; and the NBA Slam Dunk Contest, to see which player dunks the ball in the most entertaining way. These other attractions have varying names which include the names of the various sponsors who have paid for naming rights. | ||
==Playoffs== | ==Playoffs== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Championship leaders== | ==Championship leaders== | ||
| Line 307: | Line 385: | ||
! Team !! Championships !! Winning years | ! Team !! Championships !! Winning years | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Boston Celtics || 16 || 1957, 1959, 1960, 1961, 1962, 1963, 1964, 1965, 1966, 1968, 1969, 1974, 1976, 1981, 1984, 1986 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Los Angeles Lakers|Minneapolis/Los Angeles Lakers || 14 || 1949, 1950, 1952, 1953, 1954, 1972, 1980, 1982, 1985, 1987, 1988, 2000, 2001, 2002 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Chicago Bulls || 6 || 1991, 1992, 1993, 1996, 1997, 1998 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | San Antonio Spurs || 4 || 1999, 2003, 2005, 2007 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Golden State Warriors|Philadelphia/Golden State Warriors || 3 || 1947, 1956, 1975 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Philadelphia 76ers|Syracuse Nationals/Philadelphia 76ers || 3 || 1955, 1967, 1983 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Detroit Pistons || 3 || 1989, 1990, 2004 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | New York Knicks || 2 || 1970, 1973 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Houston Rockets || 2 || 1994, 1995 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Baltimore Bullets (original) || 1 || 1948 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Sacramento Kings|Rochester Royals/Sacramento Kings || 1 || 1951 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Atlanta Hawks|St. Louis/Atlanta Hawks || 1 || 1958 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Milwaukee Bucks || 1 || 1971 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Portland Trail Blazers || 1 || 1977 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Washington Wizards|Washington Bullets/Wizards || 1 || 1978 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Seattle SuperSonics || 1 || 1979 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Miami Heat || 1 || 2006 |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Presidents and commissioners=== | ===Presidents and commissioners=== | ||
| − | * | + | *Maurice Podoloff, President from 1946 to 1963 |
| − | * | + | *Walter Kennedy, President from 1963 to 1967 and Commissioner from 1967 to 1975 |
| − | * | + | *Larry O'Brien, Commissioner from 1975 to 1984 |
| − | * | + | *David Stern, Commissioner since 1984 |
| − | == | + | ==Awards== |
| − | + | *NBA Most Valuable Player Award | |
| − | * | + | *NBA Finals Most Valuable Player Award |
| − | ** | + | *NBA Rookie of the Year Award |
| + | *NBA Most Improved Player Award | ||
| + | *NBA Defensive Player of the Year Award | ||
| + | *NBA Sixth Man of the Year Award | ||
| + | *NBA Coach of the Year Award | ||
| + | *All-NBA Team | ||
| + | *NBA All-Defensive Team | ||
| + | *J. Walter Kennedy Citizenship Award | ||
| − | === | + | ==Notes== |
| − | + | <references/> | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==References== |
| − | * | + | *Bradley, Bill. ''Values of the Game''. New York, New York: Artisan (A Division of Workman Publishing Company, Inc.), 1998. ISBN 1-57965-116-X |
| − | + | *Kirchberg, Connie. ''Hoop lore: a history of the National Basketball Association''. Jefferson, N.C.: McFarland, 2007. ISBN 9780786426737 | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Ominsky, Dave, and P.J. Harari. ''Basketball Made Simple, A Spectator's Guide''. Los Angeles, California: First Base Sports, Inc., 1994. ISBN 1-884309-07-0 | |
| − | * | + | *[http://www.nba.com National Basketball Association Home] Retrieved April 22, 2008. |
| − | + | *NBA.com [http://www.nba.com/history/season/index.html NBA History] Retrieved April 22, 2008. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==External links== |
| − | + | All links retrieved November 10, 2022. | |
| − | + | *[http://www.nba.com NBA.com] Official Site | |
| − | *[http://www.nba.com NBA.com] Official | ||
| − | |||
*[http://www.nbpa.com National Basketball Players Association] | *[http://www.nbpa.com National Basketball Players Association] | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{NBA}} | {{NBA}} | ||
{{bb start}} | {{bb start}} | ||
| Line 408: | Line 461: | ||
{{Prohoops}} | {{Prohoops}} | ||
{{bb end}} | {{bb end}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | [[Category:Art, music, literature, sports and leisure]] |
{{credits|National_Basketball_Association|140797337}} | {{credits|National_Basketball_Association|140797337}} | ||
Latest revision as of 01:38, 11 November 2022
The National Basketball Association (NBA) is the world's premier men's basketball league. It has 30 teams; 29 in the United States and 1 in Canada. It is an active member[1] of USA Basketball, which is recognized by the International Basketball Federation as the National Governing Body (NGB) for basketball in the United States. The league was founded in New York City, on June 6, 1946 as the Basketball Association of America (BAA). The league adopted the name National Basketball Association in the Autumn of 1949 after merging with the rival National Basketball League (United States). The league's several international and individual team offices are directed out of its head offices located in the Olympic Tower (New York) at 645 Fifth Avenue in New York City. The NBA represents the highest level of competition in the world of basketball. It has grown in international popularity as the best players of the world have joined America's top players.
