Difference between revisions of "Cayman Islands" - New World Encyclopedia
(→History: History Introduction complete) |
(→Dependency of Jamaica: Dependency of Jamaica complete) |
||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
=== Dependency of Jamaica === | === Dependency of Jamaica === | ||
| − | + | Beginning in 1670, the Cayman Islands became dependencies of [[Jamaica]], although they was a considerable amount of self-government. On December 5, 1831, a Legislative Assembly was established through consent, during a meeting held by principaled locals. Elections were held on December 10th of the same year, later on December 31st the legislature passed the first local legislation. Because of this the Governor of Jamaica authorized a legislature consisting of eight magistrates appointed by the Governor himself and 10, later increased to 27, elected representatives. | |
| − | In 1835, Governor Sligo arrived in Cayman | + | In 1835, Governor Sligo of Jamaica arrived in Grand Cayman to announce that all slaves were free, in accordance with the Emancipation Act of 1833. |
| − | + | In 1863 the Cayman Islands were officially declared and administered as a dependency of Jamaica, but was more like a parish, by receiving charityof its local authoritites from Jamaica, with the elected vestrymen in their legislature and nominated justices of peace. From 1750 to 1898 the Chief Magistrate was the offical administer of the dependency, who was appointed by the Jamaican governor, but was replaced when the governor started appointing a Commissioner for the islands. In 1953, the Cayman Islands first airfield wasw built, as well as the Geoge Town Public Hospital. | |
| − | + | Beginning in 1959 the Administrator was in the position of chief official, overseeing the day to day affairs of the islands in the governor's place. Aso in 1959 with the configuration of the Federation of the West Indies coming together, the dependency status with regards to Jamaica offically ended, however, the governor of Jamaica still remained the governor of the Cayman Islands and therefor still had control over them. With Jamaica's independance in 1962, the Cayman Islands broke its administrative links with the country and choose to become a direct dependency of the British Crown. Because of this, the chief official of the islands became the Administrator. Barclays, a corporate banking company, showed the islands formalized commerce with the opening of the first commercial bank. | |
=== Independence === | === Independence === | ||
Revision as of 18:52, 18 June 2007
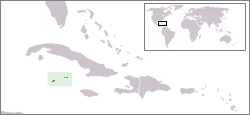
The Cayman Islands are an overseas territory of the United Kingdom in the western Caribbean Sea comprising the islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac, and Little Cayman.
Geography
The Cayman Islands are an island nation located in the British dependency. Comprised of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman the Cayman Islands are a three-island archipelago resting in the Caribbean Sea. The islands are 240 km south of Cuba and 268 km northwest of Jamaica with its geographic coordinates being 19°30 north, 80°30 west, lying the Cayman Islands between Cuba and Central America. Having a land area of 259 km² (101.2 square miles), the islands are about 1.5 times the size of Washington, D.C., with a coastline of 160 km (99 miles). These islands make a maritime claim of a 200-nautical mile exclusive fishing zone which includes 12 nautical miles of territorial sea.
The Cayman Islands' lowest elevation is sea level meeting the Caribbean Sea. The highest point is known as "The Bluff," a limestone coastal cliff of 43 meters (141 feet) above sea level on the eastern end of Cayman Brac. "Brac" in Gaelic translates to "Bluff" given in the name Cayman Brac. The terrain is mostly the low-lying limestone base, surrounded by coral reefs. In 2005 an estimate of land use determined that the Cayman Islands had only 3.85 percent fertile land and no permanent crops.
The Cayman Islands have a tropical marine climate, with a wet season of warm but rainy summers lasting from May all the way through October. And a dry season with relatively cool winters lasting from November straight though to April. Although a serious environmental issue is the lack of fresh water resources. The demand of drinking water is supplied only by catching of rainwater and desalination, which is the proccess of removing salt from water. Another problem are the tropical cyclones that form during the Atlantic hurricane season from July to November, which is the islands' end of the summer season lasting until the beginning of the winter season.
History
On May 10, 1503 Christopher Columbus discovered the Cayman Islands and named them Las Tortugas which literally translates into "the turtles" in Spanish, after the numerous sea turtles there. He had found Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, the two smaller islands. It was these two islands that he named "Las Tortugas."
