Difference between revisions of "Korean Peninsula" - New World Encyclopedia
Dan Davies (talk | contribs) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{images OK}}{{ | + | {{Copyedited}}{{approved}}{{submitted}}{{images OK}}{{Paid}} |
| − | + | {|class="infobox" style="float:right;"margin:0 0 1em 1em;" border="1" width="300" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="right" | |
| − | |||
| − | {| border="1" width="300" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="right" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! colspan="2" bgcolor="#CCCCCC" | Korean Peninsula | ! colspan="2" bgcolor="#CCCCCC" | Korean Peninsula | ||
| Line 11: | Line 9: | ||
| colspan="2" align="center" | [[Image:MapofKorea.png|295px|Map of the Korean peninsula]] | | colspan="2" align="center" | [[Image:MapofKorea.png|295px|Map of the Korean peninsula]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | The '''Korea Peninsula''' or '''Korean Peninsula''' is a [[peninsula]] in [[East Asia]] that extends southwards for about 684 miles or 1,100 | + | The '''Korea Peninsula''' or '''Korean Peninsula''' is a [[peninsula]] in [[East Asia]] that extends southwards for about 684 miles or 1,100 kilometers from the continental [[Asia]] into the [[Pacific Ocean]]. The East Sea/[[Sea of Japan]] surrounds the peninsula on the east, the [[East China Sea]] to the south, the [[Yellow Sea]] to the west while the [[Korea Strait]] connects the first two bodies of water. Until the end of [[World War II]], [[Korea]] comprised a single political entity whose territory roughly coincided with the Korean Peninsula. Since the [[Ceasefire|cessation]] of the [[Korean War]] in 1953, the northern half has been occupied by [[North Korea]], while the southern half has been occupied by [[South Korea]]. "Korean (or Korea) Peninsula," or "Korea," sometimes refers to these two [[Country|states]] together, though in South Korea the word "Korea" refers specifically to the South. |
| − | + | {{toc}} | |
| − | The northern boundaries for the Korean Peninsula coincide with today's political borders between North Korea and her northern neighbors, [[China]] (1,416 km) and [[Russia]] (19 km). The rivers [[Yalu River|Yalu]]/ | + | The northern boundaries for the Korean Peninsula coincide with today's political borders between North Korea and her northern neighbors, [[China]] (1,416 km) and [[Russia]] (19 km). The rivers [[Yalu River|Yalu]]/Amnok and [[Tumen River|Tumen]]/Tuman/Duman naturally form those borders. Taking that definition, the Korean Peninsula has an area of approximately 220,000 [[square kilometre|km²]]. The peninsula has two names: ''Chosun Bando'' (조선반도) in [[North Korea]] and ''Han Bando'' ([[Hangul]]: 한반도) in [[South Korea]] due to the [[Names of Korea|different names for Korea]]. |
==Physical geography== | ==Physical geography== | ||
| Line 19: | Line 17: | ||
Mountains cover seventy percent of the Korean Peninsula, with small, arable plains | Mountains cover seventy percent of the Korean Peninsula, with small, arable plains | ||
| − | widely scattered far in between the successive mountain ranges. The peninsula becomes more mountainous towards the north and the east, with the highest mountains (including [[Baekdu Mountain]] which stands at 2,744 m) found in the north. The south and west coasts of the peninsula, highly irregular, extend 8,460 | + | widely scattered far in between the successive mountain ranges. The peninsula becomes more mountainous towards the north and the east, with the highest mountains (including [[Baekdu Mountain]] which stands at 2,744 m) found in the north. The south and west coasts of the peninsula, highly irregular, extend 8,460 kilometers. Most of the 3,579 islands lay off the peninsula along the south and the west coasts. |
==Climate== | ==Climate== | ||
| − | [[Image:Ewiniar radar RKSG 0619Z 10 Jul 2006.png|thumb| | + | [[Image:Ewiniar radar RKSG 0619Z 10 Jul 2006.png|thumb|right|250px|Severe Tropical Storm Ewiniar, South Korea.]] |
| − | The climate of the Korean Peninsula differs dramatically from north to south. | + | The climate of the Korean Peninsula differs dramatically from north to south. The southern regions experience a relatively warm and wet climate similar to that of [[Japan]], affected by warm ocean waters including the [[East Korea Warm Current]]. The northern regions experience a colder and to some extent more inland climate, in common with [[Manchuria]]. For example, the [[Yalu River]] valley (600 mm) receives less than half the annual precipitation of the south coast (1500 mm). <!--<ref>KOIS 2003, p. 17.</ref>—> Likewise, the peninsula's southern and northern tips experience a 20 °C difference in January temperature. Still, similar general patterns affect the entire peninsula including the East Asian [[monsoon]] in midsummer and the frequent incidence of typhoons in autumn. |
| − | The | + | The majority of [[rain]]fall takes place during the summer months, with nearly half during the monsoon alone. [[Winter]]s are cold, with January [[temperature]]s typically below freezing outside of [[Jeju]] Island. Winter [[precipitation]] is minimal, with little [[snow]] accumulation outside of mountainous areas. |
==Biology== | ==Biology== | ||
| − | Surveys of Korean flora have identified more than 3,000 species on the peninsula, of which more than 500 are [[endemic (ecology)|endemic]]. | + | [[Image:Trees around Seoul.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Pine Tree near Seoul]] |