History
1940s: BAA & NBL merge to include 17 teams
Madison Square Garden in New York City played an instrumental role in the formation of the Basketball Association of America (BAA). On November 1, 1946, the Toronto Huskies hosted the New York Knickerbockers, which the NBA now regards as the first game played in the league's history.[2]
1946-47
In the first season of the BAA, a new professional star emerged, one who had gained little notoriety in college. Joe Fulks, a 6-5 forward from Kentucky, averaged 23.2 ppg, an astonishing amount considering most games were won by teams scoring in the 70s and 80s and nearly seven points per game more than any other player in the league. Field goal percentages were in the 30 percent range, and Ernest Calverley of the Providence Steamrollers led the league with 3.4 assists per game. Other stars in the fledgling league were Washington's Bob Feerick and Bones McKinney, Detroit's Stan Miasek and Chicago's Max Zaslofsky.
The 60-game regular season title belonged to the Washington Capitols, coached by Red Auerbach with a 49-11 record, including a 29-1 mark at home. But in the Playoffs, Chicago shocked the Capitols behind the play of Max Zaslofsky and center Chuck Halbert to advance to the Finals. Philadelphia, coached by Eddie Gottlieb, who had the most extensive pro background of anyone in the BAA, defeated St. Louis and New York to advance to the Finals. Fulks, Howie Dallmar and Angelo Musi led Philadelphia past Chicago as the Warriors won the first league title 4-1 (four games to one). The first year of the BAA was no indication of what was to come, as television was still a thing of the future and games on radio were not universal.
As the end of the 1940s approached, the 60 game BAA schedule was reduced to 48 games. Of the 11 teams original teams, four of them folded, and the Baltimore Bullets were brought in to make it an even 8 teams and balance the number of teams. To everyone's surprise, the Bullets won the title in 1947 in six games as an expansion team.
Although basketball didn't begin until mid-decade in the ‘40s, it was quickly known for its physical style of play. One of the players, Buddy Jeanette of the Bullets said, "I remember in the last game with Philly, George Senesky hit me in the mouth and split my lip open." "Right after the game I had to go get my mouth sewed up. Then we went out and had a few beers."
1948-49: The Year of the Center
When George Mikan stepped foot on the basketball court, he completely changed the way the game was played. For the first time, a dominant center playing with his back to the basket became the cornerstone of a team. He took the league by storm, and led his Minneapolis Lakers to the first of their five titles by beating the 1st seeded Baltimore Bullets in six games.
On August 3, 1949, the BAA agreed to merge with the National Basketball League, creating the National Basketball Association, with seventeen franchises located in a mix of large and small cities, as well as large arenas and smaller gymnasiums.
1950s:24-second shot clock introduced
This decade began with a three division bracket (Eastern, Western, and Central Division) and a total of 17 teams. Mikan's Lakers won again to win back to back titles, and were clearly head and shoulders above the rest of the teams in the league.
1950-51
This season marked the introduction of the first black player to be given a contract to play in the NBA. Nat "Sweetwater" Clifton, Chuck Cooper, and Early Lloyd opened the doors for African-American players to enter the NBA.
1952-54
1952 marked the emergence of young talents Paul Arizin and Bob Cousy, and the extension of the lane from six feet to twelve feet. This period marked a three-peat for the Minneapolis Lakers, making it five championships in the league's first six years.