A map from 1523 shows the islands being referred to as Lagartos, meaning alligators or large lizards, but by 1530 they were known as the Caymanas after the Carib Indian word for the marine crocodile that also lived in the area.
Sir Francis Drake was the first recorded English visitor who came in 1586. He allegedly reported that the caymanas, the marine crocodiles, were edible. However, it was the abundant turtles that which ships were attracted to, in search of fresh meat for their crews. Overfishing the turtles nearly extinguished them from the local waters.
Around 1700 the first recorded permanent inhabitant of the Cayman Islands was born, Isaac Bodden. He was the grandson of one of the original settlers named Bodden, who was likely to be one of Oliver Cromwell's soldiers at the taking of Jamaica in 1655.
Over time and throughout history a variety of people have settled on the Cayman Islands and have called it home, pirates, refugees from the Spanish Inquisition, slaves and shipwrecked sailors. Although the majority of Caymanians are from African and British descent, with considerable interracial mixing.
British rule
After the first settlers came from Jamaica in 1661-1671, to Little Cayman and Cayman Brac, Great Britain took formal control of the Cayman Islands along with Jamaica under the Treaty of Madrid in 1670. These first settlements on the islands were later abandoned after attacks by Spanish privateers. British privateers would often use the islands as a base. However, in the 18th century Cayman Islands became a popular hideout for pirates, even long after the end of legitimate privateering in 1713. Permanent settlements began to appear in the 1730s, after several unsuccessful attempts. In November of 1794, ten vessels that were part of a convoy escorted by HMS Convert, wrecked on the reef in Gun Bay, on the East side of Grand Cayman, but with the help of local settlers, there was no loss of life. This incident is now remembered as 'The Wreck of the Ten Sail'. According to legend there was a member of the Royal Family onboard one of the ships, and in gratitude for their bravery, King George III decreed that Caymanians should never be held to account for war service. Also that Parliament legislated that they should never be taxed. However, there is no real evidence that has been found to support this theory.
Dependency of Jamaica
Beginning in 1670, the Cayman Islands became dependencies of Jamaica, although they was a considerable amount of self-government. On December 5, 1831, a Legislative Assembly was established through consent, during a meeting held by principaled locals. Elections were held on December 10th of the same year, later on December 31st the legislature passed the first local legislation. Because of this the Governor of Jamaica authorized a legislature consisting of eight magistrates appointed by the Governor himself and 10, later increased to 27, elected representatives.
In 1835, Governor Sligo of Jamaica arrived in Grand Cayman to announce that all slaves were free, in accordance with the Emancipation Act of 1833.
In 1863 the Cayman Islands were officially declared and administered as a dependency of Jamaica, but was more like a parish, by receiving charityof its local authoritites from Jamaica, with the elected vestrymen in their legislature and nominated justices of peace. From 1750 to 1898 the Chief Magistrate was the offical administer of the dependency, who was appointed by the Jamaican governor, but was replaced when the governor started appointing a Commissioner for the islands. In 1953, the Cayman Islands first airfield wasw built, as well as the Geoge Town Public Hospital.
Beginning in 1959 the Administrator was in the position of chief official, overseeing the day to day affairs of the islands in the governor's place. Aso in 1959 with the configuration of the Federation of the West Indies coming together, the dependency status with regards to Jamaica offically ended, however, the governor of Jamaica still remained the governor of the Cayman Islands and therefor still had control over them. With Jamaica's independance in 1962, the Cayman Islands broke its administrative links with the country and choose to become a direct dependency of the British Crown. Because of this, the chief official of the islands became the Administrator. Barclays, a corporate banking company, showed the islands formalized commerce with the opening of the first commercial bank.
Independence
Following a two year campaign by women to change their circumstances, in 1959 Cayman received its first written constitution which, for the first time, allowed women to vote. Cayman ceased to be a dependency of Jamaica.
During 1966, legislation was passed to enable and encourage the banking industry in Cayman.
In 1971 the governmental structure of the Islands was again changed with a Governor now running the Cayman Islands. Athel Long CMG, CBE was the last Administrator and the first Governor of the Cayman Islands.