| + | Surveys of Korean [[flora]] have identified more than 3,000 [[species]] on the peninsula, of which more than 500 are [[endemic (ecology)|endemic]]. The peninsula's [[floristic province]]s are commonly divided between [[warm-temperate]], [[temperate]], and [[cold-temperate]] zones. The warm-temperate zone prevails over the southern coast and islands, including [[Jeju]]. It is typified by a large number of [[broad-leaved evergreen]]s. The temperate zone covers the great majority of the peninsula, away from the southern coast and high mountains. It is dominated by the [[Korean pine]] and various broad-leaved deciduous trees. Cold-temperate vegetation is found along the peninsula's northern fringe and in the high mountains, including the upper reaches of [[Hallasan]] on Jeju. Evergreens in this area include [[larch]] and [[juniper]]. Much of this vegetation is shared with Manchuria. | ||
==Geology== | ==Geology== | ||
| − | [[Image:Gwaneum Peak at Songnisan.jpg|thumb| | + | [[Image:Gwaneum Peak at Songnisan.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Gwaneum Peak at Songnisan in South Korea.]] |
| − | The terrain of the Korean Peninsula is rumpled, covered with low mountains. | + | |
| + | The terrain of the Korean Peninsula is rumpled, covered with low mountains. Most rocks are of [[Precambrian]] origin, although isolated pockets of [[Paleozoic]], [[Mesozoic]], and [[Cenozoic]] rock can also be found. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are no active volcanoes on the peninsula. However, [[Baekdu Mountain]] in the north and Hallasan in the south have [[crater lake]]s, indicating that they were active not long ago. In addition, [[Ulleungdo]] and [[Dokdo]] in the Sea of Japan (East Sea) is believed to have been of volcanic origin. Furthermore, [[hot springs]] indicative of low-level volcanic activity are widespread throughout the peninsula. Roughly two earthquakes are recorded per year, but few have any major impact. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Gallery== | ||
| − | + | <gallery> | |
| + | Image:Flowers around Seoul.jpg|Flower bush in Seoul, Korea | ||
| + | Image:Flowers around Seoul 2.jpg|Rose bush blooming near Seoul, Korea | ||
| + | Image:Flowers around Seoul 3.jpg|Flower in Spring time near Seoul | ||
| + | Image:Flowers around Seoul 4.jpg|Scotch Broom in Korea | ||
| + | Image:Flowers around Seoul 5.jpg|Tree blossoming with Scotch Broom in background, Korea | ||
| + | Image:Flowers around Seoul 6.jpg|Tree blossoming in Korea | ||
| + | Image:Flowers around Seoul 7.jpg|Bloosming tree in Seoul | ||
| + | Image:Flowers around Seoul 8.jpg|Flower about to open, Korea | ||
| + | Image:Trees around Seoul 2.jpg|Spring new growth on Korean pine tree | ||
| + | Image:Trees around Seoul 3.jpg|Lichen on tree in Korea | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| − | ==Notes== | + | <!-- ==Notes== |
| − | + | ---------------------------------------------------------- | |
| − | + | See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Footnotes for a | |
| − | + | discussion of different citation methods and how to generate | |
| − | + | footnotes using the <ref>, </ref> and <reference /> tags | |
| − | ----------------------------------------------------------- | + | ----------------------------------------------------------- <div class="references-small"> |
| − | <div class="references-small"> | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | + | —> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 56: | Line 66: | ||
*[[North Korea]] (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) | *[[North Korea]] (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) | ||
*[[South Korea]] (Republic of Korea) | *[[South Korea]] (Republic of Korea) | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[Geography of South Korea]] | *[[Geography of South Korea]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | *Korea (South). Handbook of Korea. Seoul, Korea: Korean Overseas Information Service, 2003. ISBN 978-8973750054 | ||
| + | *Nestor, Martin J. R. The environment of South Korea and adjacent sea areas. Monterey, CA: Naval Environmental Prediction Research Facility, 1977. {{OCLC|4161649}} | ||
| + | *U.S Army Topographic Engineering Center. Korean peninsula. Manual of environmental effects. Alexandria, VA: U.S. Army Topographic Engineering Center, 1995. {{OCLC|38929625}} | ||
| + | *Walters, Kenneth R., and Kathleen M. Traxler. North Korea: a climatological study. USAFETAC/TN, 94/003. Scott Air Force Base, Ill: USAF Environmental Technical Applications Center, 1994. {{OCLC|31043081}} | ||
{{Asia in topic|Geography of}} | {{Asia in topic|Geography of}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:History]] |
| − | [[Category:Geography | + | [[Category:Geography]] |
| + | [[Category:Korea]] | ||
{{credits|125083904}} | {{credits|125083904}} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:28, 24 April 2018
| Korean Peninsula | |
|---|---|
| |
|
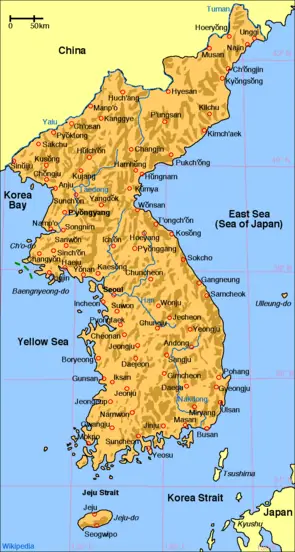
The Korea Peninsula or Korean Peninsula is a peninsula in East Asia that extends southwards for about 684 miles or 1,100 kilometers from the continental Asia into the Pacific Ocean. The East Sea/Sea of Japan surrounds the peninsula on the east, the East China Sea to the south, the Yellow Sea to the west while the Korea Strait connects the first two bodies of water. Until the end of World War II, Korea comprised a single political entity whose territory roughly coincided with the Korean Peninsula. Since the cessation of the Korean War in 1953, the northern half has been occupied by North Korea, while the southern half has been occupied by South Korea. "Korean (or Korea) Peninsula," or "Korea," sometimes refers to these two states together, though in South Korea the word "Korea" refers specifically to the South.