In the 1954-55 season, Danny Biasone came up with the idea of the shot clock to prevent teams from stalling after building a large lead. This increased scoring (from 79 points to 93 points per game) drastically and increased the pace of the game.
The Boston Celtics had been waiting in the Lakers shadows, and with the arrival of rookie center Bill Russell, their time had come. The 1956-57 NBA Finals was one for the ages, as the Celtics earned their first NBA title in a dramatic, double OT victory over the St. Louis Hawks. Their big men, Russell and Tom Heinsohn produced monster games: 19 points and 32 rebounds for Russell, and 37 points and 23 rebounds for Heinsohn. They would go on to win 11 titles in 13 years and become the greatest sports dynasty in United States history.
The 1957-58 seasons marked a break from Celtic brass, and brought glory to explosive scorer Bob Petit, who scored 50 points in the clinching Game 6 of the NBA finals, leading the St. Louis Hawks to victory against the Celtics.
The end of the '50s brought Laker great Elgin Baylor onto the scene. After several losing seasons following Mikan's retirement, Baylor brought the Lakers back to the playoffs, and eventually to the NBA finals, where they would be swept by the Celtics. The Celtics would go on to win eight straight titles and separate themselves from the other great teams in NBA history.
1960s: Boston Dominance
Wilt Chamberlain entered the NBA with a bang. He captured the Rookie of the Year and the Most Valuable Player in the same year with astounding numbers: 37.6 ppg and 27 rebounds per game. This, however, was not enough to stop the Russell lead Celtics, as they easily disposed of Chamberlain and the Warriors. Once again, the Celtics captured the title.
The NBA was not short on excitement, but with the arrival of young stars Oscar Robertson and Jerry West, the NBA was throbbing with excitement and highlight-reel plays.
1961-62
This season was the stuff of legends and folklore that would be passed down from generation to generation. As if what Wilt did in his first few seasons was mere child's play, what he did in his third season will likely never be duplicated. Chamberlain, who played all but eight possible minutes of the entire season and averaged 48.5 minutes per game, averaged 50.4 points per game, a full 12 points more than his NBA record set the year before. On March 2, 1962, Chamberlain scored 100 points against the New York Knicks in Hershey, PA in a 169-147 triumph. Although 4,124 were in attendance, many thousands more would claim to have been there for decades afterward. The end result was still the same; Wilt lead the league in scoring, and the Celtics added one more title to their dynasty.
1964-65
In an effort to lessen the dominance of big men and keep the game open and moving, the NBA widened the foul lane from 12 to 16 feet. A major trade that took place at the NBA All-Star break would have far-reaching implications for years to come. Wilt Chamberlain, in the midst of his greatness at 28 years old, was dealt by the San Francisco Warriors to the Philadelphia 76ers for Paul Neumann, Connie Dierking, Lee Shaffer and cash. The immediate results: San Francisco went from 48-32 the season before to 17-63, while Philadelphia improved slightly, from 34-46 to 40-40. More importantly, Chamberlain was back in the same division as the Celtics, and would have to be dealt with even before the NBA Finals.
After trailing the Lakers for the majority of the series in Red Auerbach's last season as coach, the Celtics sent him off a winner with their eighth consecutive title.
1966-67
In this magical season, the Wilt Chamberlain-led Sixers posted the (then) best record in league history with 68 wins and 13 losses. Bill Russell was chosen as Red Auerbach's successor, becoming the first ever African-American coach in the NBA. The Sixers demolished the Celtics and Russell in five games (4-1), and went on to win the NBA title in an almost flawless season. Celtics player, K.C. Jones, put it best: "They're playing the same game we've played for the last nine years. In other words, team ball."
In 1967, the league faced a new external threat with the formation of the American Basketball Association. The leagues engaged in a bidding war for talent. The NBA landed the most important college star of the era, Kareem Abdul-Jabbar (then known as Lew Alcindor), who together with Oscar Robertson led the Milwaukee Bucks to a title in his second season, and who later played on five Los Angeles Lakers' championship teams.
In 1968, the Celtics were predicted to crumble due to age. They fell behind 3-1 in the Eastern Conference finals to Wilt's Sixers, but overcame the deficit and won the NBA title with a seventh game victory over the Lakers on the Lakers' home court. After a one-year hiatus, they were back at the top.
