Difference between revisions of "Lake Huron" - New World Encyclopedia
({{Contracted}}) |
Betsy Brooks (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
Lake Huron was generally labeled "Lac des Hurons" (Lake of the Huron Indians) on most early maps. | Lake Huron was generally labeled "Lac des Hurons" (Lake of the Huron Indians) on most early maps. | ||
| − | + | ////Shipwrecks | |
| + | First Nations | ||
| + | Salt mining | ||
| + | Agriculture | ||
| + | de Champlain//// | ||
please expand this section | please expand this section | ||
Revision as of 03:00, 4 July 2007
| Huron | |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | |
| Lake type | Glacial |
| Primary sources | St. Marys River |
| Primary outflows | St. Clair River |
| Basin countries | Canada, USA |
| Max length | 332 km |
| Max width | 245 km |
| Surface area | 23,010 square miles (59,596 km²)[1] |
| Average depth | 59 m |
| Max depth | 750 feet (229 m)[1] |
| Water volume | 3,540 km³ |
| Residence time (of lake water) | 22 years |
| Shore length1 | 6,157 km |
| Surface elevation | 577 feet (176 m)[1] |
| Islands | Manitoulin |
| Settlements | Bay City, Michigan Alpena, Michigan Cheboygan, Michigan St. Ignace, Michigan Port Huron, Michigan Goderich, Ontario Sarnia, Ontario |
| 1 Shore length is an imprecise measure which may not be standardized for this article. | |
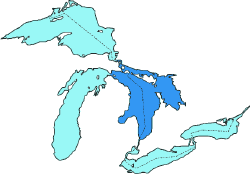
Lake Huron, bounded on the west by Michigan, USA, and on the east by Ontario, Canada, is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. The name of the lake is derived from early French explorers who named it based on the Huron people inhabiting the region.
History
Since its French discoverers knew nothing as yet of the other lakes, they called it La Mer Douce, the sweet or fresh-water sea. A Sanson map in 1656 refers to the lake as Karegnondi.
Lake Huron was generally labeled "Lac des Hurons" (Lake of the Huron Indians) on most early maps. ////Shipwrecks First Nations Salt mining Agriculture de Champlain////
please expand this section
Geography
Lake Huron (45°00′N 83°00′W) is the second-largest of the Great Lakes, with a surface area of 23,010 square miles (59,596 km²)—nearly the size of West Virginia, making it the third largest fresh water lake on earth (4th largest lake if you include the saline Caspian Sea). It contains a volume of 850 cubic miles (3,540 km³), and a shoreline length of 3,827 miles (6,157 km).
The surface of Lake Huron is 577 feet (176 m) above sea level. The lake's average depth is 195 feet (59 m), while the maximum depth is 750 feet (229 m). It has a length of 206 miles (332 km) and a breadth of 183 miles (245 km).
Major cities on Lake Huron include: Bay City, Michigan; Alpena, Michigan; Cheboygan, Michigan; St. Ignace, Michigan; Port Huron, Michigan; Goderich, Ontario; and Sarnia, Ontario.
A notable feature of the lake is Manitoulin Island, which separates the North Channel and Georgian Bay from Lake Huron's main body of water. It is the world's largest lake island.
Geology
Lake Huron is separated from Lake Michigan, which lies at the same level, and connects by the narrow Straits of Mackinac, making them geologically and hydrologically the same body of water (sometimes called Lake Michigan-Huron). Lake Superior is slightly higher than both. It drains into the St. Marys River at Sault Ste. Marie which then flows southward into Lake Huron. The water then flows south to the St. Clair River, at Port Huron, Michigan and Sarnia, Ontario.
The Great Lakes Waterway continues thence to Lake St. Clair; the Detroit River and Detroit, Michigan; into Lake Erie and thence—via Lake Ontario and the St. Lawrence River—to the Atlantic Ocean.
Like the other Great Lakes, it was formed by melting ice as the continental glaciers retreated.
Ecology
Lake Huron has a lake retention time of 22 years.
Major industries that drain into Lake Huron include: iron and steel mills, automobile manufacturing, heavy machinery, paper mills, metalworking, and shipbuilding.
See also
- Georgian Bay
- Saginaw Bay
- Mackinac Island
- Thunder Bay
- Les Cheneaux Islands
- Drummond Island
- Sauble Beach
- Wasaga Beach
- Hurricane Huron
- Great Lakes Areas of Concern
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Wright, John W. (ed.) and Editors and reporters of The New York Times (2006). The New York Times Almanac, 2007, New York, New York: Penguin Books, 64. ISBN 0-14-303820-6.
Sources and Further Reading
- Armbruster, Ann. 1996. Lake Huron. A true book. New York: Children's Press. ISBN 0516200127 and ISBN 9780516200125
- Ylvisaker, Anne. 2004. Lake Huron. Fact finders. Mankato, Minn: Capstone Press. ISBN 0736822097 and ISBN 9780736822091
- Beckett, Harry. 1999. Lake Huron. Vero Beach, Fla: Rourke Corp. ISBN 0865935254 and ISBN 9780865935259
External links
- The Fish of Lake Huron. University of Wisconsin Sea Grant. Retrieved May 26, 2007.
- Eastern Great Lakes Recent Marine Data. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved May 26, 2007.
- Chapter One - Introduction: The Great Lakes. United States Enviornmental Protection Agency. Retrieved May 26, 2007.
- Lake Huron 2006 Lake Wide Management Plan. United States Enviornmental Protection Agency. Retrieved May 26, 2007.
- Lake Huron Map. Offical State of Michigan Portal. Retrieved May 26, 2007.
- Lake Huron Data. A Geographic Information System. Retrieved May 26, 2007.
| North American Great Lakes |
| Lake Superior | Lake Michigan | Lake Huron | Lake Erie | Lake Ontario |
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.