Difference between revisions of "Hydrozoa" - New World Encyclopedia
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
[[Trachylinae]] | [[Trachylinae]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Hydrozoa''' is a diverse and wide-ranging [[taxonomic]] [[Class (biology)|class]] (sometimes superclass) of marine and freshwater [[invertebrate]]s within the [[phylum]] [[Cnidaria]], whose members are characterized by a [[life cycle]] that always includes the presence of planula larva, with some species having a polyp stage, and the | + | '''Hydrozoa''' is a diverse and wide-ranging [[taxonomic]] [[Class (biology)|class]] (sometimes superclass) of [[marine]] and [[freshwater]] [[invertebrate]]s within the [[phylum]] [[Cnidaria]], whose members are characterized by a [[life cycle]] that always includes the presence of planula larva, with some species having a polyp stage, and the medusa stage, if present, involving a distinctive medusa having a velum or muscular projection from the subumbrellar margin. Hydrozoans generally display alternation of generations between polyp and medusa, although hydras exhibit only the polyp form and some species are represented only by medusae and lack the polyp stage. |
| − | + | Hydrozoans are carnivorous animals that can be solitary or colonial. Most are small (an umbrella of less than 50 millimeters or two inches), but some can be large (40 centimeters or 17.7 inches), and some colonies can be very large (30 meters or 98 feet). Hydrozoans include marine hydroids, freshwater hydras, some known as [[jellyfish]] and [[coral]]s, and the well-known [[Portuguese man-of-war]]. | |
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
==Overview and description== | ==Overview and description== | ||
| − | + | ===Overview=== | |
| − | + | Cnidaria, the phylum to which Hydrozoa belongs, contains some 11,000 [[species]] of relatively simple [[invertebrate]] [[animal]]s found exclusively in aquatic, mostly marine, environments. Cniderians include [[coral]]s, [[sea anemone]]s, [[jellyfish]], sea pens, sea pansies, and sea wasps, and tiny freshwater hydra. The name of the phylum comes from cnidocytes, which are specialized cells that carry stinging organelles. | |
| − | The name of the phylum comes from | ||
There are four main classes of Cnidaria: | There are four main classes of Cnidaria: | ||
| + | * Class Hydrozoa (Portuguese Man o' War, Obelia, etc.) | ||
* Class [[Anthozoa]] ([[anemone]]s, sea fans, [[coral]]s, etc.) | * Class [[Anthozoa]] ([[anemone]]s, sea fans, [[coral]]s, etc.) | ||
| − | |||
* Class [[Scyphozoa]] (true jellyfish) | * Class [[Scyphozoa]] (true jellyfish) | ||
* Class [[Cubozoa]] (box jellies) | * Class [[Cubozoa]] (box jellies) | ||
| − | + | These are sometimes listed as superclass, rather than class. | |
| + | |||
| + | In the idealized [[life cycle]], members of Cnidaria alternate between asexual ''polyps'' and sexual, free-swimming forms called ''medusae'' (singular medusa). However, the Anthozoa live only as polyps, while Scyphozoa live most of their life cycle as medusae. The Hydrozoa live as polyps, medusae, and species that alternate between the two (Towle 1989). Invertebrates belonging to the class Cubozoa are named for their cube-shaped medusae, which form the dominant part of their life cycle. The non-anthozoan classes may be grouped into the subphylum ''Medusozoa''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the idealized life cycle, during sexual reproduction, a larva (or planula) forms from the blastula. The larva have flagella and swim until its encounters a firm substrate, on which it anchors itself and then passes through [[metamorphosis]] to the polyp stage, if present. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Description=== | ||
| + | Hydrozoa is a very diverse class with members that vary considerably from this idealized life cycle. The life cycle does always include the presence of planula larva (Boero and Bouillon 2004). However, among many in Hydrozoa, the medusae remain on the polyps in a reduced form, known as gonophores. A few hydrozoans, such as the hydra, have no medusa stage whatsoever; instead the polyp itself forms male or female gametes. And in many hydrozoans, there are no polyp stage (Boero and Boullon 2004). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The main characteristic that distinguishes the medusae of members of Hydrozoa from that of other classes is the presence of the velum, which is a muscular extension of the subumbrellar margin that allows the subumbrellar cavity to be partially closed (Boero and Boullon 2004). | ||
| − | + | sizes ** | |
Revision as of 17:14, 19 December 2008
| Hydrozoa | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
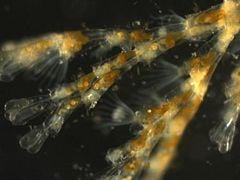 Closeup of a hydrozoan colony
| ||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
|
Leptolinae |
Hydrozoa is a diverse and wide-ranging taxonomic class (sometimes superclass) of marine and freshwater invertebrates within the phylum Cnidaria, whose members are characterized by a life cycle that always includes the presence of planula larva, with some species having a polyp stage, and the medusa stage, if present, involving a distinctive medusa having a velum or muscular projection from the subumbrellar margin. Hydrozoans generally display alternation of generations between polyp and medusa, although hydras exhibit only the polyp form and some species are represented only by medusae and lack the polyp stage.