Wilt Chamberlain was again traded. In 1969, the Lakers acquired Wilt's rights for Jerry Chambers, Archie Clark and Darrall Imhoff prior to the beginning of the season. Wilt or no Wilt, it made no difference to the Celtics. They escaped again with a two point game seven win in Los Angeles when Don Nelson's shot careened high off the rim and through the hoop, marking the 11th title in 13 seasons as the sun set on the 1960's.
Through this period, the NBA continued to expand its scope with the shift of the Minneapolis Lakers to Los Angeles, the Philadelphia Warriors to San Francisco, and the Syracuse Nationals to Philadelphia, as well as the addition of its first expansion franchises.
1970s- NBA-A New Era
The 1969-70 year presented many new opportunities, largely because Bill Russell, the Celtic coach and defensive juggernaut, retired from his position as a player/coach. A rejuvenated New York Knicks team, led by Walt Frazier, Willis Reed, and Bill Bradley defeated the Lakers in game seven of the NBA Finals, to capture their first title.
1970-71: From the Sky
Kareem Abdul Jabbar's sky hook was the most dangerous weapon in the NBA. His talent, along with Oscar Robertson, allowed the Milwaukee Bucks to surge to only the second NBA Finals sweep in history.
1971-72: Resurrection
After years and years of getting to the Finals and being turned back by the Celtics, the Lakers put together a streak that still stands: 33 straight victories, en route to a 69-13 record (then the best record in NBA history).
While the Knicks regained their championship form in 1972-73, it was 6 foot guard, Nate Archibald, that stole the show, and the passion of the fans. The Cincinnati Royals failed to make the playoffs but Archibald led the league in both scoring and assists, with 34 ppg and an astounding 11.4 assists, a feat that has yet to be repeated.
In 1973-74, the old stars were about to set. Wilt Chamberlain, Jerry West, Oscar Robertson, and Willis Reed were all playing in their final season. The Celtics teams benefited the most from this, as they once again rose to the top to win championship number 12.
The 1974-75 season was a return to dominance for the Baltimore Bullets, and surprising success for the Golden State Warriors. Led by star Rick Barry, they shocked the Bullets 4-0, only the third sweep in NBA finals history. After the series, Barry said, "It has to be the greatest upset in the history of the NBA Finals. It was like a fairy-tale season. Everything just fell into place. It's something I'll treasure for the rest of my life."
After six straight losing seasons, a healthy Bill Walton and the Blazers shocked the world as they defeated the 76ers to win their first championship.
The transfer of Dr.J from the ABA to the NBA, and thereafter the trade that sent him to Philadelphia had great ramifications. Julius Erving electrified the NBA with hair-raising dunks, particularly the "tomahawk," en route to leading his team to the NBA finals against Portland.
The National Basketball Association adapted the ABA's innovative three-point field goal beginning in 1979 to create spacing of all ten players on the court. That same year, rookies Larry Bird and Magic Johnson joined the Boston Celtics and Los Angeles Lakers respectively, continuing a rivalry that began when the two played in the 1979 NCAA Basketball Finals, sparking a period of significant growth in fan interest in the NBA throughout the country and the world. Bird went on to lead the Celtics to three NBA titles, while Johnson led the Lakers to five.
1980s: Lakers Dynasty
Earvin "Magic" Johnson was absolutely magical in the 1979-80 season. Lakers' stars Magic and Kareem shouldered the load and dominated in the NBA Finals against Dr. J's 76ers. Game 6 was a classic. The rookie point guard Magic Johnson started at center for the injured Kareem Abdul-Jabaar and turned in the game of his life: 42 points, 15 rebounds, and 7 assists, while playing at every position during the game.
Not surprisingly, the very next season, the Celtics countered with a title of their own, the first of the Larry Bird, Robert Parish and Kevin McHale era.
In the 1981-82 season, the Lakers and the 76ers faced off again, as the Lakers prevailed for the second straight time against the 76ers, to win the second title of the 1980s.
"Fo-Fi-Fo"
The famous prediction Moses Malone made when signing with the 76ers almost came true. "Fo-Fo-Fo" indicated a sweep of every team, but they ended up going 12-1 in the playoffs, hence, "Fo-Fi-Fo." While the 1960s were dominated by Celtics-Lakers NBA Finals, three of the first four years of the 1980s saw Lakers-Sixers NBA Finals.
