Difference between revisions of "Beehive tomb" - New World Encyclopedia
Nick Perez (talk | contribs) |
Nick Perez (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[Category:Anthropology]] | [[Category:Anthropology]] | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Treasure_of_Atreus.jpg|right|250px|thumb|[[Dromos]] entrance to the [[Treasury of Atreus]]]] |
| − | + | '''Beehive tombs''', also known as '''Tholos tombs''' (plural '''tholoi'''), are a monumental Late [[Bronze Age]] development of the [[Mycenaean Civilization]], that eventually replaced the old style of ''chamber tombs''. The new beehive tombs came to be the resting place of the societies' elite upper class. | |
| − | '''Beehive tombs''', also known as '''Tholos tombs''' (plural '''tholoi'''), are a monumental Late [[Bronze Age]] development of | + | |
| + | ==Description== | ||
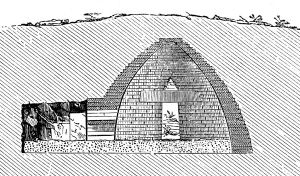
| + | [[Image:Atreus-2.jpg|left|thumb|Cross section of a beehive tomb ([[Treasury of Atreus]])]] | ||
| + | Most often, beehive tombs were placed underground, either built lowly into the side of a hill, or, in areas with flat parcels of land, entirely subterrariean. In the case of the latter, if any part of the structure protruded above the ground it was carefully covered using earth that was held in place by a retaining wall<ref>(2000) Prehistoric Archaeology of the Aegean Project. [[http://projectsx.dartmouth.edu/classics/history/bronze_age/credits.html"Lesson 19: Mycenaean Tholos Tombs and Early Mycenaean Settlements"]] Dartmouth College, Retrieved September 5, 2007</ref> Inside, they were built as corbelled arches, layers of stone placed closer together as the arch tapers toward the top of the tomb. The tombs usually contained more than one [[burial]], in various places in the tomb either on the floor, in pits and cists or on stone-built or rock-cut benches, and with various [[grave goods]]. | ||
| − | + | The tripartite structure of the tombs is not always evident in the earliest mainland examples (for example at [[Voidhokoilia]]) but by the time the architectural type had left [[Messenia]] the separation into chamber, stomion and dromos was fixed. The chamber is always built in [[masonry]], even in the earliest examples, as is the stomion or entrance-way, which provided an opportunity for conspicuous demonstration of wealth. The dromos was often just cut from the [[bedrock]], even in some of the earlier examples at [[Mycenae]] itself. In later examples, all three parts were constructed of fine [[ashlar]] masonry. | |
==Origins== | ==Origins== | ||
| − | The | + | The oldest beehive tomb discovered thus far is in Messenia. Previously, the [[Minoan Civilization|Minoan]] style of burial, the chamber tomb, had been the most frequent style used, from about 1600 B.C.E. to 1100 B.C.E., due probably to the large influence the Minoans had over the [[Aegan region]] at the time. After about 1500 B.C.E.., beehive [[tomb]]s became more widespread, suggesting to many archaeologists that the influence of the Minoans was in decline. From Messenia, the beehive tomb spread to other areas of [[Greece]], particularly [[Argolid]], [[Laconia]], and [[Attica]].<ref>(2000) Prehistoric Archaeology of the Aegean Project. [[http://projectsx.dartmouth.edu/classics/history/bronze_age/credits.html"Lesson 19: Mycenaean Tholos Tombs and Early Mycenaean Settlements"]] Dartmouth College, Retrieved September 5, 2007</ref> Why the switch from chamber to beehive tombs took place remains a contention among archaeologists, but there are many implications arising from the change. As beehive tombs became more popular in Greece, they began to become regulated to the highest class of citizens; usually royalty and the highest non-royalty bueacrats and their families were only entombed in beehive structures. This suggests that there was a strict social stratigraphy in Greece at the time. The infrequency of later beehive tombs also indicates the eventual consolidation of power in Greece, as the once city states became larger conglomerates, requiring fewer beehive tombs for the fewer persons with power.<ref>(2000) Prehistoric Archaeology of the Aegean Project. [[http://projectsx.dartmouth.edu/classics/history/bronze_age/credits.html"Lesson 19: Mycenaean Tholos Tombs and Early Mycenaean Settlements"]] Dartmouth College, Retrieved September 5, 2007</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:Banditaccia1.jpg|thumb|200px|left|View of the [[Etruscan civilization|Etruscan]] necropolis of Banditaccia, in [[Cerveteri]], Italy.]] | |