The northern boundaries for the Korean Peninsula coincide with today's political borders between North Korea and her northern neighbors, China (1,416 km) and Russia (19 km). The rivers Yalu/Amnok and Tumen/Tuman/Duman naturally form those borders. Taking that definition, the Korean Peninsula has an area of approximately 220,000 km². The peninsula has two names: Chosun Bando (조선반도) in North Korea and Han Bando (Hangul: 한반도) in South Korea due to the different names for Korea.
Physical geography
Mountains cover seventy percent of the Korean Peninsula, with small, arable plains widely scattered far in between the successive mountain ranges. The peninsula becomes more mountainous towards the north and the east, with the highest mountains (including Baekdu Mountain which stands at 2,744 m) found in the north. The south and west coasts of the peninsula, highly irregular, extend 8,460 kilometers. Most of the 3,579 islands lay off the peninsula along the south and the west coasts.
Climate
The climate of the Korean Peninsula differs dramatically from north to south. The southern regions experience a relatively warm and wet climate similar to that of Japan, affected by warm ocean waters including the East Korea Warm Current. The northern regions experience a colder and to some extent more inland climate, in common with Manchuria. For example, the Yalu River valley (600 mm) receives less than half the annual precipitation of the south coast (1500 mm). Likewise, the peninsula's southern and northern tips experience a 20 °C difference in January temperature. Still, similar general patterns affect the entire peninsula including the East Asian monsoon in midsummer and the frequent incidence of typhoons in autumn.
The majority of rainfall takes place during the summer months, with nearly half during the monsoon alone. Winters are cold, with January temperatures typically below freezing outside of Jeju Island. Winter precipitation is minimal, with little snow accumulation outside of mountainous areas.
Biology
Surveys of Korean flora have identified more than 3,000 species on the peninsula, of which more than 500 are endemic. The peninsula's floristic provinces are commonly divided between warm-temperate, temperate, and cold-temperate zones. The warm-temperate zone prevails over the southern coast and islands, including Jeju. It is typified by a large number of broad-leaved evergreens. The temperate zone covers the great majority of the peninsula, away from the southern coast and high mountains. It is dominated by the Korean pine and various broad-leaved deciduous trees. Cold-temperate vegetation is found along the peninsula's northern fringe and in the high mountains, including the upper reaches of Hallasan on Jeju. Evergreens in this area include larch and juniper. Much of this vegetation is shared with Manchuria.
Geology
The terrain of the Korean Peninsula is rumpled, covered with low mountains. Most rocks are of Precambrian origin, although isolated pockets of Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic rock can also be found.
There are no active volcanoes on the peninsula. However, Baekdu Mountain in the north and Hallasan in the south have crater lakes, indicating that they were active not long ago. In addition, Ulleungdo and Dokdo in the Sea of Japan (East Sea) is believed to have been of volcanic origin. Furthermore, hot springs indicative of low-level volcanic activity are widespread throughout the peninsula. Roughly two earthquakes are recorded per year, but few have any major impact.
Gallery
See also
- Korea
- North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
- South Korea (Republic of Korea)
- Geography of South Korea
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Korea (South). Handbook of Korea. Seoul, Korea: Korean Overseas Information Service, 2003. ISBN 978-8973750054
- Nestor, Martin J. R. The environment of South Korea and adjacent sea areas. Monterey, CA: Naval Environmental Prediction Research Facility, 1977. OCLC 4161649
- U.S Army Topographic Engineering Center. Korean peninsula. Manual of environmental effects. Alexandria, VA: U.S. Army Topographic Engineering Center, 1995. OCLC 38929625
- Walters, Kenneth R., and Kathleen M. Traxler. North Korea: a climatological study. USAFETAC/TN, 94/003. Scott Air Force Base, Ill: USAF Environmental Technical Applications Center, 1994. OCLC 31043081
| ||||||||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.