Larry Bird and the Celtics won their second title of the decade in 1983-84 against Magic's Lakers. It took them seven games to do it, and after the series, Larry Bird said, "To be honest, they should have swept."
1984-85 Lakers Finally Put Garden Leprechaun to Sleep
Magic and Kareem finally accomplished what no other Laker great could before. In fact, they did what only Bob Petit's St. Louis Hawks had done in 1958 by beating the Celtics at the Garden.
A Draft Like No Other
The 1984 draft is arguably the deepest draft in NBA history. It has produced future Hall of Famers Hakeem Olajuwon, Michael Jordan, Charles Barkley, and John Stockton.
The 1985-1986 season continued the trend of Lakers/Celtics domination. After the Lakers earned their third title of the decade, Larry Bird was intent on doing the same for his Celtics, winning back to back MVP awards and leading the Celtics to the best record in franchise history, 67-15, and a stellar 40-1 home record. Title number 16 was brought to Boston after Bird and company dispatched the Rockets in six games.
Showtime
In 1986-87, the Lakers had entered the phase in their franchise's history that would always be remembered as "Showtime." The Lakers coasted to their fourth title of the decade. During the championship celebration, coach Pat Riley made a daring statement guaranteeing a repeat. It took them seven games against the Detroit Pistons, but that is just what they did, making them only the second team in NBA history (Boston Celtics) to accomplish the feat. Somewhat overshadowed in their loss, Isaiah Thomas's third quarter in the deciding game will never be forgotten. On a sprained ankle, Thomas scored 25 points in the third quarter to give the Pistons a chance to win. The Pistons finally beat the Lakers, sweeping them in 1988-89 to close out the decade.
1990s: The Years of the Bull
The 1990s opened up with the Detroit Pistons posting the second straight repeat (Lakers 1986-87,1987-88).
The 1991 NBA Finals was billed as a matchup between two larger-than-life superstars, Michael Jordan and Magic Johnson. But as the series played out, it became obvious that it took a team, not one superlative individual, to win an NBA Championship. Jordan was superb, as his series averages of 31.2 points, 11.4 assists and 6.6 rebounds demonstrated, but the Bulls were no one-man team. Their defense held the Lakers to a record-low 458 points for a five-game series. Jordan, who had won his fifth straight scoring title in April, had finally silenced those who said he couldn't lead the Bulls all the way.
The next season proved to be Larry Bird's last. Coupled with Magic's shocking revelation that he had contracted the HIV virus, Jordan's way had been opened up. The Jordan-led Bulls put their stamp on the 1990s decade by winning six titles, and more astoundingly, two three-peats.
1993-94
Michael Jordan shocked the NBA world by announcing his retirement at the peak of his career. More shocking news was yet to come, however, as the 63-win Seattle Supersonics were toppled by the number eight seeded Denver Nuggets, in the first round of the playoffs. The Houston Rockets would go on to beat the New York Knicks in seven to win the first of their back-to-back titles.
1995-96 72-10: The Bulls Dominate
The Chicago Bulls returned to dominance with the return of their star, Michael Jordan. In fact, they posted the best record in NBA history, and coasted to their 4th championship of the decade. John Stockton captured his ninth straight assist title, and became the all-time steals leader in NBA history. A bit more surprising was Magic Johnson's announcement that he was coming out of retirement, although concerns from other players would scuttle the attempt. The National Basketball Association went international with the birth of the Vancouver Grizzlies and the Toronto Raptors.
The Bulls went on to complete their three-peat in 1996-97 and 1997-98.
The end of the decade saw a lockout by the owners to institute a salary cap, one that lasted 191 days. As a result, only 50 games were played in the 1998-99 season. The Spurs went 37-13 and beat the Knicks in five games in the finals in what many claim was an "asterisk" championship season.
2000s: Lakers and Spurs Dominate
The end of the 1990s and this decade thus far have been a stage for utter domination by two teams: the Los Angeles Lakers and the San Antonio Spurs. The Lakers sandwiched their three-peat in between Spurs' titles in 1999 and 2003. The Spurs have since won in 2005 and again in 2007.
The Lakers 2001 championship was marked by a historic 15-1 route in the NBA playoffs of the Spurs, Blazers, Kings, and Sixers. In fact, the Lakers were the only team in Playoff history to go unbeaten on the road.