| − | The | + | The beehive tomb design for the most stayed within Greece. However, there are examples of similar designs from around the world, although it is not clear if they were culturally defused from Greece, or if they were concurrently separated phenomena. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Famous Examples== | ==Famous Examples== | ||
===Treasury of Atreus=== | ===Treasury of Atreus=== | ||
| − | [[Image:07Mykene Atreus02.jpg|thumb| | + | [[Image:07Mykene Atreus02.jpg|thumb|right|150 px|Inside the [[Treasury of Atreus]]]] |
| − | + | Perhaps the most famous beehive tomb in Greece is the '''Treasury of [[Atreus]]''', located in [[Mycenae]], Greece (on the Panagitsa Hill) constructed around 1250 B.C.E. The [[lintel (architecture)|lintel stone]] above the doorway weighs 120 tons. The tomb was used for an unknown period of time. With an interior height of 13.5m and a diameter of 14.5m,<ref name = "Structurae.de: Treasury of Atreus"> Structurae.de: [http://en.structurae.de/structures/data/index.cfm?ID=s0003185 Treasury of Atreus]</ref> it was the tallest and widest dome in the world for over a thousand years until construction of the [[Temple of Mercury (Baiae)|Temple of Mercury]] in [[Baiae]]. | |
| + | |||
| + | ===Oman=== | ||
| + | The earliest stone-built tombs which can be called 'beehive', are in [[Oman]], built of stacked flat stones which occur in nearby geological formations. They date to between 3,500 and 2,500 years B.C.E., to a period when the Arabian peninsula was subject to much more rainfall than now, and supported a flourishing civilisation in what is now desert, to the west of the mountain range along the Gulf of Oman. No burial remains have ever been retrieved from these 'tombs', though there seems no other purpose for their building. They have only superficial similarities with the Aegean tombs (circular shape) as they are built entirely above ground level and do not share the same tripartite structure - the entrances are usually an undifferentiated part of the circular walling of the tomb. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Thracian tomb of Kazanlak=== | ||
| − | + | Not far from the ancient [[Thracian civilization|Thracian]] capital [[Seuthopolis]], in [[Bulgaria]], lies the famous brick beehive tomb of Kazanlak. Situated within a [[necropolis]], the tomb is composed of a narrow corridor and vaulted burial chamber, decorated with murals of ritual funeral feasts.<ref>(1997) World Heritage Site. [[http://www.worldheritagesite.org/sites/kazanlak.html"Thracian tomb of Kazanlak"]] Retrieved September 5, 2007 </ref>. Dating back to the 4th century B.C.E., the site is similar to the one in Oman in that it the similarities with Aegan beehive tombs are minimal. This may due in part to the idea that beehive tomb designs did not necessarily originate in Greece, but are common phenomena in other parts of the world. | |
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 14:54, 5 September 2007
Beehive tombs, also known as Tholos tombs (plural tholoi), are a monumental Late Bronze Age development of the Mycenaean Civilization, that eventually replaced the old style of chamber tombs. The new beehive tombs came to be the resting place of the societies' elite upper class.
Description
Most often, beehive tombs were placed underground, either built lowly into the side of a hill, or, in areas with flat parcels of land, entirely subterrariean. In the case of the latter, if any part of the structure protruded above the ground it was carefully covered using earth that was held in place by a retaining wall[1] Inside, they were built as corbelled arches, layers of stone placed closer together as the arch tapers toward the top of the tomb. The tombs usually contained more than one burial, in various places in the tomb either on the floor, in pits and cists or on stone-built or rock-cut benches, and with various grave goods.