Hydrozoans are carnivorous animals that can be solitary or colonial. Most are small (an umbrella of less than 50 millimeters or two inches), but some can be large (40 centimeters or 17.7 inches), and some colonies can be very large (30 meters or 98 feet). Hydrozoans include marine hydroids, freshwater hydras, some known as jellyfish and corals, and the well-known Portuguese man-of-war.
Overview and description
Overview
Cnidaria, the phylum to which Hydrozoa belongs, contains some 11,000 species of relatively simple invertebrate animals found exclusively in aquatic, mostly marine, environments. Cniderians include corals, sea anemones, jellyfish, sea pens, sea pansies, and sea wasps, and tiny freshwater hydra. The name of the phylum comes from cnidocytes, which are specialized cells that carry stinging organelles.
There are four main classes of Cnidaria:
- Class Hydrozoa (Portuguese Man o' War, Obelia, etc.)
- Class Anthozoa (anemones, sea fans, corals, etc.)
- Class Scyphozoa (true jellyfish)
- Class Cubozoa (box jellies)
These are sometimes listed as superclass, rather than class.
In the idealized life cycle, members of Cnidaria alternate between asexual polyps and sexual, free-swimming forms called medusae (singular medusa). However, the Anthozoa live only as polyps, while Scyphozoa live most of their life cycle as medusae. The Hydrozoa live as polyps, medusae, and species that alternate between the two (Towle 1989). Invertebrates belonging to the class Cubozoa are named for their cube-shaped medusae, which form the dominant part of their life cycle. The non-anthozoan classes may be grouped into the subphylum Medusozoa.
In the idealized life cycle, during sexual reproduction, a larva (or planula) forms from the blastula. The larva have flagella and swim until its encounters a firm substrate, on which it anchors itself and then passes through metamorphosis to the polyp stage, if present.
Description
Hydrozoa is a very diverse class with members that vary considerably from this idealized life cycle. The life cycle does always include the presence of planula larva (Boero and Bouillon 2004). However, among many in Hydrozoa, the medusae remain on the polyps in a reduced form, known as gonophores. A few hydrozoans, such as the hydra, have no medusa stage whatsoever; instead the polyp itself forms male or female gametes. And in many hydrozoans, there are no polyp stage (Boero and Boullon 2004).
The main characteristic that distinguishes the medusae of members of Hydrozoa from that of other classes is the presence of the velum, which is a muscular extension of the subumbrellar margin that allows the subumbrellar cavity to be partially closed (Boero and Boullon 2004).
sizes **
Some examples of hydrozoans are the Freshwater Jelly (Craspedacusta sowerbyi), the freshwater polyps (Hydra), Obelia, the Portuguese Man o' War (Physalia physalis), the chondrophores (Porpitidae), "air fern" (Sertularia argenta) and the pink-hearted hydroids (Tubularia).
Life cycles
Some colonial hydrozoans have both a medusa stage and a polyp stage in their life cycle (but more hydrozoan species do not have the medusa stage). Each colony has a base, a stalk, and one or more polyps. Hydroid colonies are usually dioecious, which means that they have separate sexes - all the polyps in each colony are either male or female, but not usually both sexes in the same colony. Hydrozoan colonies are composed of a number of specialized polyps (or "zooids") - including feeding, reproductive, and sometimes, protective zooids. In some species, the reproductive polyps, known as gonozooids (or "gonotheca" in thecate hydrozoans) bud off asexually-produced medusae. These tiny, new medusae (which are either male or female) mature and spawn, releasing gametes freely into the sea in most cases. Zygotes become free-swimming planula larvae or actinula larvae that either settle on a suitable substrate (in the case of planulae), or swim and develop into another medusae or polyp directly (actinulae). Colonial hydrozoans include siphonophore colonies, Hydractinia, Obelia, and many others.
The medusa stage, if present, is the sexually-reproductive life cycle phase (that is, in hydrozoan species that have both polyp and medusa generations). Medusae of these species of Hydrozoa are known as "hydromedusae". Most hydromedusae have shorter life spans than the larger scyphozoan jellyfish. Some species of hydromedusae release gametes shortly after they are themselves released from the hydroids (as in the case of fire corals), living only a few hours, while other species of hydromedusae grow and feed in the plankton for months, spawning daily for many days before their supply of food or other water conditions deteriorate and cause their demise.
Systematics
Hydrozoan systematics is highly complex. Several approaches for expressing their interrelationships were proposed and heavily contested since the late 19th century, but in more recent times a consensus seems to be emerging.