Ethnic Diversity
Worldwide, basketball tournaments are held for boys and girls of all age levels. The global popularity of the sport is reflected in the nationalities represented in the NBA. Players from all over the globe can be found in NBA teams. Steve Nash, who won the 2005 and 2006 NBA Most Valuable Player Award, is Canadian; Kobe Bryant is an American who spent much of his childhood in Italy; Dallas Mavericks superstar and 2007 NBA MVP Dirk Nowitzki is German; All-Star Pau Gasol of the Memphis Grizzlies is from Spain; 2005 NBA Draft's top overall pick Andrew Bogut of the Milwaukee Bucks is Australian; 2006 NBA Draft's top overall pick Andrea Bargnani of the Toronto Raptors is from Italy; Houston Rockets Center Yao Ming is from China; Cleveland Cavaliers big man Zydrunas Ilgauskas is Lithuanian; and the San Antonio Spurs feature Tim Duncan of the U.S. Virgin Islands, Manu Ginobili of Argentina (like Chicago Bulls player Andrés Nocioni) and Tony Parker of France. The all-tournament teams at the two most recent FIBA World Championships, held in 2002 FIBA World Championship in Indianapolis and 2006 FIBA World Championship in Japan, demonstrate the globalization of the game equally dramatically. Only one member of either team was American, namely Carmelo Anthony in 2006. The 2002 team featured Nowitzki, Ginobili, Predrag Stojaković of Yugoslavia, Yao Ming of China, and Pero Cameron of New Zealand. Ginobili also made the 2006 team; the other members were Anthony, Gasol, his Spanish teammate Jorge Garbajosa and Theodoros Papaloukas of Greece. The only players on either team to never have joined the NBA are Cameron and Papaloukas. The only Japanese NBA player is Kenny Nakazawa.
30 Teams
The National Basketball Association originated in 1946 with 11 teams. Through a sequence of team expansions, reductions, and relocations, the NBA currently consists of 30 teams. The United States is home to 29 teams and one is located in Canada (Toronto Raptors). The Boston Celtics have won the most championships, with 16 NBA Finals wins. The next most successful franchise is the Los Angeles Lakers, who have 14 championships. Following the Lakers are the Chicago Bulls with six championships, all of them won over an eight-year span during the 1990s. The San Antonio Spurs, who have won four championships since 1999, are the defending champions.
The current league organization divides the teams into two conferences. Each conference has three divisions, and each division has five teams. The current divisional alignment was introduced in the 2004-05 NBA season.
Eastern Conference
| Division | Team | City | Colors | Arena | Founded |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atlantic Division | Boston Celtics | Boston, Massachusetts | Green and White | TD Banknorth Garden | 1946 |
| New Jersey Nets | East Rutherford, New Jersey | Midnight Blue, Red, Silver | Continental Airlines Arena | 1967* | |
| New York Knicks | New York, New York | Blue, Black, Orange | Madison Square Garden | 1946 | |
| Philadelphia 76ers | Philadelphia, Pennsylvania | Black, Red, Gold, Blue | Wachovia Center | 1939* | |
| Toronto Raptors | Toronto, Ontario | Purple,Red,Black,Silver,White | Air Canada Centre | 1995 | |
| Central Division | Chicago Bulls | Chicago, Illinois | Red, Black, White | United Center | 1966 |
| Cleveland Cavaliers | Cleveland, Ohio | Wine, Gold, Navy Blue, White | Quicken Loans Arena | 1970 | |
| Detroit Pistons | Auburn Hills, Michigan | Blue, Red, White | The Palace of Auburn Hills | 1941* | |
| Indiana Pacers | Indianapolis, Indiana | Navy Blue, Gold, Gray | Conseco Fieldhouse | 1967 | |
| Milwaukee Bucks | Milwaukee, Wisconsin | Green, Red, Silver | Bradley Center | 1968 | |
| Southeast Division | Atlanta Hawks | Atlanta, Georgia | Navy Blue, Red, Silver | Philips Arena | 1946* |
| Charlotte Bobcats | Charlotte, North Carolina | Orange, Blue, Black, Silver | Charlotte Bobcats Arena | 2004 | |
| Miami Heat | Miami, Florida | Black, Red, White, Yellow | AmericanAirlines Arena | 1988 | |
| Orlando Magic | Orlando, Florida | White, Blue, Black | Amway Arena | 1989 | |
| Washington Wizards | Washington, D.C. | Blue, Black, Bronze | Verizon Center | 1961* |