In 1991 a review of the 1972 constitution recommended several constitutional changes to be debated by the Legislative Assembly. The post of Chief Secretary was reinstated in 1992 after having been abolished in 1986. The establishment of the post of Chief Minister was also proposed. However, in November 1992 elections were held for an enlarged Legislative Assembly and the Government was soundly defeated, casting doubt on constitutional reform. The "National Team" of government critics won 12 (later reduced to 11) of the 15 seats, and independents won the other three, after a campaign opposing the appointment of Chief Minister and advocating spending cuts. The unofficial leader of the team, Thomas Jefferson, had been the appointed Financial Secretary until March 1992, when he resigned over public spending disputes to fight the election. After the elections, Mr. Jefferson was appointed Minister and leader of government business; he also held the portfolios of Tourism, Aviation and Commerce in the Executive Council. Three teams with a total of 44 candidates contested the general election held on November 20, 1996: the governing National Team, Team Cayman and the Democratic Alliance Group. The National Team were returned to office but with a reduced majority, winning 9 seats. The Democratic Alliance won 2 seats in George Town, Team Cayman won one in Bodden Town and independents won seats in George Town, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman.
Although all administrative links with Jamaica were broken in 1962, the Cayman Islands and Jamaica continue to share many links and experiences, including membership in the Commonwealth of Nations (and Commonwealth citizenship) and a common united church (the United Church in Jamaica and the Cayman Islands) and Anglican diocese (although there is debate about this) as well as a common currency (until 1972). Also, by 1999, 38-40% of the population of the Cayman Islands was of Jamaican origin and in 2004/2005 little over 50% of the expatriates working in the Cayman Islands (i.e. 8,000) were Jamaicans (with the next largest expatriate communities coming from the United States, United Kingdom and Canada).
Hurricane Ivan 2004
In September 2004, Hurricane Ivan hit the Cayman Islands. The results were devastating, with loss of human life, animal life both domestic (livestock) and wild. Flooding was major throughout the island of Grand Cayman with some accounts reporting that 25% or more of the island was underwater and reports that lower floors of buildings were completely flooded. This disaster even led to bankruptcy of a heavily invested insurance company known as Doyle. The company released estimates covering 20% of damages to be reinsured at minimal fees when in actuality the damage was over 65% and every claim was in the millions. The company was unable to continue to keep paying out and the adjusters couldn't help lower the payments any further due to the high building codes that the islands follow.
It was clear that the islands were damaged in vegetation as well as in an apparent lack of construction in some places. The islands were regaining movement again as some things were being freshly rebuilt if they hadn't been already. However, still, as of late 2005, many housing and residental issues remain for many of the islanders.
Government and Politics
Although the Cayman Islands is a British dependency, they are largely self-governing in the areas of concerning local affairs. Every four years an election occurs to determine who will represent in the Legislative Assembly's 15 opening positions, to handle domestic affairs. Five out of the elected 15 Members of the Legislative Assembly are chosen to serve as government ministers. The head of the government is the Leader of Government Business.
The British government appoints a governor to represent the monarch. In recent years, the powers of the governor has been limited to handling defence, the police force and foreign affairs. However, most of these affairs are handled by the chief secretary, who acts as governor when the governor is unable to fulfill his usual duties for one reason or another. On a day-to-day basis the governor usually oversees the civil service including the portfolio of Internal & External Affairs.
Since becoming part of the British Crown Colony in 1962, the islands have been governed by a written constitution. Although, the Governor has called for the constitution to be modernized, an issue which is being debated with the Legislative Assembly. Great Britain has made it well known that such an action (modernizing the constitution) should originate within the people of the Cayman Islands and follow the elected route.
Foreign relations
Because the Cayman Islands are an overseas territory of the United Kingdom, their foreign relations are therefore largely managed through and by the U.K. However, the islands' government often handles important issues with foreign governments solitarily, without any intervention from the United Kingdom. Although in the country's beginning years, the Cayman Islands relied majorly on its mother nation, the United Kingdom, and help from neighboring country Jamaica, but in recent years the focus has been shifted to getting help mostly from the United States.
The Cayman Islands are not involved in any major international disputes, however, they have come under constant criticism pertaining to the use of their country's territory for narcotics trafficking and money laundering. In an attempt to address this, the Cayman Islands' government entered into the 'Narcotics Agreement' in 1984 and the 'Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty' in 1986 with the United States, in order to reduce the use of their facilities associated with said activities. In more recent years though, they have tried to keep the fight against money laundering to a minimum, by limiting banking secrecy, requiring banks to cooperate with any foreign investigators and by introducing requirements for customer identification and record keeping.