For long, the hydrozoans were divided into a number of orders, according to their mode of growth and reproduction. Most famous among these was probably the assemblage called "Hydroida", but this group is apparently paraphyletic, united by plesiomorphic (ancestral) traits. Other such orders were the Anthoathecatae, Actinulidae, Laingiomedusae, Polypodiozoa, Siphonophora and Trachylina.
As far as can be told from the molecular and morphological data at hand, the Siphonophora for example were just highly specialized "hydroids," whereas the Limnomedusae - presumed to be a "hydroid" suborder - were simply very primitive hydrozoans and not closely related to the other "hydroids." Therefore, today the hydrozoans are at least tentatively divided into two subclasses, the Leptolinae (containing the bulk of the former "Hydroida" and the Siphonophora) and the Trachylinae, containing the others (including the Limnomedusae). The monophyly of several of the presumed orders in each subclass is still in need of verification.[1]
In any case, according to this classification, the hydrozoans can be subdivided as follows, with taxon names emended to end in "-ae":[1]
CLASS HYDROZOA
- Subclass Leptolinae
- Order Anthomedusae (= Anthoathecata(e), Athecata(e), Stylasterina(e)) - includes Laingoimedusae but monophyly requires verification
- Order Leptomedusae (= Leptothecata(e), Thecaphora(e), Thecata(e))
- Order Siphonophorae
- Subclass Trachylinae
- Order Actinulidae
- Order Limnomedusae - monophyly requires verification; tentatively placed here
- Order Narcomedusae
- Order Trachymedusae - monophyly requires verification
ITIS uses the same system but unlike here does not use the oldest available names for many groups.
In addition, there exists a weird cnidarian parasite, Polypodium hydriforme, which lives inside its host's cells. It is sometimes placed in the Hydrozoa, but actually its relationships are better treated as unresolved for the time being - a somewhat controversial 18S rRNA sequence analysis found it to be closer to Myxozoa. It was traditionally placed in its own class Polypodiozoa and this view is presently often seen to reflect the uncertainties surrounding this highly distinct animal.[2]
Other classifications
Some of the more widespread classification systems for the Hydrozoa are listed below. Though they are often found in seemingly authoritative Internet sources and databases, they do not agree witnh the currently available data. Especially the presumed phylogenetic distinctness of the Siphonophora is a major flaw that was corrected only recently.
The obsolete classification mentioned above was as follows:
- Order Actinulidae
- Order Anthoathecatae
- Order Hydroida
- Suborder Anthomedusae
- Suborder Leptomedusae
- Suborder Limnomedusae
- Order Laingiomedusae
- Order Polypodiozoa
- Order Siphonophora
- Order Trachylina
- Suborder Narcomedusae
- Suborder Trachymedusae
A very old classification that is sometimes still seen is:
- Order Hydroida
- Order Milleporina
- Order Siphonophorida
- Order Stylasterina (= Anthomedusae)
- Order Trachylinida
Catalogue of Life uses the following:
- Order Actinulida
- Order Anthoathecata (= Anthomedusae)
- Order Hydroida
- Order Laingiomedusae
- Order Leptothecata (= Leptomedusae)
- Order Limnomedusae
- Order Narcomedusae
- Order Siphonophora
- Order Trachymedusae
Animal Diversity Web uses the following:
- Order Actinulida
- Order Capitata
- Order Chondrophora
- Order Filifera
- Order Hydroida
- Order Siphonophora
Hydra, a freshwater genus
The most widely-known and researched freshwater hydrozoan is Hydra, which is found in slow-moving waters.
Hydra has a pedal disc composed of gland cells that helps it attach to substrates, and like all cnidarians uses nematocysts, or "stinging cells," to disable its prey. Hydra eat small crustaceans (such as brine shrimp), insect larvae, and annelid worms. Hydra may reproduce sexually, through the spawning of sperm (and thus insemination of eggs on the female body column), or through asexual reproduction (budding).
Footnotes
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Schuchert, Peter (2005): The Hydrozoa Directory - Hydrozoan Phylogeny and Classification. Retrieved 2008-JUL-08.
- Zrzavý, Jan & Hypša, Václav (2003): Myxozoa, Polypodium, and the origin of the Bilateria: The phylogenetic position of "Endocnidozoa" in light of the rediscovery of Buddenbrockia. Cladistics 19(2): 164–169. Digital object identifier (DOI): 10.1111/j.1096-0031.2003.tb00305.x (HTML abstract)
External links
- J. Bouillon, M.D. Medel, F. Pagès, J.M. Gili, F. Boero and C. Gravili. 2004. Fauna of the Mediterranean Hydrozoa. Scientia Marina, 68 (Suppl. 2).
- Hydroids from Reunion Island and Indian Ocean
- http://zygote.swarthmore.edu/intro6.html
- Puget Sound Online
- Aquascope
- The Hydrozoa Directory
- - A general page about hydromedusae
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.