Western Conference
| Division | Team | City | Colors | Arena | Founded |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Southwest Division | Dallas Mavericks | Dallas, Texas | Navy Blue, Royal Blue, Silver, Green | American Airlines Center | 1980 |
| Houston Rockets | Houston, Texas | Red, White, Silver, Black | Toyota Center | 1967* | |
| Memphis Grizzlies | Memphis, Tennessee | Navy Blue, Light Blue, Smoke Blue, Gold | FedExForum | 1995* | |
| New Orleans Hornets | New Orleans, Louisiana | Teal, Purple, Gold | New Orleans Arena | 1988* | |
| San Antonio Spurs | San Antonio, Texas | Black, Silver | AT&T Center | 1967* | |
| Northwest Division | Denver Nuggets | Denver, Colorado | Light Blue, Gold, Cobalt Blue | Pepsi Center | 1967 |
| Minnesota Timberwolves | Minneapolis, Minnesota | Forest Green, Black, Tan, Green | Target Center | 1989 | |
| Portland Trail Blazers | Portland, Oregon | Black, Red, Silver | Rose Garden Arena | 1970 | |
| Seattle SuperSonics | Seattle, Washington | Green, Gold | KeyArena | 1967 | |
| Utah Jazz | Salt Lake City, Utah | Navy Blue, Ice Blue, Silver | EnergySolutions Arena | 1974* | |
| Pacific Division | Golden State Warriors | Oakland, California | Navy Blue, Orange, Gold | Oracle Arena | 1946* |
| Los Angeles Clippers | Los Angeles, California | Red, Blue, White | Staples Center | 1970* | |
| Los Angeles Lakers | Los Angeles, California | Purple, Gold, White | Staples Center | 1946* | |
| Phoenix Suns | Phoenix, Arizona | Purple, Orange, Gray | US Airways Center | 1968 | |
| Sacramento Kings | Sacramento, California | Purple, Black, Silver, White, Gold | ARCO Arena | 1945* |
Notes:
- An asterisk (*) denotes a franchise move. See the respective team articles for more information.
- The Fort Wayne Pistons, Minneapolis Lakers and Rochester Royals all joined the NBA (BAA) in 1948 from the NBL.
- The Syracuse Nationals and Tri-Cities Blackhawks joined the NBA in 1949 as part of the BAA-NBL merger.
- The Indiana Pacers, New York Nets, San Antonio Spurs, and Denver Nuggets all joined the NBA in 1976 as part of the NBA-ABA merger.
- Due to arena damages caused by Hurricane Katrina, the New Orleans Hornets played most of their 2005-06 home schedule in Oklahoma City. They did the same for the 2006-07 season. The NBA and the Hornets organization have announced that the team will be returning to New Orleans on a full-time basis for the upcoming 2007-08 season. The 2008 All Star game will be held in New Orleans as well.
Regular season
Training camp (begins in October) is a type of guess and check for the coaching staff to evaluate which players fit, which don't, and scout the team's strengths and weaknesses. After training camp, a series of preseason exhibition games are held. The NBA regular season begins in the first week of November.
In the regular season, each team plays 82 games, which are divided evenly between home and away games. A team faces opponents in its own division four times a year, teams from the other two divisions in its conference either three or four times, and teams in the other conference twice apiece. A team can therefore have a relatively easy or difficult schedule, depending on the division and conference it is located in.
All-Star Weekend
In February, the regular season is at its halfway point, the time to celebrate the annual National Basketball Association All-Star Game. Then, Eastern conference players face the Western conference players in the All-Star game. The player with the best performance during the game is rewarded with a Game MVP award. Other attractions of the All-Star break include the Rookie Challenge game, which pits the best rookies and the best second-year players against each other; the Skills Challenge, a competition between players to see who could complete an obstacle course comprising shooting, passing and dribbling in the fastest time; the Three Point Contest, a competition between players to see who is the best three-point shooter; and the NBA Slam Dunk Contest, to see which player dunks the ball in the most entertaining way. These other attractions have varying names which include the names of the various sponsors who have paid for naming rights.