The tripartite structure of the tombs is not always evident in the earliest mainland examples (for example at Voidhokoilia) but by the time the architectural type had left Messenia the separation into chamber, stomion and dromos was fixed. The chamber is always built in masonry, even in the earliest examples, as is the stomion or entrance-way, which provided an opportunity for conspicuous demonstration of wealth. The dromos was often just cut from the bedrock, even in some of the earlier examples at Mycenae itself. In later examples, all three parts were constructed of fine ashlar masonry.
Origins
The oldest beehive tomb discovered thus far is in Messenia. Previously, the Minoan style of burial, the chamber tomb, had been the most frequent style used, from about 1600 B.C.E. to 1100 B.C.E., due probably to the large influence the Minoans had over the Aegan region at the time. After about 1500 B.C.E., beehive tombs became more widespread, suggesting to many archaeologists that the influence of the Minoans was in decline. From Messenia, the beehive tomb spread to other areas of Greece, particularly Argolid, Laconia, and Attica.[2] Why the switch from chamber to beehive tombs took place remains a contention among archaeologists, but there are many implications arising from the change. As beehive tombs became more popular in Greece, they began to become regulated to the highest class of citizens; usually royalty and the highest non-royalty bueacrats and their families were only entombed in beehive structures. This suggests that there was a strict social stratigraphy in Greece at the time. The infrequency of later beehive tombs also indicates the eventual consolidation of power in Greece, as the once city states became larger conglomerates, requiring fewer beehive tombs for the fewer persons with power.[3]
The beehive tomb design for the most stayed within Greece. However, there are examples of similar designs from around the world, although it is not clear if they were culturally defused from Greece, or if they were concurrently separated phenomena.
Famous Examples
Treasury of Atreus
Perhaps the most famous beehive tomb in Greece is the Treasury of Atreus, located in Mycenae, Greece (on the Panagitsa Hill) constructed around 1250 B.C.E. The lintel stone above the doorway weighs 120 tons. The tomb was used for an unknown period of time. With an interior height of 13.5m and a diameter of 14.5m,[4] it was the tallest and widest dome in the world for over a thousand years until construction of the Temple of Mercury in Baiae.
Oman
The earliest stone-built tombs which can be called 'beehive', are in Oman, built of stacked flat stones which occur in nearby geological formations. They date to between 3,500 and 2,500 years B.C.E., to a period when the Arabian peninsula was subject to much more rainfall than now, and supported a flourishing civilisation in what is now desert, to the west of the mountain range along the Gulf of Oman. No burial remains have ever been retrieved from these 'tombs', though there seems no other purpose for their building. They have only superficial similarities with the Aegean tombs (circular shape) as they are built entirely above ground level and do not share the same tripartite structure - the entrances are usually an undifferentiated part of the circular walling of the tomb.
Thracian tomb of Kazanlak
Not far from the ancient Thracian capital Seuthopolis, in Bulgaria, lies the famous brick beehive tomb of Kazanlak. Situated within a necropolis, the tomb is composed of a narrow corridor and vaulted burial chamber, decorated with murals of ritual funeral feasts.[5]. Dating back to the 4th century B.C.E., the site is similar to the one in Oman in that it the similarities with Aegan beehive tombs are minimal. This may due in part to the idea that beehive tomb designs did not necessarily originate in Greece, but are common phenomena in other parts of the world.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ (2000) Prehistoric Archaeology of the Aegean Project. ["Lesson 19: Mycenaean Tholos Tombs and Early Mycenaean Settlements"] Dartmouth College, Retrieved September 5, 2007
- ↑ (2000) Prehistoric Archaeology of the Aegean Project. ["Lesson 19: Mycenaean Tholos Tombs and Early Mycenaean Settlements"] Dartmouth College, Retrieved September 5, 2007
- ↑ (2000) Prehistoric Archaeology of the Aegean Project. ["Lesson 19: Mycenaean Tholos Tombs and Early Mycenaean Settlements"] Dartmouth College, Retrieved September 5, 2007
- ↑ Structurae.de: Treasury of Atreus
- ↑ (1997) World Heritage Site. ["Thracian tomb of Kazanlak"] Retrieved September 5, 2007
External links
- Mycenaean tholos tombs paintings
- Treasury of Atreus in the Structurae database
- Treasury of Atreus 360° Interactive virtual tour
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.