Military
The United Kingdom is in charge of the Cayman Islands' military defence. Because of this the islands have no permanent established military. However, they do have their own police force, the Royal Cayman Islands Police Service. And still yet, in 2001 the small Cayman Islands Cadet Corps was formed in place of a traditional military army.
Taxation
As a tax haven from the British government and local income tax, both Caymanians and Caymanian companies are not subject to any form of direct taxation. However, an import tax of between 5%-20%, and sometimes even 40% on up-scale automobiles, is placed on almost all imported goods.
Demographics
As of July 2000 the population of the Cayman Islands stood at 34,763. About half of the 34,763 people living on the islands at the time (17,381) were of Caymanian descent, but 60% of the population is of mixed race. And of the remaining 40%, about 20% is Caucasian and the other 20% are from African descent. The islands are almost majorly Christian, except for a large number of Presbyterians and Anglicans. The vast majority of the population is on Grand Cayman, with Cayman Brac being populated with about 2,000 residents; leaving Little Cayman to be the least populated with around 200 permanent residents. However, approximately one quarter of the Islands' population left following Hurricane Ivan in 2004, due to the many problems consisting of financial and otherwise, caused by the hurricane.
The major and capital city of the Cayman Islands is George Town, located on the west coast of Grand Cayman.
Education
The public schools on the islands are operated by the Cayman Islands Education Council.
Economy
The Cayman Islands' major natural resource and high region of income is fish. The economy of the islands' used to be built around turtling. However, turtling began to disappear in the 20th century while tourism and financial services began to become dominant in the economy. The United States of America happens to be the Cayman Islands' largest product trading partner.
With a national average income of around $35,000, Caymanians are on the highest end of living expenses in the entire Caribbean. The country prints their own currency, the Cayman Islands dollar (C.I. dollar), which is tied to the U.S. dollar at a fixed rate of 1 KYD = 1.227 USD. Therefore, the C.I. dollar's rate of exchange with every other country in the world is the same exchange rate with the U.S. dollar's rate of exchange with those same countries.
Indirect taxation is the government's primary source of income. An import fee imposed and enforceable by law or custom is known as duty. As there is a duty of 20% charged on goods imported into the islands. However, a few goods are not taxed, for example, books, cameras and baby formula. Duty on automobiles is charged on a curved scale with the duty reaching as much as 40% for expensive models. The government charges a flat fee for licensing to financial institutions that operate on the islands. A small fee is also placed on each tourist that lands on the islands.
Tourism
Climate and beaches foster tourism, which is Cayman Islands' major industry. Tourism accounts for 70%-75% of the annual Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of the Cayman Islands and because of it, it is a major part of the islands' economy. Out of the millions of tourists that visit the islands each year, 99% of the them stay on Grand Cayman; possibly because George Town serves as a major cruise-ship port, which brings in 2,000 - 3,000 tourists a day, 5 days a week.
Grand Cayman's major tourist attraction is the world-famous Seven Mile Beach. Where because of its luscious waters and endless strip of sand, many hotels and resorts are located here. The Seven Mile Beach was recently named the "Caribbean's Best Beach" by Caribbean Travel and Life Magazine. It is also famed as one of the best beaches in the world.
The Cayman Islands are also well known and world famous for being a scuba diving destination because of their proximity to the Cayman Wall, an underwater wall of coral reef ideal for deep sea scuba diving while still being near enough to land. And also being well known for the Cayman Trench, which extends deep into the coral reefs of the Caribbean. Even the less populated islands of the Cayman Islands, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman are also considered to be elite dive destinations.
Financial services industry
As of 2000, nearly 40,000 companies were incorporated on the Cayman Islands because of the lack of local income tax, as well as a lack of taxation by the British government. This is because since the lack of taxation The Cayman Islands hold as an international offshore-banking and tax haven for millions, including 600 banking and trust companies with assets in excess of $500 billion. In fact approximately 6,000 out of the world's 8,000 hedge funds are located in the Cayman Islands.
External links
- Cayman Islands Government
- Cayman Islands Department of Tourism
- Cayman Islands Investment Bureau
- Grand Cayman Islands Vacation Directory
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
- Cayman_Islands history
- Geography_of_the_Cayman_Islands history
- History_of_the_Cayman_Islands history
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.