Playoffs
Championship leaders
| Team | Championships | Winning years |
|---|---|---|
| Boston Celtics | 16 | 1957, 1959, 1960, 1961, 1962, 1963, 1964, 1965, 1966, 1968, 1969, 1974, 1976, 1981, 1984, 1986 |
| Minneapolis/Los Angeles Lakers | 14 | 1949, 1950, 1952, 1953, 1954, 1972, 1980, 1982, 1985, 1987, 1988, 2000, 2001, 2002 |
| Chicago Bulls | 6 | 1991, 1992, 1993, 1996, 1997, 1998 |
| San Antonio Spurs | 4 | 1999, 2003, 2005, 2007 |
| Philadelphia/Golden State Warriors | 3 | 1947, 1956, 1975 |
| Syracuse Nationals/Philadelphia 76ers | 3 | 1955, 1967, 1983 |
| Detroit Pistons | 3 | 1989, 1990, 2004 |
| New York Knicks | 2 | 1970, 1973 |
| Houston Rockets | 2 | 1994, 1995 |
| Baltimore Bullets (original) | 1 | 1948 |
| Rochester Royals/Sacramento Kings | 1 | 1951 |
| St. Louis/Atlanta Hawks | 1 | 1958 |
| Milwaukee Bucks | 1 | 1971 |
| Portland Trail Blazers | 1 | 1977 |
| Washington Bullets/Wizards | 1 | 1978 |
| Seattle SuperSonics | 1 | 1979 |
| Miami Heat | 1 | 2006 |
Presidents and commissioners
- Maurice Podoloff, President from 1946 to 1963
- Walter Kennedy, President from 1963 to 1967 and Commissioner from 1967 to 1975
- Larry O'Brien, Commissioner from 1975 to 1984
- David Stern, Commissioner since 1984
Awards
- NBA Most Valuable Player Award
- NBA Finals Most Valuable Player Award
- NBA Rookie of the Year Award
- NBA Most Improved Player Award
- NBA Defensive Player of the Year Award
- NBA Sixth Man of the Year Award
- NBA Coach of the Year Award
- All-NBA Team
- NBA All-Defensive Team
- J. Walter Kennedy Citizenship Award
Notes
- ↑ USA Basketball Retrieved April 22, 2008.
- ↑ History of Basketball in Canada NBA Media Ventures, LLC. Retrieved April 13, 2007.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Bradley, Bill. Values of the Game. New York, New York: Artisan (A Division of Workman Publishing Company, Inc.), 1998. ISBN 1-57965-116-X
- Kirchberg, Connie. Hoop lore: a history of the National Basketball Association. Jefferson, N.C.: McFarland, 2007. ISBN 9780786426737
- Ominsky, Dave, and P.J. Harari. Basketball Made Simple, A Spectator's Guide. Los Angeles, California: First Base Sports, Inc., 1994. ISBN 1-884309-07-0
- National Basketball Association Home Retrieved April 22, 2008.
- NBA.com NBA History Retrieved April 22, 2008.
External links
All links retrieved November 10, 2022.
- NBA.com Official Site
- National Basketball Players Association
| National Basketball Association (2007-08) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western Conference | Eastern Conference | ||||
| Northwest | Pacific | Southwest | Atlantic | Central | Southeast |
| Denver Nuggets | Golden State Warriors | Dallas Mavericks | Boston Celtics | Chicago Bulls | Atlanta Hawks |
| Minnesota Timberwolves | Los Angeles Clippers | Houston Rockets | New Jersey Nets | Cleveland Cavaliers | Charlotte Bobcats |
| Portland Trail Blazers | Los Angeles Lakers | Memphis Grizzlies | New York Knicks | Detroit Pistons | Miami Heat |
| Seattle SuperSonics | Phoenix Suns | New Orleans Hornets | Philadelphia 76ers | Indiana Pacers | Orlando Magic |
| Utah Jazz | Sacramento Kings | San Antonio Spurs | Toronto Raptors | Milwaukee Bucks | Washington Wizards |
| Miscellaneous | |||||
| Annual events: Playoffs - Finals - All-Star Game - All-Star Weekend - Rookie Challenge - Three-point Shootout - Skills Challenge - Shooting Stars Competition - Slam Dunk Contest - Draft | |||||
| Other: Current team rosters - Midwest Division - Dress code - Salary Cap - Arenas - D-League - WNBA - WNBA Finals - Europe Live Tour - Larry O'Brien Trophy - Finals MVP - 50 Greatest Players | |||||
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||
| |||||||
| |||||||
| |||||||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.